Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 History Chapter 7 The World After the Second World War
RBSE Class 11 History Chapter 7 Text Book Questions and Answers
RBSE Class 11 History Chapter 7 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Which organization was established after the first world war for maintaining peace in the world?
Answer:
After the first world war, league of Nations was established in 1920 CE-for maintaining peace in the world.
Question 2.
Cold war was fought between which two superpowers?
Answer:
Cold war was fought between America and Russia.
Question 3.
The writer cum journalist of USA Walter Lippmann wrote which book?
Answer:
The writer cum journalist of USA Walter Lippmann wrote the book ‘Cold War’.
Question 4.
Who said that British-American cooperation is essential for lighting the flame of freedom and for the protection of Christian civilization?
Answer:
British Prime minister Winston Churchill said that British American cooperation is essential for lighting the flame of freedom and for the protection of Christian Civilization.
Question 5.
When did enviroment conservation-related earth summit happen in Rio-de- Janeiro?
Answer:
Environment conservation related earth summit happened in Rio-de-Janeiro in 1992 CE.
Question 6.
Who said that terrorists use methods which are inhuman, menacing and violent and violate international laws to fulfil their immediate objectives?
Answer:
Berger said that terrorists use methods which are inhuman, menacing and violent and violate international laws to fulfill this immediate objectives.
Question 7.
Where did the 17th Summit of Non-Aligned movemnt took place?
Answer:
The 17th Summit of Non-Aligned movement took place in Venezuela.
Question 8.
Name the five member states of BRICS.
Answer:
The five member states of BRICS are : Brazil, Russia, China, India and South Africa.
Question 9.
In the 12th India-ASEAN Summit, Prime minister Narendra Modi named ‘look east policy’ as?
Answer:
In the 12th India-ASEAN summit Prime minister Narendra Modi named look east policy as ‘Act East Ploicy5.
Question 10.
Which country became the 8th member of SAARC?
Answer:
Afghanistan became the 8th member of SAARC.
RBSE Class 11 History Chapter 7 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What do you understand by cold war?
Answer:
The term ‘Cold War’ stands for hostile and tense international relations between USA and USSR. It was based on political distrust, espionage and diplomatic manoeuvering. When both parties (America and USSR) involved, threaten each other on international platform to wage open war if their interests are not secured, this situation is termed as ‘Cold War’.
Cold War was the result of ideological differences which fose in the post world war era. One ideology was capitalist led by USA and another was communist headed by USSR. The idea of armed supremacy was visualised to become the superpower of the world.
Question 2.
Write the hymh of 10th Mandal of Rigveda which says it is sin to eat alone.
Answer:
It has been stated in the ninth mandal of Rigveda :
- Moghamanna Vindate Apracheta
- Satya bravimi Vadh itsa tatsya
- Narmana Pusyati No Sankayam
- Kewatagho bhavati Kevatadi
It means the one who eats alone without sharing with others intake sins. This implies that the resources must be shared commonly without concentration to one class of the society.
Question 3.
Write the names of any ten nations formed after the disintegration of Soviet Union.
Answer:
As a result of disintegration of Soviet Union, the following nations were formed :
- Armenia
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Estonia
- Georgia
- Kazakhastan
- Kyrgyzstan
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Moldova
Question 4.
NAM’s 10th, 11th, 13th, 14th and 16th summit were held when and where?
Answer:
NAM’s 10th summit was held in 1992 in Indonesia, 11th summit in 1995 in Columbia, 13th summit in 2003 in Malaysia, 14th summit in 2006 in Cuba and 16th summit in 2012 in Iran.
Question 5.
India is a NAM country, but still until the collapse of Soviet Union, its inclination was towards the Soviet Union. Why?
Answer:
The main causes of India’s inclination towards the Soviet Union were the following :
- In 1971 when Pakistan was threatening to wage war and China sided with Pakistan and USA also decided to stay neutral, India’s inclination became towards Soviet Union and India signed a treaty with Soviet Union.
- The first prime minister of India Jawahar Lai Nehru was also interested in communism from the beginning.
- America favoured Pakistan in the matter of Kashmir and provided military aid to it. Due to this also, India’s inclination towards Soviet Union increased.
Question 6.
State the differences between capitalism and communism.
Answer:
Capitalism: An economic and political system in which a country’s trade and industry are controlled by private owners for profit, rather than by the state. It the oldest and most common of all economic systems. The government of USA is an example of capitalism.
Communism: Economic and social system in which all property and resources are collectively owned by a classless society and not by individual citizens. It is the political belief that all people are equal and that workers should control the means of producing things. The government of Cuba is an example of communism.
Question 7.
What do you mena by CTBT? Write full form of CTBT.
Answer:
CTBT is Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty. This treaty came into existence on 24 September 1996. At that time 71 countries signed on it. Later, this number of states increased and became 178. This is the treaty banning all nuclear explosion, everywhere by anyone. Till now, India and Pakistan has not signed on it.
Question 8.
What do you know about agenda 21? Explain with references?
Answer:
In 1992 in Rio-de-Janeiro in Brazil was convened the ‘Environment and Development conference’, also known as earth summit. More than 150 representatives of the world participated in it. The important subjects related to the environment were discussed in the summit. It was also decided to establish Global Environment Facility (GEF), a world bank for financial assistance. It was also expected to protect biodiversity of the world. In the conference a historic document ‘Agenda 21’ of 800 pages was also prepared. It highlighted the important points which needed the attention of the world.

In the earth summit 1992, the developing countries tried to prove the fact that developed countries were more responsible for the damage of environment in comparison to developing countries, which of course divided the summit into two groups. Thus develped nations accepted their greater responsibility and agreed to provide financial assistance through ‘Agenda 21’.
Question 9.
With reference to foreign relations what is the core of Modi Experiment?
Answer: In the context of foreign relations of countries, the main element of Modi is experiment is ‘development’. On May 2014, after becoming the prime minister, Narendra Modi had made it clear to various states of the world that there would be differences on various matters but not on the matter of development. Thus the world must get united for the development.

Question 10.
What do you mean by modern and institutional form of terrorism?
Answer:
Modern Nature of Terrorism : The terrorism visible in modern world, not only targets specific people of various places, but also affects each and every person of the world, whether women or children. It has been a matter of shame that the creation of God, the man, turned into a devil and undertook such violent activities. The nature of terrorism could be understood on the basis of some examples : Hijack of Indian plane from Kathmandu in 1999, Attack on world trade centre of New York in 2001 and attack on Parliament in 2001 are such events which showcase the horrific barbarities inflicted by terrorists in different parts of the world.

Institutional nature of Terrorism : This peculiar feature of Terrorism observed today is the ‘Human Bomb’. The youth of the world is being brainwashed by such terrorist institutions that in turn are raising a population of ‘Human Bombs’. Every part of the world is affected by this type of t errorism. They themselves are the victims and very meticulously they carry out terrorist activities in other countries.
RBSE Class 11 History Chapter 7 Very Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Throw light on Cold War while explaining various stages of Cold War.
Answer:
Cold War was the result of ideological differences which rose in the post-world war era. One ideology was capitalist led by USA and another was communist headed by USSR. The cold war between these two superpowers had begun informally in 1917 with the outbreak of Bolshevik revolution and lasted till the disintegration of Soviet Union in 1990. Its main phases were the following :
1. First Stage (1917-1945 AD)
- Communist government was established in Russia by Bolshevik revolution in 1917 CE.
- After that the incidents such as establishment of control over eastern European Nations by Soviet Union, holding a different view regarding acquisition of Italy by Germany, raising voice agaisnt the bombardment of Japan by USA, etc. laid the foundation of Cold War.
2. Second Stage (196 CE-1953 CE)
- In 1948, western Germany was separated from eastern Germany by USSR,
- In 1949 North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO) was established under the leadershhip of USA as an armed force. Through NATO a message was given to Soviet Union that attack on any member of NATO would invite wrath of itself,
- In the same year communism was established in China and it accelerated the conflict between USA and Soviet Union over the issue of admission of China in UNO.
- The bitterness turned into hostility finally in 1950 when communist North Korea attacked capitalist South Korea.
3. Third Stage (1953-1958 CE)
- USSR tested its first nuclear device in 1953.
- To check the spread of Russia, President Eisenhower of America formed SEATO (South East Asian Treaty Organisation).
- The USSR retaliated this move by forming a communist defense pact consisting of Eight nations known as Warsow Pact in 1955. It was an answer to NATO, o In the opposition of communist Russian invasion, American Senate passed a bill regarding privilege for President.
- Russia criticized the attack on Egypt in 1956. Due to this, tension was created between these two superpowers.
4. Fourth Stage
- In May 1960, a helicopter of America was caught manouvering on the borders of Soviet Union. This event led to the failure of Paris conference,
- In 1961, Berlin wall crisis and rise of Fidel Castro of Cuba were the main events of Cold war.
5. Fifth Stage (1963-1979 CE)
- In 1963, America and Russia signed ‘Hotline Agreement’. According to which in the time of emergency, they would communicate through radio and telephones,
- in 1968, they both signed Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT).
- In 1971, America, Soviet Union, Britain and France signed treaty to allow the movement of people from western to eastern Germany and Vice-versa.
- In 1971, Indo-Pak war, America favoured Pakistan and Russia favoured India,
- In 1973, 1974 and 1977, three European security conferences were convened for mutual cooperation and peace in the countries.
6. Last Stage 1980-1990 AD
- In 1983, Soviet Union destroyed a South Korean plane. This was condemned by the US.
- In 1986, Soviet Union conducted Nuclear Test after removing restriction from itself. It also warned Ameria not to retaliate back.
- In 1989, Germany was unified again.
Thus, due to continuous Cold War Soviet Union became financially weak and lost the power to remain in conflict with America. So in the reign of President Mikhail Gorbachev, Soviet Union disintegrated in 1990, and along with it the Cold War came to end.

Question 2.
Under what circumstances did Non-Aligned Movement begin?
Answer:
After the second World War, America and Russia emerged as superpowers. Contemporary independent states wanted to enjoy real freedom and to get rid of any vestige of the dominance of superpowers. So these nations were called Non-aligned. Non-Aligned movement (NAM) came into existence in 1961 which is working till now. The circumstance which gave birth to NAM were the following :
1. Beginning of Cold War : In the post-war period, most of the countries believed that division of nations into two blocs and consequent Cold War was not in the larger interest of world community. This polarisation might endanger world peace. That’s why the countries related to NAM wanted to stay non aligned from the superpowers.
2. Fear of Superpowers : The non-aligned nations believed that by maintaining distance from both the blocs (America & Russia), they might put off nuclear war indefinitely and remove doubts, misunderstandings and illusions from the minds of great powers and persuade them to accept the policy of peaceful co-existence and cooperation, and to defer destruction.
3. Protection of Sovereignty : A sovereign nation has the right to take its internal and external decisions. But if any nation joins any bloc, definitely its sovereignty would get compromised. So for the protection of sovereignty it was necessary to be non-aligned from any group.
4. Protection of Political and Cultural Traditions : Every nation has its own cultural and political traditions, and every nation tries to keep these traditions intact so that their identity could be preserved. This is possible when a country would not come under the influence of any super power and it should be non-aligned also.
5. Protection of Resources : If in special circumstances any nation gets military and financial help from any superpower, it has to pay more cost for it and it loses its prosperity. So to protect their valuable resources, newly independent nations adopted the policy of non alignment.
6. Economic Dependence : The most important cause for opting for non-alignment was economic. The newly-independent nations were economically backward and wanted to accelerate their development. They did not like to join any bloc and thought it better to get both these things from wherever they could, without any strings attached with them. Thus these nations kept themselves away from the two blocs and this ideology came to be known as Non-Aligned movement.
7. Comfortable Situation : After the second World War it has become comfortable for non-aligned countries to progress by making a separate organization.
Thus, due to above reasons NAM came into existence.

Question 3.
Who gave the theory of ‘End of History’? Analyse the reason of its failure.
Answer:
After the second World War as the result of Cold War Soviet Union got disintegrated. After the disintegration of Soviet Union the world became unipolar and leadership of world came in the hands of America. After the disintegration of Soviet Union, Socialists also concluded that the world has accepted the liberal democracy of west. America’s politico-economist Francis Fukuyama declared the end of History but these principles proved irrelevant because :
- Fukuyama could not understand that there could be no end of history nor the destruction of supreme form which dissolves humanity.
- World has not given recognition to the end of History.
- A group of thinkers said that another superpower will arise which is superior in the world.
- Philosophers have not declared the end of history. On this saying rather they ended the declaration of Fukuyama.
- Criticising communism, Fukuyama forgets that it was the end of Soviet Union and not the end of communism or socialism as an ideology.
- Even today communist philosophy attracts the people.
- Liberal democracy could not solve all the problems faced by humanity.
- Due to the concept of Globalisation, unipolar world headed by USA would not last for long.
- Now the interaction of civilizations would be written in the place of Nations.
- So it should be hoped that the situation of unipolar world would not remain for a long period of time.
Question 4.
Which issues were discussed in the Rio-de-Janeiro summit of conservation of environment?
Answer:
In 1992 in Rio De-Janeiro in Brazil convened environment and development conference, also known as Earth summit’. More than 150 representatives of the world participated in it. The important subjects related to the environment were discussed in the summit.
1. Issue Related to Climate Change : Earth summit on climate change in Rio-de-Janeiro was ratified by the member countries in which they pledged to reduce the emission of harmful gases to the level of 1990 by 2000. It was also decided to establish Global Environment Facility (GEF), a world bank for financial assistance.
2. Protection of Biodiversity : The nations which participated in this summit hoped to protect biodiversity of the world.
3. Agenda 21 : In this conference a historic document Agenda 21 of 800 pages was also prepared. It highlighted the important points which needed the attention of the world. Also under Socio-economic council of UNO, sustainable development commission was established.
4. Financial Help to Developing Countries for the Implementation of Agenda 21: In the earth summit 1992 the developing countries tried to prove the fact that developed countries were more responsible for the damage of environment in comparison to developing countries. Thus developed nations accepted their greater responsibility and agreed to provide financial assistance through ‘Agenda 21’.
5. Criticism of Developed Countries for not Shouldering the Responsibility of Environmental Pollution : The representatives of the summit showed environmental concerns, however they resisted the ratification of treaties related to this. For this action 77 developing countries criticised developed countries in Rio-De-Janeiro summit for not shouldering the responsibility of environmental pollution.
Question 5.
Which conventions were presented to prevent the spread of terrorism by UNO?
Answer:
The supreme organisation where a nation could raise voice for assistance against terrorism is United Nations Organisation (UNO). However UNO has itself become a toy in the hands of its five founding members, mainly USA. Still for the welfare of mankind, UNO has been makking attempts to eradicate terrorism from the Earth. For this international court has been established, but it has various shortcomings.
The prominent one is that the law could not be implemented mandatorily, still UNO has been successful to put moral obligations on the part of the nations to not nourish terrorism on their soil, as it would jeopardize world peace. To fight the problem of terrorism, various agencies have framed documents related to agreements and treaties, from time to time. They are as follows :
- In a convention in Tokyo in 1963 crime related to plane hijacking and measures to prevent it.
- At the Harare convention of 1970, some important provisions were made to stop hijacking activities.
- Again in 1973, a convention was held in New York to punish the criminals targeting internationally recognised people.
- Then a convention was held in Rome in 1988 in relation to maritime security.
Apart from various agencies, General assembly of UNO also took certain measures in conventions.
- A convention was held in 1979 against the fugitive matters, where the country extending asylum to the criminal has to surrender the person otherwise it would face sanctions.
- Convention held in General assembly against attack on the official of UNO.
- In 1999, the person involved in terrorist funding to face extradition from the victim country.
Thus, it is evident that terrorism is one of the major challenges faced by the world today, which the world has to solve with patience, solidarity and unity.

Question 6.
Explain the objectives and principles of SAARC.
Answer:
SAARC was established in 1985 at Dhaka in Bangladesh. In this the heads of seven nations (India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, Sri Lanka, Maldives) formed a union named South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation. The secretariat of SAARC is in the capital of Nepal, Kathmandu. Afghanistan is the eighth member of this organization. Till now 18 summits have taken place by November 2014. 19th summit is to be organised in Pakistan.

The Objectives of SAARC
- Promote the welfare of the people of South Asia and improve their quality of life.
- Accelerate economic growth, social progress and cultural development in the region by providing all individuals, the opportunity to live in dignity and realise their full potential.
- Promote and strengthen collective self reliance among the countries of South Asia.
- Strengthen cooperation with other developing countries.
- Contribute to mutual trust, understanding and sensitivity to one another’s problems.
- Promote active collaboration and mutual assistance in the economic, social, cultural, technical and scientific fields.
- Cooperate with international and regional organisations having similar aims and purposes.
Principles of SAARC
- Sovereign equality, territorial integrity, national independence, non-use of force and non interference in the internal affairs of other states.
- Bilateral and multilateral cooperation.
- Reaffirming their determination to promote such cooperation within an institutional framework.
Question 7.
Do you believe that India is a forerunner for world peace? Explain with reasons.
Answer: India has rich culture and traditions. From ancient time India has peaceful and strong relationship with other countries. According to our ancient literature Vedas and Upanishads we should live peacefully for the public welfare. In ‘Atharva Veda’ it is said :

Maintaining world peace is a thought to establish non-violence on the whole earth. Under this, nations cooperate with a system of administration so that the situation of conflict cannot be created and future wars can be prevented. India contributes in maintaining world peace by the following ways.
- From the beginning India became the founder member of UNO, which was established for international peace and protection.
- After the second World War when America and Russia emerged as superpowers, India decided to be non-aligned from any superpower.
- India’s first Prime minister Pt. Jawaharlal Nehru gave five principles as stated by the Panchsheel treaty signed on April 29, 1954.
- Mutual respect for each other’s territorial integrity and sovereignty.
- Mutual non-agression.
- Mutual non-interference in each other’s internal affairs.
- Equality and cooperation for mutual benefit.
- Peaceful co-existence.
India always follows these principles. So it can be said that India is a forerunner for world peace.
RBSE Class 11 History Chapter 7 Other Important Questions
RBSE Class 11 History Chapter 7 Tick the Correct Options
Question 1.
The term ‘Cold War’ is used firstly by which writer?
(a) Water Lippman
(b) Lui Halle
(c) Fisher
(d) George Orwell
Answer:
(d) George Orwell
Question 2.
In which year did the Bolshevik Revolution occur?
(a) 1912
(b) 1917
(c) 1920
(d) 1914
Answer:
(b) 1917
Question 3.
Which military force was formed under the leadership of America in 1949?
(a) BRICS
(b) NATO
(c) SEATO
(d) SAARC
Answer:
(b) NATO
Question 4.
The countries which signed Nuclear Non-proliferation Treaty (NPT) in.1968 were
(a) America-Russia
(b) Britain-France
(c) India-Pakistan
(d) Italy-Germany
Answer:
(a) America-Russia
Question 5.
How many members of UNO adopted the policy of Non-alignment?
(a) One third
(b) One fourth
(c) Two third
(d) Half
Answer:
(c) Two third
Question 6.
Who is the writer of ‘The Scope of Neutralism’?
(a) Beriger
(b) Lippman
(c) Lui Halle
(d) Fisher
Answer:
(a) Beriger
Question 7.
Which summit of NAM was held in India?
(a) Thirteenth
(b) Seventh
(c) Second
(d) Eleventh
Answer:
(b) Seventh
Question 8.
In 1997 world environment and Green House summit was held in which country?
(a) In Russia
(b) In Australia
(c) In India
(d) In Japan
Answer:
(d) In Japan
Question 9.
When did India become the member of Regional Forum of ASEAN?
(a) In 1996
(b) In 1997
(c) In 1998
(d) In 1999
Answer:
(a) In 1996
Question 10.
On which place was the eighth summit of BRICS group held?
(a) Japan
(b) India
(c) Italy
(d) Sri Lanka
Answer:
(b) India
RBSE Class 11 History Chapter 7 Matching Questions
Question 1.
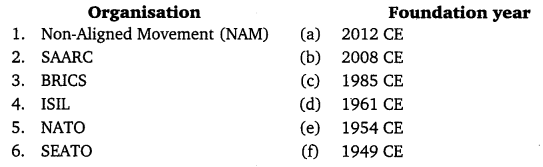
Answer:
1. (d)
2. (c)
3. (b)
4. (a)
5. (f)
6.(e)
Question 2.

Answer:
1. (c)
2. (a)
3. (b)
4. (e)
5. (d)
6.(h)
7. (f)
8. (g)
RBSE Class 11 History Chapter 7 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Who had used the term ‘Cold War’ and why?
Answer:
The term Cold War was used by George Orwell in the context of bitter relations between the countries in modern international politics.
Question 2.
Mention any one definition of cold war.
Answer:
Louis Hall writes that “It was a bitter state of tension between the two blocs, more dangerous than the armed conflict. It was the war of nerves.”
Question 3.
Which historical event occured in Russia in 1917 CE?
Answer:
In 1917 the Bolshevik Revolution occured in Russia which became the cause of Cold War.
Question 4.
Which military force was formed under the leadership of America in 1949?
Answer:
In 1949 under the leadership of America, North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO) was formed.
Question 5.
After Stalin the leadership of Russia came in the hands of which leader?
Answer:
In 1953 after the death of Stalin the leadership of Russia came in the hands of Khrushchev.
Question 6.
Who formed SEATO and why?
Answer:
To prevent Russian influence in Asia, American leader Eisenhower formed South East Asian Treaty Organisation (SEATO).
Question 7.
What was hotline agreement?
Answer:
In 1963 America and Russia signed ‘Hotline Agreement’ according to which in the time of emergency, they would communicate through radio and telephones.
Question 8.
Which countries signed on Nuclear Non Proliferation Treaty (NPT) of 1968?
Answer:
America and Russia signed on Nuclear Non Proliferation Treaty (NPT) of 1968.
Question 9.
In whose reign was the Soviet Union disintegrated?
Answer:
Soviet Union was disintegrated in the regime of President Mikhail Gorbachev.
Question 10.
What was the most important result of the Cold War?
Answer:
The most importnat result of the Cold War was the disintegration of Soviet Union.
Question 11.
Which policy was adopted by India after Independence?
Answer:
Non Aligned policy was adopted by India after independence.
Question 12.
As a result of which revolution the autocratic rule of Czar came to end in Russia?
Answer:
In Russia the autocratic rule of Czar came to end as a result of Bolshevik Revolution.
Question 13.
What are the six principles of Non Alignment?
Answer:
The six principles of Non Alignment are as follows :
- Separatism
- Irrelevance
- Neutralism
- Neutralization
- Monotheism
- Non attachment.
Question 14.
Who were the founder leaders of Non Aligned movemnt?
Answer:
The founder leaders of Non Aligned movement were : India’s Prime minister Jawahar Lai Nehru, The President of Egypt Gamen Abdel Naser and the President of Yugoslavia Josef Broz Tito.
Question 15.
When was the alliance and cooperation treaty signed between India and Soviet Union?
Answer:
The alliance and cooperation treaty was signed between India and Soviet Union in 1971.
Question 16.
What is the main objective of Islamic State terrorist organization?
Answer:
The main objective of Islamic State terrorist organization is to establish control over nations of Muslim majority.
Question 17.
Who was declared as Khalifa of Muslims by ISIS terrorist organization?
Answer:
ISIS terrorist organization declared their head Abubakr A1 Baghdadi as Khalifa of Muslims.
Question 18.
What is the name of the highest international institution of the world?
Answer:
The highest international institution of the world is United Nations Organisation.
Question 19.
What were the two major challenges of the modern world?
Answer:
The two major challenges of the modern world are : Environment and terrorism.
Question 20.
How many member of states were in BR1CS group in the beginning.
Answer:
In the beginning four member states were there in BRICS group : Brazil, Russia, India and China.
Question 21.
Who first gave the idea of BRICS?
Answer:
The idea of BRICS was given first by American economist Zim-O-Nile in 2001.
Question 22.
How many provisions are there in the charter of SAARC?
Answer:
There are 10 provisions in the charter of SAARC.
Question 23.
Mention the name of organising venue of 19th summit of SAARC.
Answer:
The organising venue of 19th summit of SAARC is Islamabad, the capital of Pakistan.
Question 24.
Which summits of SAARC were organised in India?
Answer:
SAARC’s second summit in 1986, Eighth summit in 1995 and fourteenth summit in 2007 were organised in India.
Question 25.
Who took an oath as the Prime Minister of India in 2014?
Answer:
In 2014, Shri Narendra Modi took an oath as the Prime Minister of India.
RBSE Class 11 History Chapter 7 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
How was the preface of Cold War formed?
Answer:
After the second World War, tension and hostility increased between USA and USSR. It was based on political distrust, espionage and diplomatic manoeuvering. When both the parties involved, threaten each other an international platform to wage open war if their interests are not secured, this situation is termed as ‘Cold War’. The cause of this were the following :
- To establish control over Eastern European countries by Soviet armies.
- Holding a different view regarding acquisition of Italy by Germany.
- Raising voice against the bombardment of Japan by USA.
The above events laid the foundation of the Cold War.
Question 2.
What was ‘Warsaw Pact’?
Answer:
To check the onward march of communism in South East Asia, America formed SEATO (South East Asian Treat Organisation). The USSR retaliated this move by forming a communist defence pact consisting of eight nations knows as ‘Warsaw Pact’ in 1955. It was an answer to NATO and SEATO. This pact was done in Warsaw (Poland) for formally gaining cooperation and mutual friendship.
Question 3.
Why did India adopt the policy of Non Alignment after independence?
Answer:
In 1947 Indian got independence. After independence India followed a middle path of not joining any hostilecamp and walked on the path of welfare and actively placed itself in international politics. Along with this, the contemporary Indian leaders knew very well that refined Indians would not like the idea of capitalism and communism. So India adopted the policy of non alignment.
Question 4.
How did the Cold War become responsible for non-alignment Movement (NAM)?
Answer:
In the period of Cold War, the competition to be superpower between USA and USSR created a prolonged crisis. However, they both did not use real weapons against each other, but their diplomatic invasions created a great fear for newly independent states and they thought if they joined any one bloc, the other would destroy them. In that condition it was more suitable to be non-aligned. Thus Non-aligned Movement came into existence and newly independent states adopted the policy of non alignment.
Question 5.
Which are the two major institutions of NAM and what are their functions?
Answer:
The two major institutions of NAM are the following :
1. Co-ordination Bureau : It was the function of co-ordination Bureau to choose the matters for discussion and deliberations on different platforms of the world by the member states. It consisted of 66 members who were elected.
2. Summit or Conference : It is divided into two parts. First in ‘Ministerial level summit’ whose participants are foreign ministers of the member nations. The second part in the summit, the heads of the government of the member countries participated in the top-level summit’. It meets once in three years.
Question 6.
What is top-level summit in the context of Non-Alignment?
Answer:
Top-level sumit is the highest-level conference of member states in which the heads of the government of member states participate. It is held once in three years. Four types of representatives can take part in its meeting full-members, observer states, non-member states and Guests. This summit is seen dias an important event in international politics. Till 2015, NAM has had 17 sessions.
Question 7.
Describe in brief the efforts of UNO for environmental conservation.
Answer:
- Till two decades of the establishment of UNO, environmental agenda was not given priority by UNO. After 1960, oil spills leading to water pollution matters were taken up by UNO.
- In 1970, an ambitious programme of reducing expansion of desertification in South Africa was run by UNO.
- In 1972 at Stockholm convention, the matter was highlighted that non-conservation would lead to economic impediment.
- After this convention, countries established United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP).|
- In the 1980’s, the general assembly of UNO organised a convention on environment and development, where importance on aim of sustainable development was highlighted otherwise future generations would be affected.
- The same decade, witnessed the agreements related to protection of ozone layer and emission of hazardous chemicals.
Question 8.
What was the main issue discussed in world environment and greenhouse summit in Japan? What solution was decided for it?
Answer:
In 1997, world environment and greenhouse summit was organised in Kyoto (Japan) which discussed the reduction in the emission of gases responsible for global warming. They came up with a solution to set binding targets for the emission of gasses. It was decided in the protocol to limit the emission of EU by 8%, USA 7% and Japan 6% between 2008 and 2018.
Question 9.
Write a short note on Islamic State terrorist organisation.
Answer:
Islamic State (IS) also known as Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS) or Islamic state of Iraq and Levant (ISIL), was established in 2013. The methodology of ISIS is more barbarous as compared to Al-Qaeda. The motive of ISIS is to establish control over nations of Muslim majority. To fulfil this, it wanted to control the regions of Jordan, Israel, Palestine, Lebanon, Kuwait, Cyprus and Southern Turkey and then to expand in other areas. For this ISIS in 2014 declared their leader Abubak A1 Baghdadi as the Khalifa of the Muslim community. Their
working pattern include undertaking violent activities in an area and when people of that area migrate, then they also migrate with them to enter other nations. This could be understood from the example of Syria.
Question 10.
How far did the efforts of UNO become successful in preventing terrorism.
Answer:
The supreme organisation where a nation could raise its voice for assistance against terrorism is United Nations Organisation (UNO). For the welfare of mankind, UNO has been making attempts to eradicate terrorism from the earth. For this, international court has been established. UNO has been successful to put moral obligations on the part of the nations to not nourish terrorism on their soil as it would jeopardize world peace. To fight the problem of terrorism, various agencies have framed documents related to agreements and treaties from time to time.
Question 11.
What was Gujral doctrine?
Answer:
I.K. Gujral became prime minister after H.D. Devegowda. When he was foreign minister, he gave certain principles related to foreign policy which are popularly known as ‘Gujaral Doctrine’. According to which, with neighbours like Bangladesh, Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal and Sri Lanka, India does not ask for reciprocity, but gives and accommodatees what it can in good faith and trust—mutual non-aggression, mutual non-interference in each other’s internal affairs, mutual respect for each other’s territorial integrity, and sovereignty, and equality and mutual benefit and peaceful co-existence.
Question 12.
‘String of Pearl’ policy was adopted by whom and why?
Answer:
China is trying from many years to surround India from the seas. For this, China is working towards the policy of ‘String of Pearls’. The first mention of ‘String of Pearls’ are found in the report ‘Future of Energy5 released by Defence Department of Pentagon of USA. ‘Pearls’ here means establishment of bases by China starting from South China sea to Malacca Strait, Bay of Bengal, Arabian Sea. India has always resisted this policy of China.
Question 13.
What in Mekong-Ganga Project?
Answer:
Under Mekong-Ganga Project, Mekong-Ganga cooperation was consistuted consisting of five members : India, Laos, Thialand, Cambodia and Vietnam. This began the cooperation in the fields of trade investment, technology, tourism, education and culture.
Question 14.
What were the main features of Delhi declaration of BRICS conference?
Answer:
In the fourth top-level summit, the members of BRICS issued a document known as Delhi Declaration. The main features of this declaration were as following :
- It proposed the methods and solutions to do away with financial crisis and to restore faith in the international market.
- Under this declaration, the major achievement of BRICS summit was that the members signed an accord according to which they could trade with each other without the use of dollar as a currency.
- Delhi Declaration also condemned terrorism and its related activities.
- It also showed its concern over growing political uncertainty in West Asia. It also discussed violence in Syria and violation of human rights.
Question 15.
Which seven national leaders contributed in the establishment of SAARC?
Answer:
SAARC was established in 1985 at Dhaka in Bangladesh. For the mutual cooperation and improvement among the nations, national state heads of seven countries formed an organisation named South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC). These seven national leaders were the following :
- Rajiv Gandhi, Prime minister of India
- Zia-Ul-Haq, President of Pakistan
- Hussain Khurshid, President of Bangladesh.
- Bir Bikram Birendra Shah, king of Nepal.
- Jigme Singye Wangchuk, king of Bhutan.
- Julius Richard Jayawardane, President of Sri Lanka.
- Maumun Gayum, President of Maldives.
RBSE Class 11 History Chapter 7 Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Define Cold War and describe its result.
Answer:
The term ‘Cold War’ stands for hostile and tense international relations between USA and USSR. It was based on political distrust, espionage and diplomatic manoeuvering. When both parties (America and Russia) involved, threaten each other on international platform to wage open war if their enterests not secured, this situation is termed as ‘Cold War’.
Definition of ‘Cold War’
1. Lewis Hall in his book ‘The Cold War as History’ writes that “It was a bitter state of tension betwen the two blocs more dangerous than the armed conflict”.
2. Nature of cold war as explained by M.S. Rajan was “Ideological hatred, political distrust military competition and bitter relations”.
The seeds of Cold War were planted with Russian Revolution in 1917 but it fully developed in mid of 20th century after the second World War. The results of this Cold War (1917-1990) are as follows :
- Converted Concept of Balance Power : Before Cold War, balance of power was based on military strength, but after that it took the shape of ‘Balance of Terror’. This became the subject of concern which superpower would maintain greater influence by its activities and terrify other countries of the world.
- Peaceful End of Cold War : That, the Cold War would turn into hot war was uncertain. But it ended as a Cold War only with the disintegration of Soviet Union.
- Loss of Public and Property : Loss of public and property during the Cold War was not any less than the loss in world wars.
- Disintegration of Soviet Union : Due to the situation of continuous war, the economic balance of Russia was disturbed and Russia became weak. Small states took advantage of it and declared themselves independent. As a result, Soviet Union was disintegrated.
- Shock for United Nations Organisation : UNO was deeply hurt by this cold war. This organisation was established for the welfare of world but now it had become the only centre for fulfilling the incomplete ambitions of these two superpowers (America and Russia).
- Loss of Humanity : During the Cold War then contemporary generation of Europe and America took birth in the atmosphere of tension and distrust. Due to this, humanity was deprived of moving forward in positive and creative direction.
Question 2.
What were the causes of disintegration of the Soviet Union? Or How did the communism of Russia come to end?
Answer:
After the second World War, Soviet Union emerged as a superpower. For the next seven decades, it became one of the major powers of the international scenario. It also indulged in a Cold War with America. It did not turn into Hot War but paved the way for the downfall of Soviet Union.
The year of 1989 was unforgettable in the history of Russia when the meeting of ‘Congress of People Deputies’ took a great step in the history of Russia. As a result of this change, the communism of Russia came to end. The causes of disintegration of Soviet Union were the following :
1. Defective Economic policy : The economic model adopted by the Soviet Union was very much different from capitalism, but it was also bad on the investment of finance, when only industries are increased in an economy, it leads to imbalance of consumption and production. This happened in Soviet Union also when prises of basic necessities inflated.
2. Desire to get Foreign Currency : Demand of oil rose in 1970’s. Soviet Union had vast oil reserves. So it started exporting petroleum products. This increased foreign reserves and gave a setback to technical development. It became a mere exporter of oil. But after some years, consumer goods diminished. Due to lack of consumer goods, Russian citizens could not get required things at reasonable prices and faults of marketism emerged in the society.
3. Economic Imbalance : During the period of cold war, both America and Russia had to invest money in different countries to strengthen their bloc. Due to this the economy of Russia got imbalanced and it became weak internally.
4. Transformation of Power : The citizens of Russia became dissatisfied with the one- party rule of Lenin and one-person dictatorship of Stalin. So during the time of disintegration of Soviet Union, the people began to raise their demands.
5. The Policies of Mikhail Gorbachev : In 1988, the leadership of Soviet Union came in the hand of Mikhail Gorbachev. He announced a new economic policy based on the two important concepts of ‘Perestroika’ (restructuring) and glasnost (openness). He implicitely brought capitalism in the communist economy. His biggest mistake was that he lost control over political affairs which resuled in the revolt for independence of its constitutent states.
6. Emergence of New States : Due to the policies of Mikhail Gorbachev the war broke out between Armenia and Azerbaijan in 1988. Then in 1990 Lithuania, Estonia and Latvia declared their independence and sovereignty. By April 1991 Georgia and Ukaraine declared themselves independent. In 1993, an independent Czech republic also emerged.
Thus, one by one, European countries became free from the influence of communism and this system which was baed on dictactorship came to end.
Question 3.
What is BRICS? Describe its all top-level summits?
Answer:
BRICS presently is a group of nations which are part of emerging economies. This group was established in 2008. Initially it had four members : Brazil, Russia, India and China, and was known as BRIC. In 2010 when South Africa became its fifth member, it came to be known as BRICS. It extent lies from Asia, Africa to South America. In this competititve age, BRICS nations are ready to face the challenges to work together on an international platform.

BRICS Top-level Summit
- The first summit of BRICS was held in June 2009 at Ketinburg in Russia. They proposed that the decisions on economic, political and defence issues were to be based on democratic ideas.
- Second BRICS summit took place in 2010 in the capital city of Brazil, Brasilia in which a 33 point declaration was adopted.
- The third summit was convened in April 2011 at Sanya city of China. The summit reiterated the reforms in Security Council, International Monetary Fund and World Bank to make it more representative and democratic.
- The fourth summit was held at New Delhi in India in March 2012. After deliberations, consensus was made to increase the share of BRICS nations in shaping global stability, security and wealth of the world.
- Fifth summit was held in South Africa. In the declaration letter of this summit, it insisted on promoting international law, multinational cooperation and strengthening the central power of UNO.|
- Sixth summit of BRICS group was held in Brazil in 2014. The main subject of this summit was inclusive growth and sustainable development.|
- In 2015 the seventh summit of BRICS was held in Russia. In this summit the discussion was held regarding promotion of cooperation in the economic field.|
- In 2016 the eighth summit of BRICS was organised in New Delhi (India).
Question 4.
Describe the condition of India during the period of Cold War.
Answer:
During the Cold War India was a vast and important colony of England. Under the British
government Indians were trying to free their country from British clutch. During the period of
the Cold War, many changes occurred in the political system of India :
1. Independence of India : India gained independence in 1947. Indian leadership was in a dilemma about which camp to join.
2. Disbelief in Capitalism and Communism : After independence, India wanted neither to join capitalist America nor communist Russia because of its principles.
3. An Assumption of Political Leadership (Non Alignment) : Indian leaders knew that India could not imbibe either capitalism or communism. Therefore, India developed a parallel ideology of Non-Alignment which was followed later on by other countries also.
Thus, India chose the path of Non-Alignment to prevent itself from embroiled in the Cold War.
Later on most of the countries of the world followed this path to preserve their specific identity
and cultural traditions.
Question 5.
Mention the achievements and failures of Non-Aligned movement.
Answer:
Achievements of NAM
- The popularity of NAM is proved by the fact that in first top-level summit held in Belgrade in 1961, 25 members states were there, and in the 16th summit held in Tehran in 2012 this number increased to 120.
- Non-Alignment has prevented the eruption of war among the nations.
- The cold war got slowed down by the policy of Non-Alignment.
- NAM played a major role in maintaining peace in areas like Germany, Korea, China, Indo-China, Congo, etc. NAM got international recognition as it tried to dilute the tense situations in the above countries.
- Being a founder member of NAM, India placed the matter of nuclear test ban before international platform in 1954. As a result in 1963, partial ban was placed on Nuclear tests.
- It was the attempt of NAM that the voice of developing countries could be heard by the world, otherwise it would have been suppressed by the developed nations.

- NAM tried to give a creative outlook in international politics.
Failures of Non-Aligned Movement
- In principle, the responsibility of NAM is to ensure the neutrality of nations, but in practice many NAM countries have not lived up to it.
- The policy of NAM has failed to provide any security to the member countries.
- To get cooperation Non-Aligned countries have signed many contracts with both super powers.
- NAM has not also provided the economic security to its member states.
- The founders of NAM India, Egypt and Yugoslavia could not make any change in the hostile policies of the two leaders. For example : China tightened its hold on Tibet.
- The Arabs and Israel fought four wars but no NAM country played any active role in stalling them.
- In the freedom struggle of countries like Algeria, Angola and Mozambique, the role of NAM countries has been negligible.
- NAM was unsuccessful in ending the aggressive policy of superpowers.
Question 6.
Mention the meaning and objectives of Non-Alignment and Explain its relevance at the present time.
Answer:
Meaning of Non-Alignment: Every nation needs the recognition of the contemporary world. Its glorification does not depend on its being part of a bloc or superpower but on its independent stand. When two or more nations raise their voice to remain independent on an international platform then it is termed as ‘Non-Alignment’. This movement came into existence in 1961.
Objectives : The main objectives of NAM are as follows :
- It opposed colonialism and imperialism.
- Criticisim of racial discrimination.
- Peaceful coexistence among the nations. .
- It must not be a member of a military group.
- Promotion of world peace. ,
- Disarmament.
- Establishment of exploitation-free economic relations among nations on the basis of equality.
Relevance of Non-Aligned movement at the present time
- NAM continues to be a global movement, a movement of all the third-world countries which constitute 2/3rd of the total membership of the world community.
- It has all along been a movement against neo-colonialism.
- NAM stood committed to secured restructuring of international economic relations with a view to make these fair and equitable for all the countries, developed as well as developing.
Question 7.
Explain in detail the efforts for solution of problems related to environment conservation.
Answer:
Environment is a sensitive issue of discussion in today’s world as it is getting polluted day by day. It is a good sign that the countries of the world are deliberating on the international platform on this issue. The following efforts have been done by the different nations of the world for environment conservation.
1. UN Environment Programme
- In 1972 at Stockholm convention over the matter of Environment was highlighted.
- o In 1970 an amibitious programme of reducing expansion of desertification in South Africa was run by UNO.
- In 1980’s the General Assembly of UNO organised a convention on Environment and Development where importance and aim of sustainable development was highlighted, without which future generations would be adversely affected,
- The same decade witnessed the agreements related to protection of Ozone layer and control on emission of hazardous chemicals.
2. The Earth Summit of 1992 : In 1992 in Rio-de-Janeiro in Brazil, Environment and Development Conference also known as ‘Earth Summit’ was convened. More than 150 representatives of the world participated in it. The important subjects related to the environment were discussed in the summit.
3. World Environment and Green House Summit: In 1997 ‘World Environment and Green House Summit’ was organised in Kyoto (Japan) which mooted the reduction in emission of gases responsible for global warming.
4. New York Earth Sumit of 1997 : An Earth summit took place in June 1999 in New York to estimate the progress of Rio-De-Janeiro summit.
5. Johannesburg Earth Summit : A convention took place in Johannesburg of South Africa in 2002 in which persisting issues were discussed.
6. United Nations Climate Agreement Summit : This summit was held in Montreal (Canada) in 2005 in which issues related to Climate were discussed.
7. Climate Change Summit 2015 : This summit was held in Paris in 2015.134 countries participated to find ways to mitigate the dangerous effects of climate change. After a prolonged deliberation it was decided to limit the rise of Earth’s temperature and to implement the provisions of the Paris agreement by 2020.
Question 8.
Explain the India-ASEAN relations. Or Write a note on Look East Policy.
Answer:
ASEAN stands for Association of South East Asian Nations. There are 10 members : Indonesia, Malaysia, Phillipines, Singapore, Thailand, Brunei, Vietnam, Laos, Myanmar and Cambodia. India has worked really hard to maintain deep commercial and tactical relations with these nations.
1. The 1997, China rose as a powerful nation who supported undemocratic rule based on violence and the assistance given by China to illegal military groups of Myanmar. Thus India decided to establish relations with such countries so that attempts could be made in the direction to bring some change and to transform them to democratic economy.
2. In June 2015 India signed border agreement with Bangladesh through which two parts Chittagong and Mongla were restructured. India has secured itself from Bangladesh and Sri Lanka.
3. India signed three commercial agreements with Singapore under ‘look east policy’. In 2001 Prime Minister Vajpayee visited Vietnam and Indonesia which bore fruitful results. We signed bilateral agreement with Vietnam on the issues of nuclear energy, trade and commerce, art and culture. Then we concluded defence agreement with Indonesia.
4. In the same year, on the tour of Malaysia, both countries decided to increase the trade relation from 2.5 million dollars to 5 million dollars in 5 years.
5. In Singapore visit of 2002 Vajpayee concluded with Goh Chok Tong agreements related to terrorism, trade and bio technology. Then he went to Cambodia and signed 3 agreements.
6. The establishment of close relation with SE Asia led to the ambitious project of Mekong-Ganga. Its members were India, Laos, Thailand, Cambodia and Vietnam. This began the cooperation in the fields of trade, investment, technology, tourism, education and culture.
7. A milestone was established in India-ASEAN relationship under Prime Minister Mahmohan Singh in 2004, when they decided to act unaninously against terrorism.
8. Till November 2014, 12 sessions of India-ASEAN top-level summit took place. In the 12th ASEAN summit, P.M. Narendra Modi instead of ‘look east policy1 gave the slogan of ‘Act East Policy’. This motto raised the prestige of India on the world stage.
9. The 13th India-ASEAN summit is to be held in Cambodia.