RBSE Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 9 Quadrilaterals Ex 9.3 is part of RBSE Solutions for Class 9 Maths. Here we have given Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 9 Maths Solutions Chapter 9 Quadrilaterals Ex 9.3.
| Board | RBSE |
| Class | Class 9 |
| Subject | Maths |
| Chapter | Chapter 9 |
| Chapter Name | Quadrilaterals |
| Exercise | Ex 9.3 |
| Number of Questions Solved | 9 |
| Category | RBSE Solutions |
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 9 Maths Solutions Chapter 9 Quadrilaterals Ex 9.3
Question 1.
Construct a quadrilateral ABCD, when AB = 3.5 cm, BC = 4.8 cm, CD = 5.1 cm, AD = 4.4 cm and diagonal AC = 5.9 cm.
Solution.
Steps of construction:
1. Draw AB = 3.5 cm as base.
2. With centre A, draw an arc AC = 5.9 cm.
3. With B as centre, draw an arc BC = 4.8 cm. These (RBSESolutions.com) arcs intersect at C.
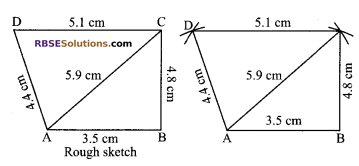
4. Join A to C and B to C.
5. Now take C as centre and draw an arc of radius 5.1 cm and with A as centre and radius 4.4 cm mark an arc. These arcs intersect each other at D.
6. Join A to D and D to C.
Hence, ABCD is the required quadrilateral.
![]()
Question 2.
Construct a quadrilateral PQRS, when PQ = 4 cm, QR = 3 cm, QS = 4.8 cm, PS = 3.5 and PR = 5 cm.
Solution.
Steps of construction:
1. Draw PQ = 4 cm as base.
2. With P as centre and radius 5 cm draw an arc.
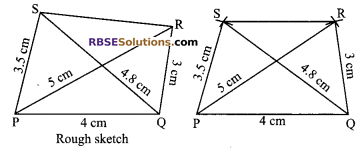
3. With Q as centre, draw another arc QR = 3 cm. These arcs intersect at R.
4. With centre P, draw an arc SP = 3.5 cm and (RBSESolutions.com) with centre Q draw an arc QS = 4.8 cm. These arcs intersect at point S. Join QR, RS, SP, PR and SQ.
Hence, PQRS is required quadrilateral.
Question 3.
Construct a quadrilateral ABCD, when AB = 4 cm, BC = 4.5 cm, CD = 3.5 cm, AD = 3 cm and ∠A = 60°.
Solution.
Steps of construction:
1. Draw AB = 4 cm as base.
2. At A draw an angle of 60°.
3. By taking P as centre, draw an arc of radius 3 cm which gives point D.

4. Again by taking D as centre, draw an arc (RBSESolutions.com) of radius 3.5 cm and from B drawn an arc of 4.5 cm which intersects at C.
5. Join CD and BC.
6. Hence, ABCD is the required quadrilateral.
Question 4.
Construct a quadrilateral ABCD, when AB = 3.5 cm, BC = 3 cm, AD = 2.5 cm, AC = 4.5 cm and BD = 4 cm.
Solution.
Steps of construction:
1. Draw AB = 3.5 cm as base.
2. By taking A and B as centres, draw an arc (RBSESolutions.com) of radius 4.5 cm and 4 cm respectively.
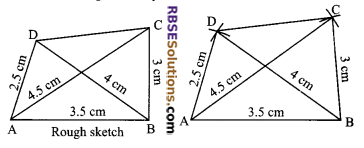
3. Also from B, draw an arc of radius 3 cm which intersects the previous arc of radius 4.5 cm at C.
4. Again from A, draw an arc of 2.5 cm which intersects the arc of 4 cm at D.
5. Join A to D, B to C, B to D and C to D.
6. Hence, ABCD is the required quadrilateral.
Question 5.
To construct (RBSESolutions.com) a quadrilateral PQRS when PQ = 3.0 cm, QR = 4.0 cm, PS = 4.5 cm, QS = 5.5 cm and PR = 6 cm.
Solution.
Steps of construction:
1. Draw PQ = 3.0 cm as base.
2. With P as centre and radius 6 cm draw an arc.
3. With Q as centre, draw another arcs of radius 4 cm, these arcs intersect at R.
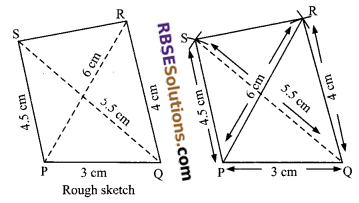
4. With centre P, draw an arc PS = 4.5 cm and with centre Q, draw an arc QS = 5.5 cm. These arcs intersect at point S. Join QR, RS, SP, PR and SQ. Hence, PQRS is (RBSESolutions.com) the required quadrilateral.
Question 6.
Construct a quadrilateral ABCD, when AB = BC = 3 cm, AD = 5 cm, ∠A = 90° and ∠B = 120°.
Solution.
Steps of construction:
1. Draw AB = 3 cm as base.
2. At A make an angle of 90°.
3. At B make an angle of 120°.
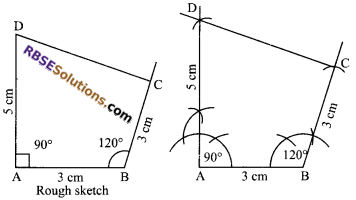
4. With A and B as centres and radius 5 cm and 3 cm, draw arcs which (RBSESolutions.com) cut line segments at D and C.
5. Finally, join D to C.
Hence, ABCD is the required quadrilateral.
![]()
Question 7.
To construct a quadrilateral ABCD, when AB = 3.8 cm, BC = 2.5 cm, CD = 4.5 cm, ∠B = 30° and ∠C = 150°.
Solution.
Steps, of construction:
1. Draw BC = 2.5 cm as base.
2. At B and C, make ∠B = 30° and ∠C = 150°.
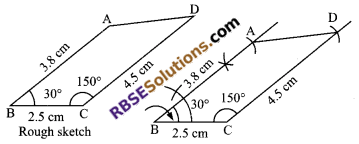
3. With B and C as centres, (RBSESolutions.com) draw an arc of 3.8 cm and 4.5 cm respectively.
4. Join A to D.
Hence, ABCD is a required quadrilateral.
Question 8.
Construct a quadrilateral PQRS, when PQ = 3 cm, QR = 3.5 cm, ∠Q = 90° and ∠P = 105°, ∠R = 120°.
Solution.
Steps of construction:
1. Draw a line segment PQ = 3 cm as base.
2. At P draw a ray PX such that ∠QPS = 105°.
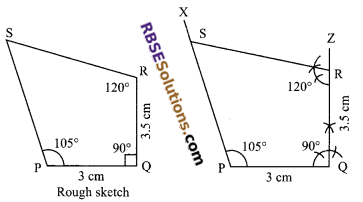
3. At Q draw a ray QZ such that ∠PQZ = 90° and mark an arc (RBSESolutions.com) of radius 3.5 cm on it. Mark this point as R.
4. At R draw ∠QRS = 120° which cuts PX at S.
Hence, PQRS is the required quadrilateral.
Question 9.
Construct a quadrilateral PQRS, when PQ = 2.5 cm, QR = 3.7 cm, ∠Q = 120°, ∠S = 60° and ∠R = 90°.
Solution.
Steps of construction:
∵∠P + ∠Q + ∠R + ∠S = 360°
∴ ∠P = 360° – (120° + 90° + 60°)
=> ∠P = 90°
1. Draw a line segment PQ = 2.5 cm.
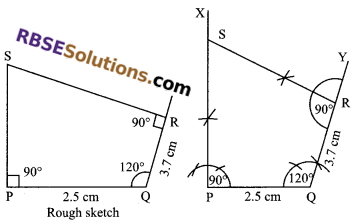
2. At P draw a ray PX such that ∠XPQ = 90° and at Q draw a ray QY such that ∠PQY = 120°.
3. With Q as centre, take an arc (RBSESolutions.com) of radius 3.7 cm and mark it as R.
4. Also at point R construct an angle of 90° which will meet ray PX at S.
Hence, PQRS is the required quadrilateral.
![]()
We hope the given RBSE Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 9 Quadrilaterals Ex 9.3 will help you. If you have any query regarding RBSE Rajasthan Board Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 9 Quadrilaterals Ex 9.3, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.