Make use of our RBSE Class 12 Accountancy Notes here to secure higher marks in exams.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Accountancy Notes Chapter 9 Accounting for Non-Trading Organisations and Professional Persons
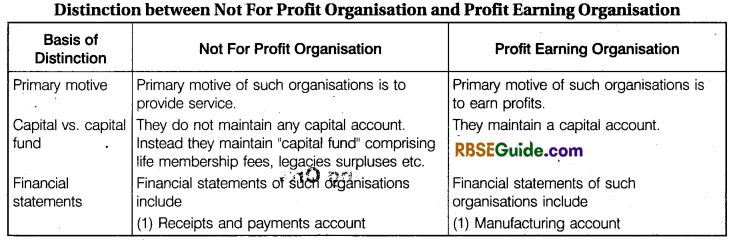
Meaning of Non-Profit or Non-Trading Organisations:
Not for profit organisations are those organisations which are established for a charitable or social purpose and not with a view to earn profit. These organisation render services to their members and to the society on voluntary basis or for the promotion of art, culture, education, sports and other social and charitable purposes.
They include schools, colleges, hospitals, public libraries, clubs, literary societies, sports associations etc. Just to elaborate, schools and colleges provide education hospitals’ render medical services to the society, literary societies organise debate, symposium, seminars etc. for the advancement of knowledge and awareness. Sports associations work for the development of various games etc.
As these institutions are legal entities established for the welfare of society and not with a view to earn profit so these institutions do not prepare profit and loss account. Instead they prepare receipts and payments account, income and expenditure account and balance sheet.
A receipts and payments account is similar to consolidated cash book for the accounting year. The income and expenditure account is prepared to know whether income for the institution is sufficient to meet current expenses. Thus financial statements of “Not for profit organisation” reflect the objects for which they are prepared.
![]()
Characteristics of Not For Profit Organisation
1. Main Aim is Service: Such organisations are set up to provide service to a specific group or the public at large, such as education, health care, sports, entertainment etc. The main aim of these organisations it to provide service either free of cost or at nominal rates and not to earn profit.
2. Form: These organisations are set up as charitable trusts or societies and subscribers to these organisations are called Members.
3. Separate Entity: Not for profit organisations are treated as a separate entity distinct from its members. In other words, it is not effected by admission of new members and the death or insolvency of an existing members
4. Managed by Elected Members: These organisations care usually managed by a managing or
executive committee elected by its members.
5. Major Sources of Income : The major sources of their incomes usually are
- Subscription from their members
- Donations
- Financial assistance from government in the form of grant-in-aid
- Income from investment etc.
6. Surplus not Distributed Among its Members: Current year’s surplus in the form of excess of income over expenditure is not distributed amongst its members. It is added to capital fund.
7. Accounts : These organisations also have to maintain proper accounts to meet the legal requirement and to exercise proper control over utilisation of their funds.
8. Form of Accounts : They prepare their financial statements of the end of each accounting period (usually a financial year) in the form of receipts and payment account, income and expenditure account and a balance sheet.

Accounting Procedures of Not For Profit Organisations:
Not for Profit Organisations prepare annual accounts for consideration of its members and to obtain financial grants from government departments.
- The books of accounts kept by these organisations include :
- Cashbook
- Ledger
- Register of members
- Register of assets.
![]()
Important Items Related to Not For Profit Organisations:
Following guidelines are followed by “Not for Profit Organisations” in the absence of specific instructions:
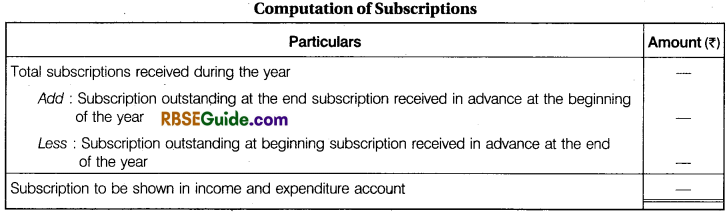
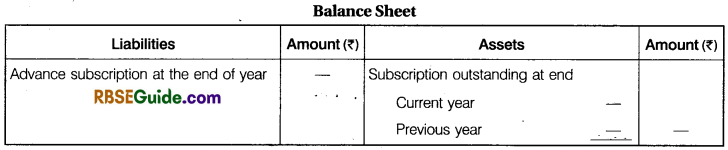
(1) Subscriptions : Subscription is the amount paid by the members of not for profit organisations periodical basis (i.e., monthly, quarterly, half yearly or on yearly basis) so that their membership is not cancelled. Thus, it is a recurring source of revenue from its members.
It is the main source of revenue of not for profit organisations, so it is credited to income and expenditure account. It is appeared on the debit side of receipts and payments account. Since accounts of not for profit organisations are prepared on accurate basis so subscription of current year (whether received or not) comes on the credit side of income and expenditure account. It is calculated as under :
Computation of Subscriptions
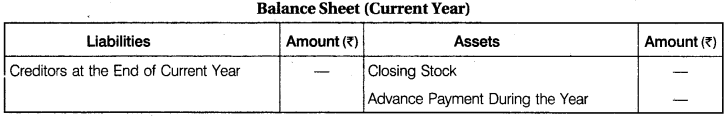
(2) Consumable Stores: If institution consumes certain items such as medicines by hospital or sports items by clubs, relevant figures for receipts’and payments account and income and expenditure account will be calculated. The value of goods consumed is shown in income and expenditure account and the amount paid to creditors is shown in receipts and payments account.
Calculation of stationary consumed during the year:

(3) Entrance Fees/Admission Fees : It is received from the new members apart from the amount of annual subscriptions. Some people favour capitalising the entrance fee on the ground it is collected once for all and as such it is not of the recurring nature. However, these are others who argue that though, it is paid by each member only once. It is received fairly regularly every year and as such should be treated as revenue income.

(4) Legacy: Legacy is the amount which a not for profit organisation will receive as per will of a deceased person. Since it is non-recurring in nature so it is capitalised and added to capital fund on the liabilities side of the balance sheet. However, if it is for a specific purpose it should be capitalised in the name of the “fund”.
(5) Sale of Old Assets: If an asset is sold the amount realised is compared with the book value of that asset to ascertain profit or loss on sale of assets. Profit on sale is credited and loss on sale of asset is debited to income and expenditure account. The book value of the assets sold is deducted from the concerned assets in the balance sheet.
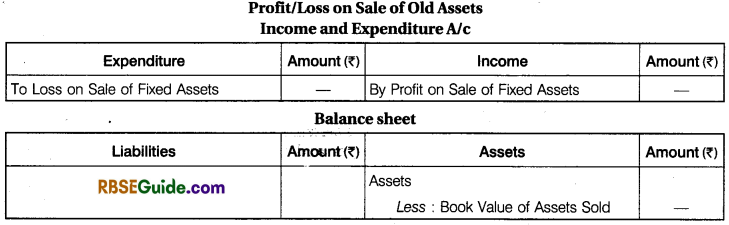
For instance, furniture appeared in the balance sheet at ₹ 12,000. During the year furniture of book value ₹ 3,000 was sold for ₹ 2,200. It will be shown as under :
Loss on sale of furniture is ₹ 800 (3,000 – 2,200). It should be debited to income and expenditure account.
The book value of furniture sold ₹ 3,000 will be deducted from the furniture on the asset side and furniture will be shown as ₹ 9,000 {i.e. 12,000 – 3,000).
(6) Donation: Charitable institution may receive donation from time to time. If the amount is small and if such collections are frequent, then they may be treated as an income. Donation may also be of two types: general donation and specific donation. Any donation received not for a specific purpose are treated as general donation.
General donation of comparatively small amount may be taken to income and expenditure account. General donations of comparatively huge amount, which are of non-recurring nature may be added to the capital fund. The nature and size of the organisation decide about the amount of donation being small or big.
In case of donations received for any specific purpose then it is termed Specific Donations. Such amount cannot be used for any other purpose except the purpose of donor. Therefore, such amount may be shown in balance sheet (liabilities side).
All the donation debited to receipts and payments account and these amounts may be credited to income and expenditure account or liability side of the balance sheet, if it is for a specific purpose.
(7) Payment of Honorarium : It is a payment of remuneration to a person who is not an employee of the organisation. Such as any special performance is done, by an outsider, at the organisation, then the payment is honorarium and is taken to income and expenditure account as it is a revenue expenditure.
(8) Sale of Old Newspaper and Sports Material: The sale of old newspaper is an income and is credited to income and expenditure account. As regards sale of sports material is concerned, it is also considered as income of the organisation.
Sports material asset to the organisation-sports material consumed is in the nature of depreciation of sports material so it is shown on the debit side of income and expenditure account. If this consumed sports material is sold, money realised is in the nature of income to be credited to income and expenditure account.
(9) Endowment Fund : Endowment fund arises from a bequest or gift, the income generated from it is utilised for a specific purpose while the original amount is kept intact either forever or for a specific period, it is shown on the liabilities side of the balance sheet as a separate item.
![]()
Special Item related to Non-trading Institutions are divided in four part like as follows :
(i) Fully Revenue Nature Items :
- Subscription
- Consumable Stores
- Realise from consumable
- Realise Capital from Sale of Residual Material
- Sale and Purchase of Journals
- Sale of Old Sports Material
- Honorarium
- P&L from sale and purchase of fixed assets
- Other revenue income and expenditure
(ii) Fully Capital Nature Items:
- Life Membership Fees
- Legacies
- Purchase and Sale of Fixed Assets
- Endowment Fund
- Annuity Fund
(iii) Capital & Revenue Nature and Situation:
- Entrance Fee: It should be assumed revenue nature, but in question mentioned about it specially can do that.
- Donation : (A) Generally, donation is low it is a revenue nature. But it amount is big it should treated as capital nature.
- special donation, if donation received for special purpose it should treated as capital nature.
- Grants: Govt, gives a grant treated Revenue Income. But govt, gives a grant for special work it should treated as capital nature.
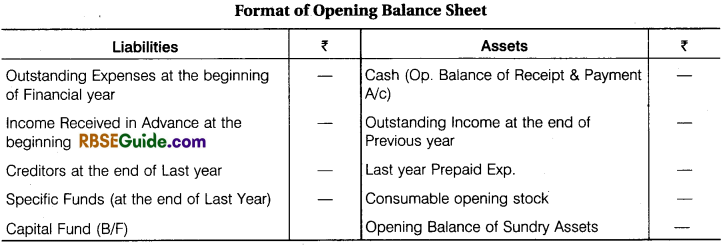
(iv) Calculation of Opening Capital:
Difference of total amount of opening assets and total of opening liabilities called opening capital fund. Opening Assets – Opening Liabilities
Calculation of Opening Assets:
- (1) Opening Cash Balance of Receipt & Payment A/c and Opening Balance of Assets in Current year.
- + (2) Advance payment in last year
- + (3) Accrued Income in last year
Calculation of Opening Liabilities:
- Advance receipts in last year and outstanding expenses in last year are treated opening liabilities.
![]()
Illustration 1.
Rajeev Sports Club received subscription during the 2017 ₹ 20,000, 20 members not paid @ ₹ 100 each. Subscription was outstanding last year 2016 ₹ 1,000. Show the amount of subscription in Income and Expenditure and Balance Sheet in year 2017.
Solution:
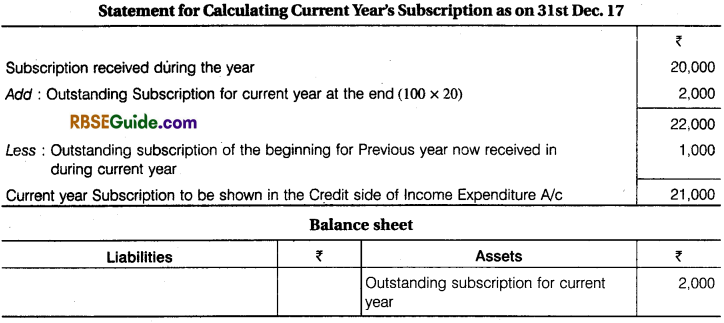
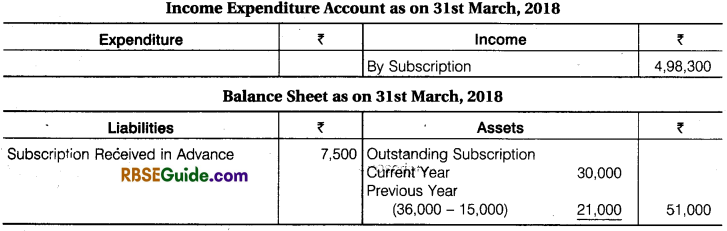
Illustration 2.
How will you deal with the subscription while preparing the Income & Expenditure Account and Balance Sheet of Hans Club for the year ending 31st March, 2018. Subscription received during the year ₹ 4,87,500, ₹ 15,000 included for previous year. Other information are as follows :

Solution:

![]()
Illustration 3.
There are 1125 members of a institution each member gives ₹ 10, yearly subscription. Advance subscription received beginning the year ₹ 3,250 and end of the year ₹ 3,500. Subscription was outstanding at the end ₹ 3,250. Subscription received during the year ₹ 10,000. Calculate the unpaid subscription at the beginning.
Solution:
Calculation amount of subscription Unpaid at the beginning of the year.

Illustration 4.
How stationery expenses will show in Income & Expenditure A/ c and Balance Sheet at 31 March 2017 by following information:

Solution:
Calculation of Stationery which will be shown in Income and Expenditure account for the year ended 31.3.2017.
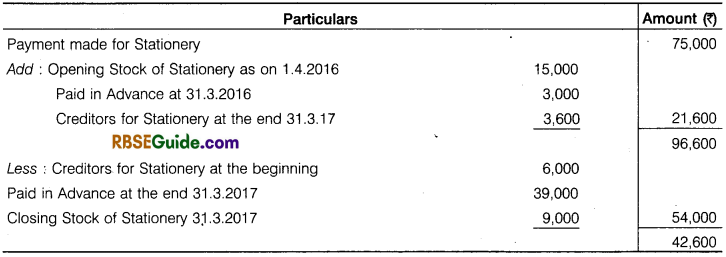
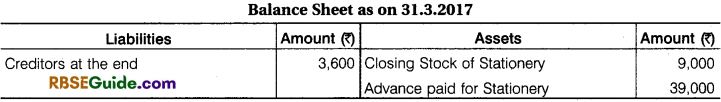
![]()
Illustratidn 5.
From the following information how the information related to Furniture will be shown in Incptne and Expenditure Account for the year ending 31st March, 2018 and the Balance Sheet On that date Opening Balance of Furniture ₹ 1,50,000 during the year 31.12.2017 ₹ 30,000 Book Value (Opening) of Furniture was sold ₹ 27,000 new Furniture was purchased on 1 Jan. 2018 ₹ 37,500 Depreciation on Furniture 10% p.a.
Solution:
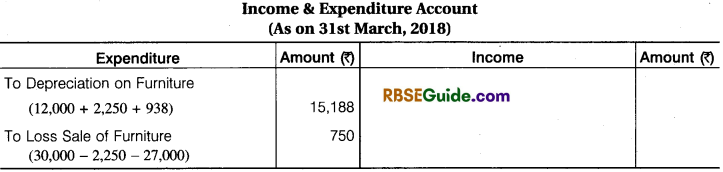
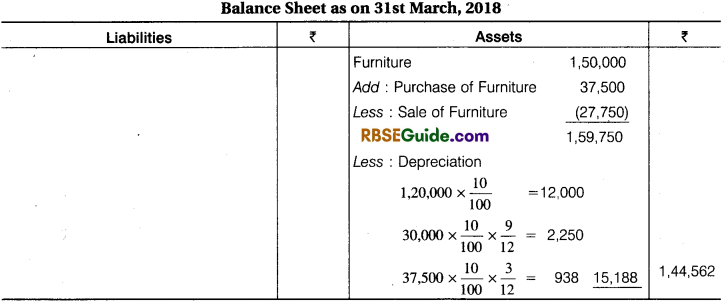
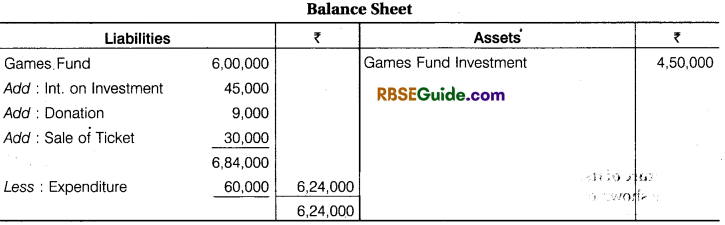
Illustration 6.
From the following how games fund information will be shown in Balance Sheet at the end.

Solution:
![]()
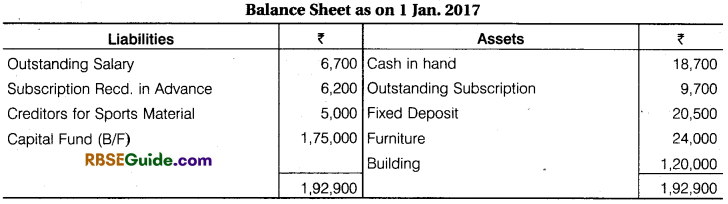
Illustration 7.
From the following information calculate opening Capital Fund as on 1 Jan. 2017 : building 1,20,000, furniture 24,000, cash in hand (1.1.2017) 18,700, fixed deposit (1.1.17) 20,500, Outstanding Subscription for 1 Jan. 2017, 9,700, Outstanding salary 6,700, Subscription Received in Advance for 1 Jan. 2017, 6,200, Creditors for Sports material as on 1 Jan. 2017, 5,000.
Solution:
Final Accounts of Not For Profit Organisation
These organisations also prepare their accounts annually on the pattern of profit earning organisations. They includes :
- Receipts and payments account
- Income and expenditure Account
- Balance sheet.
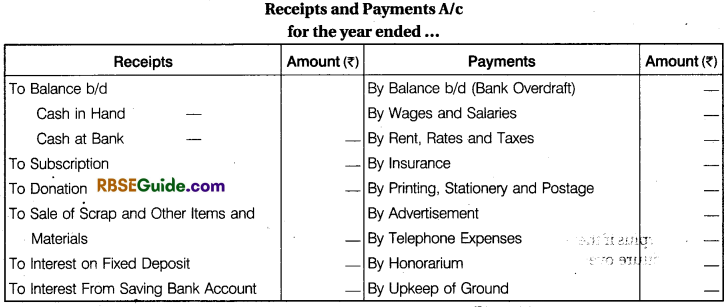
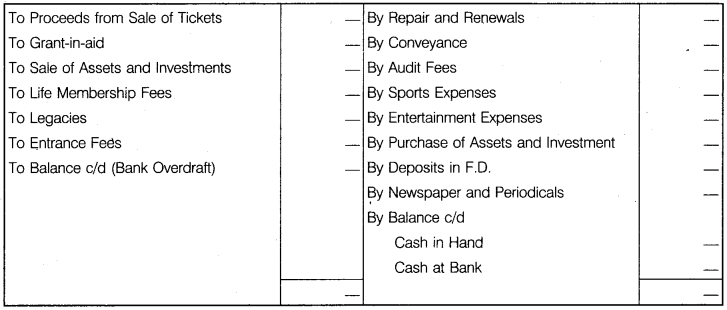
1. Receipts and Payments Account
A receipts and payments account is a summary of cash and bank transactions during an accounting year of a not for profit organisation. Receipts and payments account is prepared at the end of the year from the cash book. For instance, a club receives subscription from its members on different dates.
These are recorded in the cash book in a chronological (date wise) order while the receipts and payments account will contain total subscription received from the members. The receipts and payments account includes all receipts and payments of cash including bank despite the fact whether they relate to current year, preceding year or future period of whether they are of capital or revenue nature.
It begins with opening cash and bank balance on the debit side. All receipts are recorded on the debit side and all payments on the credit side, the balance represents closing cash and bank balance. A specimen of receipts and payments account will clarify how the transactions are recorded.
![]()
Characteristics of Receipts and Payments Account:
Nature of Account: It is a real account and hence the rule of real account i.e., “debit what comes in and credit what goes out” is followed while preparing it. Thus, receipts are recorded on its debit side and payments on the credit side.
It Starts with the Opening Balance of Cash in Hand and at Bank: Cash in hand always shows a debit balance and will therefore, be written on its debit side. Cash at bank may show a debit or favourable balance, in which case it will be written on its debit side. But if bank balance is an overdraft or unfavourable balance, it will be placed on the credit side.
Nature of Items Recorded on the Debit Side: It is a summary of the cash book, all cash receipts are shown on the debit side of this account irrespective of the fact whether they are of capital nature or revenue nature or whether they relate to previous year, current year or next year.
For example, receipt of subscription is a revenue receipt and receipt from sale of furniture is a capital receipt but both will be recorded on its debit side. Moreover, the receipt for subscription whether for the year ending 31st March, 2016,2017 or for 2018 will be written on its debit side.
Nature of Items Recorded on the Credit Side: Likewise all cash payments are shown on its credit side, irrespective of the fact whether they are of capital nature or revenue nature and whether they relate to current year, previous year or next year.
Closing Balance of this Account shows Closing Balance of Cash in Hand and at Bank: This account is balanced at the end of the year by entering the closing balance of cash in hand and at bank on the credit side. However, if the closing balance is bank overdraft it shall be shown on the debit side.
Non Cash Items are Not Recorded in this Account: This amount records only the actual receipts and payments of cash. Non-cash items such as depreciation, outstanding expenses and accrued incomes are ignored while preparing it.
Purpose : This account does not tell us whether the current incomes exceed the current expenditure or vice-versa. It merely shows the closing balance of cash in hand and at bank. In order to ascertain the net income or loss of a particular period, income and expenditure account has to be prepared with the help of receipts and payments account and after considering the various adjustments.
![]()
Steps in the Preparation of Receipts and Payments Account:
Take the opening balances of cash in hand and cash at bank and enter them on the debit side. In case there is bank overdraft at the beginning of the year enter the same on the credit side of this account.
Show the total amounts of all receipts on its debit side irrespective of their nature (whether capital or revenue) and whether they pertain to past, current and future periods.
Show the total amounts of all payments on its credit side irrespective of their nature (whether capital or revenue) and whether they pertain to past, current and future periods.
Name of the receivable income and payable expenses is to be entered in this account as they do not involve inflow or outflow of cash.
Find out the difference between the total of debit side and the total of credit side of the account and enter the same on the credit side as the closing balance of cash/bank. In case however, the total of the credit side is more than that of the total of the debit side. Show the difference on the debit as bank overdraft and close the account.
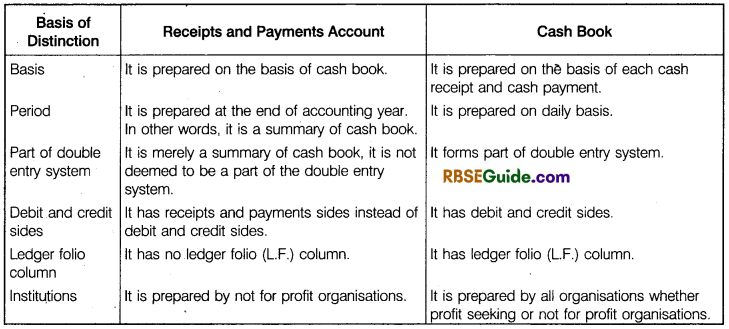
Distinction between Receipts and Payments Account and Cash Book:
Both receipts and payments accounts and cash book record cash transactions i.e., cash receipts and cash payments. Inspite of such similarity, there are some differences between the two which are enumerated below.
![]()
2. Income and Expenditure Account
Income and expenditure account is a nominal account. It is prepared to depict the result of not for profit organisation during an accounting period. The principles of preparation of profit and loss account applies for the preparation of income and expenditure account as well.
It is prepared on accrual basis of accounting based on principle of matching concept i.e., adjustments relating to outstanding expenses, prepaid expenses, accrued income, income received in advance and depreciation are made. Incomes are shown on the credit side while expenses are shown on the debit side.
There is no opening balance in income and expenditure account but the closing balance reveals surplus if there is an excess of income over expenditure and reveals deficit if there is an excess of expenditure over income. Thus, it can be said that income and expenditure account serves the same purpose for a not for profit organisation which is served by profit and loss account for a profit earning organisation.
Characteristics of Income and Expenditure Account:
Nature of Account: It is a nominal account and hence the rule of nominal account i.e., “debit all expenses or losses and credit all incomes and gains” is followed while preparing it.
Nature of Items Recorded in it: Only items of revenue nature are recorded in it. All items of capital nature are ignored while preparing it. For example, amount received from the sale of furniture will not be recorded in it but the profit earned or less suffered on the sale of furniture will be recorded in it.
Omission of Opening and Closing Balance of Cash: No opening and closing balance of cash and bank are recorded in it.
Adjustments: This account is prepared in the same manner in which a profit and loss account is prepared. As such, all adjustments relating to the current year such as depreciation, outstanding expenses, prepaid expenses, earned income etc. are taken into consideration while preparing the income and expenditure account.
It Records Income and Expenditure of Current Period : It includes all items of income and expenditure which do not pertain to the current period. In other words, all items relating to previous years and future years are excluded while preparing it.
Purpose : The closing balance of this statement reveals surplus or deficit. If the credit side exceeds the debit, it reveals surplus and on the other hand, if the debit side exceeds the credit it reveals deficit. The surplus is added to the capital fund and the deficit is deducted from it.
![]()
Steps in the Preparation of Income and Expenditure Account:
Following steps may by helpful in preparing an income and expenditure account from a given receipts and payments account:
- Persue the receipts and payments account thoroughly.
- Exclude the opening and closing balances of cash and bank as they are not an income.
- Exclude the capital receipts and capital payments as these are to be shown in the balance sheet.
- Consider only the revenue receipts to be shown on the income side of income and expenditure account.
- Some of these needs to be adjusted by excluding the amounts relating to the preceding and the succeeding periods and including the amounts relating to the current year not yet received.
- Take the revenue expenses to the expenditure side of the income and expenditure account with due adjustments as per the additional information provided relating to the amounts received in advance and these not yet received.
- Consider the following items not appearing in the receipts and payments account that need to be taken into account for determining the surplus/deficit for the current year:
- Depreciation on fixed assets
- Provision for doubtful debts if required
- Profit or loss on sale of fixed assets.

3. Preparation of Balance Sheet
Balance sheet is a statement dravtfn on a particular date to depict the financial position of an organisation. The position revealed by balance sheet is true only on a particular date as it will change with the change in the transactions. For instance, payment of an expense will reduce cash balance and will also reduce the surplus and thus, affects capital fund.
Balance sheet reveals the financial position of an entity i.e., the position of assets and liabilities on a particular date. Generally not for profit organisation do not maintain complete set of books of accounts, so trial balance is also not pfepared.
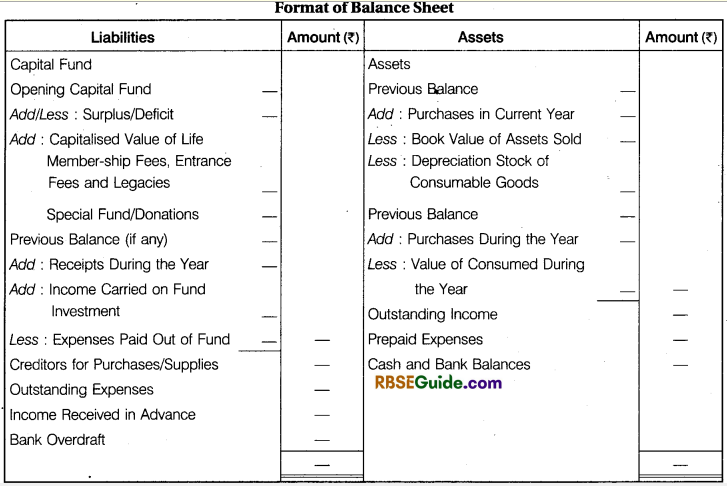
The balance sheet of not for profit organisation is also prepared in the same way as it is prepared for a business entity. The excess of assets over liabilities is called Capital Fund. Following points should be kept in mind while preparing balance sheet in the absence of trial balance :
![]()
Assets
All the fixed assets appearing in the previous balance sheet (opening balance sheet) have to be adjusted for assets purchased-sold and depreciation charged. The adjusted amount will be shown in the closing balance sheet. The adjustments are made in the following manner:
New assets purchased during the year are added to previous year’s assets.
If an asset has been sold during the year the book of such an asset must be deducted from the concerned asset.
Depreciation of assets must be deducted form the concerned assets.
Prepaid expenses and accrued income are shown on the asset side.
Investment is shown on the asset side. Any addition during the year be added and sale of investment be deducted at cost.
Cash and bank balance of receipts and payments account at the end are shown on the assets side however, bank overdraft is shown on the liabilities side of the balance sheet.
Liabilities
All loans appearing on the liabilities side are also shown in the new balance sheet. The receipts and payments account should be checked. If the loan has been paid during the year, it should be deducted and new loan raised be added to loan account to find out the net amount of loan.
Donation for specific purpose like donation for building, prize fund, tournament fund be shown on the liabilities side.
Similarly, special funds created to meet specific expenses are also shown on the liabilities side after adjustment viz. Tournament fund Less: Tournament expenses
[Note: If fund has negative balance, it is to be taken to income and expenditure account.] Outstanding expenses and unearned incomes (income received in advance) are shown on the liabilities side.
Surplus (excess of income over expenditure) is added to capital fund and vice-versa.
If capital fund is not given old balance sheet is prepared and excess of assets over liabilities represents capital fund. Surplus/Deficit depicted by income and expenditure account is added/deducted from the capital fund to find out the capital fund of the current year. It is always shown on the liabilities side.
Preparing Receipts and Payments A/c with the Help of Cash Book
![]()
Illustration 8.
From the following Cash Book, prepare Receipts and Payments Account for that period.
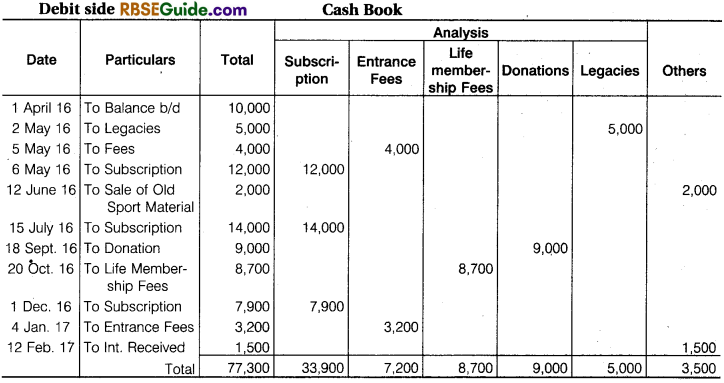
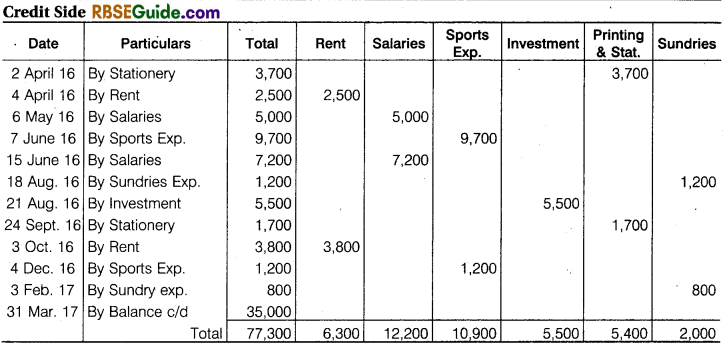
Solution:
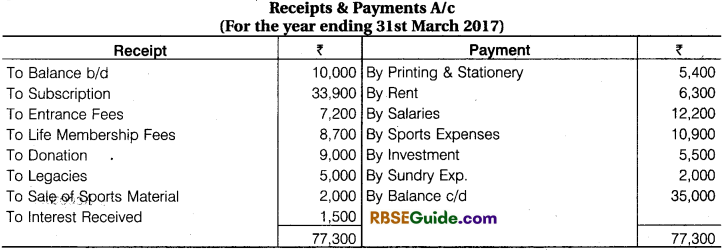
From Receipts and Payments A/c Preparing income and Expenditure A/c
Illustration 9.
From the following Receipts and Payments Account of Mayoor Club, Udaipur, prepare Income and Expenditure Account for the year ended 31st March, 2018.
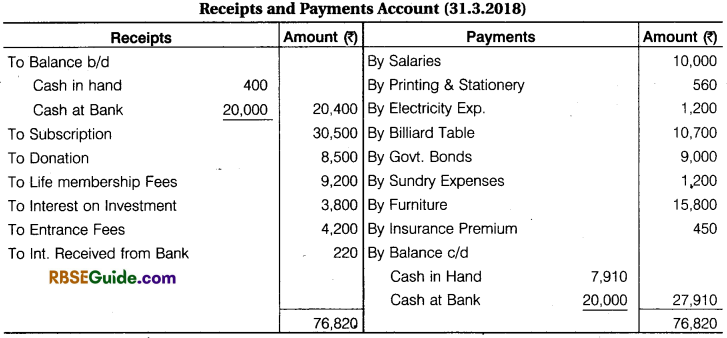
Additional Information:
- Subscription in arrear for the year ended 31st March, 2018 ₹ 300 and Subscription received in advance for the year ended 31st March, 2018 ₹ 800.
- Donations are Reserved for endowment funds.
- Outstanding Sundry Expenses ₹ 150
- In Insurance Premium ₹ 50 is included which related to next year.
- 60% Entrance fees are to be capitalised.
Solution:
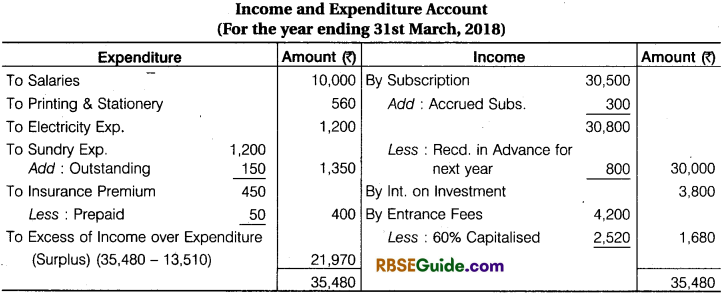
![]()
Working Note:
- Billiard Table, Govt. Bonds. Furniture are to Fixed assets so it will be not shown in Income & Expenditure Account.
- Life Membership are to be capitalised income.
Preparing Income & Expenditure Account and Balance Sheet with the help of Receipts & Payments A/c
Illustration 10.
Receipts & Payments Account of a Club prepare Income & Expenditure Account and Balance Sheet for the year ended 31st March, 2018.
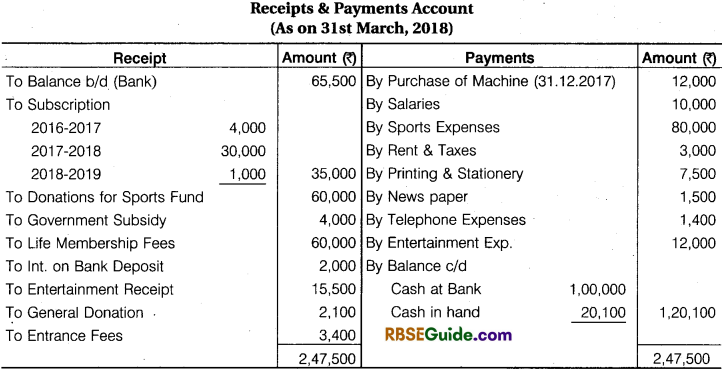
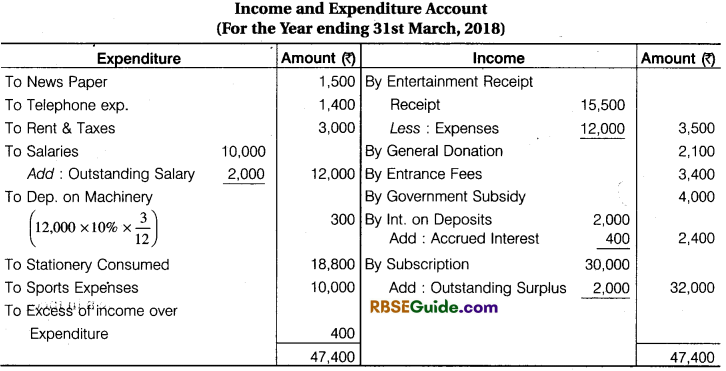
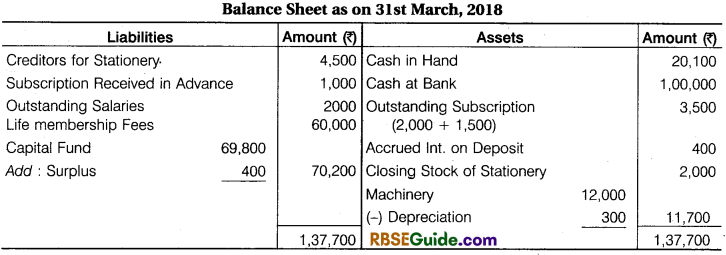
Additional Informations:
- Depreciation on Machinery @ 10% P. A.
- Bank Deposit interest Receivable 400
- Opening Balance of Sports Fund 10,000
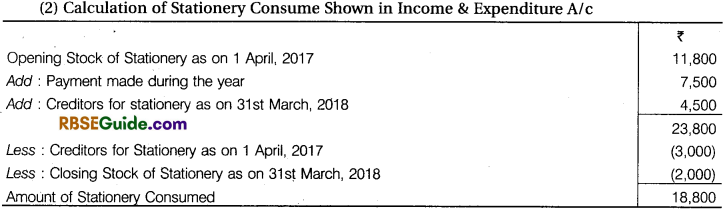
- Opening Stock of Stationery 11,800 & Closing 2000
- Opening Creditors for Stationery ₹ 3000 and Closing creditors for ₹ 4,500
- Outstanding subscription for the year 2016-17 ₹ 5,500
- Salary Paid for 10 months
- There are 160 members of a club, who contribute ₹ 200 per year for subscription
- Opening Capital Fund ₹ 69,800.
Solution:

![]()
Illustration 11.
Prepare Income & Expenditure Account from Opening Balance Sheet and Receipts & Payments Account are given below:
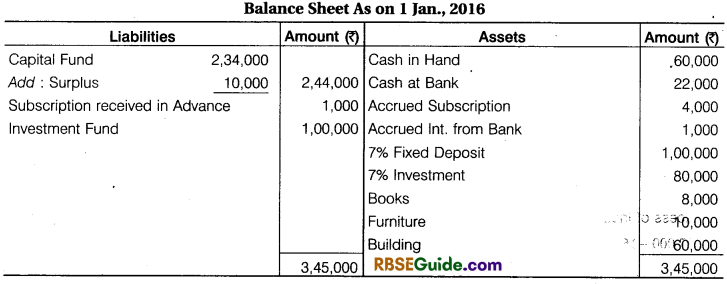
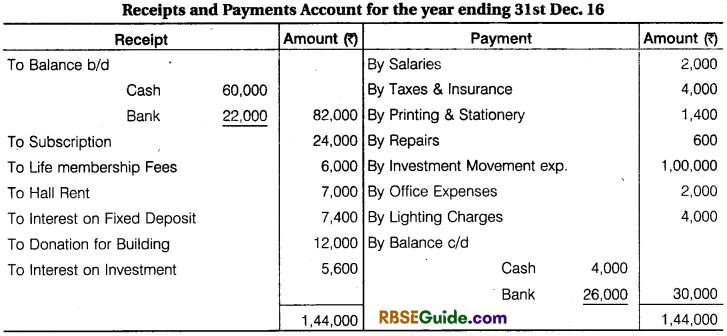
Additional Information:
- Depreciation is to be Provided @ 10% P.A. on Fixed assets.
- The Number of Members in the club is 500 annual subscription payable by each member is ₹ 40.
- Subscription received during the year go for the next year amounted is ₹ 2,000.
- The rent of the Club Hall is ₹ 1000 per day and the hall was let out for 10 days in current year.
- Taxes and Insurance ₹ 500 for related to next year.
- Outstanding Salary at the end of financial year ₹ 1,000.
Solution:
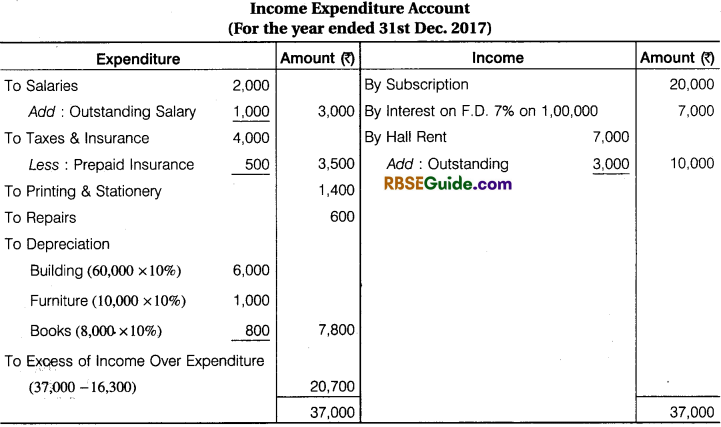
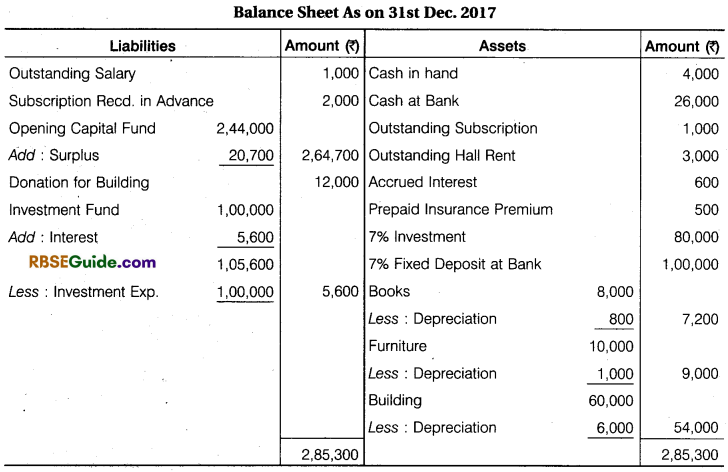


![]()
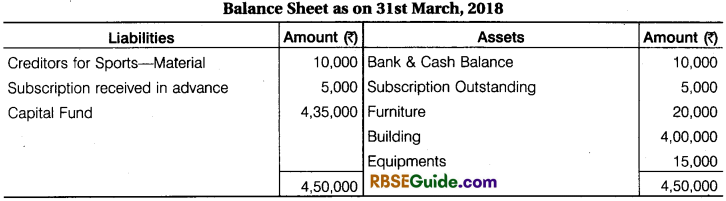
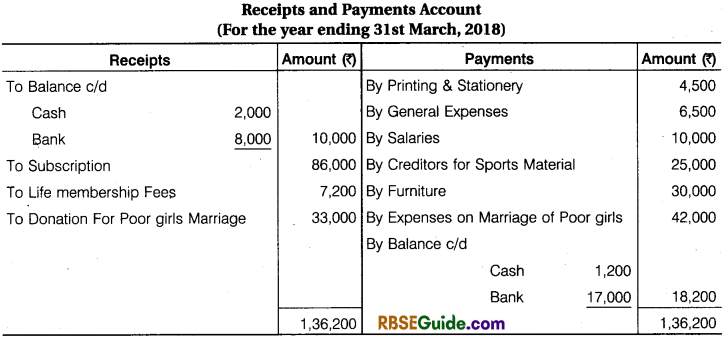
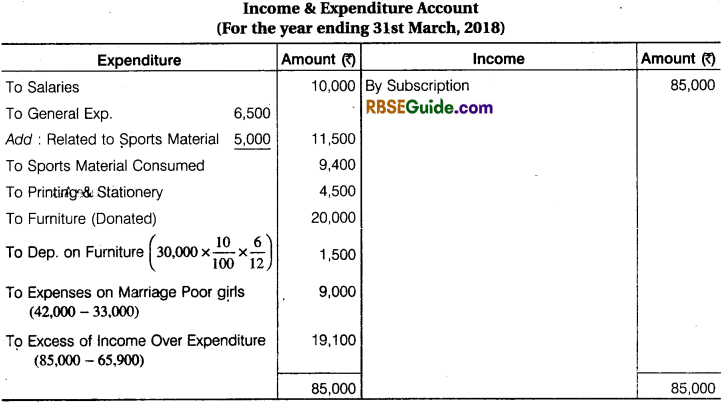
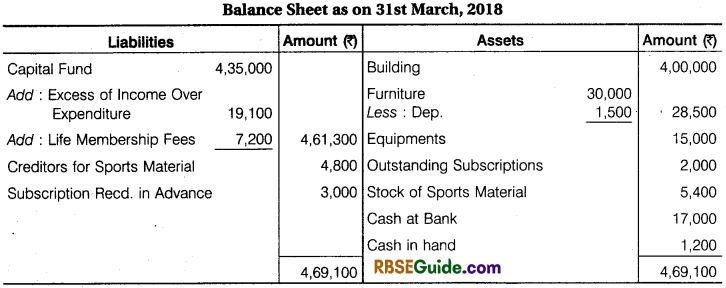
Illustration 12.
From the following information of Jai Club, prepare Income & ExpettdifufcerAccount and Balance Sheet for the year ended 31st March, 2018:
Additional Information:
- Outstanding Subscription at the end ₹ 2,000 and advance Subscription received for next year at the end ₹ 3,000.
- On April, 2017 the Old Furniture was given to Government Hospital and new Furniture was purchased on 1 Oct., 2018. Depreciation @ 10 p.a. is to be provided on furniture.
- A payment of ₹ 5,000 for sports material was to be Debited to General Expenses.
- On 31st March, 2018 value of sports materials ₹ 5,400.
- On 31st March, 2018 the Creditors for sports material were ₹ 4,800.
Solution:


![]()
Illustration 13.
A Receipts & Payments Account of Red-Cross Help Society for the year ended 31st March, 2017 are given below, with the help of these prepare Income and Expenditure Account for the year ending 31st March, 2017 and a Balance Sheet on that date.
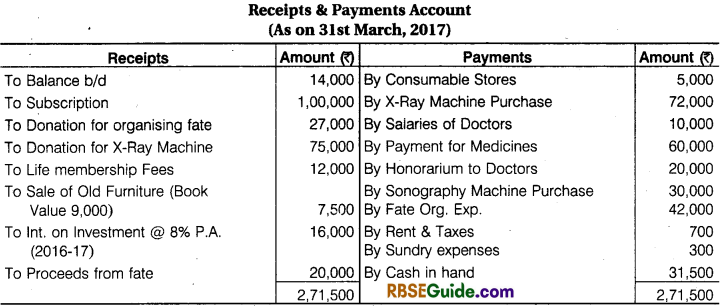

Solution:
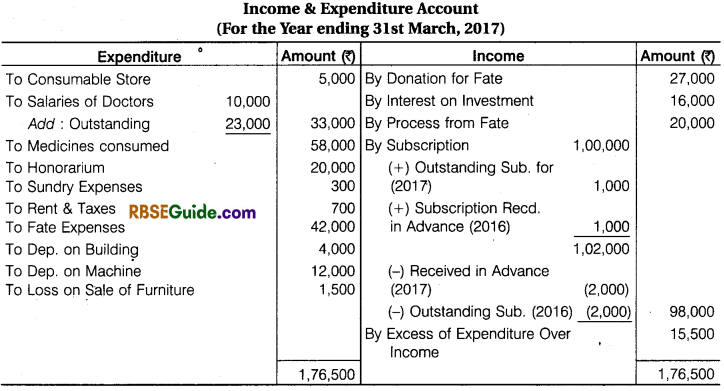
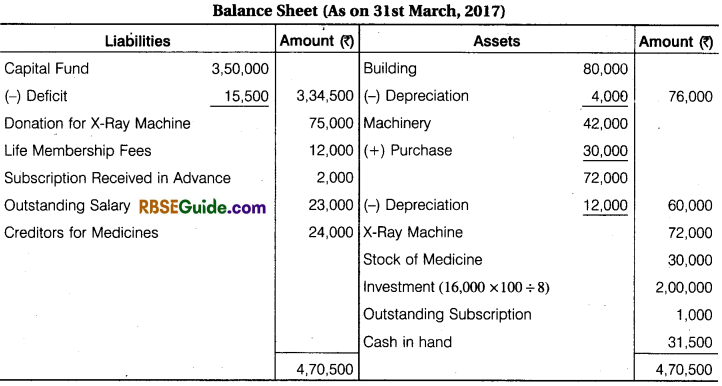
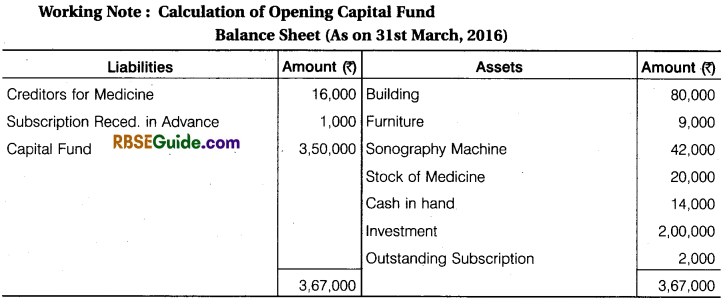

![]()
Illustration 14.
Prepare Income & Expenditure Account for the year ended 31st March, 2018 and Balance Sheet on that date of Young men Sports Club with the help of Receipts & Payments Account for the year ended 31st March, 2018.
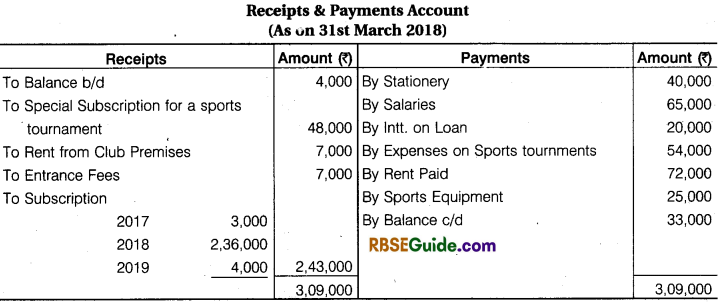
Additional Information:
- The club took a loan of ₹ 2,00,000 during the year @ 10% p.a. interest
- Subscription unpaid at the end ₹ 12,000
- On 1st April, 2017 the Club owned some sports equipments the value of ₹ 2,00,000 and on 31st March, 2018 all the sports equipment was valued at 1,130,000
- Stationery Expenses ₹ 4,000 for Previous year and ₹ 5,000 unpaid for current year.
- Entrance Fees to be capitalised.
Solution:
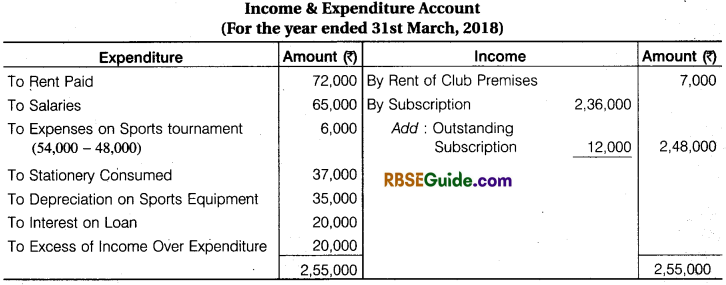
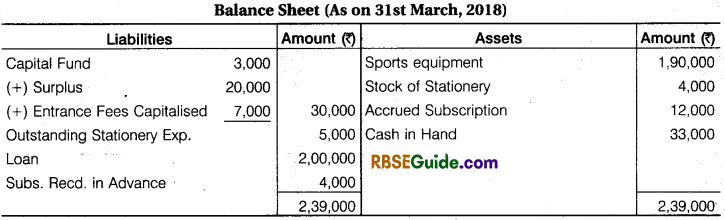
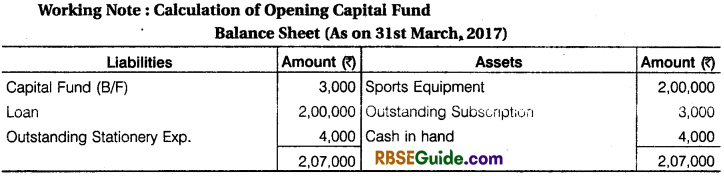
![]()
Illustration 15.
Receipts and Payments Accounts for the year ended 31st March, 2018 of Sachin Cricket Club prepare Income Expenditure Account and Balance Sheet on that date.
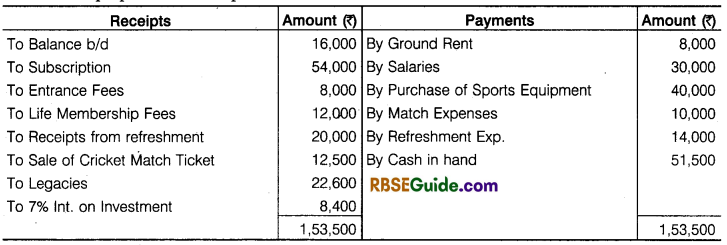
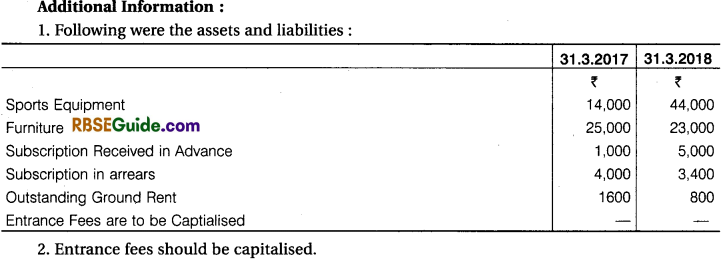
Solution:
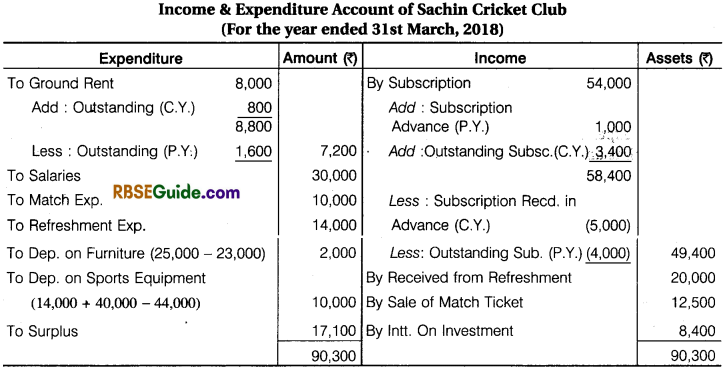
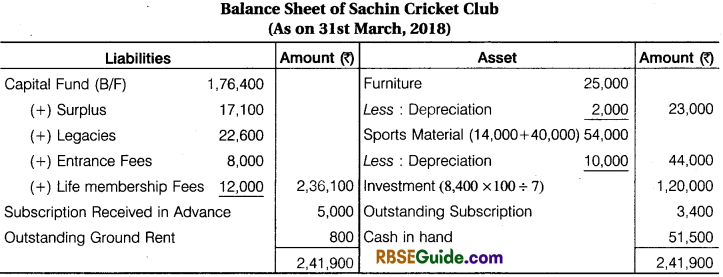
Preparation of Opening Balance Sheet and Closing Balance Sheet from a given Receipts and Payments Account and Income and Expenditure Account
![]()
Follow the following steps:
(i) Opening Balance Sheet
- Consider opening cash and bank balance from receipts and payments account and write them in the assets side of the balance sheet.
- Consider other adjustments from income and expenditure account either income or expenses and put them in assets side or liabilities side of the balance sheet.
- The difference between the assets side and liabilities side will reflect the capital fund as balancing figure.
(ii) Closing Balance Sheet
- Take all the assets from opening balance sheet after due effect of depreciation (from income and expenditure account) additions (from receipts and payments account) and sold (from receipts and payments account), the net figure will be written in the asset side of the balance sheet.
- Take the capital fund from opening balance sheet and add surplus or deduct deficit-and all other liabilities (from income and expenditure account) go to liabilities side of the balance sheet.
- Closing cash and bank balances (from receipts and payments account) will be written on assets side.
- Compare each item from income and expenditure with receipts and payments account and write suitably to close balance sheet.
- Preparation of Receipts and Payments Account from Income and Expenditure Account
- Sometimes, income and expenditure is given and students are required to prepare receipts and payments account and in such a situation the following procedure may be followed :
- All expenditure whether capital or revenue irrespective of the periods are shown on the payment side.
- All receipts whether capital or revenue irrespective of the periods are shown on receipts side.
- Pick up opening balance and closing balance to the account.
- Eliminate all adjustments made while preparing income and expenditure account.
- Purchase of assets may be calculated and shown on the payments side. For the compare the values of the assets at the beginning and closing of the period.
Income Side:

Expenditure Items:

Amount of Stationery Consumed:

Illustration 16.
The Receipts and Payments Account and Income & Expenditure Account of a Club for the year ending 31 st March, 2017.
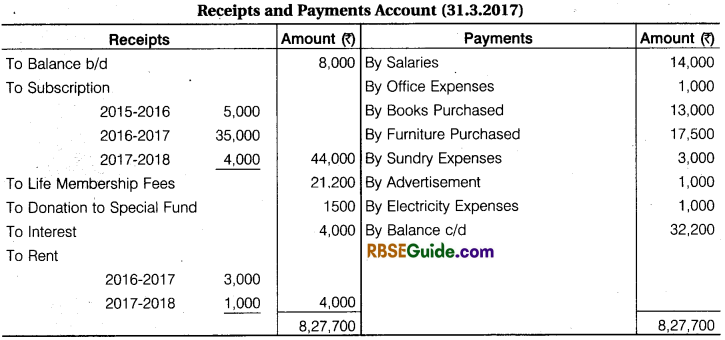
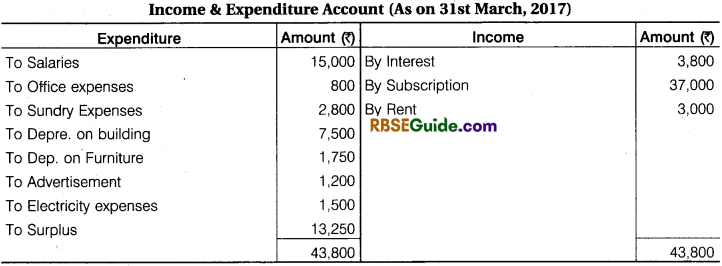
Additional Information:
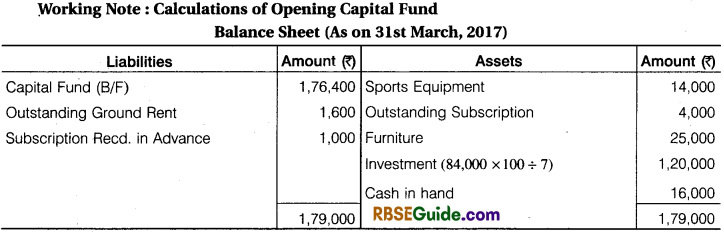
It is informed that assets as on 01-04-2016 included the following and there was no liabilities on that date. Building ₹ 1,60,000, Books ₹ 1,40,000, Furniture ₹ 10,000, Investment ₹ 45,000. You are required to prepare balance sheet of a club as on 1 April, 2016 and 31st March, 2017.
Solution:
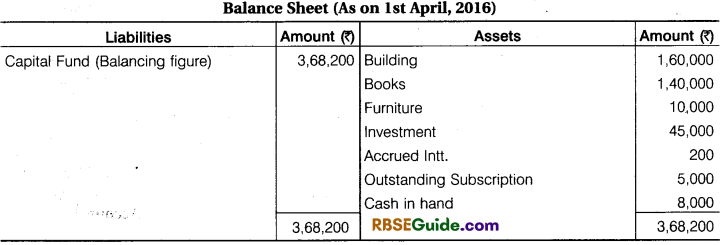
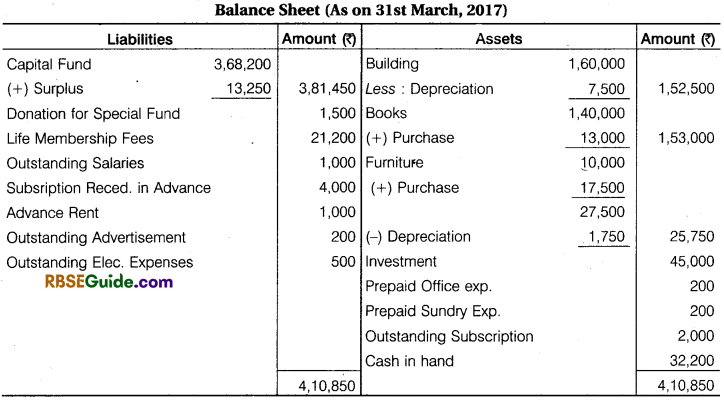
Working Note:
- Opening cash balance is taken from Receipts & Payments A/c and Opening Balance of Assets are taken while preparation of opening balance sheet.
- ₹ 5,000 of subscription is outstanding in last year 2015-16. So, it is shown in asset side.
- Preparation of closing balance sheet, Particular Assets added by new purchasing assets and deducted by depreciation.
- ₹ 35,000 outstanding subscription is shown in Receipts & Payments A/c in 2016-17 while ₹ 37,000 are shown in Income & Expenditure A/c difference amount ₹ 2,000 of subscription is outstanding of current year. So, it will shown in assets side and ₹ 4,000 received subscription in advance in 2017-18. So, it will shown in liabilities side.
- Adjustment made for difference amount of advertisement expenses and sundry expenses.
![]()
Illustration 17.
From Income and Expenditure A/c for the year ending 31st March, 2017 and from additional informations, prepare Receipts and Payments A/c and Balance Sheet for the year ending 31st March, 2017.
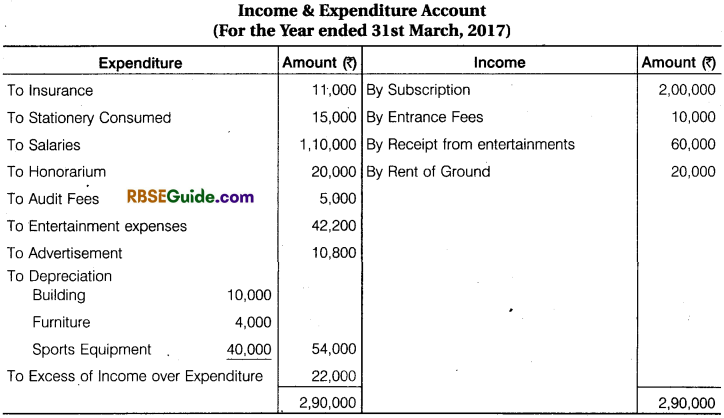
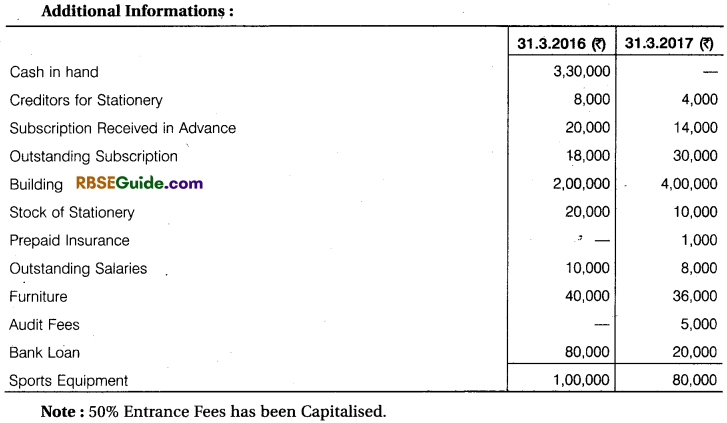
Solution:
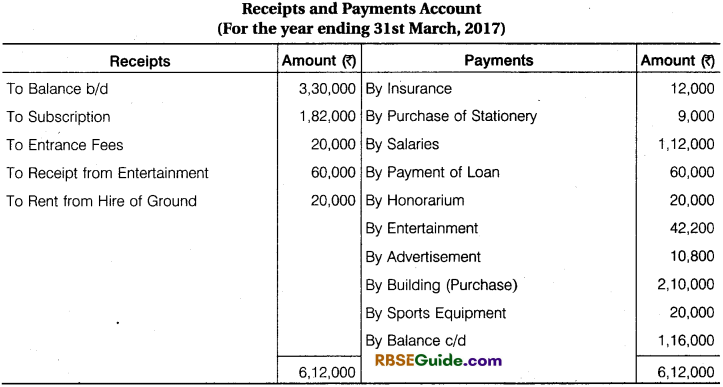
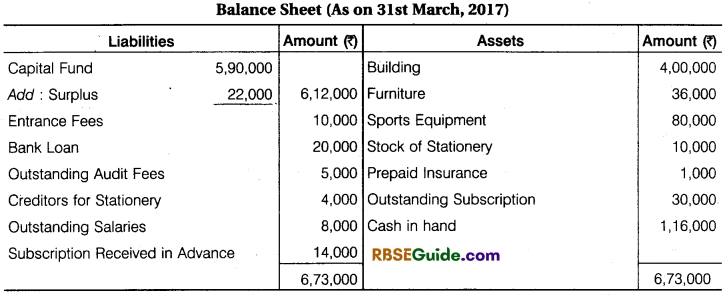
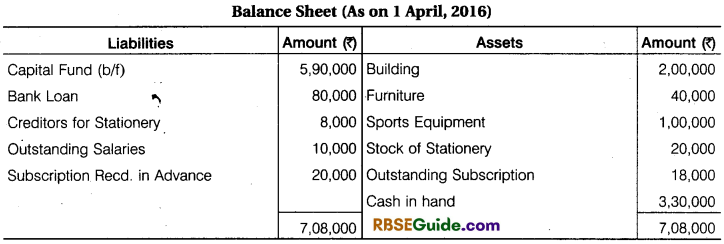



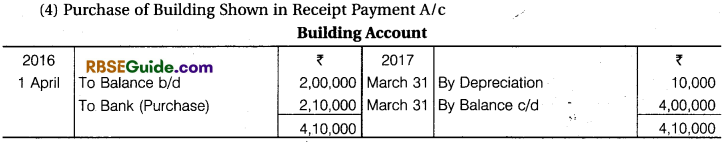
![]()
Accounting for Non-Trading Organisations and Professional Persons Notes Important Terms
→ Not For Profit or Non-Trading Organisation : Not for profit organisations are those organisation whose objective is not to earn profit but to render services to its members and to the society.
→ Receipts and Payments Account: Receipts and payments account is a summary of cash and bank transactions prepared at the end of the accounting period. It records all receipts and payments whether of revenue or capital nature and irrespective of the period to which they relate.
→ Income and Expenditure Account: Income and expenditure account is the summary of income and expenditure of the year. It is like profit and loss account. It shows surplus or deficit. It is prepared on accrual basis of accounting.
→ Surplus : Excess of income over expenditure of a not for profit organisation is termed as surplus.
→ Deficit: Excess of expenditure over income of a not for profit organisation is termed as deficit
→ Subscription : Amount received on an annual basis at the time of renewal of the membership by a non-profit organisation is called subscription.
→ Legacy : Legacy is the amount received by an organisation from a deceased person.
→ Donation : It is the amount donated to the organisation in cash or kind.
→ General Donation : When the donor does not specify any condition for using the amount of donation, it is known as General Donation.
→ Specific donation : It is the donation is for a specific purpose say for the construction of a room or pavilion, it is known as Specific Donation.
→ Life Membership Fees : It is the amount received from a member in lump-sum for which he is given the membership of the organisation for the whole life.
