RBSE Class 12 History Model Paper 1 English Medium are part of RBSE Class 12 History Board Model Papers. Here we have given RBSE Class 12 History Sample Paper 1 English Medium.
| Board | RBSE |
| Textbook | SIERT, Rajasthan |
| Class | Class 12 |
| Subject | History |
| Paper Set | Model Paper 1 |
| Category | RBSE Model Papers |
RBSE Class 12 History Sample Paper 1 English Medium
Time: 3.15 Hours
Marks: 80
General Instructions to the Examinees
- Candidates must write first his/her Roll No. on the question paper compulsorily.
- All the questions are compulsory.
- Write the answer to each question in the given answer book only.
- For questions having more than one part, the answers to those parts are to be written together in continuity.
-
Section Question Numbers Marks per Question Word Limit of the Answer A 1-10 1 10 Words B 11-18 2 20 Words C 19-27 4 60 Words D 28-30 6 200 Words - Mark the answer of Q 30 on the outline map of India. It carries 6 marks.
- There are internal choices in Question Nos. 28 and 29.
Section – A
Question 1.
Who is called the prince of the travelers? [1]
Question 2.
Who was the founder of the Shunga dynasty? [1]
Question 3.
Name the author of ‘Raj Tarangini’. [1]
![]()
Question 4.
Name the Saka ruler who restored the ‘Sudarshan Lake’. [1]
Question 5.
Why is Nagarjuna called ‘Einstein of India’? 1
Question 6.
Describe one of the main features of ‘Gandhar sculpture’. [1]
Question 7.
Which Me war Emperor was coronated on holi festival? [1]
Question 8.
In which year was the First Battle of Tarain fought? [1]
Question 9.
Why is Rao Chandrasena called Pratap’s pioneer? [1]
![]()
Question 10.
Vijay stambh was constructed by Rana Kumbha in memory of which victory? [1]
Section – B
Question 11.
Explain the difference between the Sabha and the Samiti. [2]
Question 12.
Which historical and literary sources are currently valid as judicial evidence? [2]
Question 13.
Describe any two characteristics of Nalanda University. [2]
Question 14.
Describe the two characteristics of Greek coins that are currently visible on them? [2]
Question 15.
If you had been present in the Battle of Khanwa as Rana Sanga, then which errors would you try to avoid? [2]
Question 16.
What do you think of‘Blue Water Policy’? [2]
![]()
Question 17.
Write any two reasons for the rise of nationalism. [2]
Question 18.
Who was the founder of the Samp Sabha? What was its main purpose? [2]
Section – C
Question 19.
What is the importance of records in history writing? [4]
Question 20.
At present, clarify the relevance of Ashoka’s Dhanuna. [4]
Question 21.
Why is Kanishka called the ‘Second Ashoka’? [4]
Question 22.
Write any four reasons of attacking Chittor by Alauddin Khilji. [4]
Question 23.
Write the results of the Revolution of 1857 AD. [4]
Question 24.
What is the use of ‘Dastak’? How was it misused? [4]
Question 25.
What are the teachings of Swami Dayanand Saraswati that can give the new direction to the present generation? Explain. [4]
![]()
Question 26.
In the freedom struggle of Rajasthan in 1857 AD, if the revolutionaries of the princely states had supported, the results would be different. Explain. [4]
Question 27.
Mention how the Matsya Sangh merged with Greater Rajasthan? Explain. [4]
Section – D
Question 28.
Describe the progress made in the field of art, literature and science in Gupta period. [6]
OR
Describe the development of art and literature in Chola period.
Question 29.
Explain the importance of the Civil Disobedience movement in the Independence movement of India. [6]
OR
Describe the Non-Cooperation Movement in detail.
Question 30.
Mark the following historical places in the outline map of India. [6]
1. Goa
2. Vijaynagar
3. Kalinga
4. Delhi
5. Ahmedabad
6. Patna
![]()
Answers
Answer 1:
Hieun Tsang is the prince of travellers.
Answer 2:
Pushyamitra Shunga was founder of the Shunga dynasty.
Answer 3:
Kalhana is the author of ‘Raj Tarangini’.
Answer 4:
Rudradaman restored the ‘Sudarshan Lake’.
Answer 5:
Nagarjuna is called Einstein of India because he propounded the ‘theory of relativity’. –
Answer 6:
Primacy of Greek adornment and ornamentation.
Answer 7:
Maharana Pratap was coronated on holi festival.
![]()
Answer 8:
The First Battle of Tarain was fought in 1191 A.D.
Answer 9:
Rao Chandrasena started to struggle against the Mughals on the same line on which Pratap fought so he is called the pioneer of Pratap.
Answer 10:
Vijay stambh was constructed by Rana Kumbha in memory of victory over the Sultan of Malwa Mahmud Khilji.
Answer 11:
The Samiti was a general public assembly meeting in which important political and social topics were discussed. The king also participated in its meeting whereas the Sabha was smaller hs compared to the Samiti in which well-known persons used to participate. This helped the king in consultation and judicial work.
Answer 12:
At present, the genealogy written by the priests has been certified as documents valid in these judicial evidence. These include the papers, etc, regarding family relationships.
Answer 13:
- Students from India and abroad used to come for getting education at Nalanda University,
- Education was provided here in the field of religious science.
![]()
Answer 14:
- The name of the king on Greek coins along with title and date,
- Greek coins were superior in art in comparison of others.
Answer 15:
- Not giving opportunity to Babar for war preparations.
- Not using conventional weapons like arrows, spears and swords in the war.
Answer 16:
D. Almeida was the first emperor of Portuguese official territories in India. He increased his navy power, which is called ‘Blue Water Policy’.
Answer 17:
- Development of transportation and communication system.
- Exploitative economic policies of the British.
Answer 18:
Govind Guru was the founder of the Samp Sabha. Its main purpose was to work for the social upliftment of the Bhils and organize them socially.
Answer 19:
Records have a significant place in history writing. Records are engraved articles on hard surfaces such as stone or metal utensils. Due to being ancient and contemporary, they are more important historical proofs. Information about the particular times and accomplishments of the regime comes from these records. The records also contain economic, social, religious and political information of the past time.
![]()
Answer 20:
The Dhamma of Ashoka was based on toleration, non-violence and virtue. At present, the threat of war all over the world, terrorism, violence, corruption excessive profiteering, black marketing, dominant casteism, decline in ethics, etc. are dominating the society. Solutions to all these problems is possible only by following the Dhamma. It emphasizes on the superior and sacred morality and welfare, which is needed today.
Answer 21:
Kanishka was the most glorious ruler of the Kushan dynasty. Kushan power had reached its peak during Kanishka’s time. Kanishka got victories like the Ashoka, he was also a Patron of Buddhism. Influenced by Buddhism he built stupas and viharas. He also sent Buddhist monks in central Asia, China, Tibet, and Japan. Kanishka organized fourth Buddhist convention in Kundalvan at Kashmir; For all these reasons, Kanishka is called the Second Ashoka.
Answer 22:
Reasons for Allauddin Khilji’s attack on Chittor
- Alauddin Khilji’s Imperialistic Ambitions: Alauddin Khilji was an ambitious ruler. He wanted to be a great winner like Alexander. Attack on Chittor was a part of this policy.
- Rising Power of Mewar: Alauddin Khilji wanted to reinforce the growing power of Mewar.
- Geographical and Strategic Importance of Chittor: From Delhi to Malwa, the main route to Gujarat and south India passed near Chittor and that is why Alauddin Khilji wanted to win Chittoor.
- Desire to get Padmani: Some historians believe that Alauddin Khilji wanted to get Padmini, wife of Ratan Singh, ruler of Mewar. For this, he attacked Mewar.
Answer 23:
Result of the Revolution of 1857 AD:
- End of Company Regime: As a result of the Revolution of 1857 AD, the rule of India came out from the hands of the East India Company from 1 November 1858 into the British Crown.
- Army reconstitution: The British army was reconstituted. Major posts of army and artillery were reserved for Europeans only.
- Policy Changes Towards Indian Kings: The rights of local kings were guaranteed to protect their honour and dignity and the Indian rulers were allowed to adopt sons.
- Promotion to the Policy of Divide and Rule: Due to communal harmony in the Revolution of 1857, the British started to rule by dividing the different religions.
![]()
Answer 24:
There was a special type of permit letter called Dastak by which the East India company was exempted from the tax.
In 1717 AD, the Mughal Emperor Farrukhshiyar exempted the company from customs duty in Bengal by giving a special permit letter called Dastak. The British started misusing commercial facilities.Company officers used to sell their Dastak to Indian businessmen. This caused economic damage to Nawab of Bengal.
Answer 25:
These were:
- Opposing caste system and untouchability.
- Efforts to improve the situation of women, attempts to eliminate the evils of child marriage, dowry practice and polygamy, etc.
- To promote education among women and to emphasize equality of male and female.
- Resisting rituals and superstitious beliefs and accepting God as formless, omnipotent and omnipresent.
- Efforts to reform religion and society by eliminating superstitions and promoting educational institutions.
- Trying to establish Hindi as a national language.
Answer 26:
In 1857 AD in Rajasthan, if the revolutionaries of the princely states had supported to the freedom struggle, the result would definitely be different. The rulers of the princely states of Rajasthan did not give any help to the revolution. This was a main reason for its failure. Not only this but most of them provided complete support to the British. This shadowy policy of rulers made important contribution towards restoring British power.
If they had provided support to the revolutionaries instead of the British rule, the freedom struggle of 1857 AD would be successful and the country would be free from the slavery of the British earlier.
Answer 27:
At the time of the formation of Matsya Sangh the rulers of Alwar, Bharatpur, Dholpur, and Karauli, who were involved in Matsya Sangh made this clear that in the future this association could be merged in Rajasthan or Uttar Pradesh. Alwar and Karauli were in favour merging in Rajasthan, but Bharatpur and Dholpur were in favour of merging in Uttar Pradesh. A committee headed by Shri Shankar Rao Dev was formed to solve this problem. According to the recommendation of this committee, Bharatpur and Dholpur also agreed to merge in Rajasthan. Matsya Sangh joined Greater Rajasthan on May 15, 1949.
Answer 28:
Architecture: The Gupta period temples offer examples of Nagar style. Tigwan’s Vishnu Temple, Shiva temple of Bhoomra, Parvati Temple of Nachna Kuthar and Dashavtar temple of Devgarh are the main examples of this style.
Sculpture: Mathura, Sarnath and Patliputra were the main centers of sculpture. Sculptures were made of metal, stone and clay. Their main examples are the Buddha statue of Sultanganj, Mahavira statue of Mathura, Vishnu statue of Deogarh and Mathura.
Painting: The best examples of painting are found in Ajanta and Gwalior tiger caves.
Art and Music: During the Gupta period, there was a unique advancement in the field of music, drama, acting and dancing art.
Development of literature: During the Gupta period, there was a remarkable progress in the field of literature. During this period, Prayag and Mehrauli Prashasti were written. In Gupta period, many comedy dramas and epics were written, for example Swapnavasavdutta of Bhaas, Mudrarakshasa of Vishakhdutta, Abhijnan Shakuntlam of Kalidas, etc. Vishnu Sharma composed ‘Panchtantra’.
Development of science: There had been significant developments in various branches of science and technology during the Gupta period. Mathematics, astrology, chemistry, physics, Ayurveda and surgery etc., developed in this period. Aryabhatta, Bhaskar-I, Varahmihira, Brahmagupta, Vagbhatt, Dhanvantari, Palkapv, Kanaad Rishi, Nagarjuna were the chief scholars of this period.
![]()
OR
Development of Art in Chola Period: Chola rulers were art lovers. They built huge palaces, artificial lakes, widened dams, built beautiful cities, metal and stone sculptures and grand temples.
- Architecture: The main contribution of Cholas is the construction of temples. These temples were constructed in Dravid style. The famous temples of the Cholas are Sundareswar temple of Tirukattlai, Vijyalaya Choleshwar temple of Naramtalai.
- Sculpture: Examples of excellent sculpture in this period are statues of stone, bronze and metal of Brahma, Vishnu, Natraj, kings, queens, etc. The metal statues of this period include the Bronze statue of Natraj Shiva.
- Painting: Examples of excellent painting are found in Tanjavur.
- Development of Chola literature: Chola rulers were the lovers of education and literature. Temples and village councils were the centers of education. Tamil and Sanskrit languages were prevalent. During the reign of Cholas, Kamban composed Ramavtar. Jayangondar composed Kalitungparni. Many other books were also written Ramanuj, Yamunacharya and Venkat Madhav composed Sanskrit books on Rigveda.
Answer 29:
Importance of Civil Disobedience movement in India’s Independence movement: This movement was one of the mass movements run by the Indian National Congress against British imperialism. The dissatisfaction among the Indian leaders was widespread due to the failure of the British government to allow colonial independence after the Nehru Report of 1929 AD was rejected. After the declaration of the goal of‘Purna Swaraj’ in the Congress session of December 1929, the feeling of hope and glee was filled among the Indians as Mahatma Gandhi placed a 11-point demand before the Viceroy Lord Irwin through his letter ‘Young India’.
These demands included reduction in military expenditure, eliminating tax on salt, reducing the exchange rate, controlling the import of foreign textiles, discontinuing the sale of narcotics, releasing political prisoners, etc. Civil disobedience was adopted when Viceroy Irwin ignored these demands. The Congress working committee handed over the task of launching the Civil Disobedience Movement to Gandhi. Anti-Indian policies of the British attracted more and more people to join the activities of the Civil Disobedience Movement.
This movement created political consciousness in a very large social class. Women, youth workers and less educated rural people also participated in this movement. As result of the movement, the quantity of clothes imported from the UK decreased to one-third. Thus, the Civil Disobedience movement proved to be a milestone in the independence movement of India.
![]()
OR
The main causes of Non-Cooperation Movement were the following:
(1) First World War: The British government announced that the purpose of this world war would be to secure the world for democracy and to give every country the right for self-determination. But after the end of the war, the British government turned away from its promise.
(2) The Russian Revolution of 1917 AD: The Russian Revolution of 1917 demonstrated the Indians how the common masses could achieve their rights on the basis of power and courage.
(3) Rowlatt Act: By imposition of this Act the government got the right to imprison any person without trial, to reject their bail, etc. In addition to the above, the Jallianwala Bagh massacre and Khilafat movement were also important reasons for this movement.
Non-cooperation movement programs:
- Leaving government posts and honorary posts
- A boycott of government and semi-official festivals
- A boycott of government schools, colleges, and courts
- Not using foreign goods, etc.
Apart from this, people also resigned from government jobs and refused to pay taxes.
Importance of the movement: Congress gave a new direction to this movement. It became mass movement. It awakened the strong will of Indians to achieve Swaraj. This movement organized the Indians to Challenge the British government.
![]()
Answer 30:
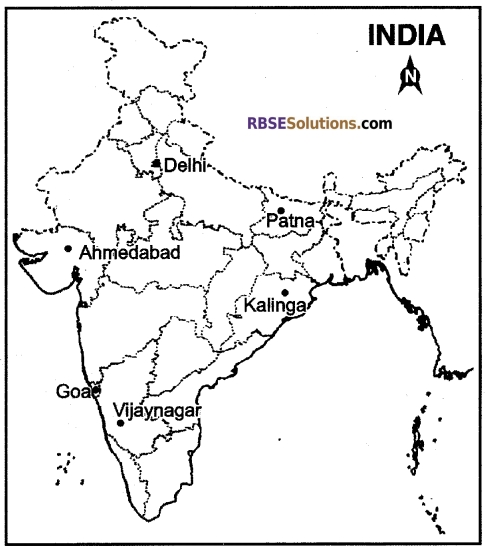
We hope the given RBSE Class 12 History Model Paper 1 English Medium will help you. If you have any query regarding RBSE Class 12 History Sample Paper 1 English Medium, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.