Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 24 Indian Botanical Gardens and Herbarium
RBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 24 Multiple Choice Objective Questions
Question 1.
Which famous doctor is given credit to established Botanical garden in India?
a. Maharshi Parashar
b. Shushrut
c. Jivak Komar Britiya
d. Charaka
Question 2.
Botanical garden are useful for the study of:
a. For acclimatization and adaptation of plants
b. Control and eradication of weeds
c. Pollution control
d. All of the above
Question 3.
Which of the following is not necessary to collect plant specimens from field?
a. Secateur
b. Vasculum
c. Electric heater
d. Plant press
Question 4.
What is standard size of a plant press?
a. 12″x 18″
b.12″x 16″
c. 10″ x 18″
d. 10″ x 16″
Question 5.
Which plant classification is the basis to establish a Herbarium in England and India?
a. De Condole
b. Bentham and Hooker
c. Ostwald Tippo
d. Hutchinson
Answers.
1. (c)
2. (d)
3. (c)
4. (a)
5. (b)
RBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 24 Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is Herbarium?
Answer :
A herbarium (plural: herbaria) is a systematically arranged collection of’preserve (dried) plant specimens and associated data used for scientific study.
Question 2.
Write the name of instrument used for study of plant taxonomy.
Answer :
Botanical garden, museum and Herbarium are the device to study plant taxonomy.
Question 3.
What is plant press? Define.
Answer :
Plant Press: it is a set of equipment used by botanists to flatten and dry field samples so that they can be easily stored. A professional plant press is made to the standard maximum size for biological specimens to be filed in a particular herbarium.
Question 4.
What is standard size of a plant press?
Answer :
A plant press is 12″ x 18″ (30 x 45 cm) in size.
Question 5.
What is the standard size of a Herbarium sheet?
Answer :
The dried specimens are mounted on herbarium sheets of standard size 11.50″ x 16.50″ (28.75 x 41.25 cm).
Question 6.
Define botanical gardens.
Answer :
A botanical garden or botanic garden is a garden dedicated to the collection, cultivation and display of a wide range of plants labeled with their botanical names. A botanical garden is a controlled and staffed institution for the maintenance of a living collection of plants under scientific management for purposes of education and research, together with such libraries, herbaria, laboratories, and museums as are essential to its particular undertakings.
Question 7.
What is Herbarium?
Answer :
A herbarium (plural: herbaria) is a systematically arranged collection of’preserve (dried) plant specimens and associated data used for scientific study.
Question 8.
How plant specimen is protected from fungal infection and attack of insects?
Answer :
The mounted specimens are sprayed with fungicides like 2% solution of mercuric chloride for preservation.
Question 9.
Write the names of two famous Herbaria.
Answer :
- The Central National Herbarium Kolkata, CNH
- The Herbarium of National Botanical Research Institute, Lucknow
Question 10.
Write the names of two famous botanical gardens of world.
Answer :
| S.NO. | Name of Botanical Garden | Year of establishment |
| 1 | Padua Botanical Garden, Italy | 1545 |
| 2 | Pisa Botanical Garden, (Pisa)Italy | 1543 |
Question 11.
When, where and which botanical garden was founded by American botanist Henary Shaw?
Answer :
Modern concept of Botanical garden came in existence 150 years back and credit to make this Botanical garden useful goes to Henery Shaw who established Missouri Botanical Garden in Same Louis, USA (1859).
Question 12.
What is the role of Digger to collect the plant samples?
Answer :
Digger: it is an instrument to dig earth to take out root or tuber part of plant from soil.
Question 13.
Name the gas which is used for fumigation of plant specimens once in year?
Answer :
Almirah and segments in which herbarium are kept also protected from insects by spraying DDT, Naphthalene balls etc. once in year all herbarium sheets are fumigated by CS2 (Carbon disulphide) in closed room or box.
Question 14.
What newspaper plant samples in plant press should be changed in every 24 hours?
Answer :
Blotting paper or newspaper should change every 24 hours for proper drying of plant part so fungal growth can be avoided.
Question 15.
What do you mean by filing?
Answer :
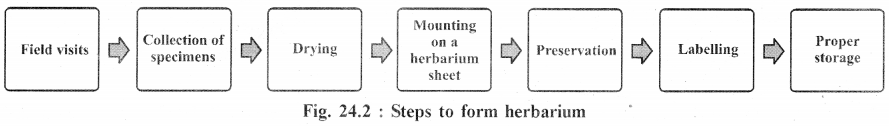
The process to keep properly dried, pressed and identified plant specimens in sequential, scientific and approved classifications method is called Filing.
RBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 24 Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are the importance’s of Botanical Gardens?
Answer :
Role and Functions of Botanical Gardens :
- Useful for accurate morphological and anatomical scientific research of plants
- Useful for comparative and taxonomical studies of plants.
- Useful for classification and nomenclature of plants.
- It provide plant material for various laboratories studies such as cytology, plant physiology, tissue culture, plant breeding.
- Various Botanical gardens useful for acclimatization of plants in various ecological conditions.
- Useful in Horticulture to improvise plants qualities for human use such as fruit giving plant, medicinal plants
- Botanical gardens are useful for Asthetic sense such as tree shade, fragrance from flowers etc.
- Useful to grow’ glasshouse plants (Green house) of different climates for research purpose.
- Botanical gardens are also known as Outdoor laboratories for studies of botany and plants because they are used for research and investigation work.
- A botanical garden is a collection of living plants which are used for Pure and applied study of plants.
- Plants in botanical garden not only used for beautification but used for Horticulture, Plant breeding etc.
- Botanical gardens are useful in studies of Introduction and Acclimatization of plants, Control and eradication of weeds, use of plants for Pollution control etc.
Question 2.
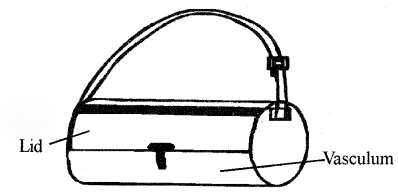
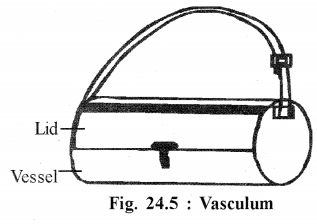
Draw a labeled diagram of vasculum.
Answer :
Question 3.
Explain various steps and technique to make a Herbarium in detail.
Answer :
Preparation of herbarium sheet
- The dried specimens are mounted on herbarium sheets of standard size 11.50″x 16.50″ (28.75 x 41.25 cm).
- Herbarium sheets are very thick and strong handmade card sheet which can be kept safe for long time.
- Name of herbarium is printed on the top of herbarium sheet and on right bottom comer of sheet contains all necessary information.
- Mounting is the process to paste dried specimens on the sheet.
- For mounting take a tray of 12″ x 18″ size and mix glue or fevicol with Mercuric chloride.
- Now dried specimen is dipped in it from one side so glue stick with it on one side.
- Now this dried specimen is paste on sheet properly.
- The bulky plant parts like dry fruits seeds, cones etc. are dried without pressing and are put in small envelops called fragment packets. Succulent plants are not mounted on herbarium sheets but are collected in 4% formalin or FAA (Formalin Acetic Alcohol).
Question 4.
Explain tools of making Herbarium in detail.
Answer :
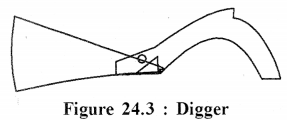
Digger : It is an instrument to dig earth to take out root or tuber part of plant from soil.
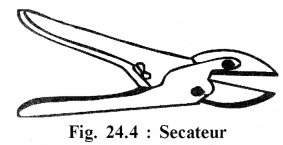
Secateur : It is an instrument to cut branches of woodyplants.
Vasculum : It is Aluminum container to collect plant parts. Its inner wall is lined by cork sheet which prevent plants from drying.
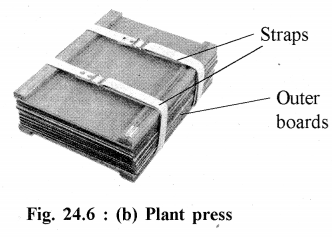
Plant Press : It is a set of equipment used by botanists to flatten and dry field samples so that they can be easily stored. A professional plant press is made to the standard maximum size for biological specimens to be filed in a particular herbarium. A plant press is 12″ x 18″ (30 x 45 cm) in size. A flower press is a similar device of no standard size that is used to make flat dried flowers or pressed flower craft. A modem plant press consists of two strong outer boards with straps that can be tightened around them to exert pressure. Between the boards, fresh plant samples are placed, carefully labelled, between layers of paper. Further layers of absorbent paper and corrugated cardboard are usually added to help to dry the samples as quickly as possible, which prevents decay and improves color retention. Layers of a sponge material can be used in order to prevent squashing parts of the specimens, such as fruit. Older plant presses and some modem flower presses have screws to supply the pressure, which often limits the thickness of the stack of samples that can be put into one press. It sample specimens are larger in size than it has to be folded in ‘v’ or ‘w’ shaped.
Field Diary or Note Book : A person has to collect maximum information of plants during collection of plants from field related With it habitat and habits. It is a specific field diary in which a specific number has to be given to every collected specimen and on a page all necessary information are recorded as follows:
- Place of collection or locality
- Date of collection
- Local name of plant and serial number of collection
- Botanical name and Family of plant
- Color of flower
- Habitat
- Abundance
- Plant Association
- Type of soil
- Collector’s name
- Other information
Polythene bags : Various types of Polythene bags used to collect fruit or inflorescence or other parts of plant.
Forceps : It is instrument to pluck off the leaves of plants.
Hand Lens : It can be use to see plant part in enlarge view.
Rubber bands : Used to keep all the things safe and one place.
Blotting papers and newspapers : To dry the leaves.
Question 5.
What is the importance of plant taxonomy?
Answer :
Plant taxonomy help to categories plants in different groups on the basis of similarities and dissimilarities.
Question 6.
What is the importance of botanical gardens in plant taxonomy?
Answer :
- Useful for accurate morphological and anatomical scientific research of plants.
- Useful for comparative and taxonomical studies of plants.
- Useful for classification and nomenclature of plants.
Question 7.
Give a list of famous botanical gardens of India and their year of establishment.
Answer :
| S.NO. | Name of Botanical Garden | Year of establishment |
| 1 | Indian Botanical Garden. Sibpur, Hawarh(Koikata. India) | 1787 |
| 2 | National Botanical Garden, Lucknow | 1865 |
| 3 | The Lloyd Botanical Garden in Darjeeling | 1865 |
| 4 | Botanical Garden and Forest Research Institute, Dehradun | 1874 |
| 5 | Lai Bagh Garden, Bengaluru | 1799 |
| 6 | Company Garden, Mussoorie | 1799 |
| 7 | Botanical Garden of Saharanpur | 1799 |
| 8 | Government Botanical Gardens, Ootacamund. Nilgiris district | 1848 |
| 9 | Shalimar and Nishat Garden, Srinagar | 1619 |
Question 8.
Give a list of five famous botanical gardens of world and their year of establishment.
Answer :
| S.NO. | Name of Botanical Garden | Year of establishment |
| 1 | Padua Botanical Garden Italy | 1545 |
| 2 | Pisa Botanical Garden, (Pisa)Italy | 1543 |
| 3 | National Museum of Natural History, Penis (France) | 1635 |
| 4 | Botanical Garden and Museum, Berlin (Germany) | 1646 |
| 5 | Uppsala Botanical Garden. Sweden | 1655 |
| 6 | Roval Botanical Garden. Edinburgh (Scotland, England) | 1670 |
| 7 | Botanical Garden and Botanical Institute of University of Vienna (Austria) | 1754 |
| 8 | Indian Botanical Garden, Shibpur, Hawarh (Kolkata, India) | 1787 |
| 9 | Botanical Garden, Washington D.C., USA | 1820 |
| 10 | Roval Botanical Garden of Kew, UK | 1841 |
| 11 | Arnold Arboretum of Howard University, USA | 1872 |
| 12 | The New York Botanical Garden, New York, USA | 1895 |
| 13 | Jardira Botanical Garden, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil | 1808 |
Question 9.
What will you do to protect plant specimen on Herbarium sheet from fungal infection or bacterial infection?
Answer :
- In England and India Bentham and Hooker’s system of classification is used for this purpose.
- The mounted specimens are sprayed with fungicides like 2% solution of mercuric chloride for preservation.
- Alnurah and segments in which herbarium arc kept also protected from insects by spraying DDT, Naphthalene balls etc. once in year all herbarium sheets are fumigated by CS2 (Carbon disulphide) in closed room or box.
Question 10.
What is the role of Herbarium in modern taxonomy? Explain.
Answer :
- Herbarium is used for identification of plants.
- Specimen along with description on herbarium sheet constitutes a storehouse or repository of knowledge for future reference and research work in the field of plants. Herbarium gives necessary information and plant specimen for better understanding.
- Study of plant is not interesting and easy w hen studied by diagrams, photographs and description but herbarium makes it interesting and learning oriented.
Question 11.
Give a list of five famous Herbarium of world and number of specimens.
Answer :
| S.No. | Name | Number of specimens |
| 1 | Roval Botanical Garden of Kew, UK | 60 Lac (6 Million) |
| 2 | V.L Komarov Botanical Institute.,Leningrad | 50 Lac (5 Million) |
| 3 | British Museum of Natural history, London | 40 Lac (4 Million) |
| 4 | Perris Botanical Garden | 1 Crore (10 Million) |
| 5 | Harvard University, Cambridge | 50 Lac (5 Million) |
| 6 | Indian Botanical Garden. Kolkata | 25 Lac (2.5 Million) |
Question 12.
Give a list of any five famous Herbaria of India and number of specimens.
Answer :
| S.No. | Name | Number of specimens |
| 1 | The Central National Harbarium, Kolkata | 4 Lac |
| 2 | National Botanical Garden (NBG), Lucknow | 1 Lac |
| 3 | Botanical Garden and Forest Research Institute, Dehradun | 3 Lac |
| 4 | Plant Harbarium of Botanical Department, Delhi University | 50 Thousand |
| 5 | Science Museum, Department of Botany, University of Rajasthan, Jaipur | 40 Thousand |
Question 13.
Why botanical gardens are called outdoor laboratories?
Answer :
Botanical gardens are also known as Outdoor laboratories for studies of botany and plants because they are used for research and investigation work.
Question 14.
Explain importance of field diary during plants sample collection from field.
Answer :
Field Diary or Note Book: A person has to collect maximum information of plants during collection of plants from field related with it habitat and habits. It is a specific field diary in which a specific number has to be given to every collected specimen and on a page all necessary information are recorded.
Question 15.
What is the method adopted for drying plant specimens in hilly areas?
Answer :
These days electric heater is used in rainy season or hilly areas to dry plant specimens.
Question 16.
Explain Filing technique in maintenance of Herbarium sheet.
Answer :
- The process to keep properly dried, pressed and identified plant specimens in sequential, scientific and approved classification method is called Filing.
- All specimen of a species are placed in thin paper folds (specimen covers) which are kept together in thicker paper folders genus covers, and finally they are incorporated into the herbarium cupboards in their proper position according to a well known system of classification.
RBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 24 Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by Herbarium? Explain main Herbaria of India.
Answer :
Definition of Herbarium :
- A herbarium (plural: herbaria) is a systematically arranged collection of preserve (dried) plant specimens and associated data used for scientific study.
- Largest herbarium of the world is Royal Botanical Garden, Kew (6.5 million specimens).
- Largest herbarium of the India is Indian Botanical Garden or Central National Herbarium, Kolkata (2 million specimens).
Objectives of Herbarium :
- Herbarium is used for identification of plants.
- Specimen alongwith description on herbarium sheet constitutes a storehouse or repository of knowledge for future reference and research work in the field of plants. Herbarium gives necessary information and plant specimen for better understanding.
- Study of plant is not interesting and easy when studied by diagrams, photographs and description but herbarium makes it interesting and learning oriented.
- Some time herbarium is helpful to compare and study- plants from an area if their specimens are systematically arranged in the form of herbarium sheet.
- Useful to keep specimens of newly described taxa.
- Helpful to study flora of different places.
- Ecology of different places can be understood by herbarium.
- Helpful to identify plants.
Technique of plant collection :
- For a better quality collection of specimen for herbarium we should know correct and best method.
- By adopting correct method plant specimens can be kept preserved for long time as well as it will give correct identification of plants.
- Plant specimens should be collected in different phase of growth and period of reproduction in plants from different geographical areas.
- A specimen should have all part of plant for example it should have root. stem, leaves, inflorescence, flower and fruit etc.
- To collect all part of plant is easy task for a herbaceous plant but difficult for large woody tree and shrubs so herbarium sheet can be made for wood tree and shrubs by collecting twig with inflorescence or with fruit.
- Specimens should collect from healthy plants and floral specimens should be collected in end of its flowering phase so a young or unripe fruit can also be collected.
- Should visit a area twice or thrice to collect specimens of plants in different stages of growth.
Digger : It is an instrument to dig earth to take out root or tuber part of plant from soil.

Secateur : It is an instrument to cut branches of woody plants.

Vasculum : It is Aluminum container to collect plant parts. Its inner wall is lined by cork sheet which prevent plants from drying.

Plant Press : It is a set of equipment used by botanists to flatten and dry field samples so that they can be easily stored. A professional plant press is made to the standard maximum size for biological specimens to be filed in a particular herbarium. A plant press is 12″ x 18″ (30 x 45 cm) in size. A flower press is a similar device of no standard size that is used to make flat dried flowers or pressed flower craft. A modem plant press consists of two strong outer boards with straps that can be tightened around them to exert pressure. Between the boards, fresh plant samples are placed, carefully labelled, between layers of paper. Further layers of absorbent paper and corrugated cardboard are usually added to help to dry the samples as quickly as possible, which prevents decay and improves color retention. Layers of a sponge material can be used in order to prevent squashing parts of the specimens, such as fruit. Older plant presses and some modem flower presses have screws to supply the pressure, which often limits the thickness of the stack of samples that can be put into one press. It sample specimens are larger in size than it has to be folded in ‘v’ or ‘w’ shaped.

Field Diary or Note Book : A person has to collect maximum information of plants during collection of plants from field related With it habitat and habits. It is a specific field diary in which a specific number has to be given to every collected specimen and on a page all necessary information are recorded as follows:
- Place of collection or locality
- Date of collection
- Local name of plant and serial number of collection
- Botanical name and Family of plant
- Color of flower
- Habitat
- Abundance
- Plant Association
- Type of soil
- Collector’s name
- Other information
Polythene bags : Various types of Polythene bags used to collect fruit or inflorescence or other parts of plant.
Forceps : It is instrument to pluck off the leaves of plants.
Hand Lens : It can be use to see plant part in enlarge view.
Rubber bands : Used to keep all the things safe and one place.
Blotting papers and newspapers : To dry the leaves.
Drying of specimens :
- For drying of specimens plant press usually kept in some lighted condition.
- The specimens are spread out between the folds of old newspapers or blotting sheets avoiding overlapping of parts.
- The larger specimen may’ folded in ‘V’ or’ W’ shapes.
- Blotting paper or newspaper should change every 24 hours for proper drying of plant part so fungal growth can be avoided.
- The blotting sheets with plant specimen should be placed in the plant press for drying. After 24 to 48 hrs the press is opened.
- These days electric heater is used in rainy season or hilly areas to dry plant specimens.
Preparation of herbarium sheet :
- The dried specimens are mounted on herbarium sheets of standard size 11.50″ x 16.50″ (28.75 x 41.25 cm).
- Herbarium sheets are very thick and strong handmade card sheet which can be kept safe for long time.
- Name of herbarium is printed on the top of herbarium sheet and on right bottom comer of sheet contains all necessary information.
- Mounting is the process to paste dried specimens on the sheet.
- For mounting take a tray of 12″ x 18″ size and mix glue or fevicol with Mercuric chloride.
- Now dried specimen is dipped in it from one side so glue stick with it on one side.
- Now this dried specimen is paste on sheet properly.
- The bulky plant parts like dry fruits seeds, cones etc. are dried without pressing and are put in small envelops called fragment packets. Succulent plants are not mounted on herbarium sheets but are collected in 4% fomralin or FAA (Formalin Acetic Alcohol).
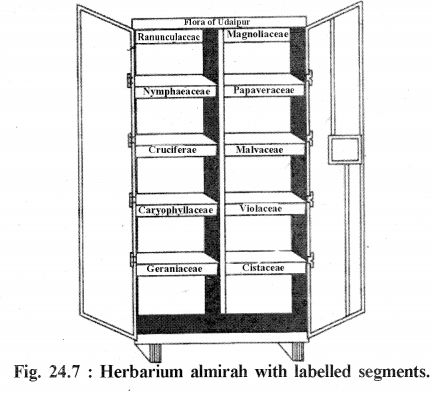
Labelling of the herbarium sheet :
- A label of 3″ x 5″ (7.5 x 12.5 cm) is pasted or printed on the lower right hand comer.
- The label should indicate the following information :
- Firstly name of institute where this herbarium is situated, e.g, Herbarium. Department of Botany, College of Science, Udaipur.
- Locality from where specimen is collected, e.g., Flora of Udaipur district or Flora of Rajasthan
- Name of family
- Botanical name of plant
- Name of locality
- Date of collection
- Altitude
- Habit
- Complete information about the area from where specimen collected
- Name of collector
- Collector’s field number
- Local or Common name and other information get from local peoples of the area.
Filing of herbarium sheet or Storage :
- The process to keep properly dried, pressed and identified plant specimens in sequential, scientific and approved classification method is called Filing.
- All specimen of a species are placed in thin paper folds (specimen covers) which are kept together in thicker paper folders genus covers), and finally they are incorporated into the herbarium cupboards in their proper position according to a well known system of classification.
- In England and India Bentham and Hooker’s system of classification is used for this purpose.
- The mounted specimens are sprayed with fungicides like 2% solution of mercuric chloride for preservation.
- Almirah and segments in which herbarium are kept also protected from insects by spraying DDT. Naphthalene balls etc. once in year all herbarium sheets are fumigated by CS2 (Carbon disulphide) in closed room or box.
Role of Herbarium in Modern Plant Taxonomy :
- Herbarium is basis for studies of plants such as Identification of plants, Nomenclature. Classification of plants etc.
- Without knowing about the species, genus, family and characteristics of plants categorization of plants would not be possible.
- Herbarium is the source to get information about habitat and characteristics of plants which helps in categorization of plants.
Some Important Herbarium of World :
| S.No. | Name | Number of specimens |
| 1 | Roval Botanical Garden of Kew, UK | 60 Lac (6 Million) |
| 2 | V.L Komarov Botanical Institute. Leningrad | 50 Lac (5 Million) |
| 3 | British Museum of Natural history, London | 40 Lac (4 Million) |
| 4 | Perris Botanical Garden | 1 Crore (10 Million) |
| 5 | Harvard University, Cambridge | 50 Lac (5 Million) |
| 6 | Indian Botanical Garden. Kolkata | 25 Lac (2.5 Million) |
Question 2.
What do you mean by Botanical garden? Explain historic importance of botanical gardens.
Answer :
Definition :
- A botanical garden or botanic garden is a garden dedicated to the collection, cultivation and display of a wide range of plants labeled with their botanical names.
- A botanical garden is a controlled and staffed institution for the maintenance of a living collection of plants under scientific management for purposes of education and research, together with such libraries, herbaria, laboratories, and museums as are essential to its particular undertakings.
- Each botanical garden naturally develops its own special fields of interests depending on its personnel, location, extent, available funds, and the terms of its charter.
- It may include greenhouses, test grounds, a herbarium, an arboretum, and other departments.
- It maintains a scientific as well as a plant-growing staff, and publication is one of its major modes of expression.
- A botanical garden is a collection of living plants which are used for Pure and applied study of plants.
- Plants in botanical garden not only used for beautification but used for Horticulture, Plant breeding etc.
- Botanical gardens are useful in studies of Introduction and Acclimatization of plants, Control and eradication of weeds, use of plants for Pollution control etc.
- Botanical gardens are also known as Outdoor laboratories for studies of botany and plants because they are used for research and investigation work.
- Although the Botanical Gardens were slow to develop, however from the early period of the history man started cultivation of plants in garden for easy availability of plants for his needs such as food, medicine etc.
- Many ornamental and floral plants were cultivated for easy availability near to temples in India, Egypt and China.
- First Botanical Garden of world was established approximately 2350 years ago (350 BC) by Great Greece scientist Aristotle though in India, Botanical Gardens were established 550 years before Aristotle by famous doctor Jivak Komar Britiya as per the historical evidences.
- Modem concept of Botanical garden came in existence 150 years back and credit to make this Botanical garden useful goes to Henery Shaw who established Missouri Botanical Garden in Saint Louis, USA (1859).
1. Royal Indian Botanical Garden, Shibpur, Kolkata, BG :
- This is not only famous Botanical Garden of India but also one of the famous in Asia.
- The gardens were founded in 1787 by Colonel Robert Kyd, an army officer of the British East India Company

- It was renamed in 2009 as Acharya Jagadish Chandra Bose Indian Botanic Garden to honor Indian plant physiologist and physicist Sir Jagadish Chandra Bose. It is operated by the Botanical Survey of India.
- The garden exhibit a wide variety of rare plants and a total collection of over 12,000 indigenous and exotic specimens of trees, shrubs, Palms, Grasses, Orchids spread over 109 hectares.
- The main attraction of this garden is a 200 years old Big Banyan tree which has a height of 100 feet and its branches covers an area of 15000 m².
- It has amazing collection of Palms, Cactus and Succulent plant.
2. National Botanic, Garden, Lucknow, NBG :
- This garden was founded by Nawabs of Oudh in between 1789 to 1814 as a Princely Garden to get Sentonim medicine from a plant Artemisia maritima.
- It has good collection of Palms, Ferns, Orchids, Cactii, Citrus plants and many verities of Rose plant.
- Now it is famous as National Botanical Research Institute, Lucknow.
3. Lloyd Botanical Garden, Darjeeling :
- Lloyd’s Botanical Garden, or Darjeeling Botanical Garden, is a botanical garden in Darjeeling in the Indian state of West Bengal.
- William Lloyd donated 40 acres (160,000 m²) land for garden to Government of India in 1878.
- The Darjeeling Botanical Garden preserves several species of Evergreen and Deciduous plant species such as Tree Ferns (Cythaea), Callitris with blue leaves, Living fossil plant Ginko biloba and Metasequoia etc.
- The Cacti and Succulent collection of 150 species is displayed in the Conservatory.
- The collection of native Orchids from the Singalila Ridge in present-day Singalila National Park is rare and notable.
4. Botanical Garden, Saharanpur :
- This garden covers 40 acre area of land.
- It was founded in 1799 by Zabita Khan.
- This garden is famous for great plant taxonomist J.F. Duthie and his famous book “The Flora of Upper Gangetic Plains and adjacent Shivalik Hills” This book authentic text for description, identification of North Indian floral plants.
- It has a good collection of useful plants for humans such as Potato. Tobacco, Guava, Apple. Papaya, Chilli etc.
5. LalBagh Garden, Bangalore :
- LalBagh Garden name was given by King Hayder Ah.
- It covers approximately 240 acre land.
- Here useful plants for humans were established from Australia. Africa and North and South America.
- It is also famous as “Bonsai garden LalBagh” because it has approximately 1000 bonsai plants.
- It is the place of regular research and one of the famous botanical garden in the world.
Question 3.
What do you mean by plant collection techniques? Explain various tools used for plant collection with labeled diagram.
Answer :
Definition of Herbarium :
- A herbarium (plural: herbaria) is a systematically arranged collection of preserve (dried) plant specimens and associated data used for scientific study.
- Largest herbarium of the world is Royal Botanical Garden, Kew (6.5 million specimens).
- Largest herbarium of the India is Indian Botanical Garden or Central National Herbarium, Kolkata (2 million specimens).
Objectives of Herbarium :
- Herbarium is used for identification of plants.
- Specimen alongwith description on herbarium sheet constitutes a storehouse or repository of knowledge for future reference and research work in the field of plants. Herbarium gives necessary information and plant specimen for better understanding.
- Study of plant is not interesting and easy when studied by diagrams, photographs and description but herbarium makes it interesting and learning oriented.
- Some time herbarium is helpful to compare and study- plants from an area if their specimens are systematically arranged in the form of herbarium sheet.
- Useful to keep specimens of newly described taxa.
- Helpful to study flora of different places.
- Ecology of different places can be understood by herbarium.
- Helpful to identify plants.
Technique of plant collection :

- For a better quality collection of specimen for herbarium we should know correct and best method.
- By adopting correct method plant specimens can be kept preserved for long time as well as it will give correct identification of plants.
- Plant specimens should be collected in different phase of growth and period of reproduction in plants from different geographical areas.
- A specimen should have all part of plant for example it should have root. stem, leaves, inflorescence, flower and fruit etc.
- To collect all part of plant is easy task for a herbaceous plant but difficult for large woody tree and shrubs so herbarium sheet can be made for wood tree and shrubs by collecting twig with inflorescence or with fruit.
- Specimens should collect from healthy plants and floral specimens should be collected in end of its flowering phase so a young or unripe fruit can also be collected.
- Should visit a area twice or thrice to collect specimens of plants in different stages of growth.
Digger : It is an instrument to dig earth to take out root or tuber part of plant from soil.

Secateur : It is an instrument to cut branches of woodyplants.

Vasculum : It is Aluminum container to collect plant parts. Its inner wall is lined by cork sheet which prevent plants from drying.

Plant Press : It is a set of equipment used by botanists to flatten and dry field samples so that they can be easily stored. A professional plant press is made to the standard maximum size for biological specimens to be filed in a particular herbarium. A plant press is 12″ x 18″ (30 x 45 cm) in size. A flower press is a similar device of no standard size that is used to make flat dried flowers or pressed flower craft. A modem plant press consists of two strong outer boards with straps that can be tightened around them to exert pressure. Between the boards, fresh plant samples are placed, carefully labelled, between layers of paper. Further layers of absorbent paper and corrugated cardboard are usually added to help to dry the samples as quickly as possible, which prevents decay and improves color retention. Layers of a sponge material can be used in order to prevent squashing parts of the specimens, such as fruit. Older plant presses and some modem flower presses have screws to supply the pressure, which often limits the thickness of the stack of samples that can be put into one press. It sample specimens are larger in size than it has to be folded in ‘v’ or ‘w’ shaped.

Field Diary or Note Book : A person has to collect maximum information of plants during collection of plants from field related With it habitat and habits. It is a specific field diary in which a specific number has to be given to every collected specimen and on a page all necessary information are recorded as follows:
- Place of collection or locality
- Date of collection
- Local name of plant and serial number of collection
- Botanical name and Family of plant
- Color of flower
- Habitat
- Abundance
- Plant Association
- Type of soil
- Collector’s name
- Other information
Polythene bags : Various types of Polythene bags used to collect fruit or inflorescence or other parts of plant.
Forceps : It is instrument to pluck off the leaves of plants.
Hand Lens : It can be use to see plant part in enlarge view.
Rubber bands : Used to keep all the things safe and one place.
Blotting papers and newspapers : To dry the leaves.
Drying of specimens :
- For drying of specimens plant press usually kept in some lighted condition.
- The specimens are spread out between the folds of old newspapers or blotting sheets avoiding overlapping of parts.
- The larger specimen may’ folded in ‘V’ or’ W’ shapes.
- Blotting paper or newspaper should change every 24 hours for proper drying of plant part so fungal growth can be avoided.
- The blotting sheets with plant specimen should be placed in the plant press for drying. After 24 to 48 hrs the press is opened.
- These days electric heater is used in rainy season or hilly areas to dry plant specimens.
Preparation of herbarium sheet :
- The dried specimens are mounted on herbarium sheets of standard size 11.50″ x 16.50″ (28.75 x 41.25 cm).
- Herbarium sheets are very thick and strong handmade card sheet which can be kept safe for long time.
- Name of herbarium is printed on the top of herbarium sheet and on right bottom comer of sheet contains all necessary information.
- Mounting is the process to paste dried specimens on the sheet.
- For mounting take a tray of 12″ x 18″ size and mix glue or fevicol with Mercuric chloride.
- Now dried specimen is dipped in it from one side so glue stick with it on one side.
- Now this dried specimen is paste on sheet properly.
- The bulky plant parts like dry fruits seeds, cones etc. are dried without pressing and are put in small envelops called fragment packets. Succulent plants are not mounted on herbarium sheets but are collected in 4% fomralin or FAA (Formalin Acetic Alcohol).
Labeling of the herbarium sheet :
- A label of 3″ x 5″ (7.5 x 12.5 cm) is pasted or printed on the lower right hand comer.
- The label should indicate the following information :
- Firstly name of institute where this herbarium is situated, e.g, Herbarium. Department of Botany, College of Science, Udaipur.
- Locality from where specimen is collected, e.g., Flora of Udaipur district or Flora of Rajasthan
- Name of family
- Botanical name of plant
- Name of locality
- Date of collection
- Altitude
- Habit
- Complete information about the area from where specimen collected
- Name of collector
- Collector’s field number
- Local or Common name and other information get from local peoples of the area.
Filing of herbarium sheet or Storage :
- The process to keep properly dried, pressed and identified plant specimens in sequential, scientific and approved classification method is called Filing.
- All specimen of a species are placed in thin paper folds (specimen covers) which are kept together in thicker paper folders genus covers), and finally they are incorporated into the herbarium cupboards in their proper position according to a well known system of classification.

- In England and India Bentham and Hooker’s system of classification is used for this purpose.
- The mounted specimens are sprayed with fungicides like 2% solution of mercuric chloride for preservation.
- Almirah and segments in which herbarium are kept also protected from insects by spraying DDT. Naphthalene balls etc. once in year all herbarium sheets are fumigated by CS2 (Carbon disulphide) in closed room or box.
Role of Herbarium in Modern Plant Taxonomy :
- Herbarium is basis for studies of plants such as Identification of plants, Nomenclature. Classification of plants etc.
- Without knowing about the species, genus, family and characteristics of plants categorization of plants would not be possible.
- Herbarium is the source to get information about habitat and characteristics of plants which helps in categorization of plants.
Some Important Herbarium of World :
| S.No. | Name | Number of specimens |
| 1 | Roval Botanical Garden of Kew, UK | 60 Lac (6 Million) |
| 2 | V.L Komarov Botanical Institute. Leningrad | 50 Lac (5 Million) |
| 3 | British Museum of Natural history, London | 40 Lac (4 Million) |
| 4 | Perris Botanical Garden | 1 Crore (10 Million) |
| 5 | Harvard University, Cambridge | 50 Lac (5 Million) |
| 6 | Indian Botanical Garden. Kolkata | 25 Lac (2.5 Million) |
Some Important Herbarium of India :
| S.No. | Name | Number of specimens |
| 1 | The Central National Harbarium. Kolkata | 4 Lac |
| 2 | National Botanical Garden (NBG), Lucknow | 1 Lac |
| 3 | Botanical Garden and Forest Research Institute, Deliradun | 3 Lac |
| 4 | Plant Harbarium of Botanical Department. Delhi University | 50 Thousand |
| 5 | Science Museum, Department of Botany, University of Rajasthan, Jaipur | 40 Thousand |
- In India systematic research and investigation of plants to studies plant taxonomy started in 19th century with publication of Bentham Hooker’s book “Flora of British India”
- First Herbarium of India founded by Botanical Survey of India (BSI) in Kolkata latter on many universities and institutes founded their own Herbarium for studies.
- Some famous Herbarium of India are as follows :
1. The Central National Herbarium Kolkata CNH :
- It is largest Herbarium of India as well as of Asia.
- This Herbarium founded by William Roux berg (1793).
- It has a collection of approximately 4 lac plant specimens.
- This Herbarium has collection of plants from India, Europe. America, China, Australia and Japan.etc.
- It has collection of Angiosperms, Ferns, Gymnosperms and other non floral plants.
2. The Herbarium of National Botanical Research Institute, Lucknow :
- It is one of the famous Herbarium of India.
- It is founded in 1948 state Government of UR
- It has a collection of more than 1 lac plant specimen in well preserved form.
- Apart from Herbarium NBG has big Library, Large Green house, laboratories for Palynology, Plant Physiology and Tissue Culture for research and investigation.
3. Forest Research Institute Herbarium, Dehradun :
- This Herbarium was founded by British Government in
- 1874 in Dehradun but present set up established in 1908.
- It is one of the largest plant museum and second largest Herbarium after The Central National Herbarium Kolkata.
- It has collection of 350000 plant specimens from India, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Tibet and Myanmar.
4. The Herbarium of Department of Botany, Delhi University :
- One of the famous plant museum of North India having 30000 plant specimens.
5. The Herbarium of Department of Botany, Rajasthan University, Jaipur :
- It is founded in 1965.
- It has collection of 40000 plant specimens from Rajasthan and neighboring states.
- It is used for studies of plants from Rajasthan.
Question 4.
Explain method to prepare Herbarium sheet with labeled diagram.
Ans:
Definition of Herbarium :
- A herbarium (plural: herbaria) is a systematically arranged collection of preserve (dried) plant specimens and associated data used for scientific study.
- Largest herbarium of the world is Royal Botanical Garden, Kew (6.5 million specimens).
- Largest herbarium of the India is Indian Botanical Garden or Central National Herbarium, Kolkata (2 million specimens).
Objectives of Herbarium :
- Herbarium is used for identification of plants.
- Specimen alongwith description on herbarium sheet constitutes a storehouse or repository of knowledge for future reference and research work in the field of plants. Herbarium gives necessary information and plant specimen for better understanding.
- Study of plant is not interesting and easy when studied by diagrams, photographs and description but herbarium makes it interesting and learning oriented.
- Some time herbarium is helpful to compare and study- plants from an area if their specimens are systematically arranged in the form of herbarium sheet.
- Useful to keep specimens of newly described taxa.
- Helpful to study flora of different places.
- Ecology of different places can be understood by herbarium.
- Helpful to identify plants.
Technique of plant collection :

- For a better quality collection of specimen for herbarium we should know correct and best method.
- By adopting correct method plant specimens can be kept preserved for long time as well as it will give correct identification of plants.
- Plant specimens should be collected in different phase of growth and period of reproduction in plants from different geographical areas.
- A specimen should have all part of plant for example it should have root. stem, leaves, inflorescence, flower and fruit etc.
- To collect all part of plant is easy task for a herbaceous plant but difficult for large woody tree and shrubs so herbarium sheet can be made for wood tree and shrubs by collecting twig with inflorescence or with fruit.
- Specimens should collect from healthy plants and floral specimens should be collected in end of its flowering phase so a young or unripe fruit can also be collected.
- Should visit a area twice or thrice to collect specimens of plants in different stages of growth.
Digger : It is an instrument to dig earth to take out root or tuber part of plant from soil.

Secateur : It is an instrument to cut branches of woodyplants.

Vasculum : It is Aluminum container to collect plant parts. Its inner wall is lined by cork sheet which prevent plants from drying.

Plant Press : It is a set of equipment used by botanists to flatten and dry field samples so that they can be easily stored. A professional plant press is made to the standard maximum size for biological specimens to be filed in a particular herbarium. A plant press is 12″ x 18″ (30 x 45 cm) in size. A flower press is a similar device of no standard size that is used to make flat dried flowers or pressed flower craft. A modem plant press consists of two strong outer boards with straps that can be tightened around them to exert pressure. Between the boards, fresh plant samples are placed, carefully labelled, between layers of paper. Further layers of absorbent paper and corrugated cardboard are usually added to help to dry the samples as quickly as possible, which prevents decay and improves color retention. Layers of a sponge material can be used in order to prevent squashing parts of the specimens, such as fruit. Older plant presses and some modem flower presses have screws to supply the pressure, which often limits the thickness of the stack of samples that can be put into one press. It sample specimens are larger in size than it has to be folded in ‘v’ or ‘w’ shaped.

Field Diary or Note Book : A person has to collect maximum information of plants during collection of plants from field related With it habitat and habits. It is a specific field diary in which a specific number has to be given to every collected specimen and on a page all necessary information are recorded as follows:
- Place of collection or locality
- Date of collection
- Local name of plant and serial number of collection
- Botanical name and Family of plant
- Color of flower
- Habitat
- Abundance
- Plant Association
- Type of soil
- Collector’s name
- Other information
Polythene bags : Various types of Polythene bags used to collect fruit or inflorescence or other parts of plant.
Forceps : It is instrument to pluck off the leaves of plants.
Hand Lens : It can be use to see plant part in enlarge view.
Rubber bands : Used to keep all the things safe and one place.
Blotting papers and newspapers : To dry the leaves.
Drying of specimens :
- For drying of specimens plant press usually kept in some lighted condition.
- The specimens are spread out between the folds of old newspapers or blotting sheets avoiding overlapping of parts.
- The larger specimen may’ folded in ‘V’ or’ W’ shapes.
- Blotting paper or newspaper should change every 24 hours for proper drying of plant part so fungal growth can be avoided.
- The blotting sheets with plant specimen should be placed in the plant press for drying. After 24 to 48 hrs the press is opened.
- These days electric heater is used in rainy season or hilly areas to dry plant specimens.
Preparation of herbarium sheet :
- The dried specimens are mounted on herbarium sheets of standard size 11.50″ x 16.50″ (28.75 x 41.25 cm).
- Herbarium sheets are very thick and strong handmade card sheet which can be kept safe for long time.
- Name of herbarium is printed on the top of herbarium sheet and on right bottom comer of sheet contains all necessary information.
- Mounting is the process to paste dried specimens on the sheet.
- For mounting take a tray of 12″ x 18″ size and mix glue or fevicol with Mercuric chloride.
- Now dried specimen is dipped in it from one side so glue stick with it on one side.
- Now this dried specimen is paste on sheet properly.
- The bulky plant parts like dry fruits seeds, cones etc. are dried without pressing and are put in small envelops called fragment packets. Succulent plants are not mounted on herbarium sheets but are collected in 4% fomralin or FAA (Formalin Acetic Alcohol).
Labeling of the herbarium sheet :
- A label of 3″ x 5″ (7.5 x 12.5 cm) is pasted or printed on the lower right hand comer.
- The label should indicate the following information :
- Firstly name of institute where this herbarium is situated, e.g, Herbarium. Department of Botany, College of Science, Udaipur.
- Locality from where specimen is collected, e.g., Flora of Udaipur district or Flora of Rajasthan
- Name of family
- Botanical name of plant
- Name of locality
- Date of collection
- Altitude
- Habit
- Complete information about the area from where specimen collected
- Name of collector
- Collector’s field number
- Local or Common name and other information get from local peoples of the area.
Filing of herbarium sheet or Storage :
- The process to keep properly dried, pressed and identified plant specimens in sequential, scientific and approved classification method is called Filing.
- All specimen of a species are placed in thin paper folds (specimen covers) which are kept together in thicker paper folders genus covers), and finally they are incorporated into the herbarium cupboards in their proper position according to a well known system of classification.

- In England and India Bentham and Hooker’s system of classification is used for this purpose.
- The mounted specimens are sprayed with fungicides like 2% solution of mercuric chloride for preservation.
- Almirah and segments in which herbarium are kept also protected from insects by spraying DDT. Naphthalene balls etc. once in year all herbarium sheets are fumigated by CS2 (Carbon disulphide) in closed room or box.
Role of Herbarium in Modern Plant Taxonomy :
- Herbarium is basis for studies of plants such as Identification of plants, Nomenclature. Classification of plants etc.
- Without knowing about the species, genus, family and characteristics of plants categorization of plants would not be possible.
- Herbarium is the source to get information about habitat and characteristics of plants which helps in categorization of plants.
Some Important Herbarium of World :
| S.No. | Name | Number of specimens |
| 1 | Roval Botanical Garden of Kew, UK | 60 Lac (6 Million) |
| 2 | V.L Komarov Botanical Institute. Leningrad | 50 Lac (5 Million) |
| 3 | British Museum of Natural history, London | 40 Lac (4 Million) |
| 4 | Perris Botanical Garden | 1 Crore (10 Million) |
| 5 | Harvard University, Cambridge | 50 Lac (5 Million) |
| 6 | Indian Botanical Garden. Kolkata | 25 Lac (2.5 Million) |
Some Important Herbarium of India :
| S.No. | Name | Number of specimens |
| 1 | The Central National Harbarium. Kolkata | 4 Lac |
| 2 | National Botanical Garden (NBG), Lucknow | 1 Lac |
| 3 | Botanical Garden and Forest Research Institute, Deliradun | 3 Lac |
| 4 | Plant Harbarium of Botanical Department. Delhi University | 50 Thousand |
| 5 | Science Museum, Department of Botany, University of Rajasthan, Jaipur | 40 Thousand |
- In India systematic research and investigation of plants to studies plant taxonomy started in 19th century with publication of Bentham Hooker’s book “Flora of British India”
- First Herbarium of India founded by Botanical Survey of India (BSI) in Kolkata latter on many universities and institutes founded their own Herbarium for studies.
- Some famous Herbarium of India are as follows :
1. The Central National Herbarium Kolkata CNH :
- It is largest Herbarium of India as well as of Asia.
- This Herbarium founded by William Roux berg (1793).
- It has a collection of approximately 4 lac plant specimens.
- This Herbarium has collection of plants from India, Europe. America, China, Australia and Japan.etc.
- It has collection of Angiosperms, Ferns, Gymnosperms and other non floral plants.
2. The Herbarium of National Botanical Research Institute, Lucknow :
- It is one of the famous Herbarium of India.
- It is founded in 1948 state Government of UR
- It has a collection of more than 1 lac plant specimen in well preserved form.
- Apart from Herbarium NBG has big Library, Large Green house, laboratories for Palynology, Plant Physiology and Tissue Culture for research and investigation.
3. Forest Research Institute Herbarium, Dehradun :
- This Herbarium was founded by British Government in
- 1874 in Dehradun but present set up established in 1908.
- It is one of the largest plant museum and second largest Herbarium after The Central National Herbarium Kolkata.
- It has collection of 350000 plant specimens from India, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Tibet and Myanmar.
4. The Herbarium of Department of Botany, Delhi University :
- One of the famous plant museum of North India having 30000 plant specimens.
5. The Herbarium of Department of Botany, Rajasthan University, Jaipur :
- It is founded in 1965.
- It has collection of 40000 plant specimens from Rajasthan and neighboring states.
- It is used for studies of plants from Rajasthan.
Question 5.
Explain three botanical gardens of India.
Answer :
1. Royal Indian Botanical Garden, Shibpur, Kolkata, BG :
- This is not only famous Botanical Garden of India but also one of the famous in Asia.
- The gardens were founded in 1787 by Colonel Robert Kyd, an army officer of the British East India Company

- It was renamed in 2009 as Acharya Jagadish Chandra Bose Indian Botanic Garden to honor Indian plant physiologist and physicist Sir Jagadish Chandra Bose. It is operated by the Botanical Survey of India.
- The garden exhibit a wide variety of rare plants and a total collection of over 12,000 indigenous and exotic specimens of trees, shrubs, Palms, Grasses, Orchids spread over 109 hectares.
- The main attraction of this garden is a 200 years old Big Banyan tree which has a height of 100 feet and its branches covers an area of 15000 m².
- It has amazing collection of Palms, Cactus and Succulent plant.
2. National Botanic, Garden, Lucknow, NBG :
- This garden was founded by Nawabs of Oudh in between 1789 to 1814 as a Princely Garden to get Sentonim medicine from a plant Artemisia maritima.
- It has good collection of Palms, Ferns, Orchids, Cactii, Citrus plants and many verities of Rose plant.
- Now it is famous as National Botanical Research Institute, Lucknow.
3. Lloyd Botanical Garden, Darjeeling :
- Lloyd’s Botanical Garden, or Darjeeling Botanical Garden, is a botanical garden in Darjeeling in the Indian state of West Bengal.
- William Lloyd donated 40 acres (160,000 m²) land for garden to Government of India in 1878.
- The Darjeeling Botanical Garden preserves several species of Evergreen and Deciduous plant species such as Tree Ferns (Cythaea), Callitris with blue leaves, Living fossil plant Ginko biloba and Metasequoia etc.
- The Cacti and Succulent collection of 150 species is displayed in the Conservatory.
- The collection of native Orchids from the Singalila Ridge in present-day Singalila National Park is rare and notable.
4. Botanical Garden, Saharanpur :
- This garden covers 40 acre area of land.
- It was founded in 1799 by Zabita Khan.
- This garden is famous for great plant taxonomist J.F. Duthie and his famous book “The Flora of Upper Gangetic Plains and adjacent Shivalik Hills” This book authentic text for description, identification of North Indian floral plants.
- It has a good collection of useful plants for humans such as Potato. Tobacco, Guava, Apple. Papaya, Chilli etc.
5. LalBagh Garden, Bangalore :
- LalBagh Garden name was given by King Hayder Ah.
- It covers approximately 240 acre land.
- Here useful plants for humans were established from Australia. Africa and North and South America.
- It is also famous as “Bonsai garden LalBagh” because it has approximately 1000 bonsai plants.
- It is the place of regular research and one of the famous botanical garden in the world.
Question 6.
Explain method of maintenance for Herbarium sheet in detail.
Answer :
Definition of Herbarium :
- A herbarium (plural: herbaria) is a systematically arranged collection of preserve (dried) plant specimens and associated data used for scientific study.
- Largest herbarium of the world is Royal Botanical Garden, Kew (6.5 million specimens).
- Largest herbarium of the India is Indian Botanical Garden or Central National Herbarium, Kolkata (2 million specimens).
Objectives of Herbarium :
- Herbarium is used for identification of plants.
- Specimen alongwith description on herbarium sheet constitutes a storehouse or repository of knowledge for future reference and research work in the field of plants. Herbarium gives necessary information and plant specimen for better understanding.
- Study of plant is not interesting and easy when studied by diagrams, photographs and description but herbarium makes it interesting and learning oriented.
- Some time herbarium is helpful to compare and study- plants from an area if their specimens are systematically arranged in the form of herbarium sheet.
- Useful to keep specimens of newly described taxa.
- Helpful to study flora of different places.
- Ecology of different places can be understood by herbarium.
- Helpful to identify plants.
Technique of plant collection :

- For a better quality collection of specimen for herbarium we should know correct and best method.
- By adopting correct method plant specimens can be kept preserved for long time as well as it will give correct identification of plants.
- Plant specimens should be collected in different phase of growth and period of reproduction in plants from different geographical areas.
- A specimen should have all part of plant for example it should have root. stem, leaves, inflorescence, flower and fruit etc.
- To collect all part of plant is easy task for a herbaceous plant but difficult for large woody tree and shrubs so herbarium sheet can be made for wood tree and shrubs by collecting twig with inflorescence or with fruit.
- Specimens should collect from healthy plants and floral specimens should be collected in end of its flowering phase so a young or unripe fruit can also be collected.
- Should visit a area twice or thrice to collect specimens of plants in different stages of growth.
Digger : It is an instrument to dig earth to take out root or tuber part of plant from soil.

Secateur : It is an instrument to cut branches of woodyplants.

Vasculum : It is Aluminum container to collect plant parts. Its inner wall is lined by cork sheet which prevent plants from drying.

Plant Press : It is a set of equipment used by botanists to flatten and dry field samples so that they can be easily stored. A professional plant press is made to the standard maximum size for biological specimens to be filed in a particular herbarium. A plant press is 12″ x 18″ (30 x 45 cm) in size. A flower press is a similar device of no standard size that is used to make flat dried flowers or pressed flower craft. A modem plant press consists of two strong outer boards with straps that can be tightened around them to exert pressure. Between the boards, fresh plant samples are placed, carefully labelled, between layers of paper. Further layers of absorbent paper and corrugated cardboard are usually added to help to dry the samples as quickly as possible, which prevents decay and improves color retention. Layers of a sponge material can be used in order to prevent squashing parts of the specimens, such as fruit. Older plant presses and some modem flower presses have screws to supply the pressure, which often limits the thickness of the stack of samples that can be put into one press. It sample specimens are larger in size than it has to be folded in ‘v’ or ‘w’ shaped.

Field Diary or Note Book : A person has to collect maximum information of plants during collection of plants from field related With it habitat and habits. It is a specific field diary in which a specific number has to be given to every collected specimen and on a page all necessary information are recorded as follows:
- Place of collection or locality
- Date of collection
- Local name of plant and serial number of collection
- Botanical name and Family of plant
- Color of flower
- Habitat
- Abundance
- Plant Association
- Type of soil
- Collector’s name
- Other information
Polythene bags : Various types of Polythene bags used to collect fruit or inflorescence or other parts of plant.
Forceps : It is instrument to pluck off the leaves of plants.
Hand Lens : It can be use to see plant part in enlarge view.
Rubber bands : Used to keep all the things safe and one place.
Blotting papers and newspapers : To dry the leaves.
Drying of specimens :
- For drying of specimens plant press usually kept in some lighted condition.
- The specimens are spread out between the folds of old newspapers or blotting sheets avoiding overlapping of parts.
- The larger specimen may’ folded in ‘V’ or’ W’ shapes.
- Blotting paper or newspaper should change every 24 hours for proper drying of plant part so fungal growth can be avoided.
- The blotting sheets with plant specimen should be placed in the plant press for drying. After 24 to 48 hrs the press is opened.
- These days electric heater is used in rainy season or hilly areas to dry plant specimens.
Preparation of herbarium sheet :
- The dried specimens are mounted on herbarium sheets of standard size 11.50″ x 16.50″ (28.75 x 41.25 cm).
- Herbarium sheets are very thick and strong handmade card sheet which can be kept safe for long time.
- Name of herbarium is printed on the top of herbarium sheet and on right bottom comer of sheet contains all necessary information.
- Mounting is the process to paste dried specimens on the sheet.
- For mounting take a tray of 12″ x 18″ size and mix glue or fevicol with Mercuric chloride.
- Now dried specimen is dipped in it from one side so glue stick with it on one side.
- Now this dried specimen is paste on sheet properly.
- The bulky plant parts like dry fruits seeds, cones etc. are dried without pressing and are put in small envelops called fragment packets. Succulent plants are not mounted on herbarium sheets but are collected in 4% fomralin or FAA (Formalin Acetic Alcohol).
Labeling of the herbarium sheet :
- A label of 3″ x 5″ (7.5 x 12.5 cm) is pasted or printed on the lower right hand comer.
- The label should indicate the following information :
- Firstly name of institute where this herbarium is situated, e.g, Herbarium. Department of Botany, College of Science, Udaipur.
- Locality from where specimen is collected, e.g., Flora of Udaipur district or Flora of Rajasthan
- Name of family
- Botanical name of plant
- Name of locality
- Date of collection
- Altitude
- Habit
- Complete information about the area from where specimen collected
- Name of collector
- Collector’s field number
- Local or Common name and other information get from local peoples of the area.
Filing of herbarium sheet or Storage :
- The process to keep properly dried, pressed and identified plant specimens in sequential, scientific and approved classification method is called Filing.
- All specimen of a species are placed in thin paper folds (specimen covers) which are kept together in thicker paper folders genus covers), and finally they are incorporated into the herbarium cupboards in their proper position according to a well known system of classification.

- In England and India Bentham and Hooker’s system of classification is used for this purpose.
- The mounted specimens are sprayed with fungicides like 2% solution of mercuric chloride for preservation.
- Almirah and segments in which herbarium are kept also protected from insects by spraying DDT. Naphthalene balls etc. once in year all herbarium sheets are fumigated by CS2 (Carbon disulphide) in closed room or box.
Role of Herbarium in Modern Plant Taxonomy :
- Herbarium is basis for studies of plants such as Identification of plants, Nomenclature. Classification of plants etc.
- Without knowing about the species, genus, family and characteristics of plants categorization of plants would not be possible.
- Herbarium is the source to get information about habitat and characteristics of plants which helps in categorization of plants.
Some Important Herbarium of World :
| S.No. | Name | Number of specimens |
| 1 | Roval Botanical Garden of Kew, UK | 60 Lac (6 Million) |
| 2 | V.L Komarov Botanical Institute. Leningrad | 50 Lac (5 Million) |
| 3 | British Museum of Natural history, London | 40 Lac (4 Million) |
| 4 | Perris Botanical Garden | 1 Crore (10 Million) |
| 5 | Harvard University, Cambridge | 50 Lac (5 Million) |
| 6 | Indian Botanical Garden. Kolkata | 25 Lac (2.5 Million) |
Some Important Herbarium of India :
| S.No. | Name | Number of specimens |
| 1 | The Central National Harbarium. Kolkata | 4 Lac |
| 2 | National Botanical Garden (NBG), Lucknow | 1 Lac |
| 3 | Botanical Garden and Forest Research Institute, Deliradun | 3 Lac |
| 4 | Plant Harbarium of Botanical Department. Delhi University | 50 Thousand |
| 5 | Science Museum, Department of Botany, University of Rajasthan, Jaipur | 40 Thousand |
- In India systematic research and investigation of plants to studies plant taxonomy started in 19th century with publication of Bentham Hooker’s book “Flora of British India”
- First Herbarium of India founded by Botanical Survey of India (BSI) in Kolkata latter on many universities and institutes founded their own Herbarium for studies.
- Some famous Herbarium of India are as follows :
1. The Central National Herbarium Kolkata CNH :
- It is largest Herbarium of India as well as of Asia.
- This Herbarium founded by William Roux berg (1793).
- It has a collection of approximately 4 lac plant specimens.
- This Herbarium has collection of plants from India, Europe. America, China, Australia and Japan.etc.
- It has collection of Angiosperms, Ferns, Gymnosperms and other non floral plants.
2. The Herbarium of National Botanical Research Institute, Lucknow :
- It is one of the famous Herbarium of India.
- It is founded in 1948 state Government of UR
- It has a collection of more than 1 lac plant specimen in well preserved form.
- Apart from Herbarium NBG has big Library, Large Green house, laboratories for Palynology, Plant Physiology and Tissue Culture for research and investigation.
3. Forest Research Institute Herbarium, Dehradun :
- This Herbarium was founded by British Government in
- 1874 in Dehradun but present set up established in 1908.
- It is one of the largest plant museum and second largest Herbarium after The Central National Herbarium Kolkata.
- It has collection of 350000 plant specimens from India, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Tibet and Myanmar.
4. The Herbarium of Department of Botany, Delhi University :
- One of the famous plant museum of North India having 30000 plant specimens.
5. The Herbarium of Department of Botany, Rajasthan University, Jaipur :
- It is founded in 1965.
- It has collection of 40000 plant specimens from Rajasthan and neighboring states.
- It is used for studies of plants from Rajasthan.
RBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 24 Additional Questions
Question 1.
Who established botanical gardens in India 550 BC before Aristotle?
Answer.
Jivak Komar Britiy
Question 2.
What other name is given to botanical gardens?
Answer.
Outdoor laborateries.
Question 3.
Where is shalimar and Nishat Garden located?
Answer.
Shrinagar.
Question 4.
What is the new name of Royal Indian Botanical Garden, Shibpur, Kolkata?
Answer.
Archaraya Jagdish Chandra Bose Indian Botanic Garden.
Question 5.
What are the objectives of Herbarium?
Answer.
Objectives of Herbarium :
- Herbarium is used for identification of plants.
- Specimen alongwith description on herbarium sheet constitutes a storehouse or repository of knowledge for future reference and research work in the field of plants. Herbarium gives necessary information and plant specimen for better understanding.
- Study of plant is not interesting and easy when studied by diagrams, photographs and description but herbarium makes it interesting and learning oriented.
- Some time herbarium is helpful to compare and study- plants from an area if their specimens are systematically arranged in the form of herbarium sheet.
- Useful to keep specimens of newly described taxa.
- Helpful to study flora of different places.
- Ecology of different places can be understood by herbarium.
- Helpful to identify plants.