Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 6 World: Human Settlement
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 6 Text Book Questions
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 6 Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Human settlements have many forms. Which of the following do you not consider to be a human settlement?
(a) house
(b) city
(c) village
(d) lanes
Answer:
(d) lanes
Question 2.
Which kind of settlements do people of Bushman tribe build?
(a) temporary settlements
(b) concentrated settlements
(c) permanent settlements
(d) farmhouses
Answer:
(a) temporary settlements
Question 3.
Which type of settlements are built in grasslands of Pampas and Prairies?
(a) mixed settlements
(b) clustered settlements
(c) scattered settlements
(d) dense settlements
Answer:
(c) scattered settlements
Question 4.
In which pattern is the development of settlements done along railway tracks?
(a) arrow pattern
(b) linear pattern
(c) circular pattern
(d) rectangular pattern
Answer:
(b) linear pattern
Question 5.
The size of population in metropolitan city of India is:
(a) more than 5 lakh
(b) more than 10 lakh
(c) more than 1 lakh
(d) more than 1 crore
Answer:
(b) more than 10 lakh
Question 6.
This city is not included in the megalopolis category in India:
(a) Kolkata
(b) Delhi
(c) Jaipur
(d) Chennai
Answer:
(c) Jaipur
Question 7.
In which city is Asia’s largest slum situated?
(a) Delhi
(b) Mumbai
(c) Karachi
(d) Beijing
Answer:
(b) Mumbai
Question 8.
The number of metropolitan cities in India according to 2011 census is:
(a) 53
(b) 27
(c) 35
(d) 47
Answer:
(a) 53
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 6 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 9.
What is the fundamental unit of human settlement?
Answer:
The fundamental unit of human settlement is house or dwelling or residence.
Question 10.
Mention the types of human settlements on the basis of residence.
Answer:
There are two types of human settlements on the basis of residence –
- temporary settlement
- permanent settlement.
Question 11.
For which important activity is human settlement made?
Answer:
Inhabitation is the important activity for which human settlement is made.
Question 12.
What is the main characteristic of scattered settlement?
Answer:
In a scattered settlement, dwellings are placed over large area.
Question 13.
Mention the names of any two patterns of human settlements.
Answer:
The names of two patterns of human settlements are linear pattern and rectangular pattern.
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 6 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 14.
What is meant by human settlement?
Answer:
A human settlement is defined as a place inhabited more or less permanently. It includes buildings in which they live or use and the paths and streets which they travel on. It also includes the temporary camps of the hunters and herders. It may consist of only a few dwelling units called hamlets or big cluster of buildings called urban cities.
Question 15.
What Is a rural settlement?
Answer:
Rural settlements are most closely and directly related to land. They are dominated by primary activities such as agriculture, animal-rearing or husbandry fishing, hunting, etc. The settlement size is relatively smaller than that of urban settlements. Less effect of modernisation is seen on these types of settlements
Question 16.
Mention any five problems of rural settlements.
Answer:
The main five problems of rural settlement are:
- Lack of modes of transportation.
- Lack of fresh and clean drinking water.
- Lack of health and medical facilities.
- Lack of supply of power or electrical energy.
- Lack of employment opportunities.
Question 17.
Mention five major problems of urban settlement.
Answer:
Five major problems of urban settlement are given as:
- Over population or the uncontrolled population due to large scale migration of rural population.
- A large number of people live in slums and squatter settlements or in the streets.
- Uses and disposes off a huge quantity of water and all types of materials, also an improper sewerage system increases all types of pollution.
- Lack of employment and proper education tends to aggravate the crime rates.
- Urban areas suffer from poor health conditions due to squalor and pollution.
Question 18.
Differentiate between rural and urban settlements.
Answer:
Differences between rural and urban settlements are given below:
| Bases of Difference | Rural Settlement | Urban Settlement |
| 1. Occupation | 1. Mostly, people are engaged in primary occupations like agriculture etc. | 1. Mostly, people are engaged in secondary occupations. |
| 2. Population density | 2. In rural settlements, low population density is seen. | 2. In urban settlements, there is high population density. |
| 3. Size of dwellings | 3. In rural areas, open and large houses are found. There is enough gap between them. | 3. Small houses or flats or multistoried buildings or apartments are found. |
| 4. Effect of modernisation | 4. The people in rural settlements are traditionally backward and believe in old customs and manners. | 4. The people in urban areas are modern. They have less faith in old customs and manners. |
| 5. Social organisation | 5. A strong social organisation is seen. People prefer social values over personal values. | 6. There is a weak social organisation in urban settlements. People prefer individual values. |
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 6 Essay Type Questions
Question 19.
Explain the meaning of human settlements and describe their pattern.
Answer:
Residence built and developed by humans in organised clusters on the earth’s surface is called a settlement. A human settlement is defined as a place inhabited more or less permanently. It includes dwellings in which they live or use and the paths and streets on which they travel. It also includes the temporary camps of the hunters and herders. It may consist of only a few dwelling units called hamlets or a big cluster of buildings called urban cities.
Pattern of rural settlements:
The pattern of rural settlements is defined by natural factors like surface, rivers, reservoirs, historical factors, socio – cultural factors, transportation routes and religious places, etc. The formation of settlements is also called pattern. On the basis of shape, pattern is divided into following parts:
- Linear pattern
- Arrow pattern
- Triangular pattern
- Rectangular pattern
- Radial pattern
- Circular pattern
- Star pattern
- Fan pattern
- Irregular pattern
- Ladder – shaped pattern
- Bee – hive pattern
- Other pattern.
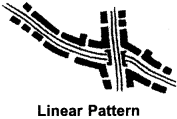
1. Linear Pattern:
When settlements develop along road routes, rail routes, canals, river valleys or sea coasts in rural areas, then the pattern of linear pattern is created. In this pattern, houses are very close together and in rows. Such settlements are found in the Ganga – Yamuna plains and Central Himalayan region.
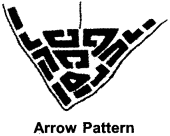
2. Arrow Pattern:
The arrow orientation develops at the top of a headland, along the bow of river or between two water bodies. It is usually said to be arrow-shaped. Due to lack of enough land in front and for development, the settlements develop at the rear. For instance ICanyakumari in South India and banks of Chilka lake in Odisha have such settlements.
3. Triangular Pattern:
The triangular settlements develop at the meeting of rivers, canals or roads but not at their intersecting point. In India, these types of settlements are found in Haryana and Punjab.
4. Rectangular Pattern:
The rectangular patterns are formed at the perpendicularly intersecting points of road or streets. These types of settlements form on the fertile land in the world.

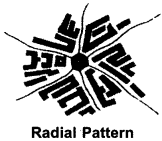
5. Radial Pattern:
This type of pattern can be seen in Northern Ganga plains and the state of Tamil Nadu. When muddy roads or tarred roads coming from different directions meet at a place, radial pattern settlement takes place.
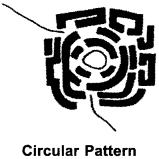
6. Circular Pattern:
Generally, such types of settlements are formed by buildings or houses around a lake, pond, well, religious place or a village chaupal. Circular pattern can be seen in most of the urban areas.
7. Star pattern:
Star pattern of settlements begin to develop initially as a radial pattern, but later on, the building of houses along the roads leading outwards, create a star-shaped settlement.
8. Fan pattern:
When houses are built around a central place in a village or hamlet, and the settlement also develops along the main contact road in a linear way, a fan-shaped pattern is formed.
9. Irregular pattern:
When without any planning, shapeless building or houses are built for human convenience, an irregular pattern is formed. In this pattern, roads and streets develop automatically in the gaps of buildings. Most of the Indian villages are the examples of such pattern.
10. Ladder-shaped pattern:
Such type of settlements are seen – in the slopes of hills and mountains, where houses are built next to one another close together and also one after another. The rows of these houses can be seen at many levels according to the slope.
11. Bee – hive pattern:
Villages of domed huts of primitive tribes in India, Toda tribes, fisherfolk villages of coastal Andhra pradesh and Zulus of Africa live in such type of pattern which look like a bee-hive from a distance.

12. Other patterns:
Other patterns are haphazard and spider. The patterns which are formed without an order or planning or by chance or irregularity aimlessly are called haphazard patterns. When patterns are formed automatically here and there, the result is a spider pattern.
Question 20.
Write an article on rural settlement.
Answer:
Meaning of rural settlement:
The economy of rural settlements is dependent on primary occupation, like agriculture, animal rearing, wood – cutting, fishing, mining and gathering of forest produce. Hence, rural settlements are mainly based on land utilisation. Rural settlements try to avoid modernisation as they have a closely knit social organisation and human values. In rural settlements, social values are always kept above individual values.
Type of rural settlements:
Rural settlements are divided on the bases of number of houses and distance among them. Generally, four types of rural settlements are found:
1. Dense or clustered settlement:
Dense rural settlements always develop in fertile plains and regions having flat surface terrain and sufficient water availability. The houses are built close together and the entire village is inhabited densely.
2. Isolated or scattered settlements:
The houses in this settlement have distance between each – other and agricultural land lies within them, so this type of settlement is called scattered settlement.
3. Mixed settlement:
This is a stage between dense and scattered settlements. This type of settlement is a result of rapid increase in houses due to rapid increase in number of families as well number of people. Instead of environmental reasons, family reasons are responsible for it.
4. Old or palli settlement:
The house of this type of settlement are built apart from one another but located in the same colony. People from different castes live in different parts of colony.
Pattern of Rural Settlements:
The pattern of rural settlements are defined by natural factors, historical factors, socio – cultural factors, transportation routes and religious places. In these, linear, arrow, triangular, rectangular, radial, circular, star – shaped, irregular, ladder – shaped, bee – hive, haphazard and spider – shaped patterns are seen.
Problems of Rural Settlements:
Very common problems of rural settlements include lack of transportation facilities, lack of fresh and clean drinking water, lack of healthcare and medical facilities, lack of power and energy supply, lack of employment opportunities, lack of proper education, lack of communication facilities, etc.
Question 21.
Mention the base of classification of urban settlements and describe its types.
Answer:
Generally, the classification of urban settlements is made on the basis of size of population, human occupations, administrative structure and other available basic facilities and conditions. Urban settlements are generally divided into four parts:
- city
- metropolitan city
- conurbation
- Megapolis or Megalopolis.
1. City:
Settlement having population more than 1 lakh but less than 10 lakh is called city. In the city, more than 50% population is engaged in non-primary occupation. Bikaner, Dausa, Bharatpur etc. are some of its examples.
2. Metropolitan City:
A settlement having population more than 10 lakh is called Metropolitan city. Metropolitan cities are the center of industrial, commercial, administrative and educational activities. Jaipur, Jodhpur, Kota and Udaipur are some metropolitan cities in Rajasthan.
3. Conurbation:
This type of settlement is huge, well developed and well-known urban area, which combines houses of different towns or cities to turn into one huge urban city. In, India, Gwalior – Laskar – Morar, Delhi – Gurugram and Delhi – Noida are few examples of conurbation. Greater London, Tokyo, Chicago are also known as conurbation. The term conurbation was first used by Patrick-Geddes in 1915.
4. Megapolis or Megalopolis:
Megapolis means very huge city. The term Megapolis was first used by Jean Gottman in 1857. The population of these cities is more than 50 lakhs. These cities are also called Global cities. Mumbai, Kolkata, Delhi, Chennai in India, and Greater London, Moscow, Beijing are the some examples of Megapolis cities.
Question 22.
Clarify the difference between the types of and pattern of human settlements. Also describe the types of rural settlements.
Answer:
There are following differences between the types and the formations of human settlements:
- Physical features, social and cultural factors and safety are responsible for the types of human settlements, while its pattern is due to its shape.
- Types of settlement is determined on the basis of distance among houses, but its pattern is determined on the basis of its shape.
- Natural conditions and occupations etc. determine the types of settlements, while type of occupation plays an important role in their pattern.
Types of Rural – settlements:
Rural settlements are divided on the basis of number of houses and distance among them. Generally, four types of rural settlements are found:
1. Dense or clustered settlement:
Dense rural settlements always develop in fertile plains, and regions having flat surface terrain and sufficient water availability. The residences are built close together and the entire village is inhabited densely.
2. Isolated or scattered settlements:
The houses in this settlement have distance between another and agricultural land lies among them, so this type of settlement is called scattered settlement.
3. Mixed settlements:
This is a state between dense and scattered settlements. This type of settlement is a result of rapid increase in houses due to rapid increase in number of families as well as number of people. Instead of environmental reasons, family-reasons are responsible for it.
4. Old or palli settlement:
The houses of this type of settlement are built apart from one another but located in the same colony. People from different castes live in different parts of colony.
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 6 Additional Questions with Answers
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 6 Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Evolution of large cities is regarded to be:
(a) 2000 years earlier
(b) 3000 years earlier
(c) 4000 years earlier
(d) 5000 years earlier
Answer:
(d) 5000 years earlier
Question 2.
Igloo is the house of:
(a) Khirgiz
(b) Eskimo
(c) Bushman
(d) Baddu
Answer:
(b) Eskimo
Question 3.
The evolution of permanent settlement is regarded to be from:
(a) Paleolithic period
(b) Mesolithic period
(c) Copper age
(d) Neolithic period
Answer:
(a) Paleolithic period
Question 4.
Which of these is known by the name of dense settlement?
(a) Clustered settlement
(b) Scattered settlement
(c) Mixed settlement
(d) Palli settlement
Answer:
(a) Clustered settlement
Question 5.
Which settlement develops near the river meander?
(a) Linear
(b) Circular
(c) Arrow
(d) Rectangular
Answer:
(c) Arrow
Question 6.
Which type of settlements are found in the lower valleys of mountainous regions?
(a) Dense
(b) Scattered
(c) Mixed
(d) Palli
Answer:
(d) Palli
Question 7.
What is the determinant minimum population of cities in Denmark?
(a) 250
(b) 500
(c) 1000
(d) 2000
Answer:
(a) 250
Question 8.
Which of the following is an example of conurbation in India?
(a) Greater London
(b) Chicago
(c) Lashkar – Murar
(d) Tokyo
Answer:
(c) Lashkar – Murar
Question 9.
What was the number of metropolitan cities in 2005?
(a) 265
(b) 370
(c) 438
(d) 512
Answer:
(c) 438
Question 10.
What is the biggest slum of Asia?
(a) Dharavi
(b) Kathputli
(c) Jawaharnagar
(d) Palam
Answer:
(a) Dharavi
Match the Following
Question 1.
Match the options given in column A with correct options given in column B:
| Column (A) Settlement Pattern | Column (B) Origin of Settlement Pattern |
| (i) Liner Pattern | (a) In tribal areas |
| (ii) Arrow Pattern | (b) Joining place of roads |
| (iii) Circle Pattern | (c) Parallel to road, rail routes |
| (iv) Bee – hive Pattern | (d) All around lakes, ponds |
| (v) Rectangular Pattern | (e) River meanders |
Answer:
(i) (c), (ii) (e), (iii) (d), (iv) (a), (v) (b).
Question 2.
Match the options given in column A with correct options given in column B:
| Column (A) Name of Nations | Colomn (B) Minimum Population for Urban areas |
| (i) Sweden | (a) 2000 |
| (ii) Iceland | (b) 5000 |
| (iii) Canada | (c) 300 |
| (iv) Columbia | (d) 3000 |
| (v) Portugal | (e) 1500 |
| (vi) Japan | (f) 250 |
| (vii) India | (g) 1000 |
Answer:
(i) (f), (ii) (c), (iii) (g), (iv) (e), (v) (a), (vi) (d), (vii) (b).
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 6 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is the use of settlement by the human?
Answer:
Humans use settlement for social, economic, cultural and religious work.
Question 2.
Define settlement according to Blache.
Answer:
According to Blache, a structure built by human for his residence and property purpose is called settlement.
Question 3.
Why were human settlements built?
Answer:
Human settlements were built for the safety purpose and storage of food.
Question 4.
When and where did the origin of cities begin?
Answer:
The cities evolved in the Valleys of Indus and Dajla – Farat in 5000 BC.
Question 5.
Origin of settlement has been divided into how many parts?
Answer:
Origin of settlement are divided into two parts – Temporary and permanent settlement.
Question 6.
What is temporary settlement?
Answer:
Those types of settlement which change according to season are called temporary settlement.
Question 7.
How do the Eskimos build their settlements?
Answer:
On the basis of seasonal conditions, Eskimo people build houses made of snow (igloo) in winter season and houses are made of skins of reindeer and seal in summer season.
Question 8.
On what factors does permanency of a human colony depend?
Answer:
The permanency of a human colony depends on availability of resources, relation with external world, safety, hope of progress in future and also on religious, social and economic factors.
Question 9.
On the basis of basic occupations, human settlements have been divided into how many parts?
Answer:
On the basis of basic occupations, human settlements have been divided into two parts – rural settlements and urban settlements.
Question 10.
Which factors are responsible for the types of rural settlements?
Answer:
For the types of rural settlements, physical factors, social and cultural factors (caste – religion) and security, etc. are responsible.
Question 11.
What are the types of rural settlement?
Answer:
These are four types of rural settlement:
- Concentrated
- Scattered or Isolated
- Mixed
- Palli or old settlement.
Question 12.
What are other names of dense settlements?
Answer:
Dense settlements are also known as concentrated, contracted, accumulated or collective settlements.
Question 13.
Where are concentrated settlements found?
Answer:
Concentrated settlements are found in fertile plains, levelled areas and regions of water availibility.
Question 14.
Where are dense settlements found in India?
Answer:
In India, dense settlements are found in fertile plains of Ganga – Satluj, Plateau of Malwa and Vindhyachal, Valley of Narmda and plains of Rajashthan.
Question 15.
What is scattered settlement?
Answer:
Those types of settlement which have distance between each – other and agricultural land lies between them are called scattered settlements.
Question 16.
What is mixed settlement?
This is a stage between dense and scattered settlements. This type of settlement is a result of rapid increase in houses due to rapid increase in number of families as well as number of people.
Question 17.
What are Palli or old settlements?
Answer:
Those types of settlements built apart from one another but located in the same colony. People from different castes live in different parts of colony.
Question 18.
What do you understand by settlement-pattern?
Answer:
The categorisation of settlements done on the basis of the shape of their formation is called settlement pattern.
Question 19.
Which are the factors that control the pattern of rural settlements?
Answer:
Factors that control the pattern of rural settlements include natural factors (landform, rivers, reservoirs), historical factors, socio – cultural factors, transportation routes and religious factors.
Question 20.
Where are linear pattern settlements found in India?
Answer:
Linear pattern settlements are found in India in Ganga – Yamuna plains and central Himalayan region.
Question 21.
Why do arrow – shaped patterns develop?
Answer:
When enough land is not available at the front end of water body for development of settlement or river front becomes an obstacle in its development, the arrow shape settlements develop at the rear end.
Question 22.
How does a star pattern form?
Answer:
Star formation of settlement begins to develop intially as a radial formation, but later the building of houses along the roads leading outwards create a star – shaped settlement.
Question 23.
When is fan – shaped pattern formed?
When houses are built around a central place in a village or hamlet, and the settlement also develops along the main contact road in a linear way, a fan – shaped pattern is formed.
Question 24.
Where are bee – hive patterns found?
Answer:
Bee – hive patterns are mostly found in tribal regions. In India, houses of Toda tribal people, villages of coastal fishermen in Andhra Pradesh and house of Zulu tribal people in South Africa exhibit this pattern.
Question 25.
Which patterns of unemployment are visible in rural settlements?
Answer:
All the three patterns of unemployment-unemployment, hidden unemployment and seasonal unemployment are visible in rural settlements.
Question 26.
What is meant by urban settlements?
Or
What is the meaning of urban settlements?
Answer:
Such man – made settlements, in which most of the people are engaged in secondary, tertiary, quaternary activities and where high level of civil facilities are found is called urban settlements.
Question 27.
Which are the major characteristics of urban settlements?
Answer:
High population density, rapid mobility, pucca roads and pucca houses, availability of employment, wide social and economic differences, lack of social bonds, etc. are the major characteristics of urban settlements.
Question 28.
What are the bases to classify urban settlements?
Answer:
The bases of classifying urban settlements are size of population, administrative structure, occupation and other social factors.
Question 29.
How many types of urban settlements are there on the basis of their size?
Answer:
There are four types of urban settlements – City, Settlement, Metropolitan city, conurbation and Megalopolis or megapolis.
Question 30.
What is a city?
Answer:
Human settlement having population of more than one lakh but less than 10 lakh is called city.
Question 31.
Pefine metropolitan city.
Answer:
The city having a population of more than 10 lakh is called a metropolitan city.
Question 32.
What is meant by conurbation?
Answer:
An extended urban area typically consisting of several towns merging with the suburbs of a central city is called a conurbation.
Question 33.
When and who used the word ‘conurbation’ for the first time?
Answer:
The word ‘conurbation’ was first used in 1915 by a scholar named Patrick Geddes.
Question 34.
Give some examples of Conurbation cities in the world.
Answer:
Some examples of Conurbation cities are Greater London, Tokyo, Chicago, Gwalior, Hyderabad – Secunderabad, Gwalior – Lashkar – Morar, Delhi – Gurugram. Delhi – Noida.
Question 35.
What is a Global city?
Answer:
The city having population more than 50 lakh is called a global city. It is also known as a Megapolis or Megalopolis.
Question 36.
Name some Megalopolises of the world.
Answer:
Greater London, Paris, New – York, Moscow, Beijing, Kolkata, Mumbai, Delhi, Chennai etc.
Question 37.
Why has the rural youth population started settling in the cities?
Answer:
Due to mechanisation in agricultural sector, development of education and population growth in the rural regions, employment opportunities have decreased and so the rural youth has started settling in cities in search of employment and jobs.
Question 38.
Why have dirty slums come into existence?
Answer:
Due to increase in population and density in the cities, lack of residential houses has emerged which has played an important role in the emergence of dirty slums.
Question 39.
Describe the origin of Dharavi slums.
Answer:
In 18th century, it was an island. Dharavi slum was built by the potters of Gujarat about seventy – five years ago. At that time its population was only 10000.
Question 40.
Which economic activities are seen in Dharavi slums?
Answer:
Economic activities like pottery, ceramics, embroidery, brocade work, metal work, making ornaments, furniture – manufacturing and tailoring are seen in Dharavi slums.
Question 41.
What is the major objective behind the programme to rehabilitate the Dharavi slums?
Answer:
Its major objective is to provide a healthy environment, clean drinking water, light, fresh air, toilet facility to the dwellers of this slum and to save the people from poverty, hunger, unemployment and diseases and provide proper education to the future generations.
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 6 Short Answer Type Questions (SA-I)
Question 1.
What is meant by settlements?
Answer:
Settlements are groups of houses. These groups can consist of five upto hundreds and thousands of houses. Home, house, building or residence place is the basic unit of settlement. These can be in the form of a hut or even a large building. Settlements may develop in a small form and later develop to take the form of cities, metropolitan cities, mega cities and million cities. Footpaths, streets, roads, canals and transportation routes maintain contact between these settlements.
Question 2.
Human settlements are built for the fulfilment of which objectives?
Answer:
Human settlements are built for the fulfilment of the following objectives:
- To lessen the adversities of natural environment, i.e., for protection from seasonal conditions.
- For the storage and safety of food grains and other useful material.
- For the safety of self and food material from wild animals and livestock.
- For social, cultural, religious, economic and educational works.
- To lead a family life with comfort.
Question 3.
Mention the characteristics of dense settlements.
Or
Write the characteristics of clustered settlements.
Answer:
Following are the characteristics of dense/clustered settlements:
- These settlements are usually found between the fields at a high place, safe from the adversity of flood.
- The houses are built close to one another.
- All the houses are concentrated at one place and their residents face the external attacks jointly.
- Due to social bonding, their residents share their joys and sorrows.
- Number of houses in these settlements can vary from 40 – 50 up to hundreds.
- Their population can be 500 to 1000 or even more according to the available resources.
Question 4.
Mention the characteristics of scattered settlements.
Or
What are the characteristics of isolated settlements?
Answer:
Following are the characteristics of scattered/isolated settlements:
- Houses in these settlements are built away from one another.
- In these settlements. People live in isolated form.
- People are used to lead an independent life.
- Spirit of mutual cooperation is less in their residents.
- Feeling of discrimination exists in the communities engaged in agriculture in these settlements.
Question 5.
Where and why do Irregular patterns develop?
Answer:
Shapeless irregular patterns develop in such regions where humans build houses according to their comfort without any prior planning. In such settlements, roads and streets are built later on remaining part of land. The pattern of these roads and streets is zigzag, rounded and narrow. Due to this, a shapeless structure is formed in these irregular settlements. These types of patterns are found in Indian villages. For example, Lisari village of Baran district of Rajasthan.
Question 6.
Write the characteristics of urban settlements.
Answer:
Following are the characteristics of urban settlements:
- Pattern of high population density.
- Rapid mobility.
- Pattern of pucca roads and pucca houses.
- Availability of employment and primacy/plenty of modes of employment.
- More availability of private and public modes of transport.
- Availability of pattern of high education and healthcare facilities.
- More than 50 per cent population engaged in non – primary activities.
- Availability of the pattern of complex division of labour.
- Lack of social bonding and presence of individualism.
- Extreme social and economic differences and presence of class division.
Question 7.
Describe the classification of cities in the world on the basis of size of population.
Or
The size of population is different for the classification of cities in the world. How?
Answer:
The limit of population is decided separately for the classification of cities in the world. The different countries of the world, in order to be included in the category of urban regions, the minimum limit of population is 250 in Denmark, Sweden and finland, 300 in Iceland, 1000 in Canada and Venezuela, 1500 in Columbia, 2000 in Portugal and Argentina, 2500 in USA and Thailand, 3000 in Japan and 5000 persons in India. In India, apart from 5000 as population, the population density should also be 400 persons per sq. km and the population engaged in primary occupations is also considered.
Question 8.
The increasing size of population is giving rise to environmental pollution and various diseases. How? Explain.
Answer:
The condition of environmental pollution intensities is due to the increasing size of population in a region. Increasing population has encouraged urbanisation. This urbnisation has promoted industrialisation by which the black poisonous smoke emitted out from chimneys and the smoke coming out of vehicles due to traffic jams in cities is increasing atmospheric pollution. Due to this process of pollution, heart, respiratory, nervous system and mental health and skin related diseases have increased. Diseases such as diarrhoea and dysentery are increasing due to increasing pollution.
Question 9.
Write the specific characteristics of urban dirty slums.
Or
On the basis of which characteristics you can identify dirty slums in an urban region?
Answer:
Urban dirty slums can be identified on the basis of the following characteristics:
- Clay – built, temporary huts are found in these type of slums.
- In the name of roads, 2 to 4 feet wide rounded and trenched streets are found in these slums.
- Dilapidated houses are found in these slums and inferior facilities of air, light, drinking water and health care are there and usually there is lack of toilet facilities.
- Excessive crowd, less wages and the tendency to perform risky works are mainly found in these slums.
- Due to poverty, custom of alcohol consumption, crime, malicious mischief, use of intoxicants are very common here.
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 6 Short Answer Type Questions (SA-II)
Question 1.
Describe origin of human settlement process. .
Or
The origination of human settlements is a result of a long process, how?
Answer:
The origination of human settlement is a long process. Human started agricultural work after crossing the stages of gathering and livestock. After these stages, human felt the necessity of permanent settlements and along with population growth number of settlements increased. Slowly, human developed and due to growth in production trade and transport developed.
Due to technical development and population growth, number of villages also increased. Urban areas originated due to the increasing size of old villages. 5000 years ago from present, mega cities originated and developed in the valleys of Egypt, Indus and Dajla – Farat. Thus, human settlements originated.
Question 2.
Describe origin of settlements on the basis of Residence.
Answer:
There are two types of settlements on the basis of residence:
- Permanent settlement
- Temporary settlement
1. Permanent settlement:
These types settlements are the result of human development. These settlements originated from the time man started living in groups. Human settlements are the symbols of human culture and civilization.
2. Temporary settlement:
Those types of settlements which undergo change according to necessity and seasons are called temporary settlements. These types of settlements are built with the point of view of hunting, livestock and favourable season. Tribes live in these types of settlements.
These types of settlements are found in steppes grasslands area of central Asia. Khirgiz tribal people build temporary settlements for animal herding. Eskimos, badoo, Red Indians and Bushman also build this type of settlement.
Question 3.
Describe the distribution pattern of dispersed settlements.
Answer:
Distribution of dispersed settlements is found in Prairies area of USA and Canada in North America, Steppes grassland area in Asia; Khadar zone of Ganga in India, wetland area and Bhabar zone of Himalayan mountains, Pampas zone of Argentina in central and south America, Dawns in Australia, Veldts in South Africa and Udaipur, Rajsamand, Dungarpur, Pratapgarh, Banswara districts and the desert region of Rajasthan.
Question 4.
Describe the problems of slums.
Answer:
Problems of slum areas are as follows:
- Settlements are built in an unhealthy environment.
- Lack of roads.
- Lack of water facility, light and fresh air.
- Danger of infection due to crowded conditions.
- Lack of toilets amenity.
- Danger of fire due to Kucha houses.
- Small, less – high and unsafe residences.
- Lack of schools for education.
- Possibilities of occurrence of many deficiency diseases due to lack of food supply.
- Problem of maintenance of law and administration.
- Lack of emergency facilities during fire or any other such accidents.
- Unsecure life due to low wages.
- Lack of employment.
Question 5.
Write a geographical note on Dharavi slums.
Answer:
Dharavi is the biggest slum in Asia. It is situated in Mumbai Metropolitan city of India. It was populated by the potters who came from Gujarat 70 years ago and settled in Dharavi. This slum is situated between suburban area of railway line in 12 km south – west from Juhu. Today surface area of this slum is 557 acres and it is a conjunction of slums. Around 600000 people reside in this slum. As compared to population, number of houses in this slum is quite less. In this slum, 10 – 15 family members live in a single room house.
RBSE Class 12 Geography Chapter 6 Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe the problems of rural settlements in detail.
Answer:
Problems of rural settlements are as given below:
- Lack of transportation modes.
- Lack of healthcare facilities.
- Lack of employment opportunities.
- Lack of communication and technical facilities.
- Lack of higher education and technical institutes.
1. Lack of transportation modes:
In rural areas, normally lack of transportation modes has been found. Here, only private modes are available. So, transportation is a major problem here.
2. Lack of drinking water:
Shortage of drinking water has become a serious problem in rural areas. Due to this problem, people face many other types of problem also.
3. Lack of healthcare facilities:
The people of rural area depend on nearest urban areas for their small health problems. Due to lack of transportation modes, many times treatment is not available on time and as a result many patients even die.
4. Lack of electricity supply:
Rural areas face problem of lack of electricity supply. Due to its irregularity, daily and agricultural works suffer.
5. Lack of employment opportunities:
Employment opportunities are also not available here. Due to this factor, young population migrates to urban area. Seasonal and complete unemployment is found here.
6. Lack of technical facilities:
Due to this problem, people are not able to connect with Internet. So they are forced to go to the nearest urban area for even small types of works.
7. Lack of higher education and technical institutes:
In rural areas, higher education facility is not available. So students are forced to discontinue their study due to this problem.
Question 2.
Give a detailed description of the bases of classification of urban settlements.
Or
On what bases is the classification of urban settlements done? Explain.
Answer:
In the world, for classification of urban settlements, mainly the size of population, structure of occupation, administrative structure and essential conditions are considered as the basis. Following is a brief description of all these basic factors:
1. Size of Population:
In order to define urban regions in the world, the basis of population is mainly considered. But variation is found in the size of population for determination of cities in the entire world. Minimum number of people required for a region to be called a city is 250 persons in Denmark, Sweden and Finland, 300 in Iceland, 1000 in Canada and Venezuela, 1500 in Columbia, 2000 in Portugal and Argentina, 2500 in USA and Thailand, 3000 in Japan and 5000 in India.
2. Occupational Structure:
Apart from the basis of population, for determination of urban settlement, occupational structure is also considered as the basis. For example, in some countries such as Italy, more than 50% population should be engaged in non-agricultural activities. In India, this criteria is 75%. Here, major economic activities have also been considered as a criteria for urban settlements.
3. Administrative Structure:
In some countries, administrative structure has been considered as the only criteria to include a settlement under urban settlement. For example, a city is considered to be an urban settlement if it has a municipal corporation, cantonment board and a scheduled urban regional committee. In Brazil and Bolivia, in place of size of population, administrative center is considered a parameter of urban center.
4. Essential Conditions:
In the world, urban settlements are also identified on the basis of disposed functions. For example, essential conditions of holiday resorts and tourist places are different from those of industrial areas, port towns and military areas.
Question 3.
Describe the major problems of urban settlements.
Answer:
The major problems of urban settlements are:
1. Very high population density:
The youth workforce is settling in cities in search of employment, livelihood and education. As a result, the size and population density of cities is increasing rapidly.
2. Ill – effects of Slums:
Due to shortage of residential buildings in metropolitan and large cities, on account of increase in population and its density, the slums are developing rapidly and their ill-effects are also being seen. These slums are devoid of all basic facilities such as light, air, and clean drinking water.
3. Environmental Pollution:
Due to rapid urbanisation, various kinds of problems related to environmental pollution are increasing in cities. The black poisonous smoke emitted from chimneys of industries and from automobiles vehicles pollute the atmosphere, which not only effects humans and animals, but also harms the vegetation.
4. High price of Consumer Products:
Essential commodities of daily use like milk, ghee, fruits, vegetables etc. come to cities from nearby rural areas. In bringing these from far away areas, the additional costs of transportation, brokerage and profit margins make them costly.
5. Adulteration in Food – Products:
Traders in cities adulterate food materials to earn more profits. The adulterated food causes harm to human health and so people often suffer from many diseases.
6. Growing Crime:
The people who come from rural areas in search for a job disbalance the sex-ratio in cities. As a result, crimes like kidnapping, rape, murder, etc. are increasing. To become rich soon, the youngsters come in contact with anti-social elements and thus crime rate increases.
7. Sharp socio – economic division and social non – cooperation:
With the disparity in availability of resources and houses in cities, a socio-economic division is observed. Driven by personal self interest, people exhibit lack of social cooperation.
8. Lack of healthcare and medical facilities:
Growing pollution in cities due to growing population, causes people to suffer from several diseases. The number of doctors and hospitals is quite less in proportion to the population.
Question 4.
Which steps should be taken to resolve the problems of temporary slums?
Or
Which measures should be adopted to resolve the problems of dirty slums?
Answer:
Following steps should be taken to resolve the problems of temporary slums:
Provision of Housing at Minimum Rates by the Government:
On the site of temporary slums, by populating these people in multistorey buildings, the facility of air, light, toilets will automatically be provided. Life expectancy will also increase in a healthy environment. Just like in Kota and Ahmadabad, slum dwellers should be provided residences according to the size of their family, on minimum rates on easy installments.
- Provision of clean drinking water through taps or tankers at minimum charges or free of cost.
- Minimum wages should be fixed and employment should be provided just like MNREGA in rural regions.
- Proper arrangement of education for children should be done by opening schools in slum area itself.
- Free healthcare facility should be provided by opening community health centers near the slum area.
- Opportunities of employment should be provided in rural areas so that minimum
migration may take places towards the urban areas. - Construction of wide roads.
- Arrangement of parks if land is available.
- Providing loans for self-employment.
- Emphasis should be given on adopting family planning programmes.
- Maintenance of law and order in strict manner.
Question 5.
Describe social, cultural and economical condition of Dharavi slum.
Answer:
Social, cultural and economical condition of Dharavi slum is described below:
1. Social Condition:
Dharavi is the biggest slum of Asia. Today, over 6 lakh people live here. In this slum, 10-15 persons of a family live in a single room. Temporary houses are found in this slum; which are mostly double or triple storyed. A single main road goes through the slum, which is known as ninety-feet road, streets are so narrow that not even an auto – rikshaw can enter. Other lanes are so narrow that even a bicycle can pass with very difficulty.
2. Social condition:
Lack of drinking water, air and sunlight is found in Dharavi slum. There is no facility of sewerage system. In this slum, lack of basic amenities like toilets, education, healthcare, etc. are common.
3. Economic condition:
In Dharavi slum, economic activities like pottery, ceramics, embroidery brocade work, metal work, ornament making; furniture-manufacturing and tailoring are seen. It is a big tourist point and also a point of junior artists of movies. 85% of population find employment in this slum. Mumbai’s 80% waste material is recycled at Dharavi slum; which emits black poisonous smoke. Things made here are sold in Mumbai and other parts of the country, and along with this, they are also exported to Arab countries, USA and European countries.