Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Political Science Notes Chapter 31 Regional Organizations -ASEAN & SAARC
Regional Organization: ASEAN:
- South East Asia is a very important region in world politics.
- In South-East Asia, in the extent between South of China and the Indian subcontinent, different countries are situated in which Myanmar, Brunei, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Singapore, Vietnam, Kamphuchea, Thailand and Philippines are included.
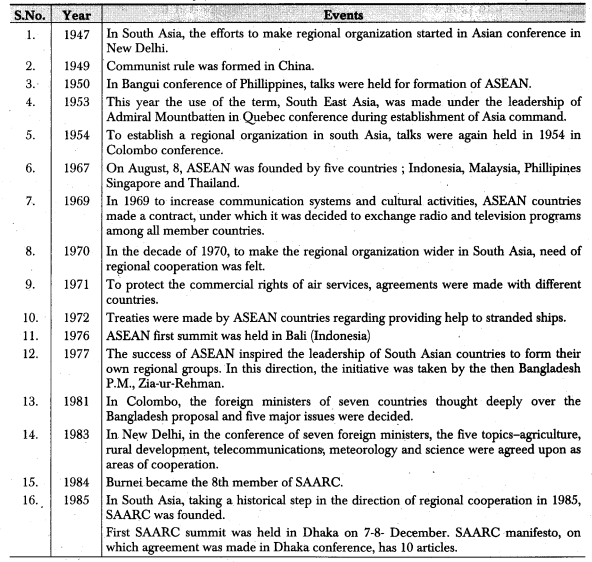
- The word ‘South East Asia’ has originated in world politics after world war II.
- The word ‘South East Asia’ has been used in Quebec Conference in 1953 during the establishment of Southern Command under the leadership of Admiral Mountbatten.
- At present 10 countries are situated in this region.
- South East Asia is strategically and geographically important, because it is located on the sea route that connects the Indian Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and connects Asia and Australia via the natural bridge.
- Due to excellent soil fertility, the region is called ‘Rice Bowl of the World’.
- Due to expansionist policy of China, all the small countries of South East Asia have become increasingly vulnerable to China.
- The countries of South East Asia established ASEAN to give pace to mutual economic corporation.
Organization of ASEAN:
- The association of South East Asian Nations was established on August 8, 1967 by 5 countries for the purpose of regional cooperation and as non-military organization. Its initial members included Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore and Thailand.
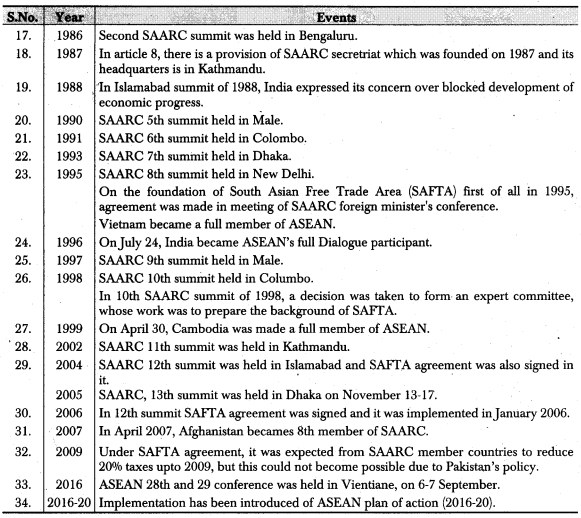
- In the year 1995, Vietnam and on 30th April 1999 Cambodia were made the full time members ofASEAN. .
- On 24th July, 1996 India was made the ‘Full Dialogue Participant of ASEAN. China and Russia were also made the ‘Full Dialogue participants’ Of ASEAN like India.
- ASEAN secretariat is in Jakarta (Indonesia) and headed by its General secretary.
- There are a total of 23 joint-member states including : USA, Russia, India, China and Japan in the ASEAN Regional forum-ARF.
- The first summit of ASEAN was held in year 1976 in Bali (Indonesia) and its 28th and 29th summits were held in Vientane (Laos) on 6th and 7th September, 2016.
Aims and Nature of ASEAN:
- The main objective of building ASEAN is to accelerate economic progress in South East Asia and to provide sustainability to the economies of its member countries.
- To enhance mutual help in political, socio-economic, cultural, commercial and scientific fields among the member countries and to find solution joindy to all problems is the main objective of ASEAN.
- This organization is totally based on economic cooperation and it never had a military agenda.
ASEAN – Function and Roles:
- ASEAN is steadily expanding its functional sphere. The organization is active in political, economic, technical, social and administrative fields.
- In the field of tourism, an organization named ‘ASEANTA’ was founded.
INDIA and ASEAN:
- INDIA is a full-fledged dialogue partner of ASEAN, and a member of ASEAN regional forum.
- INDIA’S Prime minister Narendra Modi wants to forge closer relations with South East Asian countries under his “Act East Policy”. ,
- P.M. Modi stressed on tacking terrorism and fundamentalism while addressing the 14th ASEAN-India summit in Laos’s capital Vientiane on 6th & 7th September.
- Besides Indonesia, the other ASEAN members Malaysia, Singapore, Philippines, Thailand are associated with protective agreements with western countries and they cooperate not only in international politics but also to bring global investment into Indo-China.
South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC):
- SAARC was founded in Dhaka and its secretariat is located in Kathmandu.
- There are basically 7 member countries in SAARC- India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Sri Lanka, Bhutan and Maldives.
- In April 2007, Afghanistan became the 8th member of SAARC.
- SAARC share is 21% of the world’s population, 3% in area and 9.12% in the global economy.
- SAARC itself is also an observer in the UN.
Historical Background:
- The region of entire South Asia could not fully implement comprehensive cooperation due to the mutual tension between two countries- India and Pakistan.
- The success of other regional organizations of the world, especially the success of ASEAN has forced the leadership of South Asian countries to think seriously about cooperating positively.
- The first summit of SAARC was held on 7th and 8th December, 1985 in Dhaka.
Charter of SAARC:
- In the declaration of SAARC, ten articles are there. There were agreed upon in 1985 during Dhaka conference.
- In the charter of SAARC, its main principles, objectives and institutional structures have been . defined.
Organizational Structure:
- Article 1 of the charter describes the key objectives of SAARC.
- Article 2 of the charter describes the main principles of SAARC.
- In article 3, there is a provision for the summit of the heads of SAARC member countries.
- Article 4 provides for the arrangement of at least two meetings in the year of foreign ministers ofthe member countries. .
- Article 5 contains the provision of a standing committee in, which foreign secretaries of member states are included.
- Article 6 has the provision of technical and scientific committees.
- Article 7 has the provision of a working committee.
- Article 8 has the provision of SAARC secretariat which has its headquarters in Kathmandu.
- In article 9 and 10 there is a provision of financial institution and charity.
South Asia Free Trade Area (SAFTA):
- In 2004, the SAFTA agreement was signed in Islamabad at the 12th SAARC summit. This agreement was implemented in January 2006.
- The total trade between the SAARC nations is approximately 1% of GDP of those countries, while it is 10% between ASEAN nations.
SAARC’s Assessment and Relevance:
- The declared purpose of SAARC is to develop in socio-economic and cultural fields on the basis of collective cooperation.
- Kashmir problem, border cross terrorism, Chinese intervention, etc. find many other political disputes have made SAARC almost irrelevant in the present times.
Important Dates and Related Events:
RBSE Class 12 Political Science Notes Chapter 31 Important Terms
- ASEAN : The Association of South East Asian Nations is known as ASEAN in brief. Established on August 8, 1967, the number of members of ASEAN is 10.
- Ocean : Very extensive and deep depressions on earth’s surface, which are filled with saline water and are connected to one another, are called oceans. These are big water bodies. The average depth is also 4000 metres from sea level. There are 5 oceans in the world.
- Pacific Ocean : World’s biggest ocean. Its area is almost 17.9 crore square k.m.
- Indian Ocean : World third biggest ocean. Its area is almost 7.4 crore squre k.m.
- ASEAN Regional Forum : ASEAN’s associated institution, 23 countries are its membersincluding USA, India, Russia, China, Japan, etc. .
- ASEANTA : This organization was founded by SAARC members to increase mutual tourism without any visa.
- VISA : When a citizen of a country goes to other country on tour, to live, to study or to work, besides taking a passport from his government, he has to take permission from thegovernment of the other country. This permission is called visa. Visa generally can be obtained from the embassy of the concerned country.
- SAARC : To increase regional cooperation in South Asia, this organization was founded in 1985. Its full form is South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation. India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Sri Lanka, Bhutan, Maldives and Afghanistan are its member countries.
- GDP : Its full form is gross domestic product. It means the total production of goods and services in a country in a financial year.
- Communist Rule : The rule established in China in 1949. In this system, the production and distribution remain under government control.
- SAFTA : Became effective on January 01, 2006. South Asian Free Trade Area which was established to make all South Asian countries a free trade area.
- Admiral Mountbatten : He was the first to use the term ‘South East Asia’ under his leadership during the foundation of South East Asia command in the Quebec conference which was held in 1953.
- Zia-ur-Rehman : Former President of Bangladesh. He took the initiative to establish SAARC.