Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 22 Concept of Excess and Deficient Demand
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 22 Practice Questions
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 22 Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Deficient Demand is a situation when :
(a) AD < AS
(b) AD > AS
(c) AD = AS
(d) AD ≠ AS
Answer:
(a)
Question 2.
Aggregate Demand includes :
(a) Consumption and Investment Expenditure
(b) Government Expenditure
(c) Net exports
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d)
Question 3.
Fiscal measures during deflation are :
(a) Increase in taxation
(b) Increase in Public Expenditure
(c) Reduction in Public Expenditure
(d) Increase in prices
Answer:
(b)
Question 4.
To control inflation, the measure adopted in monetary policy is :
(a) Increase in bank rate
(b) Reduction in taxation
(c) Increase in public expenditure
(d) Reduction in bank rate
Answer:
(a)
Question 5.
The aggregate supply curve in the figure reflects which concept ?
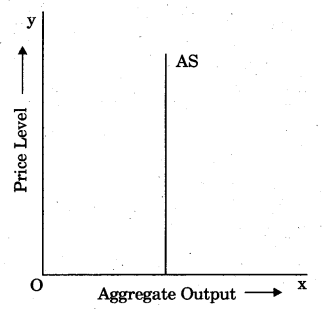
(a) Keynesian
(b) Classical
(c) Moneterism
(d) Ratex
Answer:
(b)
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 22 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Define Aggregate Demand.
Answer:
Total demand of goods and services is called Aggregate Demand. It is the sum total of Consumpton Expenditure and Investment Expenditure.
Question 2.
Write down four components of Aggregate Demand.
Answer:
Four components of Aggregate Demand are :
- Consumption Expenditure
- Investment Expenditure
- Government Expenditure
- Net Exports.
Question 3.
Define Aggregate Supply.
Answer:
Aggregate Supply expresses the production of total goods and services at different possible prices by the firms. It is equal to the National Income and National Production.
Question 4.
What is Macro Economic Equilibrium ?
Answer:
It is an economic state in an economy which indicates the actual state of short-term equilibrium economy. Here, the quantity of Aggregate Demand equals the quantity of Aggregate Supply.
Question 5.
Define depression.
Answer:
When there is a sufficient reduction in economic activities like-production of goods and services, employment, income, demand and price level, etc.
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 22 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain Deficient Demand.
Answer:
When Aggregate Demand is less than Aggregate Supply, it is called Deficient Demand. Under this situation, producer reduces production. He cannot sell the produced output because of the reduced demand. A large stock of produced goods gets assembled and the prices start decreasing.
Question 2.
What do you mean by excess demand ?
Answer:
If Aggregate Demand exceeds the Aggregate Supply, it is called Excess Demand. Excess demand motivates the producer to produce more output. This, in turn, increases the factor cost. This results into increase in prices of goods.
Question 3.
What is monetary policy ?
Answer:
Monetary policy is the policy adopted for supply and availability of credit in an economy. Central Bank adopts this policy to control the money supply or to attain objectives of economic policy.
Question 4.
What are the instruments of Fiscal Policy ?
Answer:
Fiscal Policy has two instruments :
- Revenue Tools : Many types of direct or indirect taxes collected by the government come under revenue tool.
- Spending Tools : Spending or expenditure tool can be reduced or raised according to the economy. It includes government transfer payment expenditure, current expenditure or capital expenditure.
Question 5.
What measures of monetary policy are adopted during inflation ?
Answer:
In the period of inflation, following measures of monetary policy can be adopted :
- To arrest the increase in prices due to excess demand, Central Bank increases the bank rate, sells securities in an open market and raises the Cash Reserve Ratio.
- Increases the selective credit limit.
- Controls the Consumer Credit.
- Demonetisation of currency can also be done.
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 22 Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain in detail the AS and AD model.
Answer:
Short term equilibrium indicates the real state of economy. Actual GDP revolves around though potential GDP. The effectiveness of monetary and fiscal policies are proved by the.AD-AS model.
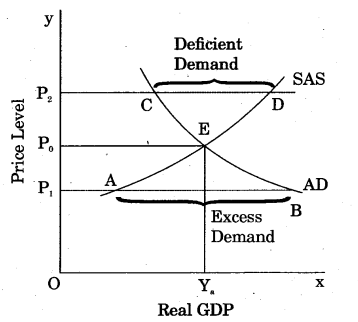
When Aggregate Demand (AD) is equal to the short run Aggregate Supply (SAS), equilibrium is at E. Here, income OY0 and Price P0 is fixed. If the price is at P2, then Aggregate Supply is greater than Aggregate Demand which is called Deficient Demand (CD). In this situation,
producers curtial production. Due to Deficient Demand, unsold goods and stock of finished goods pile up in godowns of producers. This, in turn, lowers the market prices and reaches the previous level of P0 (equilibrium level of price and income).
On the contrary, if price level is OP1; then Aggregate Demand is greater than Aggregate Supply, (AD > AS). This has been shown by AB in figure. It is called Excess Demand. Higher demand induces producers to produce more. Therefore, demand for resources (factors) of production increases, which increases the factor cost. It results into increase in prices of goods and equilibrium again reaches at price OP0.
In the short run, monetary wage rate is constant. Potential GDP may be more or less than the actual GDP. In the long run, Aggregate Demand is equal to the long run Aggregate Supply curve.
Question 2.
Differentiate between Keynesian and Classical aggregate supply curve with the help of diagram.
Answer:
Other things remaining the same, production of goods and services made by firms at different possible price levels is Aggregate Supply. The theories of classical economists are based on full employment assumption. Therefore, in full employment, aggregate supply curve is a vertical straight line parallel to the y axis. This has been shown in figure 1. Here, As curve is perfectly inelastic.
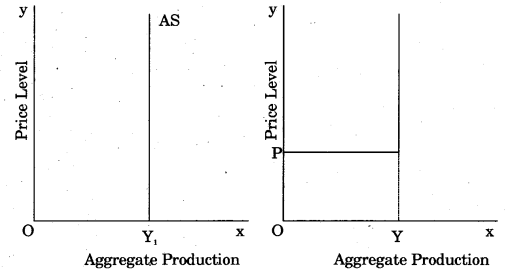
On the other hand, Aggregate Supply curve at the time of depression is horizontal initially, and at the point of Full Employment, it is vertical. Fig. 2 shows it. In horizontal area, along with the increase in Aggregate Demand, production also increases but price remains constant. In vertical Aggregate Supply curve, i.e. at Full Employment, with the increase in the Aggregate Demand, production does not change, but price level increases.
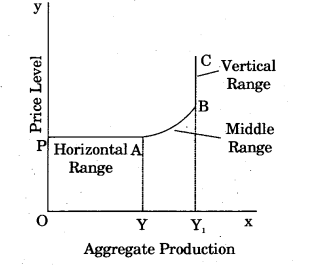
In Fig. 3, horizontal range (PA) is called Keynesian range. Due to the utilisation of unused resources, per unit cost of production does not increase, and therefore prices also do not increase. In this range, only production increased. PA range indicates the stage of depression in the economy.
In middle range (between Y and Y1) increase in Aggregate Demand, increases the price level. In situation prior to the full employment, along with the increase in production, per unit cost also increases, which ultimately pushes up the market prices. In vertical range (BC), supply curve is perfectly inelastic which shows the full employment level of resources. This is also called classical range. Here, price level changes and production quantity remains unchanged because resources are used at full capacity.
Question 3.
How can fiscal policy be effectively used at the time of depression ?
Answer:
When deficient demand appears during depression, i.e. Aggregate Demand is less than the Aggregate Supply. In this situation, government adopts a suitable fiscal policy. Government increases public expenditure like-road building, dam construction, building of schools and hospitals to raise the income as well as demand.
Similarly, taxes are reduced to increase the consumable income of the consumer. These efforts remain fruitful when government does not increase the taxes. During depression, fiscal policy proves more successful than monetary policy. During depression, producers already have a large stock of unsold goods, so, even at a reduced rate of interest, they are not motivated to invest more. Therefore, through this policy, government tries to bring Full Employment and price stability through changes in taxation and government expenditure.
Question 4.
Explain the four measures, which can be adopted by government to check inflation.
Answer:
At the time of inflation, contractionary fiscal and monetary policy must be adopted by the government. Through fiscal policy, government should increase taxation, remove unnecessary expenditure to reduce the Aggregate Demand. But such increase in taxation should not be abnormal, otherwise there will be an adverse effect on Investment and Production. Government may promote compulsory savings scheme.
Government should frame the surplus budget and repayment of public debt should stopped. In this way, rigid monetary policy may be adopted. To check rising prices due to the excess demand, central bank may resort to increase in the bank rate, sale of securities in open market and increase in Reserve Ratio. Along with it, Selective Credit Control measures like increase in the margin of credit may also be adopted. It also tries to control consumers’ credit. Along with all these methods, demonetisation may also be adopted. In this way, at the time of deficient and excess demand, through appropriate measures of monetary and fiscal policy, this problem can be solved.
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 22 Other Important Questions – Answers
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 22 Multiple-Choice Questions
Question 1.
What does AD < AS denote ?
(a) Deficient demand
(b) Excess demand
(c) Zero demand
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a)
Question 2.
Increase in the government expenditure during depression is a solution under which policy :
(a) Monetary Policy
(b) Fiscal Policy
(c) Revenue Policy
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b)
Question 3.
Fiscal Policy involves :
(a) Government Expenditure
(b) Taxes
(c) Deficit financing
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d)
Question 4.
Which of the following is an indirect tax :
(a) Producer’s fee
(b) Custom Duty
(c) Sales Tax
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d)
Question 5.
Which of the following is included in fiscal policy ?
(a) Public Debt
(b) Tax imposition
(c) Public Expenditure
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d)
Question 6.
Deficient demand exhibits
(a) Depression
(b) Prosperity
(c) Equilibrium
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a)
Question 7.
Excess demand exhibits :
(a) Prosperity
(b) Equilibrium
(c) Depression
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a)
Question 8.
Raising the bank rate to check inflation is a step taken under :
(a) Monetary policy
(b) Fiscal policy
(c) Revenue policy
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a)
Question 9.
Expansionary monetary and fiscal policy is effective in :
(a) Prosperity
(b) Depression
(c) Equilibrium
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b)
Question 10.
Which of the following is a direct tax :
(a) Income tax
(b) Asset tax / Property tax
(c) Sales tax
(d) (a) and (b)
Answer:
(d)
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 22 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
As per classical economists, determination of income is affected through which factors ?
Answer:
Through capital, stock, supply of labour, the production of income is estimated.
Question 2.
When were the Keynesian ideas propounded ?
Answer:
In the decade of 1930 during the Great Economic Depression.
Question 3.
According to Keynes, income is determined at which point ?
Answer:
It is determined where AD equals AS.
Question 4.
Which factors are included under Aggregate Demand ?
Answer:
Consumption expenditure, Private Investment Expenditure, Government expenditure on Purchase of goods and services and Net Exports are included in Aggregate Demand.
Question 5.
What does Aggregate Demand Curve indicate ?
Answer:
AD curve indicates the relationship between the demand of aggregate goods and services and general price level.
Question 6.
What is the relation between general price level and Aggregate Production?
Answer:
Inverse relation.
Question 7.
What will be the effect of pirce rise on Consumption Expenditure?
Answer:
Consumption expenditure decreases upon rise in prices.
Question 8.
What is the effect of price rise on Export and Import ?
Answer:
Exports decrease and imports increase with rise in prices.
Question 9.
What is the shape of Aggregate Supply curve in full employment situation?
Answer:
Vertical line.
Question 10.
According to the Keynes, what is the shape of AS curve during depression?
Answer:
Horizontal in the beginning and vertical later at full employment point.
Question 11.
What can be the other name for horizontal range ?
Answer:
Keynesian Range.
Question 12.
What is the type of vertical range supply curve ?
Answer:
Perfectly inelastic.
Question 13.
What is the meaning of Excess Demand ?
Answer:
When Aggregate Demand is more than Aggregate Supply.
Question 14.
What is Deficient Demand ?
Answer:
When Aggregate Supply is more than Aggregate Demand.
Question 15.
Where does equilibrium lie in the long-run?
Answer:
When Aggregate Demand is equal to aggregate supply in the long-term.
Question 16.
Name the main parts of fiscal policy.
Answer:
- Tax
- Public Expenditure
- Public Debt.
Question 17.
How does government raise the demand ?
Answer:
By increasing the public expenditure.
Question 18.
Give examples of public expenditure.
Answer:
Road building, dam construction, construction of schools and hospitals, etc.
Question 19.
Which policy is adopted during Deficient Demand ?
Answer:
Expansionary monetary and Fiscal Policy.
Question 20.
Which policy is more successful during depression : Monetary or Fiscal ?
Answer:
Fiscal policy.
Question 21.
Give examples of Direct tax.
Answer:
Income Tax and Property Tax.
Question 22.
Give examples of Indirect Tax.
Answer:
Sales Tax, Custom Duty, Goods and Service Tax.
Question 23.
What kind of monetary and fiscal policy is adopted during inflation ?
Answer:
Contractionary monetary and fiscal policy.
Question 24.
When is demonetisaton done ?
Answer:
To stop inflation, demonetisation is done.
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 22 Short Answer Type Questions (SA-I)
Question 1.
How are general prices determined according to the classical economists?
Answer:
According to the classical economists, general prices are determined by the money Supply
Question 2.
What is the assumption of Income and production principle according to Keynes ?
Answer:
According to Keynes, principle of Income and production asumes the price level to be constant.
Question 3.
What was the main cause of unemployment and additional production capacity as per Keynesian theory?
Answer:
As per Keynesian theory, deficiency of effective demand was the main cause of widespread unemployment and additional production capacity.
Question 4.
Explain the Aggregate Demand equation.
Answer:
Y = C + I + G + Xn
Where, C = Consumption Expenditure
I = Investment Expenditure
G = Government Expenditure
Xn = Net Export (X – M).
Question 5.
On which assumption was the ideology of classical economists based ?
Answer:
Full employment was the assumption on which the ideology of classical economists was based.
Question 6.
Define Aggregate Supply.
Answer:
Other things remaining the same, production of goods and services by firms at different possible price levels is called Aggregate Supply.
Question 7.
When does equilibrium occur in the long-run ?
Answer:
When Aggregate Demand equals the long-run Aggregate Supply curve, at that point ; equilibrium is attained.
Question 8.
What is Monetary Policy ?
Answer:
Policies made by the Central Bank for checking the money supply and attaining the economic policy objectives are called monetary policy.
Question 9.
What will be the effect of raising taxes on Investment ?
Answer:
There could be a negative effect on investment and production upon raising taxes.
Question 10.
When should government implement compulsory savings scheme ?
Answer:
To control inflation, government should implement compulsory savings scheme.
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 22 Short Answer Type Questions (SA-II)
Question 1.
Explain Keynesean law of income and output ?
Answer:
As per Keynesean law, price level is constant. Income is determined at the point where Aggregate Quantity (demand) equals Aggregate Supply. Keynes claimed that lack of effective demand was the major cause of economic depression.
Question 2.
Explain Aggregate Demand.
Answer:
Aggregate demand includes Consumption Expenditure, Private Investment Expenditure, government purchase of goods and services and Net Export. Other things remaining constant, the goods and services bought by the consumers, investors, government and foreigners is known as Aggregate Demand.
Y = C + I + G + Xn
Question 3.
Describe the effects of price rise.
Answer:
Following are the effects of price rise :
- Consumption expenditure increases with the price rise.
- More money is required by the people for exchange which increases the Rate of Interest and results in decrease of Investment Demand.
- Exports reduce and imports increase when prices increase.
Question 4.
Show Inverse Aggregate Demand on various price levels through a diagram.
Answer:
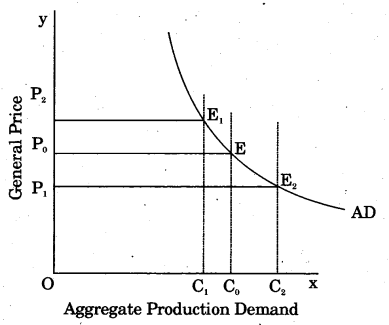
Question 5.
What do you meant by depression ?
Answer:
When there is a significant reduction in economic activities like-production of goods and services, employment, income, demand and prices, the situation is called depression.
Question 6.
What is prosperity ?
Answer:
When output, employment and income are at high level, demand of goods and services increase and there is an inflationary rise in the prices, it is called prosperity.
Question 7.
What steps are taken in monetary policy during depression ?
Answer:
- Supply of money is raised, which results in the reduction of interest rates.
- Private investment increases along with the rise in Aggregate Demand.
- Central bank sells securities in open market and reduces Cash Reserve Ratio.
Question 8.
How is depression is controlled through fiscal policy.
Answer:
- Government increases the public expenditure to raise demand.
- Public expenditure like-hospitals, roads, schools and dams construction is increased to increase employment and income.
- Reduction in taxes results in increment of consumer’s disposable income.
Question 9.
Monetary policy is not much successful during depression. Why ?
Answer:
At the time of deficient demand (depression), traders have an adequate unsold stock which they cannot sell. Therefore, reduction in interest rate cannot induce investment. Consumer class is also not ready to borrow consumer durables due to unemployment and low income. Therefore, monetary policy is not successful.
RBSE Class 12 Economics Chapter 22 Essay Type Question
Question 1.
Explain the derivation of Aggregate Demand with the help of a diagram.
Answer:
Figure (a) indicates Aggregate Expenditure (investment expenditure) at different levels of Gross National Product (GNP) as per Keynes. Whereas fig. (b) Indicates derived Aggregate Demand at different price levels.
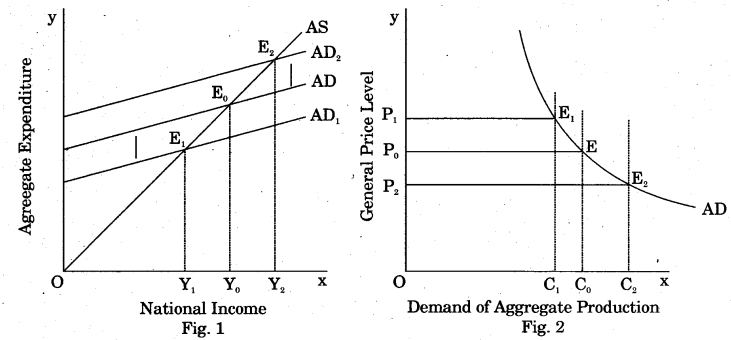
In the intial equilibrium, Aggregate Demand line intersects Aggregate Supply line (45° line) at point E0 and Y0 income is determined. In fig. 2, at Y0 level of income, Aggregated Demand is C0 and general price level is P0. Similarly, if general price level is P2 then due to the increase in , purchasing power of population, consumption expenditure shifts upward from AD to AD2. AD2 = AS at E2 and income is Y2. Aggregate demand is OC2. In this way, at lower price, Aggregate f Production Demand is high. On the contrary, at increased price level, equilibrium is at Er At this point AD = AS at income level Y1 and Aggregate Demand reduces and reaches at a level of OC1. In this way, there is an inverse relationship between general price level and Aggregate Production Demand which is very evident in fig. 2 through AD curve.