RBSE Solutions for Class 9 Social Science Chapter 20 Calamities and Management are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 10 Social Science. Here we have given Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 9 Social Science Chapter 20 Calamities and Management.
| Board | RBSE |
| Textbook | SIERT, Rajasthan |
| Class | Class 9 |
| Subject | Social Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 20 |
| Chapter Name | Calamities and Management |
| Number of Questions Solved | 43 |
| Category | RBSE Solutions |
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 9 Social Science Chapter 20 Calamities and Management
TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS SOLVED
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Question 1.
Which of the following natural disaster is not related to India?
(a) Earthquake
(b) Flood
(c) Landslide
(d) Volcano
Answer:
(d).
Question 2.
The major earthquake region of India is:
(a) Southern Plateau
(b) Himalaya
(c) Central India
(d) Coastal India
Answer:
(b).
Question 3.
The major landslide occurs in the mountainous region of India is:
(a) Aravalli
(b) Himalaya
(c) Satpura
(d) Vindhyachal
Answer:
(b).
Question 4.
The ‘river of sorrow’ of West Bengal is
(a) Kosi
(b) Damodar
(c) Ganga
(d) Swarnarekha
Answer:
(b).
Question 5.
The major drought region of India is
(a) Northern plain
(b) Eastern region
(c) Western region
(d) Coastal region
Answer:
(c).
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are natural disasters?
Answer:
Those changes in nature which are not beneficial to man are called natural disasters. Example: Landslide, Earthquake, flood, etc.
Question 2.
What is an earthquake?
Answer:
When any part of the earth has vibrations due to any event occurs in side the earth is called an earthquake.
Question 3.
What do you understand by landslide?
Answer:
Process of rolling down soil and rocks from upper slopes is called rock sliding. If the rock sliding is in a great scale then a sound of thunder occurs.
Question 4.
What is flood?
Answer:
When due to heavy rainfall water in rivers spread on large area by breaking bank is called flood.
Question 5.
Which river is called sorrow of Bihar?
Answer:
River Kosi
Question 6.
What is the main cause of drought?
Answer:
The main cause of drought is deforestation:
- Uncertainity and unequal distribution of rainfall due to monsoon climate.
- Low level of under ground water.
- Deforestation.
- No management of storage of water.
- Destruction of natural sources of water collection.
- No permanent water policy proper use and exploitation can be done.
- Rapid growth of population put an adverse effect of water resources.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What do you understand by management?
Answer:
Management is a process done by an individual society and government level before and after the disaster to control the loss of property and lives.
Question 2.
In which parts of India earthquakes are common and why?
Answer:
The Northern mountains and foothills, i.e. Himalayas are the most earthquake- prone area in India because it is young fold mountain which are not stable and still under the process of formation.
Question 3.
Which are flood-prone areas in India?
Answer:
North and Northern plains are flood prone areas in India.
Question 4.
Explain Trikal.
Answer:
When such a less rainfall occur so, no production of grain, fodder and insufficient availability of drinking water occur it is called Trikal.
Question 5.
In 1984 in which city of India a big incident occur due to leakage of chemical gas?
Answer:
On 3 Dec. 1984 a big incident occur due to leakage of chemical gas in Bhopal.
Question 6.
In which country deaths were occur first time due to Anthrax?
Answer:
The USA is the country where first time deaths occurred due to use of Anthrax.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
How can the natural disaster of earthquake be tackled?
Answer:
Earthquake can be tackled by the following:
- Government should distribute network of instrument related to earthquake measures.
- Alert should be declared through TV and radio to make people aware of earthquake.
- At individual level people should leave the place and go in open area.
- Switch off the switch of electricity and regulator of cylinder.
- Irrespective of caste, creed, religion, etc. people should help each other on the ground or humanity during such disaster.
Question 2.
Explain the main causes of landslide.
Answer:
The main causes of landslides are:
- Formation of rocks
- Slope of earth
- Vibrations caused by earthquake
- Prolonged rainfall and seepage
- Deforestation
- Uncontrolled human development such as road, bridges, etc.
- Undercutting of cliffs and banks by waves or river erosion.
- Volcanic eruptions
Question 3.
Describe the main causes of flood in India.
Answer:
The main causes of flood in India are:
- Receives a high average rainfall.
- Non-availability of drainage due to excess rainfall.
- Indiscriminate deforestation in catchment areas and upper reaches results in soil erosion and consequent silting of river courses.
- Overgrazing in the hills leaves the soil without cover.
- Farming practices like shifting cultivation result in loss of vegetation cover and consequent soil erosion and consequently lead to silting of rivers and causes flood.
Question 4.
What are the ways to check drought?
Answer:
The most greatest danger of drought is famine, less availability of water increased the intensity of famine. There are three forms of famine, occurred by drought.
- Akal:
Famine of Grain (Starvation). When production of crops fail due to less rainfall. - Dvikal:
Famine of fodder and grain. When production of crops and fodder fail due to less rainfall. It is also called double famine. - Trikal:
When less rainfall occur, insufficient production of grain, fodder and insufficient availability of drinking water occur, it is called Trikal.
Famine of Vikram Samvat 1956 (1900 BC) is also called as Chappan Akal is considered as greatest famine.
Drought Management
Ways to Check Drought: Joint river plans should be implemented so excess water of rivers should be supply to less availability areas. It would increase the level of under ground water and would indirectly help in developing greenery.
At individual level, it is the most important that one should understand the importance of water. One should personally take interest in water collection and conservation Kachcha and Pucca tank should be built which will help in increasing underground level of water while other for utilising water when rain do not occur. Water should be collected by making wall around the land. So, water will slap-down less water. Consuming seeds should be grown. Eyeiyone should help each other at the time of famine.
Coping with drought
- The government and non-government agencies should donate generously to cope up with the condition.
- Food and water should be supplied to the drought affected regions.
- Medical aid should be provided immediately.
- If there is an epidemic of a disease, people should move to other safe places
- The rescue workers should be put to action immediately.
Question 5.
Highlight the problems faced by the flood prone regions and their solutions.
Answer:
The problems faced by the flood prone regions are:
- In India more than 2000 deaths occur due to flood every year.
- 80 lakh hectares of land is flood-prone.
- 35 lakh hectare of land crop destroys every year.
- Life in 3 crore acre land becomes unbalanced.
- Loss of one thousand crore rupees every year.
- The greatest effect of flood occurs on animal wealth.
- More than 12 lakh animals and houses destroy every year.
- 60% loss caused by flood in India held in Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, Assam and Odisha are main.
- Floods disturb communication, transport, sources of water, and destroy crops and cause epidemics.
Flood Management
- In 1954, National Flood Control Plan was launched to check the great loss done by flood. Under this plan bank of rivers, water flowing drains were built.
- Under multi-purpose projects scheme dams were built on Mahanadi, Damodar, Satluj, Vyas, Chambal, Narmada rivers.
- To control flood regions of river origin should be covered with forests it would check soil erosion and result in check on loss due to floods.
- Exploitation of forests should be ban.
- Water holding capacity of river should be increased by removing debris and spreading it on banks.
- In 1954, floods forecast/prior information organization was established. At district headquarters flood control cells were established.
- In 2007, the NDMA (National Disaster management Authority) of the Government of India pointed about 13 areas of flood management. These include zoning, forecasting, risk maps, structural measures, maintenance of river banks, river basin management, construction of flood shelters, etc.
- Meterological department and irrigation department keeps a regular observation on amount of rainfall and its flow during rainy season. People are informed regularly through Television.
- At individual level, people should listen radio and watch television regularly in rainy season. If they are living in flood prone area and should follow the instructions and orders of government strictly. Electric appliances should switch off. Precious things food etc. should be shifted at secure places. Vehicles, animals, etc. should be shifted at secure places.
Question 6.
Explain the man-made disasters.
Answer:
List of the man made disasters are:
- Fire:
It takes lakh of lives every year. In a few speonds everything turns to ashes. Fire crackers, careless use of electric appliances are responsible for such disaster. - Road Accidents:
One lakh twenty five thousand people loss due to their lives road accident every year in India. Ignorance of traffic rules, drink and drive led to road accident. - Rail Accidents:
It is the cheapest means of transport but great pressure on railways has increased the possibilities of accidents. Technical problems and carelessness are also its causes. - Mass destructive weapons:
It includes atomic or nuclear weapons. They have replaced the traditional war system. Wars have become more destructive due to use of nuclear weapons. Use of one bomb can convert the whole city into ash in seconds. - Nuclear accidents:
Man made bombs are explosive and strong as well as destructive. They are of two types – Hydrogen and atom bombs. - Chemical and Industrial accidents:
Technical and scientific development has increased the use of chemicals in daily life in the form of chemical fertilizers, pesticides, insecticides, chlorination of purify water plants, etc. Some very sensitive flammable and cheap explosive chemicals are used by terrorists which cause great accidents. - Biological weapons:
These are such weapons using infections agents such as virus, bacteria and fungi with the intent to kill humans, plants and animals as an act of war.
ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS SOLVED
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
When did the National Flood Control Plan launch?
Answer:
It was launched in the year 1954 by forecasting the weather reports.
Question 2.
What is the average rainfall receive in the northeast India?
Answer:
It receiver average rainfall of more than 250 cms.
Question 3.
Name the rivers that bring less flood destruction.
Answer:
Satluj, Beas, Ravi, Chenab and Jhelum.
Question 4.
Name the east flowing rivers which are mainly responsible for flood in India.
Answer:
Gariga, Yamuna, Gomati, Ghagra, and * Gandak.
Question 5.
Write the three forms of famine.
Answer:
Akal, Dvikal and Trikal are the three forms of famine.
Question 6.
What is double famine?
Answer:
When production of crops and fodder fail due to less rainfall, it is called double famine.
Question 7.
Name the winter rainfall in North India that is useful for rabi crops.
Answer:
Mavat
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name the drought prone area in India.
Answer:
Eastern Gujarat, East Rajasthan, East Punjab, East Haryana, East Uttarakhand, West MP, Central Maharashtra, Karnataka, South Andhra, Central Karnatanka, North West Bihar, West UP, West Odisha.
Question 2.
Describe the three types of famine.
Answer:
The three types of famine are as follows:
- Akal: When production of crops fail due to less rainfall and causes starvation.
- Dvikal: When production of crops and fodder fail due to less rainfall.
- Trikal: When less rainfall occur, insufficient production of grain, fodder and insufficient availability of drinking water occur.
Question 3.
Write the cyclone-prone areas in India.
Answer:
Sea storms of Arabian Sea during April to June are parallel to west to West Bengal’s cyclones. They affect Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Odisha and West Bengal during October to December.
Question 4.
What are the causes of flood?
Answer:
The causes of flood are:
- Deforestation and pastures destruction
- Destruction of traditional water resources
- Building of constructions ignoring the natural drainage.
Question 5.
Write the problems of landslide.
Answer:
- It blocks the way of rivers, road and result in the imbalance of human life.
- Loss of lives and property occur.
- Blocking of rivers results in the formation of lakes.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Differentiate between the natural and man-made causes of earthquake.
Answer:
When any part of the earth has vibrations due to any event occurs inside the earth is called an earthquake. It is one of the greatest destructive calamities. It can cause great destruction in a moment.
Earthquakes intensity can be measured by an instrument seismograph in Richter scale. It was discovered by Charles Richter so it is named after him. On this intensity of an earthquake could be measured up to 12 up to 5. It is said normal as the speed increases it takes the most destructive form.
Causes of Earthquake:
It is caused due to movement tectonic of plates of earth. Contraction and expansion due to vapour inside the earth is also a cause of earthquake.
Earthquake Prone Area:
If we study the earthquake occurred in India we conclude that Northern mountains and foot hills is the most young fold mountain. Himalaya is the part of this young fold mountain which is still in the stage of formation. Still the balanced stage is not developed in Himalayas. Hence it is the most earthquake prone area while Deccan plateau is a balanced and stable part of earth but after the earthquake of Koyna and Latoor this region is also considered as earthquake zone region of Kachch and Bhuj of Gujarat is also falls in earthquake zone.
Earthquake a danger:
It is a natural disasters which cause the greatest change in a moment on earth which shock the heart of people. It causes thousands of death, cracks in earth surface, destruction of roads, collapse of buildings which convert into heap of soil and stones. Bridges, dams collapse and become danger in future. Relief from Earthquake and Management:
At the level of society and government: All government take relief and help measures after earthquake toll of death in India is high as it is densely populated. Hence it is necessary to implement network of instrument related to earthquake measures. So possibility of destruction of lives and property could be decrease and an alert can be declared through TV and radio to make people aware.
Question 2.
Write a short notes on cyclones.
Answer:
Sea storms are called cyclones in India. They originate in hot currents and enter in India from Indian ocean then crossing Bay of Bengal reach to India as well as from Arabian sea. They are less humid when they reach to coastal regions cause heavy rainfall as they move interior amount rainfall goes on decreasing due to high speed and heavy rainfall they cause destruction in coastal regions.
Causes of origin due to condensation and evaporation in summer season an around the surface of ocean moves up and cause low pressure to fill it arid enters from all sides this cause cyclones or storms. Their impact depends upon temperature in North Western India and centre of low pressure. In winters also cyclones occurs in North west India they cause rain in winters in North West India called “Mawaf useful for Rabi crop.
Question 3.
Describe the chemical and industrial accidents and its measures.
Answer:
Technical and scientific development has increased the use of chemicals in daily life in the form of chemical fertilizers, pesticides, insecticides, chlorination to purify water plants, etc. These simple chemicals have polluted the atmosphere. Some dangerous chemicals are found in every house like hair spray, deodorant, nail-paint, nail paint remover, toilet cleaner. Some very sensitive flamable and cheap explosive chemicals are used by terrorists which cause great accidents. Unsafe use of their chemicals and their storage as well as leakage is harmful to whole community.
In India in 1984 leakage of Poisonous gas from insecticide manufacturing industry Union Carbide in Bhopal city took 3000 lives in few hours, those who left are suffering from diseases.
Security Measures
- Such industries should be established away from residential.
- People leaving around and workers should be made informed and trained against such accidents.
- Industrial waste of such industries must treated before disposal so environment could be protected.
- Insurance and security laws should be followed strictly.
Question 4.
What are the causes of origin of natural disasters?
Answer:
Change is the continuous process of nature. Those changes which are in the interest of man kind are considered as boon of nature but when changes are not beneficial to man they are called curse of nature or natural disaster.
Natural disaster is a change or event which occurs in few seconds. Problems resulted after happening are called dangers cause by Natural disaster.
For disaster one reason is not responsible but combined reasons are responsible. External and internal forces of earth directly affect the disaster, for example, Earthquake, Volcano etc. unwise and continuous exploitation of resources by man, use of earth in different ways by growing population have deformed the earth. Deforestation, weathering of rocks, water crises are the result of such activities. Such problems have given birth to global warming.
All these above mentioned causes are combinedly responsible for natural calamities.
Natural balance is disturbed by man due to man’s greedyness and consumer satisfaction view. For his blind development he has disturbed the balance of nature. Man’s activity are indirectly inviting these natural disaster.
Classification of Natural disaster on the basis of origin:
- Change in earth:
Calamities which occur due to sudden change inside the earth. For example: Earthquake, rock sliding, glaciers sliding and volcano. In India volcanoes are not active. - Seasonal calamities:
They are caused by seasonal change. For example, Cyclones, Tsunami, flood, etc. - Calamities caused by living beings:
They are caused by bacteria and living things. For example, epidemics, dead animals, plague, malaria, etc.
Map Based Questions
Question 1.
Shade the earthquake affected area on the political map of India.
Answer:
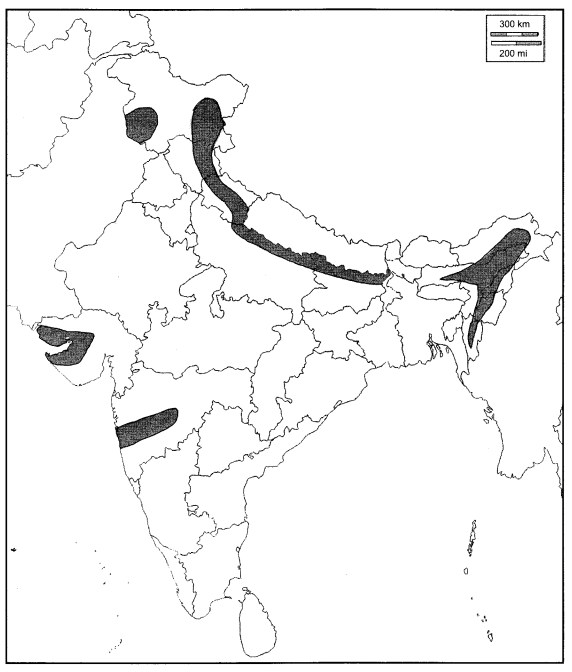
Question 2.
Shade the landslide regions on the political map of India.
Answer:
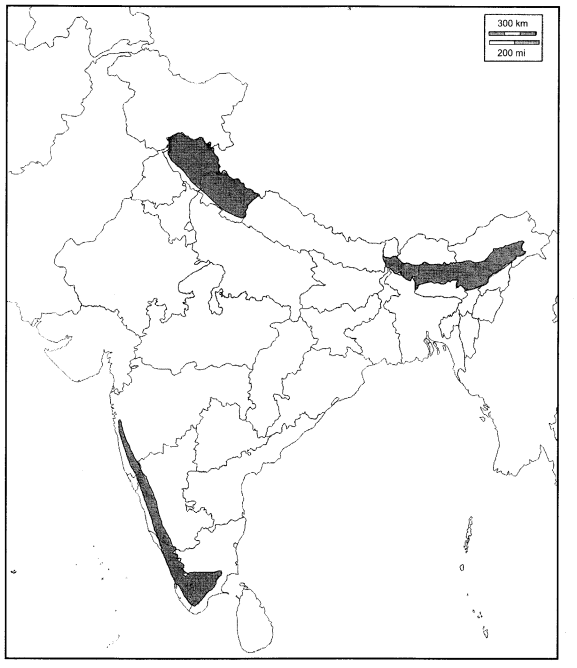
Question 3.
Mark the flood prone region on the political map of India.
Answer:
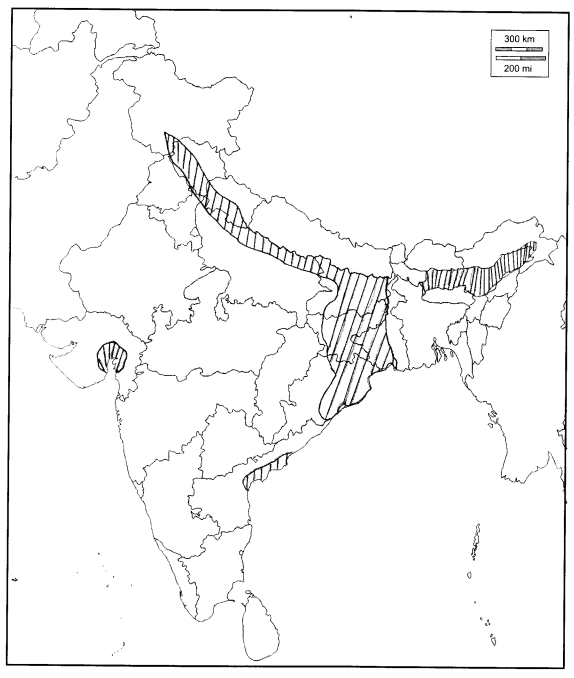
Question 4.
Mark the drought-regions of India.
Answer:
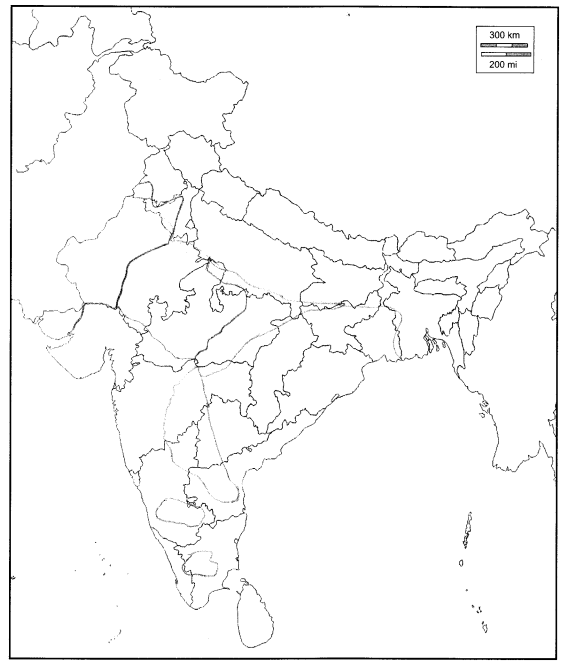
We hope the given RBSE Solutions for Class 9 Social Science Chapter 20 Calamities and Management will help you. If you have any query regarding Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 9 Social Science Chapter 20 Calamities and Management, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.