Make use of our RBSE Class 12 Accountancy Notes here to secure higher marks in exams.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Accountancy Notes Chapter 15 Database Management System
Meaning of Database
Data is the most important component in any work that we do. We either use existing data or generate more data. When this data is gathered and analysed it yields information. The word “data” is the plural of the word “datum” which means facts. Thus, data means facts. These may be numeric, textual, pictorial or even vocal. And therefore, many different types of data are handled by information technology, e.g., text, voice and picture.
A data type in a programming language is a set of data with values having predefined characteristics. Examples of data types are integer, floating point number, character, string and pointer, usually a limited number of such data types come built into a language. The language usually signifies the range of values for a given data type, how the values are processed by the computer and how they are stored. With object oriented programming a programmer can create new data types to meet application needs.
Database is a general term for any collection of related information stored in a logical way on a computer. A number of general purpose database programmes are available for PCs of which the best known is probably Microsoft’s Access. Using such software one can define new databases enter information and process the information in various ways. One of the most important processing operations is to search for data that matches certain criteria. In the transactional database model, the database is divided into a number of tables. Each table consists of a number of record.
For example, in a database of accounting information there may be a table of supplier’s details where, each record relates to an individual supplier. If a number of tables are connected logically, we have relational database. The usual term for a database which does have such relational links is a flat file database. A database is thus, a collection of data. It contains information about one particular enterprise. It is so stored that is organised so that its contents can easily be accessed, managed and updated.
![]()
Types of Database
- Relational Database: The most important type of database is the relational database. It is a tabular database in which data is defined so that it can be reorganised and accessed in a number of different ways.
- Distributed Database: A distributed database is one that can be dispersed or replicated in a different points in a network.
- Object Oriented Database : An object oriented database is one that is congruent with the . data defined in object classes and sub-classes.
Databases contain aggregations of data records or files such as a sales transactions, product catalogue, inventories and customer’s files. Typically a database manager provides users the capabilities of controlling read/write access, specifying report generation and analysing usage.
Structured Query Language (SQL) is a standard language for making interactive queries from and updating a database such as IBM’s DB2, Microsoft’s Access and database products from Oracle, Sybase and Computer Associates.
Database Management System (DBMS)
Database is an important programme or software. It records all the useful and relevant information relating to a business at one centralised place. Data may relate to number of files, salaries appointments, retirements, sales, purchases, accounts receivables and accounts payables, incomes and expenditures etc.
These data are generally stored on a floppy discs. The Database Management (DBM) converts the data into useful information. The data fed into the computer may be rearranged in a desired order and different calculations can be performed according to the need of the business.
So, if the data of sales have been fed into the computer, we may very well know total sales of the month, average sale, the amount of collection, percentage of profit on sales, etc. Database management is useful in debt collection, production planning and control, inventory control, preparing payrolls, invoicing, preparation of budgets, etc. It also helps in decision making.
Database help in organising related information in a logical manner for access and retrieval. Database management involves creating, storing, modifying, deleting and adding data in files and using this data to generate reports. It is popularly access. The software that allows to perform these functions is known as Database Management System (DBMS).
![]()
Advantages and Importance of Database Management System
- Database minimised data redundancy which makes updating easier and less error prove.
- Database saves processing effort and storage space.
- A database pool the data for a series of applications. So, data is easily available from one central source.
- DBMS helps data management much more efficient and effective.
- DBMS helps in having better access to more and better managed data.
- DBMS helps in quickly answering the queries.
- DBMS helps in preparing reports.
- Fewer programs may be needed since each can access an entire database.
- DBMS helps in ensuring data security and integrity.
Objectives of DBMS
DBMS has been involved to overcome the problems and limitations of traditional management. The following are the main objectives of DBMS :
- Complexity of an organisation information system is reduced through centralisation of data management.
- Data redundancy and inconsistency are reduced by eliminating all isolated files in which the data elements are repeated.
- Program data dependence is reduced by providing central control of data creation and definition.
- Flexibility in information system is greatly increased by permitting adhoc queries of large pool of information.
- Data once stored are accessed by multi-users. Thus, data collected for one purpose can be used to serve various purpose as the needs arise.
![]()
Basic Components of Database Management System (DBMS)
Database management system has different components which have their own functions. The following are the components of DBMS :
- Data Base
- Administrator
- Data
- Software
- User Interface
- Data Processing
- File Handling Programmes.
Entity Relationship (ER) Model
It is a popular conceptual data model which is mostly used in database oriented applications. The model is best depicted with the help of ER symbols while preparing ER diagram the following symbols are used to present the different types of entities, attributes, identifiers and relationship:
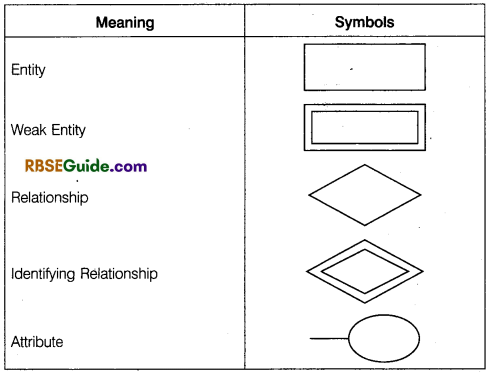
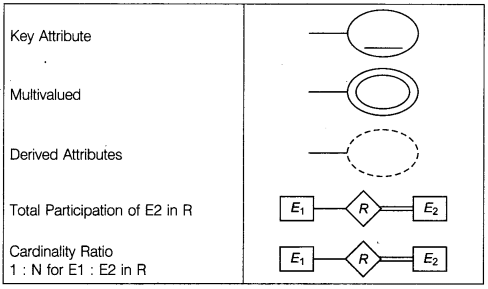
![]()
Components of ER Model
ER model has four units
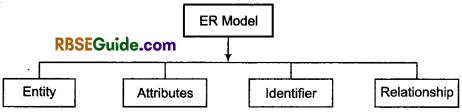
1. Entity: Any thing in the real world with independent existence is called Entity such as an object with physical existence (e.g., car, person, house) or conceptual existence (e.g., a company, job, university course, account, voucher).
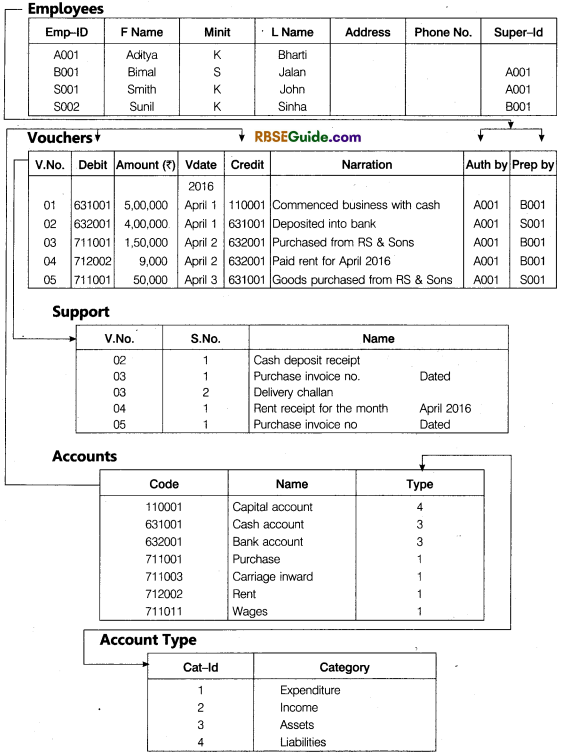
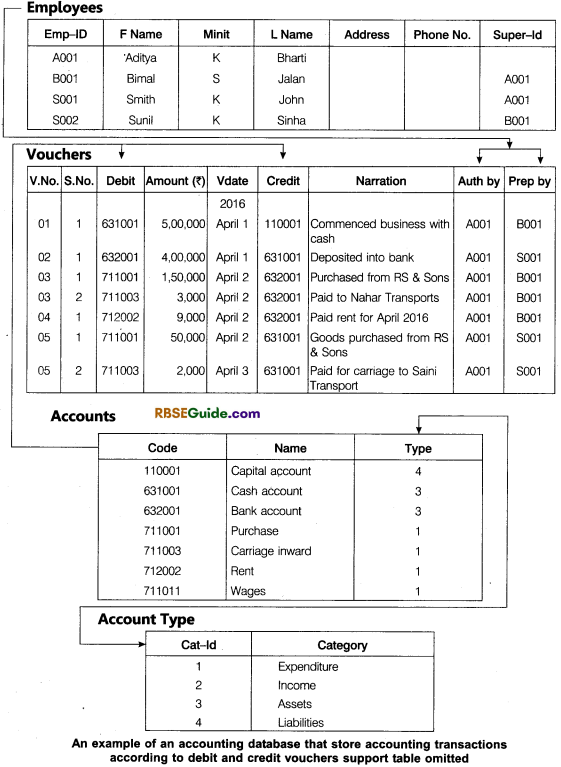
In the context of above accounting reality, there exist five entities are accounts, vouchers, employees, accounts type and support documents. The accounting data is captured through these entities.
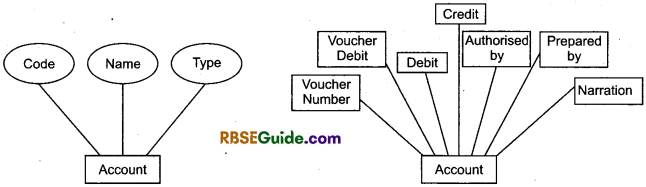
2. Attributes : Attributes are some properties of interest (or characteristics) that further describes the entity such as height,
weight and date of birth in case of a person and code and name in case of accounts.
Entity
- Customer
- Book
- Student
Attributes
- Name, Address, Customer No
- ISBN, Author, Price
- Name, Address, Roll No
An entity has value for each of its attributes, which is the data stored in the database. Attributes may be of several types tire ahead.
- Composite Vs. Simple attributes
- Single valued Vs. Multivalued
- Store Vs. Derived attributes
- Null values (for absence of data)
- Complex attributes
- Entity types of entity sets
- Value sets of attributes.
3. Identifier (or Key Attributes of an Entity Type): Almost every types has one of its attributes, which contains unique values for identifying the entity instance. For example, roll number as attribute of entity type students has unique values through which a student instance can be identified. Similarly, code is a key attribute of entity type accounts because its data values are required to be unique.
4. Relationship : A relationship is a link between two entities. It tells something about which relationship exists between our entities. For example, vouchers and accounts are related to two ways – vouchers contain debit account(s) and vouchers contain credit account(s).
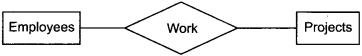
In ER model those references are represented as explicit relationships rather than attributes. Collection of relationship as called “Relationship Sheet”.
![]()
Types of Relationship
There are three types of relationship :
1. One-to-one relationship
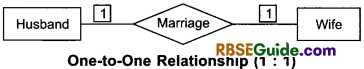
2. One-to-many relationship
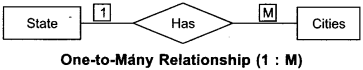
3. Many-to-many relationship
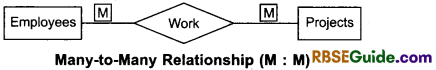
Weak Entity Types
Entity types, which do not identifier or key attributes of their own are weak entity types are identified by being related to specific entities from another type in combination with some of their attribute values. Accordingly the relationship type that relates a weak entity type to its owner is called Identifying Relationship of the weak entity.
![]()
Relationship Based on Degree
The degree of a relationship type is the number of participating entity type. A relationship type of degree one is called Unary Relationship.
A relationship types of degree two is called Binary Relationship and relationship types of degree three is called Ternary Relationship. Example,
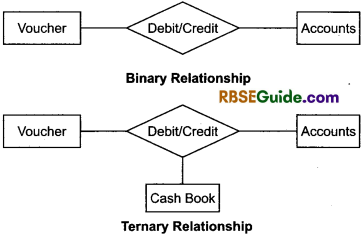
Relationship Data Model (RDM)
One of the main advantage of the relational model is that it is conceptually simple and more importantly based on mathematical theory of relation. It also frees the users from details of storage structure and access methods. In addition to being relatively easy to create and access, a relational database has the important advantages of being easy to extend. After the original database creation a new data category can be added without requiring that existing applications are modified.
The relational model like all other models consists of three basic components :
- A set of domains and a set of relations
- Operation on relations
- Integrity rules.
![]()
Concepts of a Relational Data Model
The relational model was propounded by E.F. Codd of the IBM in 1972. The basic concept in the relational model is that of a relation.
A relation can be viewed as a table which has the following properties :
- Property 1: It is column homogeneous. In other words, in any given column of a table all items are of the same kind.
- Property 2 : Each item is a simple number or a character string. That is table must be in INF (First Normal Form).
- Property 3 : All rows of a table are distinct.
- Property 4 : The ordering of rows within a table is immaterial.
- Property 5 : The columns of a table are assigned distinct names and the ordering of these columns is immaterial example of a valid relation
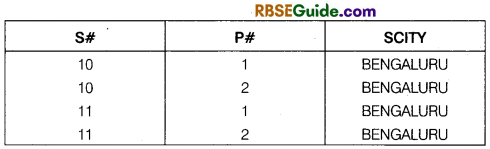
Thus, a relational database is a set of tables. It contains data fitted into predefined categories. Each table for relation, as it is sometimes called Contains one or more data in columns. Each row contains a unique instance of data for the categories defined by the columns.
For example, a typical business order entry database would include a table that described a customer with columns for name, address, phone number etc. Another table describe an order product, customer data, sale price and so forth.
A user of the database could obtain a view of the database that fitted the users needs. For example, a financial service manager of a company can obtain a report on accounts that needed to be paid. A branch manager might like a view or report on all customers that had bought products after a certain date.
![]()
Types of DBMS
DBMS programmes commonly use one of the following four database structures to link files :
1. Hierarchical Databases : Hierarchical databases were developed by IBM in 1968. A hierarchical database links data using a hierarchical relationship. In a hierarchical DBMS a group of fields is called a Segment rather a record. The data element at the type of the hierarchy is known as the Parent Element.
There may be several child element beneath the parent element. Each of these children may in turn become a parent to several lower level child elements. It should be noted that in a hierarchical structure each segment can have only one parent. The structure that is created resembles a pyramid or an organisational chart.
The problem with a hierarchical database is that the data can be accessed only by following a path down the structure access is not flexible. All the relationship among the data elements must be determined when the database is designed.
For example, employees may be categorised by departments in which they work within the department employees may be categorised by job function. Many companies continue to use hierarchical databases even though other database structures are superior IBM supports a hierarchical database on many of its mainframe computer.
2. Network Databases: The network database structure was developed by a Conference on Data System Languages (CODASYL). As in hierarchical database a net database organises data in a parent child relationship. All the relationship among the data items must be determined during the design phase. In a network structure however a child can have more than one parent or no parent at all.
3. Relational Databases : A database in which the various tables are linked by related field is called Relational Database. For example, a table of sales transaction may have records that contain a field referring to the customer’s name. This name may also occur in a table of customer details. If it is possible to retrieve information from the latter table using the information in the former, the tables are relationally linked and the database is relational.
A relational database is a collection of data items organised as a set of formally described tables from which data can be accessed or reassembled in many different ways without having to reorganise the database tables. A very important point to note here is that an RDBMS that satisfies the 12 criteria given by Dr. Codd is called a True RDBMS.
![]()
Data Processing Cycle
In order to understand the dynamics of database design let us understand the data processing cycle in the context of accounting. Data processing involves the technique of collecting, sorting, relating, interpreting and computing data items in such a manner as to provide meaningful and useful information for decision making.
The necessary steps involved in data processing cycle are data capturing, inputing processing and generating information available to the user. Data processing cycle when thought of in the context of accounting, requires a series of steps that have been described below briefly.
1. Source Documents : The first step to capture accounting data from transaction (s) so as to prepare a document, called Voucher (as already stated earlier) that expresses and documents an accounting transaction. The relevant accounting data is set out in the voucher.
2. Input of Data: The accounting data contained in vouchers is to be entered in a computer’s storage device. This is achieved by using a predesigned data entry form. This data entry form is designed in a manner that it is similar to physical voucher document. The data entry form is designed using software and it is made to appear on the computer monitor so that the data is entered.
3. Data Storage: A suitable data storage structure is required to provide for a blank data record as shown below:

The above blank record that is used for storing the input of data pertaining code of account, name of account and category type of which it belongs is shown below as :

Hypothetically, the category type 4 above refers to liabilities and the category type 1 indicates expenses. The data storage structures (also called Data Tables) are created as a part of structuring database for accounting.
4. Manipulation of Data : The stored data is manipulated for necessary transformation to generate final reports. Such transformed data may be stored separately and subsequently used for generating final reports. Alternatively, the transformed data can be directly presented in the form of a report.
5. Output of Data : The accounting report such as ledger trial balance etc. are obtained in a predesigned format by accessing the transformed data.
![]()
Designing Database for Accounting
Both computerised and computer based AIS require a definite data structure for storing the accounting data. As already mentioned the databases are used for storing accounting data. The process of designing database (for accounting) begins with a reality (or accounting reality) that is expressed using elements of a conceptual data model. The process of designing a database for accounting is best described through a flow chart.
Reality: It refers to some aspect of real world situation for which database is to be designed. In the context of accounting, it is accounting reality that is to be expressed with complete description.
ER Design : This is a formal blue print, with a pictorial presentation in which Entity Relationship (ER) model concepts are used to represent description of reality.
Relational Data Model : It is representational data model through which ER design is transformed into interrelated data tables alongwith the restriction in the form of rules that are specified to ensure the consistency and integrity of stored data.
Normalisation: This is process of refining a database design (that consists of interrelated data tables) through which the possibility of duplicate or redundant data items is reduced or eliminated.
Refinement: This is the outcome of the process of normalisation as mentioned above. The final database design is arrived at after the process of normalisation is completed.
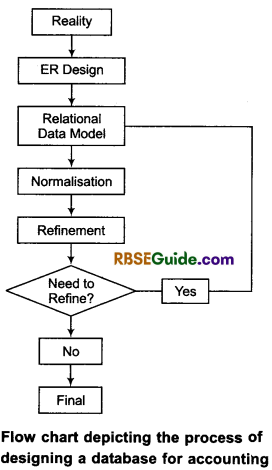
![]()
An Illustration of Accounting Database
Consider an example of Accounting database for maintaining data pertaining to accounting transactions, support documents, accounts and employees with which the students of accounting are familiar. This table shows below the database structure and some sample data for this database depicting the following transactions

Refinement: This is the outcome of the process of normalisation as mentioned above. The final database design is arrived at after the process of normalisation is completed.
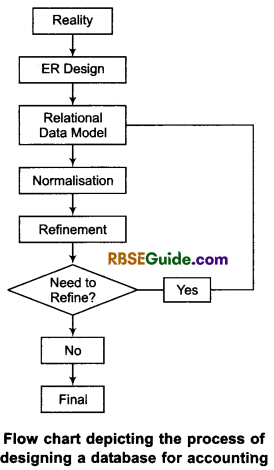
![]()
An Illustration of Accounting Database
Consider an example of Accounting database for maintaining data pertaining to accounting transactions, support documents, accounts and employees with which the students of accounting are familiar. This table shows below the database structure and some sample data for this database depicting the following transactions.

Disadvantages of a DBMS
- Danger of a Overkill: For small and simple application for single users a database system is often not advisable.
- Complexity: A database system creates additional complexity and requirements. The supply and operation of a database management system with several users and databases is quite costly and demanding.
- Qualified Personnel: The professional operation of a database system requires appropriately trained staff without a qualified database administrator nothing will work for long.
- Costs: Through the use of a database system new costs are generated for the system itself but also for additional hardware and the more complex handling of the system.
- Lower Efficiency: A database system is a multi-use software which is oftenless efficient than specialised software which is produced and optimised exactly for one problem.
![]()
MS Access and Its Components
It is one of the popularly used Database Management System (DBMS) to create store and manage data bases. It is also popularly called Access.
Every component that is created using access in an object and several such similar objects constitute a class. Access is functionally available with the following seven-object classes. Each of these object classes is capable of creating their respective object replicas.
1. Tables : This object class allows a database designer to create the data tables with their respective field names, datatypes and properties.
2. Queries : This object class is meant to create the SQL compatible query statement with or without the help of Graphic User Interface (GUI) to define tables, store data and retrieve both data and information.
3. Forms : This object class allows the designer to create an appropriate user interface to formally interact with the back end database defined by the tables and queries.
4. Reports: This object class is used to create various reports the source of information content of which is based on tables, queries or both. Such reports are designed in access according to the requirement of end-user.
5. Pages : This object class is meant to create data access pages which can be posted on a website of an organisation using internet or sent via e-mail to someone of the organisation’s network.
6. Macros : In macro programming the object using’ individual instructions called Macro-Oriented Actions are manipulated. A macro is a list of macro-oriented actions that run as a unit. Access provides for such macro programming.
![]()
Modules
These are the foundations of any application and allow the designer to create a set of programming instructions, called Functions or Subroutines that can be used throughout the application.
- The functions return a value while subroutines do not return any value.
- Access provides for creating such modules.
Each of these object classes is contained in the named database file of access with MDB extension. Whenever this file is opened a database window as shown on next page.
Opens with all the above object classes available on the left hand side. As and when the specific objects are created or designed, they get listed on right hand side on this window against each of these object classes.
Access Basics for Creating a Database
When a new database is created from the scratch, there is complete control over the database objects, their properties and the relationships. In order to create a new database without the help of database wizard (that is an automated process in access) the following steps are required
- Open access window to choose blank access database and click OK button.
- Access responds by displaying file new database dialog box, which prompts the designer to enter a file name and a location for the database. This must be followed by clicking create button.
- If the task pane is not open, choose file from menu bar and click at new to open the task pane to create a new database.
![]()
Creating of Tables in Access
The creation of tables in access requires the following steps and understanding of the components of table object.
Click at tables object of access, followed by double click at create table by design view. This results in providing a table window, the upper part of which has three columns field name, data type and description. It is meant to define the scheme of a table being created. Each of its rows corresponds to a column of the table being created. Two primary properties of the column of a table are its field name and data type.
Field Name: Refers to column name of the table being created. The name of the column should be a string of contiguous characters. The field name is meant to define the name of column to be created followed by data type of such column. The designer can optionally provide despription of the column also. Once the data type is defined, the designer can further specify the properties of each column in the lower part of the table window.
Data Types:
Access supports different data types the details of which are as given below:
- Text: It is used for a string of characters, words or numbers that are not to be used in any arithmetic calculations. The maximum length for a text field is 255 characters. It is the default data type because of being used most frequently.
- Memo: It is used for storing comments and is capable of accommodating 65536 characters. But a field with this data type is not amenable to sorting or filtering of data records.
- Number : It is meant to store numbers which could be integers (-32768 to 32767), long integers (- 2,147,483,648 to 2147,483,647), bytes (0-255), single (to store values with decimal point upto a certain limit), double (to store values in decimal point with greater magnitude and more precision) or decimal types.
- Date/Time: It is used to store dates, times or a combination of both.
- Currency: It is used for storing numbers in terms of dollars, rupees or other currencies.
- Auto Number : It is a numeric data automatically entered by access. It is of particular importance in a situation where none of the fields individually or a set of fields as a combination in a table is unique.
- Hyperlink: This data type is meant to store a Universal Resource Locator (URL) and e-mail addresses.
Structured Query Language (SQL)
As the name denotes SQL is the best at writing queries. It is available in a number of database management packages based on the relational model of data. For example, in DB2 of the IBM and UNIFY of the UNIFY corporation.
Originally defined by D.D. Chamberlain in 1974, SQL underwent a number of modifications over the years. Today SQL has become an official ANSI standard. Today SQL is used in database management systems of many platforms. It allows for data definition manipulation and data control for a relational database.
The data definition facilities of SQL permit the definition of relations and of various alternative views or relations, further the data control facility gives features for one user to authorize other users to access his data. This facility also permits assertions to be made about data integrity.
All the three major facilities of SQL namely, data manipulation, data definition and data control are bound together in one integrated language framework. The query language enables users to ask specific questions of the database. A marketing vice-president trying to decide which items to sell at a discount.
For example, might ask a database program to all inventory items with a profit margin greater than 25%. The most popular query language is Structured Query Language (SQL).
SQL is a standard interactive and programming language for getting ihformation from and updating database. Although SQL is both an ANSI and ISO standard many database products supports SQL with proprietory extensions to the standard language queries take the form of a command language. This lets you select, insert, update, find out the location of data and so forth.
![]()
Categories of SQL Commands
SQL commands can be roughly divided into three major categories with regard to their functionality. Firstly, there are those used to create and maintain the database Structure. The second category includes those commands that manipulate the data in such structures.
Thirdly there are those that control the use of the database. To have all this functionality in a single language is a clear advantage over many other systems straightway and most certainly contribute largely to the rumour of it being easy to use.
- Select: This clause is used to specify the fields to display data or information.
- From: This clause is meant to indicate the source of data in terms of tables or queries or a combination of both. TWo tables are joined by specifying a join clause based on a condition of join. There can be three types of join are inner, left and right.
- WHERE: This clause in SQL statement is used to provide the condition to restrict the records to be returned by query. The resultant records of query must satisfy the condition which is specified after WHERE clause. This is meant to filter records returned by the query.
Database Management System Notes Important Terms
→ Database : It is a group of collected figures which is used in a listing way through computer.
→ Information : If any decision is taken on the basis of results while processing data, is called information.
→ Database Management System : This is a software which is helpful to know the result of all queries demanded by the users using database.
→ Entity : Entity is a formation of real situations based on specific subject of ER model and . its characteristics are called attributes.
→ Attributes : This is the properties of any personality which describes about that entity. As height, weight, birth date in case of a person and code and name in case of accounts.
→ Entity Group : This is a group describing all types of entities in a specific entity.
→ Macro Programme : Here, in it there is a list of small functions and using different instructions, these are in a format of unit.
→ Table : This object class allows a database designer to create the data tables with their respective field names, datatypes and properties.
