RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Metals and Non-Metals are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Science. Here we have given RBSE Rajasthan Board Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Metals and Non-Metals.
Rajasthan Board Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Metals and Non-Metals
| Board | RBSE |
| Class | Class 8 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 2 |
| Chapter Name | Metals and Non-Metals |
| Number of Questions Solved | 43 |
| Category | RBSE Solutions |
Metals and Non-Metals Textbook Questions Solved
Question 1.
- Which metal is found in liquid state at room temperatures:
(a) sodium
(b) magnesium
(c) mercury
(d) aluminium - The non-metal which is conductor of electricity
(a) coal
(b) graphite
(c) sulphur
(d) nitrogen - Which is most reactive from the following metals:
(a) gold
(b) sodium
(c) magnesium
(d) silver - Metals form on reacting with oxygen-
(a) acidic oxides
(b) basic oxides
(c) neutral oxides
(d) non-reactive oxides
Answers:
- (c)
- (b)
- (b)
- (b)
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks:
- Pure gold is of………………..carat.
- The reaction of metals with acid gives out………………..gas.
- Metals are of………………..of heat and electricity.
- The oxides of non metals are generally………………..in properties.
Answers:
- 24
- hydrogen
- good conductor
- acidic
Question 3.
Match the column 1 with column 2
| Column 1 | Column 2 |
| Gold | Medicinal use |
| Sulphur | Jewellery |
| Mercury | Pencil |
| Graphite | Thermometer |
Answer:
| Column 1 | Column 2 |
| Gold | Jewellery |
| Sulphur | Medicinal use |
| Mercury | Thermometer |
| Graphite | Pencil |
Metals and Non-Metals Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is malleability?
Answer:
Metals are spread on beating by the force of a hammer. They are converted into sheets. This property is known as malleability.
Question 2.
What are mixed metals?
Answer:
When some amount of metal or non metal is mixed with main metal, then it is called mixed metal or alloy, for examples – in stainless steel chromium and nickel is mixed to protect it from rusting. In brass, zinc and copper are mixed in a fixed quantity to get desired properties such proportionate mixture is called an alloy such as bronze, brass and stainless steel.
Question 3.
What is melting point of a substance?
Answer:
That temperature at which solid changes into liquid state is called melting point of that object. Due to hardness of solid their melting point is high such as iron (Fe). The melting point of iron is 1593°C while galium is exception it melts just by putting it on hand palm as its meting point is very low.
Question 4.
Why is graphite a good conductor of electricity?
Answer:
Graphite is a good conductor of electricity because in graphite, carbon atom is combined with three nearest carbon atoms on the same surface and forms a hexagonal structure. While one end of them is free, such surfaces form weak bonds hence it is used in dry cells and electric arc.
Question 5.
Why lemon juice is not kept in iron containers?
Answer:
Lemon juice is acidic in nature it has citric acid hence when kept in iron containers it reacts with iron and causes poison and releases hydrogen.
Metals and Non-Metals Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Why sodium metal is kept in kerosene?
Answer:
Sodium is highly reactive. It reacts with water and oxygen quickly and forms sodium hydroxide and hydrogen gas hence catches fire. To disconnect its contact with air it is kept in kerosene. When a very small pieces of (Na) sodium is dried in a filter paper and then put into a beaker filled with water. It seems that piece of (Na) moves fast as it forms sodium hydroxide and hydrogen reacting with water.
Question 2.
Differentiate between metals and non-metals on the basis of their physical properties.
Answer:
Physical properties of metal:
(a) State: Most of the metals are found in solid state at normal temperature except mercury (Hg) which is found in liquid state at normal temperature.
(b) Colour: Mostly metals are grey in colour.
(c) Lustre: Most of the metals are lustrous. They are capable of reflecting rays of light from their upper surface therefore, they are lustrous such as gold, silver, copper, aluminium.
(d) Hardness: Most of the metals are hard. Hardness of different metals are different. Sodium and potassium are less hard compared to other metals.
(e) Sonorous: When metals are struck with other hard metals or objects then a special sound is produced, this property is called sonorous. Due to this property of metals they are used to manufacture bell and music instrument etc.
(f) Density: Generally metals have high density. Things made of metals are heavy so when they put in water they sink while those have less density will float in water such as sodium (Na) and potassium (K) etc.
(g) Melting Point: That temperature at which solid changes into liquid state is called melting point of that object. Due to hardness of solid their melting point is high such as iron (Fe). The melting point of iron is 1593°C while galium is exception it melts just by putting it on hand palm as its melting point is very low.
(h) Heat conductivity: When a rod of steel is heated, after sometimes it becomes hot while a wooden rod when submerged in hot water does not get heated. Silver (Ag) is the best conductor while lead (Pb) is the least conductor. This is the reason that cooking utensils are made of metals and their handles are made of non-conductors like wood, plastic etc.
- Malleability: Metals are spread on beating. Hence by the force of hammers they are converted into sheets.
- Ductility: When they are stretched, convert into wires. This property of metals is called ductility.
(k) Electricity conductivity: Metals allow electricity to pass through them. This property is called conductivity of electricity. Silver is the best conductor of electricity. Hence, those objects which are hard, lustrous, sonorous, ductile, malleable, and good conductor of heat and electricity are called metals.
Physical Properties of Non-Metals:
- Physical state: They are found in three states i.e. solid, liquid, and gas at normal temperature such as – solid- carbon (C), sulphur (S), iodine (I), ljquid – bromine (Br) and gas-oxygen (O2), nitrogen (N2), hydrogen (H2).
- Colour: Non-metals have variety of colours such as sulphur (yellow), chlorine gas (greenish yellow), phosphorous (red, white).
- Lustre: Non-metals are non lustrous. They do not reflect light. Diamond and iodine are exceptions as these are lustrous.
- Hardness: They are soft. Diamond is exception, it is the hardest non-metal found on earth.
- Sonorous: They do not produce sound.
- Density: They have less density.
- Melting point: The have low melting point except diamond and graphite. Diamond and graphite (isotopes of carbon) have very high melting point.
- Heat and electric conductivity: They are bad conductor of heat and electricity except graphite. It is a good conductor of electricity.
- Brittle: When they are beaten with hammer, convert into power or pieces it is called brittleness.
Question 3.
Write any four uses of metals.
Answer:
Use of metals:
- To make cooking wares.
- In making electric appliances, electric wires, fridge etc.
- Sheets of aluminium and iron for buildings materials.
- In manufacturing jewellery from gold, silver, coins and from copper, aluminium etc.
Question 4.
Why copper wire is use for wiring at our houses? Explain.
Answer:
Copper is very good conductor of electricity. Electricity flows through it very easily. It conducts electricity evenly in all circuits of house wiring, so copper is used for electrical wiring in houses.
Question 5.
Write differences in metals and non – metals on the basis of their chemical properties?
Answer:
Chemical properties of metals – Metals react with air, water, acid and form many chemical substances.
(a) Reaction with air:
Metals form their oxides when react with oxygen present in air. Metals + Oxygen → Metal oxides When ribbon of magnesium (Mg) is bum, it converts into white ash. When this ash is dissolved in a test tube with water and tested with a red litmus paper, it converts and turns into blue. Hence, it is proved that this solution (oxide) is alkaline in nature. In the same way copper and aluminium make their oxides due to which utensils of metals look dirty and non lustrous.
(b) Reaction with water:
They form metal hydroxide and release hydrogen. Sodium (Na)+ Water (H2O) → Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) + Hydrogen (H2)
When a very small piece of (Na) sodium is dried in a filter paper and then put into a beaker filled with water. It seems that piece of (Na) moves fast as it forms sodium hydroxide and hydrogen reacting with water. As (Na) is very reactive hence it is kept dip in kerosene, if it is kept open it bums with oxygen and reacts with water.
(c) Reaction with acid:
They produce hydrogen gas while reacting with acid.
Chemical properties of non- metals:
(a) Reaction with air: Non metals form their oxides when react with air (Oxygen). These oxide are acidic in nature. Take some powder of sulphur in a metal lid of a bottle and heat it. Wind this metal lid with a metal wire as the sulphur burn took into a gas jar cover it by a lid so the gas not to be let out. Now pour some water into a gas jar and shake it well, test the solution with blue litmus paper, it turns red. It proves that the solution is acidic. Sulphur (S) + Oxygen (O2) → Sulphur dioxide (SO2) Sulphur
powder reacts with oxygen which is an acidic oxide of non-metal.
(b) Reation with water: Generally non-metal do not react with water or steam, hence phosphorous are kept in water.
(c) Reaction with acids: Most of the non-metals do not react with dilute acids but sulphur react with concentrated nitric acid and form sulphur – dioxide, nitrogen oxide and water.
Metals and Non-Metals Additional Questions Solved
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
The most abundant metal in the earth’s crust is:
(a) Oxygen
(b) Calcium
(c) Aluminium
(d) Gold
Question 2.
The gas that burns with pop sound is:
(a) Nitrogen
(b) Hydrogen
(c) Oxygen
(d) Argon
Question 3.
Which metals burn in air at high temperature with the evolution of much heat?
(a) Cu
(b) Hg
(c) Pb
(d) A1
Question 4.
Bronze is an alloy of
(a) Copper and Zinc
(b) Copper and Tin
(c) Zinc and Iron
(d) Copper and Gold
Question 5.
Iron is galvanised by coating it with
(a) Chromium
(b) Sodium
(c) Magnesium
(d) Zinc
Question 6.
Metals react with oxygen to form their oxides which are generally
(a) Neutral in nature
(b) Basic in nature
(c) Acidic in nature
(d) None of these
Question 7.
A mineral from which a metal can be extracted on the commercial scale, economically is called
(a) Metal
(b) Metalloid
(c) Corrosion
(d) Ore
Question 8.
Some elements neither fit with the metals nor with non metals are called:
(a) Mixture
(b) Compounds
(c) Metalloids
(d) None of these
Question 9.
After the reaction of non-metals with water-
(a) Hydrogen gas formed
(b) Carbon dioxide gas is formed
(c) Non-metal oxides are formed
(d) Non-metals are unable to react with water
Question 10.
Non-metal forms:
(a) Anion
(b) Cation
(c) Anion and Cation
(d) Do not form ion
Question 11.
Metal which does not react even with steam:
(a) Potassium
(b) Iron
(c) Silver
(d) Magnesium
Question 12.
Mercury is used in thermometer because:
(a) it does not wet the glass
(b) it is a liquid
(c) it expands on heating
(d) all of these
Question 13.
Substance conduct heat and electricity because of the property of:
(a) Ductivity
(b) Conductivity
(c) Malleability
(d) Tensile strength
Question 14.
Which one of the following metal is the most ductile?
(a) Aluminium
(b) Silver
(c) Gold
(d) Copper
Question 15 .
Which one of the following matter does not displace H2 gas from dilute HC1 or H2SO4?
(a) Mg
(b) A1
(c) Zn
(d) Cu
Answers:
1. (c)
2. (c)
3. (d)
4. (b)
5. (d)
6. (b)
7. (d)
8. (c)
9. (d)
10. (a)
11. (c)
12. (a)
13. (a)
14. (c)
15. (c)
Metals and Non-Metals Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is the nature of metal oxide?
Answer:
Basic.
Question 2.
Why is the metal good conductor of electricity?
Answer:
Metals are the good conductor of electricity because they have free electrons.
Question 3.
Define conductivity.
Answer:
Metals allow the electricity to pass through them. This property of metals is called conductivity.
Question 4.
Why is aluminium used for making cooking coil?
Answer:
Aluminium is used for making cooking coil as it is very light weight metal, resistant to corrosion and is good conductor of heat.
Question 5.
Which is more metallic, sodium or aluminium?
Answer:
Sodium because it occupies higher position of the activity series.
Question 6.
What is the cause of rusting of iron?
Answer:
Rusting of iron is caused by oxide formation.
Metals and Non-Metals Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is galvanisation?
Answer:
A process employed to deposit a thin layer of zinc on the surface of iron objects to prevent them from rusting.
Question 2.
Why does copper does not displace iron from iron sulphate solution?
Answer:
Copper is less reactive than iron. A less reactive metal cannot replace more reactive metal.
Question 3.
Why do silver jewellery becomes black after sometime, whereas silver does not react easily with oxygen?
Answer:
Silver does not react with oxygen but it reacts with sulphur particles present in the air and thus forms a black layer of silver sulphide, hence silver jewellery becomes black after sometime.
Question 4.
Why do we store phosphorus in water?
Answer:
Phosphorus is very reactive non metal. It catches fire if exposed in air so to prevent the contact of phosphorus with the atmospheric oxygen it is stored in water.
Question 5.
Write the equation of
- copper with moist air
- sodium with water
- copper sulphate with zinc
- magnesium with oxygen
Answers:
- 2Cu + H2O+CO2+ O2→ Cu (OH)2+ CuCO3
- 2Na + H2O → 2NaOH + H2
- CuSO4 + Zn → Cu + ZnSO4
- 2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
Metals and Non-Metals Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the uses of non metals.
Answer:
Uses of non metals:
- Hydrogen and carbon are the essential constituents of the cells of all living beings. Without these elements life is not possible. Further more, carbon in the form of coal is used for generating heat energy for houses as well as factories.
- Nitrogen in the form of fertilizers is essential for growth and development of plants. Urea and calcium, ammonium nitrate are common fertilizers used by farmers.
- Oxygen is absolutely essential for the respiration of all kinds of plants and animals. It is also used in manufacture of steels and for artificial respiration on high altitudes, in space and deep sea diving.
- Silicon is used for making microchips and all kinds of electronic goods.
- Phosphorus is used in match industry and fertilizers.
- Sulphur is used for making fire crackers, gun powder and sulphuric acid.
- Chlorine is used in the disinfection of drinking water.
- Iodine dissolved in alcohol (tincture iodine) is antiseptic in nature and is used in dressing wounds.
- Helium is used in baloons.
- Argon is used in electric lights and advertisement signboards. Neon is also used in advertisements signboards and for lightning.
Question 2.
Show the reaction of sodium with water experimentally .
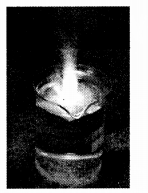
Answer:
Experiment:
Take a beaker and half fill it with water. Take a piece of sodium and cut a small wheat grain size piece from it. Press it first in a filter paper and then wrap it in cotton. Next, drop the piece in beaker. You will observe a violent reaction. Wait till the reaction stops completely. Now touch the beaker. Is it hot? Test the substafi.ee in the beaker with red and blue litmus paper. You will see that the solution is basic due to the formation of sodium hydroxide. Sodium reacts violently with cold water.
Question 3.
Give reasons for the following:
(a) Silver is used in making mirrors.
(b) Aluminium is used to make electrical wires.
(c) Food stuff should not be stored in aluminium utensils.
(d) Iron is used in constructing bridges and houses.
Answers:
(a) Silver is used in making mirrors because silver has a high reflecting power.
(b) Aluminium is used to make electrical wires because aluminium is a good conductor of electricity.
(c) Food stuff should not be stored in aluminium utensils because acids of the food stuffs react with aluminium.
(d) Iron is used in constructing bridges and houses because iron is hard, strong, and rigid metal.
Question 4.
How do you observe conduction of electricity in metals?
Answer:
Set up the circuit as shown with two free ends A and B. Check your circuit by switching on the current and touching A and B together.
Bulb should glow. Attach the wires/ fibres/thread one at a time to the ends A and B. Observe whether bulb glows or not. Tabulate your observations.
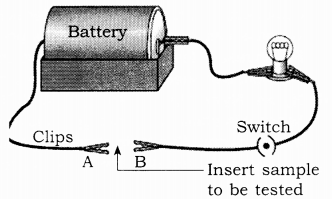
Observation: You will notice that the bulb glows in all the metallic wires tested. It shows that almost all of the metals are the good conductor of electricity.
We hope the given RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Metals and Non-Metals will help you. If you have any query regarding RBSE Rajasthan Board Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Metals and Non-Metals, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
Refer More: