RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 14 Perimeter and Area Ex 14.2 is part of RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Maths. Here we have given Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 14 Perimeter and Area Exercise 14.2.
| Board | RBSE |
| Textbook | SIERT, Rajasthan |
| Class | Class 6 |
| Subject | Maths |
| Chapter | Chapter 14 |
| Chapter Name | Perimeter and Area |
| Exercise | Ex 14.2 |
| Number of Questions | 10 |
| Category | RBSE Solutions |
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 14 Perimeter and Area Ex 14.2
Question 1.
By counting squares, estimate the (RBSESolutions.com) areas of the figures
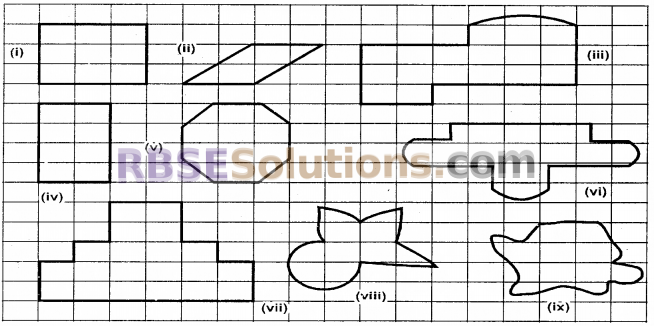
Solution:
To find the areas of figures given in question we (RBSESolutions.com) count the number of squares filled by figures. Which is the required area we ignore ‘less than half – filled squares’ and count ‘more than half – filled squares’, just as one square. Area of given figures are given in following table
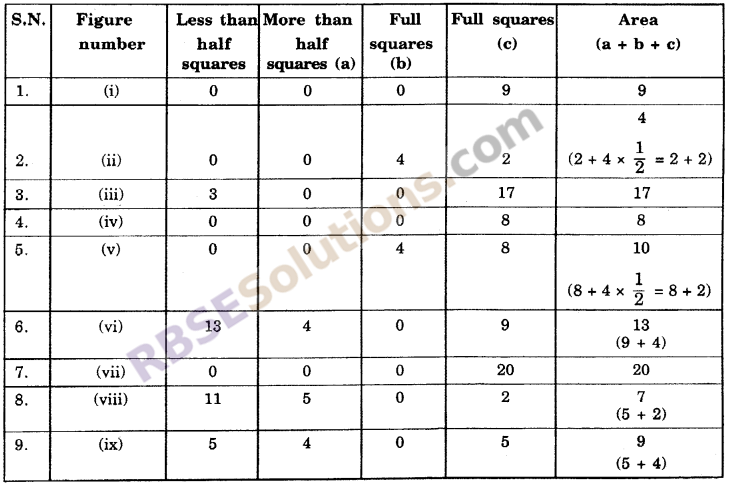
![]()
Question 2.
Find the areas of the following figures. What (RBSESolutions.com) do you infer from this?
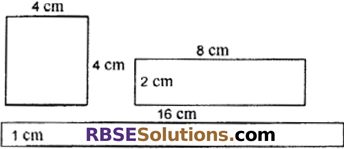
Solution:
Area of first figure (This is a square) = (side)2
= (4)2 = 16 sq. cm
Area of second figure (This is a rectangle) = l × b
= 8 × 2 = 16 sq. cm
Area of third figure (This a rectangle) = l × b
= 16 × 1 sq. cm = 16 sq. cm
Conclusion : Different figures can also have same area.
Question 3.
By splitting the following figures into rectangles, find (RBSESolutions.com) their areas. (The measures are given in centimeters)
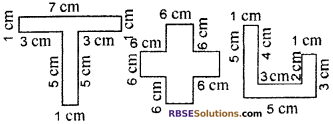
Solution:
We can split all figures (RBSESolutions.com) into rectangles as below
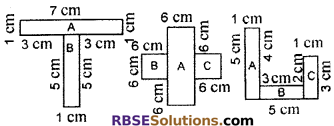
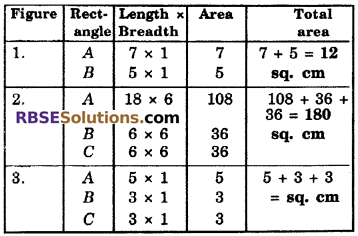
Question 4.
A room is 10 m long and 8 m wide. How many (RBSESolutions.com) square meters of carpet is required to cover the floor of the room?
Solution:
Required carpet to cover the floor of room = Area of the floor of the room
= l × b = 10 × 8 = 80 sq. m
Thus, 80 sq. m carpet will be required.
Question 5.
Find the area of a square (RBSESolutions.com) frame of side 9 cm.
Solution:
Area of squared frame,
= (side) × (side) = 9 × 9 = 81 sq.m
Thus, Area of frame is 81 sq. cm.
Question 6.
Find the areas of the following rectangles. Which rectangle has (RBSESolutions.com) least area and which one has greatest area ?
(i) l = 2 m, b = 80 cm
(ii) l = 180 cm, b = 70 cm
(iii) l = 200 cm, b = 1 m
(iv) l = 190 cm, b = 1 m
Solution:
(i) l = 2 m = 200 cm
b = 80 cm
Area = l × b = 200 × 80
= 16000 sq. cm
(ii) l = 180 cm
b = 70 cm
Area = l × b = 180 × 70
= 12600 sq. cm
(iii) l = 200 cm
b = 1 m = 100 cm
Area = 1 × b = 200 × 100
= 20000 sq. cm
(iv) l = 190 cm
b = 1 m = 100 cm
Area = I × b = 190 × 100
= 19000 sq.cm
∵ 20000 > 19000 > 16000 > 12600
Thus, (iii) rectangle has greatest and (ii) rectangle has least area.
![]()
Question 7.
The area of a rectangular garden 50 m long is 300 sq. m. Find (RBSESolutions.com) the width of the garden.
Solution:
Area of Garden = 300 sq.m
l = 50 m, b = ?
∴ l × b = area
⇒ 50 × b = 300
⇒ b = \(\frac { 300 }{ 50 } \) = 6 m
Thus, breadth of garden is 6 m.
Question 8.
Six square flower beds each of side 1 m are dug on a piece of (RBSESolutions.com) land 8 m long 6 m wide. What is the area of the remaining part of the land?
Solution:
Length of land = 8 m and b = 6 m
Area of land = 8 × 6 = 48 sq. m
Area of six squared flower beds each of sides 1 m = (side x side) × Number of flower beds
= (1 × 1) × 6 = 6 sq. m
remaining area = 48 – 6 = 42 sq. m
Thus, Area of remaining land will be 42 sq. m.
Question 9.
What will be the change in the (RBSESolutions.com) area of a rectangle if its
(i) Length and breadth are both doubled?
(ii) Length is tripled and breadth is doubled twice?
Solution:
(i) Let,
Length of rectangle = a and
breadth = b
Then, area = a × b = ab
New length of rectangle = 2a and new breadth = 2b
Then
New area = 2a × 2b = 4ab
= 4 × (ab) = 4 (initial area)
Thus, area of rectangle became 4 times of initial area.
(ii) Let, length of (RBSESolutions.com) rectangle = a,
and breadth = b
Then, area = a × b = ab
New length of rectangle = 3a and
new breadth = 45
Then New area = 3a × 4b = 12 ab
= 12 (ab)
= 12 (initial area)
Thus, area of rectangle became 12 times of initial area.
Question 10.
What will be the change (RBSESolutions.com) in the area of a square if its side is
(i) Halved?
(ii) Doubled?
Solution:
(i) (let) Side of square = a
Then, Area = a × a = a2
If length of side = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) × a = \(\frac { a }{ 2 } \)
Then Area = \(\frac { a }{ 2 } \) \(\frac { a }{ 2 } \) = \(\frac { a }{ 2 } \)
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \) a2 = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \) (initial area)
Thus, New area, remains one fourth of initial area.
(ii) Side of (RBSESolutions.com) square (let)= a
then. Area = a × a = a2
if length doubled, then side = 2a
and Area = 2a × 2a = 4a2
= 4(a2) = 4 (initial area)
Thus, New area, became four times of initial area.
![]()
We hope the RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 14 Perimeter and Area Ex 14.2 will help you. If you have any query regarding Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 14 Perimeter and Area Exercise 14.2, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.