Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Business Studies Notes Chapter 2 Management: Processor Functions Managerial Role and Levels
A process is a systematic and organised method of doings things. A process has a beginning and a termination point. It consists of distinct, but sequential steps.
Management is the process which contains certain steps or functions. All managers
perform these functions in order to get things done through others for the attainment of organisational goals. ‘
The management process begins with planning, organising, directing and controlling. This is collectively known as Management Functions or Management Model.
Functions of Process of Management :
- Management is a process of continuous and dynamic functions.
- All the functions of management are performed by managers.
- The process of management basically depends on natural relationship between people.
- Management makes attempt to achieve goals through its effect. Thus it is effective and goal-oriented.
- The process of achieving goals is applicable to all the organisations whether small or large. It is a universal process.
![]()
Management Process – Steps or Management Functions
- In the process of management, various functions are involved, but there is difference in the opinion of scholars, based on their experience, outlook and vocabulary used.
Management process/functions by different scholars :
- Ralf Davis – Planning, organising, controlling.
- Koontz O’ Donel – Planning, organising, staffing, directing and control.
- Breck – Planning, organising, motivating, coordination and controlling.
- Henry Fayol – Panning, organising, commanding, coordination and controlling.
- Lindal Urwick – Planning, organising, commanding, coordinating, communicating, forecasting, investigation.
- Luther Gullick – Planning, organising, staffing, directing, coordination, reporting and budgeting.
There is a long and comprehensive list of management functions. We divide these functions into two parts.
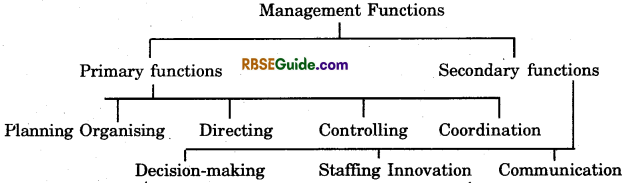
Planning is deciding in advance what is to be done in future.
Organising is related to identifying the work activities and division of work or developing a structure of relationship between human and physical factors in an organisation.
Directing means moving to action and supplying stimulating power to a group of persons. How to make optimum utilisation of resources for the attainment of organisational goals.
Controlling ensures the efficient performance of managerial functions. Controlling is the final function that every manager performs.
Coordination is the art of harmonising and unifying individual and group efforts for better actions and achievement of group goals.
Decision-making is the process of selecting the best alternative out of the available alternatives identified for doing a work.
Staffing helps in determining the right quality and quantity of human resources in an organisation.
Innovation consists of developing new and better ways of doing things. Innovation is an important function of management.
Communication is the exchange of views, ideas, facts, information and feelings between the management and employees.
Representation means representing the organisation. It is also a function of a manager. To maintain good relations with the stakeholders, to be in contact with various interest groups.
All these above-mentioned functions are performed by managers working in an organisation.
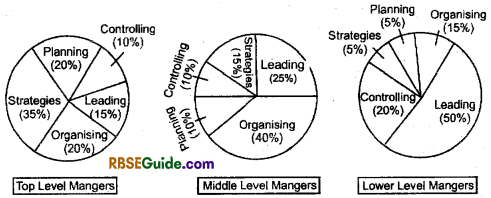
H. Hintz Berg stated, “the time spent on each management function varies with every management level.
Generally, no management function is more important than others. All functions are equally important and managers have to perform all of them.
The figures given below depict the. time spent on different managerial functions by managers at various levels.
Managerial Roles :
Role means behaviour or set of behaviours and functions. Set of functions of a manager which is expected by organisation and society is known as Managerial Role.
There are two basic approaches of studying what managers do. These are :
Functional Approach : This states that every manager must perform certain functions like planning, organising, staffing, directing and controlling.
Managerial Roles Approach : It means to study what managers are actually doing. It was developed by Henry Hintzberg and his colleagues.
According to Prof. Hintzberg, every manager plays ten related roles. These are classified into three categories :

Managerial Roles
Interpersonal Roles : Roles in which managers maintain interpersonal relations with their subordinates, peers and external persons and organisations. It includes :
- The figurehead role
- The leader role
- The liasion role.
Informational Roles: All managers maintain and develop information network by creating a network of interpersonal relations with others.
It includes :
- The monitor’s role
- Dissemination role
- Spokesperson role
Decisional Roles : It is the strategy-making role of managers. Decisional roles emerge as a result of performance of interpersonal and informational roles.
It includes :
- Entrepreneur role
- The disturbance handler role
- The resource allocation role
- The negotiation role.
Managerial Levels : Levels of management refers to the categories or layers of managerial positions in an organisation. Levels of management forms the hierarchy of management or chain of command in the organisation.
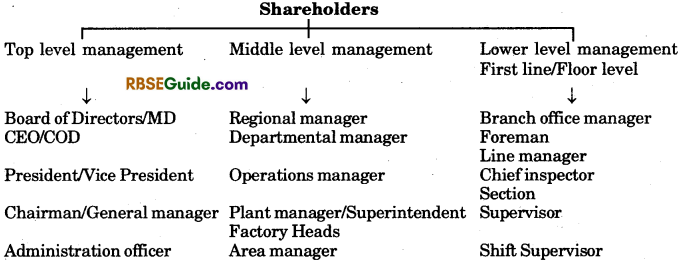
1. Top Level Management :
Top or executive management level refers to that group of executives which constitutes the highest level of management. The executives at this level represent the owners and are regarded as the centre of authority.
Main functions are :
- To determine business objectives, to prepare strategic plans and policies for the enterprise.
- To issue necessary instructions for the presentation of departmental budgets, schedules and policies.
- To bring long-term stability in the enterprise.
- To coordinate the activities of all the departments to achieve organisational goals.
- Maintain relations with stakeholders.
- To initiate organisational set up/framework.
- To control the activities of all departments.
- To act as a trustee and to provide protection to organisation assets.
2. Middle Level Management:
As suggested by name, it is in the middle managerial hierarchy. In acts as a mid way in between the top level and lower level, and managers at this level follow the order of top level and direct and control the activities of lower level.
Main functions are :
- To interpret and explain policies and plans.
- To prepare and issue instructions regarding implementation of plans and policies.
- To train, develop and motivate first line managers.
- To regularly monitor the performance of departmental activities.
- To organise and give training to supervisors.
- To participate in first line decision-making.
- To handle the complaints of lower level management.
3. Lower Level/First Line/Operational/Supervisory Level Management :
It refers to those executives who are basically concerned with the personal observation and direction of operative employees. They include managers just above the workers or the operative employees.
Main functions are :
- To make day to day operative plans within the goals set by middle managers.
- To assign jobs, to advise, assist employees in understanding plans, procedures, methods and system.
- To oversee the performance of workers.
- To impart training to the employees.
- To guide workers and to solve their problems.
- To evaluate the performance of workers.
![]()
Important Definitions
- Management Process: It consists of various steps, functions or elejhents, which are not independent but are rather inter-dependent. It is an ongoing activity which starts, with planning and ends at coordination!. Apart from thife, many other steps are there, like motivation, staffing, etc.
- Decision-making: It is the process of selecting the best alternative out of the available alternatives identified for the attainment of organisational goals.
- Innovation : Innovation consists of developing new and better ways of doing things.
- Communication : It is the exchange of views, ideas, facts, information and feelings between the management and employees.
- Representation : For the betterment of organisation, management builds cordial relationship with the stakeholders or various interest groups. This reflects the image of the organisation and how it is represented in the market. It is the manager who represents the organisation while dealing with a number of outside groups.
- Managerial Role : Managerial role means the expected roles or behaviour that a manager should show or follow for the attainment of organisational goals.
- Interpersonal Role : It means to maintain cordial relationship by the managers with their subordinates, peers and external persons and organisations.
- Informational Role: To maintain and develop information networks by creating a network of interpersonal relations with others.
- Decisional Role : It is the strategy-making role of managers. It emerges as a result of performance of interpersonal and informational roles.
- Managerial Level: Managerial levels refer to the categories or layers of managerial positions in an organisation. It forms the hierarchy of the organisation.
- Top Level Management: It represents the highest level of management. It represents the owners who are regarded as the centre of authority.
- Middle Level Management: It is in the middle of managerial hierarchy. It includes all the layers of managerial position between first line management and top level management.
