RBSE Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 9 Co-ordinate Geometry Additional Questions is part of RBSE Solutions for Class 10 Maths. Here we have given Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 9 Co-ordinate Geometry Additional Questions.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 9 Co-ordinate Geometry Additional Questions
Multiple Choice Type Questions
Question 1.
Distance of (RBSESolutions.com) point (-3, 4) from x-axis – (CBSE 2012)
(A) 3
(B) -3
(C) 4
(D) 5
Solution :
So, correct choice is (C)
![]()
Question 2.
The three vertices of rectangle AOBC are A(0, 3), (0, 0) and C(5, 0). Length of (RBSESolutions.com) its diagonal is
(A) 5
(B) 3
(C) \(\sqrt { 34 }\)
(D) 9 [NCERT Exemplar Problem]
Solution :
The three vertices of rectangle AOBC are A(0, 3), O(0, 0) and C(5, 0).
Length of diagonal AC of rectangle = Distance between the points
A(0, 3) and C(5, 0)
= AC
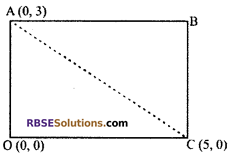
= \(\sqrt { { \left( 5-0 \right) }^{ 2 }+{ \left( 0-3 \right) }^{ 2 } } =\sqrt { { \left( 5 \right) }^{ 2 }+{ \left( -3 \right) }^{ 2 } } \)
= \(\sqrt { 25+9 } =\sqrt { 34 }\)
Hence, correct choice is (C)
Question 3.
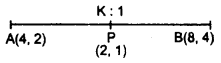
It the point P(2, 1) lies on the line segment joining (RBSESolutions.com) points A(4, 2) and B(8, 4), then :
(A) AP = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\)AB
(B) AP = PB
(C) PB = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\)AB
(D) AP = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)AB [NCERT Exemplar Problem]
Solution :
Let the point P divides the line segment in the ratio K : 1. then
Co-ordinate of point P
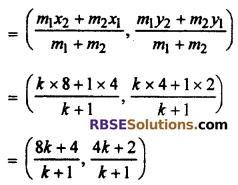
But given co-ordinate of point P = (2, 1)
∴ 2 = \(\frac { 8k+4 }{ k+1 }\) ⇒ 2k + 2 = 8k + 4
⇒ 8k – 2k = 2 – 4 ⇒ 6k = -2
⇒ k = \(\frac { -2 }{ 6 }\) = \(\frac { -1 }{ 3 }\)
Hence point P divides the line segment AB externally in the ratio 1 : 3.
So AP : PB = 1 : 3
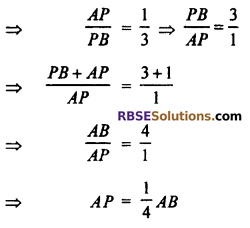
Hence, correct choice is (D).
Question 4.
If the points (0, 4),(0, 0) and (3, 0)are the vertices (RBSESolutions.com) of triangle, then perimeter of triangle is :
(A) 5
(B) 12
(C) 11
(D) 7 + \(\sqrt { 5 }\) [NCERT Exemplar Problem]
Solution :
Let the vertices of triangle are A(0, 4), B(0, 0) and C(3, 0), then.
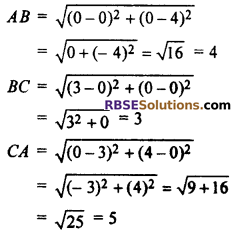
Hence, perimeter of triangle.
= AB + BC + CA
= 4 + 3 + 5 = 12
Hence, correct choice is B.
Question 5.
The co-ordinate of mid point joining the line (RBSESolutions.com) segment of points (6, 8) and (2, 4) will be
(A) (4, 6)
(B) (6, 4)
(C) (2, 2)
(D) (1, 0)
Solution :
Let co-ordinate of mid point of (6, 8) and (2, 4) is (x, y), then :
x = \(\frac { 6+2 }{ 2 }\) = \(\frac { 8 }{ 2 }\) = 4
And y = \(\frac { 8+4 }{ 2 }\) = \(\frac { 12 }{ 2 }\) = 6
Hence, co-ordinate of mid point = (4, 6)
Hence, correct choice is (A).
Question 6.
The point on x-axis which is equidistant (RBSESolutions.com) from the points (-1, 0) and (5, 0) [CBSE 2013]
(A) (0, 2)
(B) (2, 0)
(C) (3, 0)
(D) (0, 3)
Solution :
Let P(x, 0) is any point on x-axis.
∴ Point P(x, 0) ¡s equal distant from the points A(-1, 0) and B(5, 0)
∴ PA = PB
⇒ PA2 = PB2
(-1 – x)2 + (0 – 0)2 = (5 – x)2 + (0 – 0)2
⇒ 1 + x2 + 2x + 0 = 25 + x2 – 10x + 0
⇒ 1 + 2x = 25 – 10x
⇒ 2x + 10x = 25 – 1
⇒ 12x = 24
⇒ x = \(\frac { 24 }{ 12 }\) = 2
Here the point (2, 0) is on x-axis
Hence, correct choice is B
![]()
Question 7.
If A(-2, -1), B(9, 0), C(4, b) and D(1, 2) are (RBSESolutions.com) the vertices of parallelogram, then value of a and b will be :
(A) 1, 3
(B) 2, 4
(C) 2, 3
(D) 1, 4
Solution :
∵ Since the diagonals of parallelogram bisect to each other, then
∴ Mid point of diagonal AC = Mid point of diagonal BD
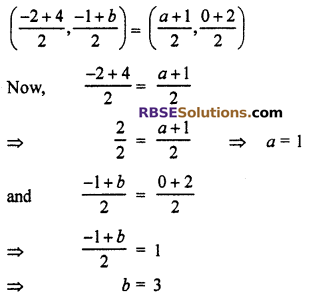
Hence correct choice is (A).
Question 8.
On the figure, P(5, -3) and Q(3, y) are the points (RBSESolutions.com) of trisection of the line segment joining the point A(7, -2) and B(1, -5), then y equals :
![]()
(A) 2
(B) 4
(C) -4
(D) \(\frac { -5 }{ 2 }\) [CBSE 2012]
Solution :
Point P and Q are trisect
![]()
∴ AP = PQ = BQ
AQ = AP + PQ = 2AP
∴ \(\frac { AQ }{ BQ }\) = \(\frac { 2AP }{ AP }\) = \(\frac { 2 }{ 1 }\) = 2 : 1
Coordinate of point Q.
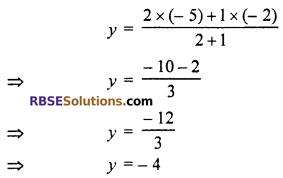
So, correct choice is (C)
Question 9.
If points (2, -2), (14, 10) and(11, 13) are the (RBSESolutions.com) vertices of triangle, then triangle is (CBSE 2014)
(A) Isosceles, triangle
(B) Scalene triangle
(C) Right angled triangle
(D) None of these
Solution :
A = (2, -2), B = (14, 10), C = (11, 13)
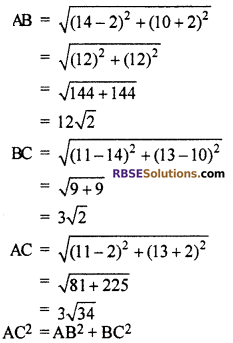
Here triangle is a right angled triangle
Hence, correct choice is (C).
Question 10.
If ordinate of any point is equal to its abscissa (RBSESolutions.com) and that point is 7 unit distance from point (-3, 4). then co-ordinate of that point is
(A) (4, 4), (3, 3)
(B) (-4, -4), (3, 3)
(C) (-4, -4), (-3, -3)
(D) (4, 4), (-3, -3)
Solution : Let point is (x, x) then, according to question
(x + 3)2 + (x – 4)2 = (7)2
x2 + 6x + 9 + x2 – 8x + 16 = 49
2x2 – 2x – 24 = 0
x2 – x – 12 = 0
(x – 4)(x + 3) = 0
x = 4, -3
∴ Point (4, 4) or (-3, -3)
Hence, Correct choice is (D).
Question 11.
On what ratio does the y-axis divide the (RBSESolutions.com) join of point (2, 4) and point (-3, 5).
(A) 2 : 3
(B) 2 : 5
(C) -3 : 2
(D) 5 : -2
Solution :
Let y-axis, divides the line joining the points A(2, 4) and B(-3, 5) at point C in the ratio m1 : m2
∵ Point C is at y axis, then
∴ x = 0
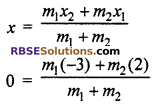
⇒ -3m1 + 2m1 = 0
⇒ 3m1 = 2m2
⇒ \(\frac { { m }_{ 1 } }{ { m }_{ 2 } } =\frac { 2 }{ 3 } \)
⇒ m1 : m2 = 2 : 3
Hence, correct choice is (A).
![]()
Question 12.
ABC is a triangle and D is a mid point of BC. If the (RBSESolutions.com) co-ordinate of vertices of ΔABC are (1, 2), (-1, -3) and (3, -5) respectively then co-ordinate of the point divides AD
internally in the ratio 2 : 1 will be :
(A) (1, -6)
(B) (-1, 6)
(C) (-1,-6)
(D) (1, -2)
Solution :
Co-ordinate of mid point D of BC
= \(\left( \frac { -1+3 }{ 2 } ,\frac { -3-5 }{ 2 } \right)\)
= (1, -4)
The co-ordinate of a point divide A(1, 2) and D(1, -4) internally in the ratio 2 : 1
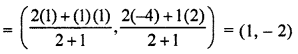
∴ Co-ordinate of a point = (1, -2)
Question 13.
That point is called where XX and Y’Y cuts (RBSESolutions.com) each other
(A) Co-ordinate
(B) Origin
(C) Vertical
(D) Horizontal line
Solution :
Correct choice is B.
Question 14.
X-co-ordinate is
(A) Abscissa
(B) Ordinate
(C) Origin
(D) None of these
Solution :
Correct choice is (A)
Question 15.
Co-ordinate of a point on X-axis.
(A) (0, x)
(B) (x, 0)
(C) (x, y)
(D) None of these
Solution :
Correct choice is (B)
Question 16.
What will the co-ordinate of point A when AB is a (RBSESolutions.com) diameter of circle and coordinate of B(1, 4) and co-ordinate of center O is (2, -3)
(A) (3, -5)
(B) (3, -6)
(C) (4, -10)
(D) (3, -10)
Solution :
Let co-ordinate of point A is (x, y) By the mid point formula
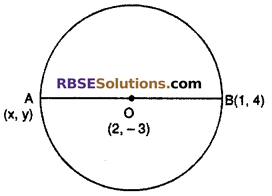
2 = \(\frac { x+1 }{ 2 }\)
⇒ x + 1 = 4
⇒ x = 4 – 1 = 3
and -3 = \(\frac { y+4 }{ 2 }\)
⇒ y + 4 = -6
y = -6 – 4 = -10
∴ co-ordinate of point A (3, -10)
Hence correct choice is (D).
Question 17.
The value of y for which distance (RBSESolutions.com) between points P(2, 3) and Q(0, y) is 10 unit, is :
(A) -9 or -3
(B) 9 or -3
(C) 9 or 3
(D) -4 or 9
Solution :
Distance between P(2, 3) and Q(10, y) = 10
\(\sqrt { { \left( 10-2 \right) }^{ 2 }+{ \left( y-3 \right) }^{ 2 } } \) = 10
square both sides
⇒ (8)2 + (y – 3)2 = 100
⇒ (y – 3)2 = 100 – 64
⇒ (y – 3)2 = 36
⇒ y – 3 = ±6
Taking the +ve sign
y – 3 = 6
y = 6 + 3 = 9
Taking -ve sign
y – 3 = -6
y = -6 + 3 = -3
So y = 9 or -3
Hence, correct choice is (B).
![]()
Question 18.
In what ratio the line segment (RBSESolutions.com) joining the points (-3, 10) and (6, -8) divides by the point (-1, 6)
(A) 2 : 7
(B) 2 : 9
(C) 4 : 3
(D) 3 : 4
Solution :
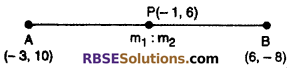
Let point P(-1, 6) divides the line segment joining the points A(-3, 10) and B (6, -8) internally in the ratio m1 : m2.
By section formula
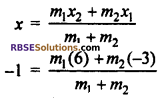
⇒ -m1 – m2 = 6m1 – 3m2
⇒ -m1 – 6m1 = -3m2 + m2
⇒ -7m1 = -2m2
⇒ \(\frac { { m }_{ 1 } }{ { m }_{ 2 } } =\frac { -2 }{ -7 } \) = \(\frac { 2 }{ 7 }\)
⇒ m1 : m2 = 2 : 7
Hence, correct choice is A
Question 19.
If the points (1, 2), (4, y), (x, 6) and (3, 5) are (RBSESolutions.com) the vertices of rhombus, then value of x and y will be
(A) x = 6, y = 2
(B) x = 6, y = 3
(C) x = 5, y = 3
(D) x = 3, y = 6
Solution :
∵ O is the mid point of diagonal AC and BD
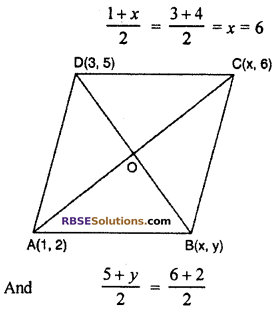
⇒ y = 3
So x = 6 and y = 3
Hence, correct choice in (B)
Question 20.
Find the coordinate of a point on y-axis which is (RBSESolutions.com) equidistant from the points A(6, 5) and B(-4, 3).
(A) (0, 9)
(B) (9, 0)
(C) (8, 0)
(D) (0, 8)
Solution :
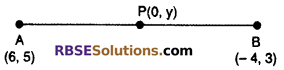
∵On y-axis, coordinate of x axis is zero. So Let co-ordinate of P is (0, y)
According to question
AP = PB
Square both sides
⇒ AP2 = PB2
⇒ (6 – 0)2 + (5 – y)2 = (0 + 4)2 + (y – 3)2
⇒ 36 + 25 + y2 – 10y = 16 + y2 + 9 – 6y
⇒ 61 + y2 – 10y = 25 + y2 – 6y
⇒ 61 – 25 = 10y – 6y
⇒ 4y = 36
y = \(\frac { 36 }{ 4 }\) = 9
Hence at y-axis the points (0, 9)
Hence, correct choice is (A)
![]()
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Find the distance between (RBSESolutions.com) the points (a, b) and (-a, -b)
Solution :
Let point is A(a, b) and B(-a, -b) then distance between them
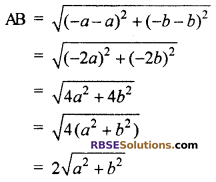
Question 2.
Prove that, the points (1, 5), (2, 3) and (-2, -11) are not collinear.
Solution :
Let the points are A(1, 5), B(2, 3) and C(-2, -11) respectively i.e. (RBSESolutions.com) co-ordinate of A is (1, 5), co-ordinate of B is (2, 3) and co-ordinate of C is (-2, -11).
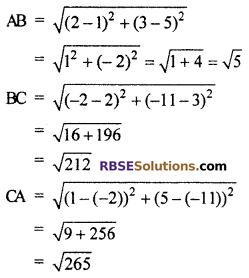
It is clear that sum of distances of any two sides is not equal to third side. So these points are not collinear.
Question 3.
Check the points (5, -2), (6, 4) and (7, -2) are the (RBSESolutions.com) vertices of isosceles triangle :
Solution :
The let vertices of triangle is A(5, -2), B(6, 4) and C(7, -2)
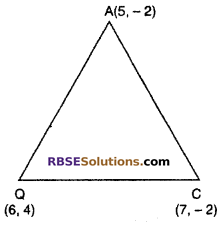
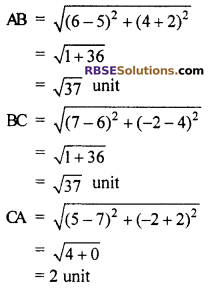
It is clear
AB = BC = \(\sqrt { 37 }\)
Hence, These points are the vertices of isosceles triangle.
Question 4.
Write the distance of point (-5, 4) (RBSESolutions.com) from x-axis. (Higher secondary board Raj. 2015)
Solution :
Distance of point (-5, 4) from x – axis = 4 unit.
Question 5.
Write the distance of point (3, -2) from y-axis. (Higher secondary board Raj. 2015)
Solution :
Distance of point (3, -2) from y – axis = 3 unit
Question 6.
Find the mid point of line segment joining the point (-3, 4) and point (7, 5). (Higher secondary board Raj. 2015)
Solution :
The mid point of line segment joining the point (-3, 4) and (7, 5)
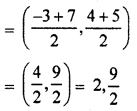
![]()
Question 7.
Find the distance of (RBSESolutions.com) point P(6, -6) from origin.
Solution :
Distance of point P(6, -6) from origin O(0, 0)
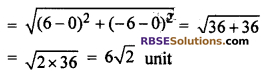
Question 8.
Answer the following
(i) What is the name of horizontal and vertical lines drawn to determine the position of any point in the cartesian plane ?
(ii) What is the name of each part of the plane formed by there two lines?
(iii) Write the name of the point where these two lines intersect.
Solution :
(i) Axis
(ii) Quadrant
(iii) Origin
Question 9.
In the following, which (RBSESolutions.com) points lie on x-axis
A(1, 1), B(1, 0), C(0, 1), D(0, 0), E(-1, 0), F(0, -1), G(4, 0), H(0, -7)
Solution :
On x-axis, y coordinate is zero of each point, so B(1, 0), D(0, 0) E(-1, 0) and G(4, 0) lie on x-axis.
Question 10.
In above question (9), which points lie on y-axis.
Solution :
On y-axis, x coordinate is zero of each point. So C(0, 1), D(0, 0), F(0, -1) and H(0, -7) lie on y-axis.
Question 11.
Draw the points A(2, 0), B(2, 2), C(0, 2) on graph (RBSESolutions.com) paper. Find the name meeting OA, AB, BC and CO.
Solution :
Draw the points A(2, 0), B(2, 2) and C(0, 2) and join OA, AB, BC and CO. we find following figure
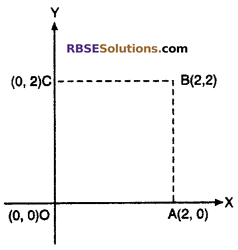
It is a quadrilateral. This figure is of a square.
Question 12.
Draw the points A(4, 4) and B(-4, 4) and join OA, OB and AB, Name (RBSESolutions.com) the figure made by such type.
Solution :
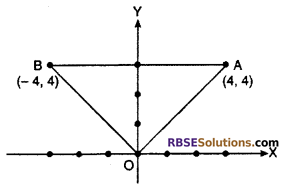
Draw the points A(4, 4) and B(-4, 4) and join OA, OB and AB. If is clear from figure it is a triangle.
Hence, ΔOAB is a equilateral triangle.
![]()
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Find the distance between the (RBSESolutions.com) points (a sin θ, a cos θ) and (a cos θ, -a sin θ)
Solution :
Distance between the points (a sin θ, a cos θ) and (a cos θ, -a sin θ)
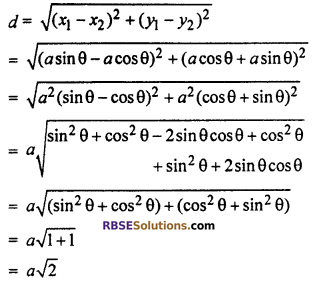
Question 2.
If distance between the points (5, 3) and (x, -1) are 5 unit, then (RBSESolutions.com) find the value of x.
Solution :
Let distance between points A(5, 3) and B(x, -1) is 5 unit, then
According to question
\(5=\sqrt { { \left( 5-x \right) }^{ 2 }+{ \left[ 3-\left( -1 \right) \right] }^{ 2 } }\)
Squaring both sides
⇒ 25 = (5 – x)2 + (3 + 1)2
⇒ 25 = (5 – x)2 + 16
⇒ 25 = 25 + x2 – 10x + 16
⇒ x2 – 10x + 16 = 0
⇒ x2 – 8x – 2x + l6 = 0
⇒ x(x – 8)-2(x – 8) = 0
⇒ (x – 2)(x – 8) = 0
if x – 8 = 0 ⇒ x = 8
and x – 2 = 0 ⇒ x = 2
Hence value of x are 8 and 2
Question 3.
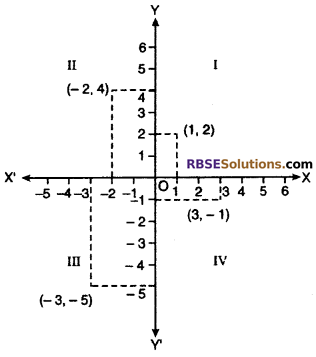
In which quadrant or on which axis do each of (RBSESolutions.com) the points (-2, 4), (3, -1), (-1, 0), (1, 2) and (-3, -5) lie ? verify, your answer by locating, then on the Cartesian plane (NCERT)
Solution :
(i) Point (-2, 4) lie in II quadrant
(ii) Point (3, -1) lie in IV quadrant
(iii) Point (-1, 0) lie at negative x-axis
(iv) Point (1, 2) lie at I quadrant
(v) Point (-3, -5) lie at III quadrant
Position of all points are seen in the following Cartesian plane.
Question 4.
If the point P(x, y) lie on a circle with the center (3, -2) and (RBSESolutions.com) radius 3 unit, then prove that x2 + y2 – 6x + 4y + 4 = 0
Solution :
Let center of circle C(3, -2) and point P(x,y) lie on a circle.
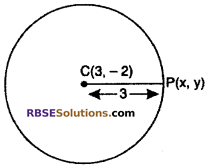
Given : radius of circle CP = 3
⇒ \(\sqrt { { \left( x-3 \right) }^{ 2 }+{ \left( y+2 \right) }^{ 2 } } \) = 3
Squaring both sides
⇒ (x – 3)2 + (y + 2)2 = 9
⇒ x2 + 9 – 6x + y2 + 4 + 4y = 9
⇒ x2 + y2 – 6x + 4y + 4 = 0
![]()
Question 5.
If point P(2, 4) is equidistant from the points A(5, K) and B(K, 7), then (RBSESolutions.com) find the value of K. (CBSE 2012)
Solution :
Point P(2, 4) is equidistant from the points A(5, K) and B(K, 7). So
PA = PB
⇒ PA2 = PB2
⇒ (5 – 2)2 + (k – 4)2 = (k – 2)2 + (7 – 4)2
⇒ 9 + K2 + 16 – 8K = K2 + 4 – 4K + 9
⇒ K2 – 8K + 16 – K2 – 4 + 4K = 0
⇒ -4K + 12 = 0
⇒ -4K = -12
⇒ K = \(\frac { -12 }{ -4 }\) = 3
Hence, K = 3
Question 6.
Find the point on x-axis which is equidistant from (-2, 5) and (2, -3)
Solution :
Let co-ordinate of any point on x axis (x, 0) because for x-axis (RBSESolutions.com) co-ordinate of y is zero. Distance between (x, 0) and (2, -5)
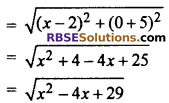
And distance between (x, 0) and (-2, 9)
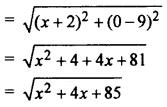
According to question
\(\sqrt { { x }^{ 2 }-4x+29 } =\sqrt { { x }^{ 2 }+4x+85 }\)
Squaring both sides.
x2 – 4x + 29 = x2 + 4x + 85
-4x – 4x = 85 – 29
-8x = 56
x = \(\frac { -56 }{ 8 }\) = -7
Hence, co-ordinate of required point = (-7, 0)
Question 7.
If M(4, 5) is a mid point of line segment AB and co-ordinate of A is (3, 4), then (RBSESolutions.com) find the co-ordinate of point B. (Higher secondary board Raj., 2014)
Solution :
Let co-ordinate of B is (x, y)
Given : co-ordinate of mid point of(3, 4) and (x, y)
4 = \(\frac { 3+x }{ 2 }\) ⇒ 3 + x = 8
⇒ x = 8 – 3 = 5
and 5 = \(\frac { y+4 }{ 2 }\)
⇒ y + 4 = 10
⇒ y = 10 – 4 = 6
Hence, co-ordinate of B = (5, 6)
Question 8.
If point A(4, 7), B(1, 3) and 6(7, 3) are the vertices of right angled triangle (RBSESolutions.com) where B is a right angle. Find the value of P.
Solution :
According to question A(4, 7), B(P, 3) and C(7, 3) are the vertices of a right angled triangle. Now from Pythagoras theorem
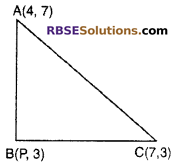
AB2 + BC2 = AC2
(3 – 7)2 + (P – 4)2 + (3 – 3)2 + (7 – p)2
= (3 – 7)2 + (7 – 4)2
⇒ (p – 4) 2 + (7 – p)2 = 9
⇒ p2 + 16 – 8P + 49 + P2 – 14P = 9
⇒ 2P2 – 22P + 56 = 0
⇒ P2 – 11P + 28 = 0
⇒ P2 – 4P – 7P + 28 = 0
⇒ P(P – 4) -7(P – 4) = 0
⇒ (P – 4)(P – 7) = 0
⇒ P = 4 or 7
Hence, value of P is 4 or 7.
![]()
Question 9.
If co-ordinate of point A, B, C are (6, -1), (1, 3) and (x, 8) respectively, then find the (RBSESolutions.com) value of x where AB = BC. (CBSE 2017)
Solution :
Co-ordinate of points A,B, C are (6, -1), (1, 3) and (x, 8) respectively.
According to question
AB = BC
\(\sqrt { { \left( 6-1 \right) }^{ 2 }+{ \left( -1-3 \right) }^{ 2 } } =\sqrt { { \left( 1-x \right) }^{ 2 }+{ \left( 3-8 \right) }^{ 2 } } \)
Squaring both sides
25 + 16 = (1 – x)2 + 25
(1 – x)2 = 16
(1 – x) = ±4
taking +ve sign = 1 – x = 4
x = 1 – 4 = -3
taking -ve sign 1 – x = -4
x = 1 + 4 = 5
So, x = -3 or 5
Question 10.
A(4, 2), B(6, 5) and C(1, 4) are the vertices of triangle ABC, AD is a (RBSESolutions.com) median through point A meet BC at point D, find the co-ordinate of D.
Solution :
Co-ordinate of mid point D of BC.
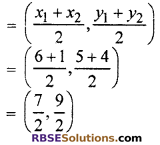
Hence, co-ordinate of D is \(\left( \frac { 7 }{ 2 } ,\frac { 9 }{ 2 } \right)\)
Question 11.
Prove that points 4(1, 1) B(-2, 7) and C(3, -3) are (RBSESolutions.com) collinear.
Solution :
Let A( 1, 1), B(-2, 7) and C(3, -3) then
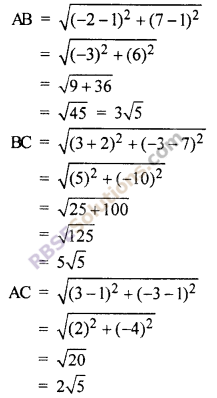
∴ AB + AC = 3\(\sqrt { 5 }\) + 2\(\sqrt { 5 }\) = 5\(\sqrt { 5 }\) = BC
So AB + AC = BC
So these point A, B, and C are collinear.
Question 12.
Find the value of y for which distance between (RBSESolutions.com) points P(2, -3) and Q(10, y) is 10 unit.
Solution :
Given points are P(2, -3) and Q(10, y)
Then PQ = \(\sqrt { { \left( 10-2 \right) }^{ 2 }+{ \left( y+3 \right) }^{ 2 } } \)
∵ PQ = 10 unit
∴ \(\sqrt { { \left( 8 \right) }^{ 2 }+{ \left( y+3 \right) }^{ 2 } } \) = 10
Squaring both sides
64 + (y + 3)2 = 100
⇒ (y + 3)2 = 100 – 64
⇒ (y + 3)2 = 36
⇒ y + 3 = ±6
taking +ve sign
y +3 = 6
y = 6 – 3 = 3
taking -ve sign.
y + 3 = -6
y = -6 – 3 = -9
Hence, required value of y is 3 or -9
![]()
Question 13.
Find the value of x which is equidistant from the (RBSESolutions.com) points A (6, 5) and B(-4, 5). (Higher secondary board Rai., 2012)
Solution :
Let co-ordinate of any point P on x-axis = (x, 0)
∴ PA = PB
⇒ PA2 = PB2
⇒ (x – 6)2 + (0 – 5)2 = (x + 4)2 + (0 – 5)2
⇒ x2 + 36 – 12x + 25 = x2 + 16 + 8x + 25
⇒ -12x + 36 = 8x + 16
⇒ -12x – 8x = 16 – 36
⇒ -20x = -20
⇒ x = \(\frac { -20 }{ -20 }\) = 1
Hence, the co-ordinate of required point = (1,0)
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Points M, N, O and P divide the time segment joining the (RBSESolutions.com) points A(-5, 0) and B(0, 15) in five equal parts. Find out the co-ordinate of N and O.
Solution :
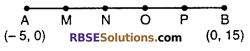
According to question, a line segment joining the points A (-5, 0) and B(0, 15) divides 5 equal parts. Then point N divides line segment AB in the ratio 2 : 3 and point O divides AB in the ratio 3 : 2.
Let coordinate of N is (x, y)
For point N
x1 = -5, y1 = 0, m1 = 2
x2 = 0, y2 = 15, m2 = 3
By section formula
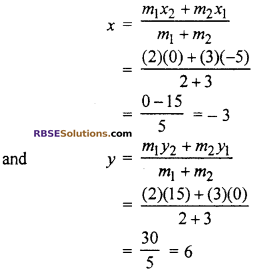
Hence, co-ordinate (RBSESolutions.com) of N is (-3, 6)
Again let co-ordinate of O is (x’, y’) then
x1 = 5, y1 = 0, m1 = 3
x2 = 0, y2 = 15, m1 = 2
By section formula
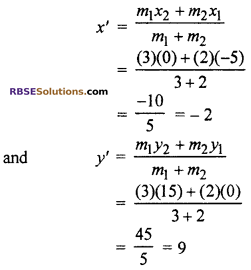
Hence, co-ordinate of point O = (-2, 9)
Question 2.
If the points A(6, 1), B(8, 2), C(9, 4) and D(x, y) are (RBSESolutions.com) vertices of parallelogram respectively, then find the point D(x, y). (Higher secondary board Raj., 2012)
Solution :
Let point A(6, 1), B(8, 2), C(9, 4) and D(x, y) are the vertices of parallelogram.
∴ Diagonals of parallelogram bisects each other.
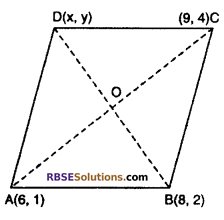
So,
= co-ordinate of mid point (RBSESolutions.com) diagonal AC
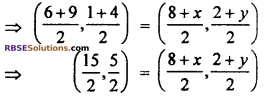
comparing
\(\frac { 8+x }{ 2 }\) = \(\frac { 15 }{ 2 }\) and \(\frac { 2+y }{ 2 }\) = \(\frac { 5 }{ 2 }\)
⇒ 8 + x = 15 and 2 + y = 5
⇒ x = 15 – 8 and y = 5 – 2
⇒ x = 7 and y = 3
Hence, co-ordinate of point D(7, 3)
![]()
Question 3.
Find the co-ordinate of the points of trisection of the (RBSESolutions.com) line segment joining the points P(-3, 4) and Q(4, 5). (Higher secondary board Raj., 2014)
Solution :
Let A(x1 y1) and B(x2 Y2)
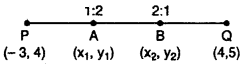
Let PA = AB = QB = x
AQ = x + x = 2x
PB = x + x = 2x
\(\frac { PA }{ AQ }\) = \(\frac { x }{ 2x }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) = 1 : 2
\(\frac { PB }{ BQ }\) = \(\frac { 2x }{ x }\) = \(\frac { 2 }{ 1 }\) = 2 : 1
Hence, point A, divide PQ in the ratio 1 : 2 and point B, divide PQ in the ratio 2 : 1.
For point A
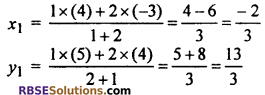
∴ Co-ordinate of point A \(\left( \frac { -2 }{ 3 } ,\frac { 13 }{ 3 } \right)\)
Co-ordinate of point B
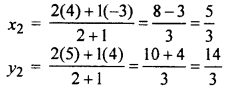
∴ Co-ordinate of point B \(\left( \frac { 5 }{ 3 } ,\frac { 14 }{ 3 } \right)\)
Hence, co-ordinate of point A and B are \(\left( \frac { -2 }{ 3 } ,\frac { 13 }{ 3 } \right)\) and \(\left( \frac { 5 }{ 3 } ,\frac { 14 }{ 3 } \right)\) respectively.
Question 4.
If the co-ordinates of the mid points of the sides of the (RBSESolutions.com) triangle are (3, 4), (8, 9) and (6, 7) respectively. Find the co-ordinate of vertices of triangle. (NCERT Exemplar Problem)
Solution :
Let mid points of sides of triangle are P(3, 4), Q(8, 9) and R(6, 7) respectively.
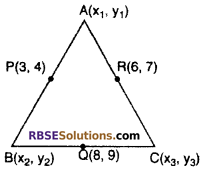
Let A(x1, y1) B(x2, y2) and C(x3, y3) be the vertices of the
triangle ABC.
Since P (3, 4) is the mid point of A (x1, y1) and B(x2, y2)
3 = \(\frac { { x }_{ 1 }+{ x }_{ 2 } }{ 2 } \) and 4 = \(\frac { { y }_{ 1 }+{ y }_{ 2 } }{ 2 } \)
x1 + x2 = 6 and y1 + y2 = 8 …..(i)
since Q(8, 9) is the mid point of B(x2, y2) and C(x3, y3)
So 8 = \(\frac { { x }_{ 2 }+{ x }_{ 3 } }{ 2 } \) and 9 = \(\frac { { y }_{ 2 }+{ y }_{ 3 } }{ 2 } \)
x2 + x3 = 16; y2 + y3 = 18 …..(ii)
Since R(6, 7) is the mid (RBSESolutions.com) point of A(x1, y1) and C(x3, y3). So
6 = \(\frac { { x }_{ 1 }+{ x }_{ 3 } }{ 2 } \) and 7 = \(\frac { { y }_{ 1 }+{ y }_{ 3 } }{ 2 } \)
⇒ x1 + x3 = 12 and y1 + y3 = 14 …..(iii)
Adding equation (i), (ii) and (iii)
2x1 + 2x2 + 2x3 = 34
and 2y1 + 2y2 + 2y3 = 40
⇒ x1 + x2 + x3 = 17 …..(iv)
and y1 + y2 + y3 = 20
Subtract equation (i) from equation (iv).
x1 + x2 + x3 – x1 – x2 = 17 – 6
and y1 + y2 + y3 – y1 – y2 = 20 – 8
⇒ x3 = 11 and y3 = 12
subtract equation (ii) from equation (iv)
x1 + x2 + x3 – x2 – x3 = 17 – 6
and y1 + y2 + y3 – y2 – y3 = 20 – 8
⇒ x1 = 1 and y1 = 2
subtract equation (iii) (RBSESolutions.com) from equation (iv)
x1 + x2 + x3 – x1 – x3 = 17 – 12
and y1 + y2 + y3 – y1 – y3 = 20 – 14
⇒ x2 = 5 and y2 = 6
Hence, the co-ordinate of vertices of triangle A(1, 2) B(5, 6) and C(11, 12)
Question 5.
Determine the ratio in which the line x – y – 2 = 0 divides the line segment joining (RBSESolutions.com) the points A(3, -1) and B(8, 9) (CBSE 2007)
Solution :
Let the Line x – y – 2 = 0
divides the line segment joining the point A (3, -1) and B (8, 9) at point P (x, y) in the ratio λ : 1.
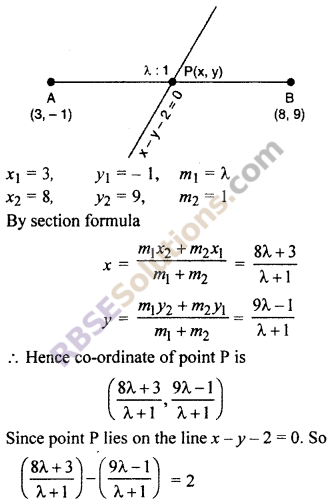
⇒ 8λ + 3 – 9λ + 1 = 2(λ + 1)
⇒ -λ + 4 = 2λ + 2
⇒ 3λ = 2
⇒ λ = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)
⇒ λ : 1 = 2 : 3
Hence, required ratio 2 : 3.
![]()
Question 6.
Find the ratio in which the line 2x + 3y – 5 = 0 divides the line (RBSESolutions.com) segment which joining the points (8, -9) and (2, 1). Find the coordinate of dividing point. (NCERT Exemplar Problem)
Solution :
Let given line divides the line segment joining the points A(8, -9) arid B(2, 1) in the ratio λ : 1.
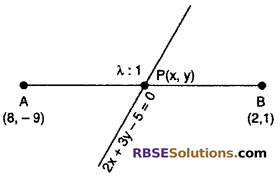
Let co-ordinate of point P
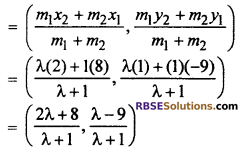
But point P lies on (RBSESolutions.com) the line 3x + 3y – 5 = 0
So, \(2\left( \frac { 2\lambda +8 }{ \lambda +1 } \right) +3\left( \frac { \lambda -9 }{ \lambda +1 } \right) -5=0\)
⇒ 2(2λ + 8) +3(λ – 9) -5(λ + 1) = 0
⇒ 4λ + 16 + 3λ – 27 – 5λ – 5 = 0
⇒ 2λ – 16 = 0
⇒ λ =
⇒ λ : 1 = 8 : 1
Hence required ratio
from equations (i), coordinate of point P.
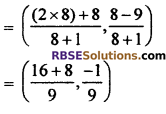
= \(\left( \frac { 24 }{ 9 } ,\frac { -1 }{ 9 } \right)\)
= \(\left( \frac { 8 }{ 3 } ,\frac { -1 }{ 9 } \right)\)
Hence required ratio = 8 : 1 and co-ordinate of point = \(\left( \frac { 8 }{ 3 } ,\frac { -1 }{ 9 } \right)\)
Question 7.
ABCD is a rectangle formed by the (RBSESolutions.com) points A(-1, -1), B(-1, 4), C(5, 4) and D(5, -1). P, Q, R and S and the mid points of AB, BC CD and DA respectively. Is the quadrilateral PQRS square, a rectangle or a rhombus. Justify your answer. (NCERT)
Solution :
According to question the given point are A(-1, -1), B(-1, 4), C(5, 4) and D(5, -1).
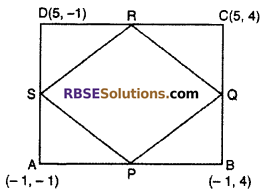
Co-ordinate of mid point P of side AB
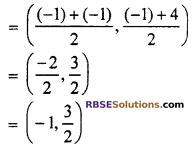
Co-ordinate of mid (RBSESolutions.com) point Q of side BC
= \(\left( \frac { 5-1 }{ 2 } ,\frac { 4+4 }{ 2 } \right)\)
= \(\left( \frac { 4 }{ 2 } ,\frac { 8 }{ 2 } \right)\)
= (2, 2)
Co-ordinate of mid point R of side CD
= \(\left( \frac { 5+5 }{ 2 } ,\frac { 4-1 }{ 2 } \right)\)
= \(\left( \frac { 10 }{ 2 } ,\frac { 3 }{ 2 } \right)\)
= \(\left( 5,\frac { 3 }{ 2 } \right)\)
Co-ordinate of mid point S of side DA
= \(\left( \frac { 5-1 }{ 2 } ,\frac { -1-1 }{ 2 } \right)\)
= \(\left( \frac { 4 }{ 2 } ,\frac { -2 }{ 2 } \right)\)
= (2, -1)
Now P \(\left( -1,\frac { 3 }{ 2 } \right)\), Q(2, 4), R \(\left( 5,\frac { 3 }{ 2 } \right)\) and S(2, -1)
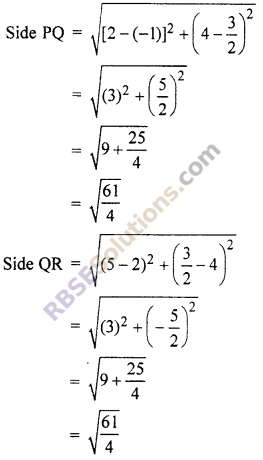
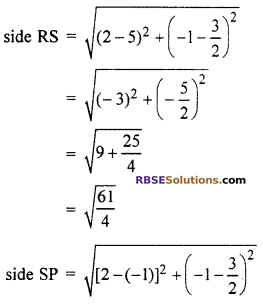
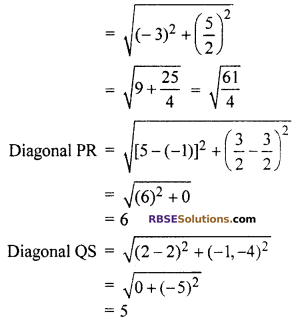
In quadrilateral PQRS, PQ = QR = RS = SP
and diagonal PR ≠ diagonal QS
Hence, quadrilateral PQRS is a rhombus.
![]()
Question 8.
The line segment joining the points (3, -4) and (1, 2) is (RBSESolutions.com) trisected at the points P and R. It the co-ordinates of P and Q are (p, -2) and \(\left( \frac { 5 }{ 3 } ,q \right)\) respectively. Find the value of p and q. (CBSE 2013)
Solution :
Let the given points be A(3, -4) and B(1, 2) since points P and Q trisected the line segment joining the points AB.
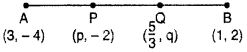
Then AP = PQ = QB = x(let)
PB = PQ + QB = x + x = 2x
and AQ = AP + PQ = x + x = 2x
∴ \(\frac { AP }{ PB }\) = \(\frac { x }{ 2x }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
⇒ AP : PB = 1 : 2
and \(\frac { AQ }{ QB }\) = \(\frac { 2x }{ x }\) = \(\frac { 2 }{ 1 }\)
⇒ AQ : QB = 2 : 1
Hence point P divide line segment AB in the ratio 1 : 2 and (RBSESolutions.com) point Q divide the live segment AB in the ratio 2 : 1 internally.
So, p = x co-ordinate of point P
= \(\frac { { m }_{ 1 }{ x }_{ 2 }+{ m }_{ 2 }{ x }_{ 1 } }{ { m }_{ 1 }+{ m }_{ 2 } }\)
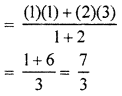
and q = y-co-ordinate of point Q
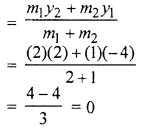
So p = \(\frac { 7 }{ 3 }\) and q = 0
Question 9.
The two opposite vertices of a square are (-1, 2) and (3, 2). (RBSESolutions.com) Find the co-ordinate of the other two vertices. (NCERT)
Solution :
Let two opposite vertices of square ABCD are A(-4, 2) and C(3, 2) and co-ordinate of point B is (x, y)
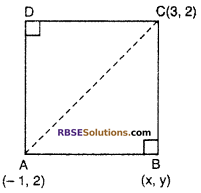
∴ Since each side of square is same in length
AB = BC
⇒ (AB)2 = (BC)2
⇒ (x + 1)2 + (y – 2)2 = (x – 3)2 + (y – 2)2
⇒ (x + 1)2 = (x – 3)2
⇒ x2 + 1 + 2x = x2 + 9 – 6x
⇒ 8x = 8
⇒ x = \(\frac { 8 }{ 8 }\) = 1 ….(i)
Now in right (RBSESolutions.com) angled ∆ABC
By Pythagoras theorem
(AB)2 + (BC)2 = (AC)2
⇒ (x + 1)2 + (y – 2)2 + (x – 3)2 + (y – 2)2 = (3 + 1)2 + (2 – 2)2
⇒ x2 + 1 + 2x + y2 + 4 – 4y + x2 + 9 – 6x + y2 + 4 – 4y = 16
⇒ 2x2 + 2y2 – 4x – 8y + 2 = 0
⇒ x2 + y2 – 2x – 4y + 1 = 0 …(ii)
Put the value ofx from equation (i) in equation (ii)
(+1)2 + (y)2 – 2(1) – 4y + 1 = 0
⇒ y2 – 4y = 0
⇒ y(y – 4) = 0
⇒ y = 0 and y – 4 = 0
⇒ y = 0, 4
Hence, other two vertices of square is (1, 0) and (1, 4)
Question 10.
Find the center of a circle passing (RBSESolutions.com) through the points (6, -6), (3, -7) and (3, 3) (NCERT)
Solution :
Let O(x, y) is a center of circle.
The circle of center O is passes through the points P(6, -6), Q(3, -7) and R(3, 3) respectively.
∵ Since radius of circle is same
∴ OP = OQ = OR
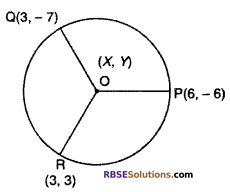
or OP2 = OQ2 = OR2
Now OP2 = OQ2
⇒ (x – 6)2 + (y + 6)2 = (x – 3)2 + (y + 7)2
⇒ x2 – 12x + 36 + y2 + 12y + 36 = x2 – 6x + 9 + y2 + 14y + 49
⇒ -12x + 6x + 12y – 14y + 72 – 58 = 0
⇒ -6x – 2y + 14 = 0
⇒ 3x + y – 7 = 0 …(i)
Now OQ2 = OR2
⇒ (x – 3)2 + (y + 7)2 = (x – 3)2 + (y – 3)2
⇒ (y + 7)2 = (y – 3)2
⇒ y2 + 49 + 14y = y2 +9 – 6y
⇒ 20y = -40
⇒ y = \(\frac { -40 }{ 20 }\) = -2
Put the value ofy in equation (i)
3x – 2 – 7 = 0
⇒ 3x – 9 = 0
⇒ 3x = 9
⇒ x = \(\frac { 9 }{ 3 }\) = 3
Hence, required center is (3, -2).
![]()
Question 11.
Prove that diagonals of rectangle (RBSESolutions.com) bisect and equal to each other.
Solution :
Let OABC is a rectangle and O(0, 0), A(a, 0), B(a, b) and C(0, 6).
Let diagonal OB and AC bisects each other at point P.
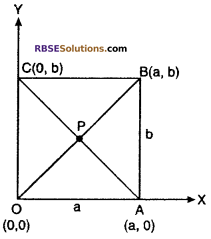
Co-ordinate of mid point P (RBSESolutions.com) of diagonal OB = \(\left( \frac { 0+a }{ 2 } ,\frac { 0+b }{ 2 } \right)\)
= \(\left( \frac { a }{ 2 } ,\frac { b }{ 2 } \right)\)
Co-ordinate of mid point P of diagonal AC = \(\left( \frac { a+0 }{ 2 } ,\frac { 0+b }{ 2 } \right)\)
= \(\left( \frac { a }{ 2 } ,\frac { b }{ 2 } \right)\)
Clearly diagonal of rectangle bisects each other at point P.
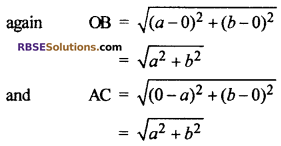
Clearly OB = AC
Hence length of diagonals of rectangle are equal.
Question 12.
In what ratio does the point P(m, 6) divide the line (RBSESolutions.com) segment joining the points A(-4, 3) and B(2, 8)? Find the value of m. (CBSE 2011)
Solution :
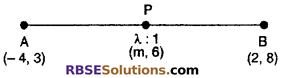
Let Point P(m, 6) divides the line segment joining the point A(-4, 3) and B(2, 8) in the ratio λ : 1
By section formula
Coordinate of y of point P
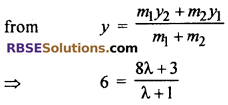
⇒ 6(λ + 1) = 8λ + 3
⇒ 6λ + 6 = 8λ + 3
⇒ 6λ – 8λ = 3 – 6
⇒ -2λ = -3
⇒ λ = \(\frac { -3 }{ -2 }\) = \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\)
λ : 1 = 3 : 2
Hence, required ratio = 3 : 2
x co-ordinate of point P
\(m=\frac { 2\lambda -4 }{ \lambda +1 }\)
Put the value of λ from equation (i)
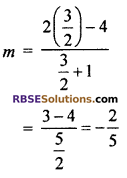
So, m = –\(\frac { 2 }{ 5 }\)
Question 13.
If the points P(x, y), A(3, 6) and B (-3, 4) and collinear, then (RBSESolutions.com) prove that 3x + y – 5 = 0. (CBSE 2012)
Solution :
Let required point P(x, y) which is equidistant from the point A(3, 6) and B(-3, 4)
So, PA = PB
⇒ PA2 = PB2
⇒ (x – 3)2 + (y – 6)2 = [x -(-3)]2 + (y – 4)2
⇒ x2 + 9 – 6x + y2 + 36 – 12y = (x + 3)2 + (y – 4)2
⇒ x2 + y2 – 6x – 12y + 45 = x2 + 6x + 9 + y2 + 16 – 8y2
⇒ x2 + y2 – 6x – 12y + 45 = x2 + y2 + 6x – 8y + 25
⇒ -6x – 12y = 6x – 8y + 25 – 45
⇒ -6x – 12y – 6x + 8y = -20
⇒ -12x – 4y = -20
⇒ 3x + y = 5
⇒ 3x + y – 5 = 0
Question 14.
Find the co-ordinate of point P on the line segment joining the (RBSESolutions.com) points A(-2, -2) and B(2, -4) such that AP = \(\frac { 3 }{ 7 }\)AB and point P is lie on line segment AB (CBSE 2012, 15)
Solution :
Let required point is P(x, y)
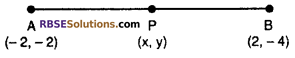
Given AP = \(\frac { 3 }{ 7 }\) AB ……(i)
But PB = AB – AP
= AB – \(\frac { 3 }{ 7 }\)AB
= \(\frac { 7AB-3AB }{ 7 }\)
PB = \(\frac { 4 }{ 7 }\) AB ……(ii)
From equation (i) and (ii)
AP : PB = \(\frac { 3 }{ 7 }\)AB : \(\frac { 4 }{ 7 }\)AB
AP : PB = 3 : 4
∴ Hence point P divides point A and B in the (RBSESolutions.com) ratio 3 : 4 respectively.
∴ Hence co-ordinate of point P.
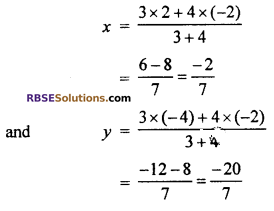
Hence co-ordinate of point P = \(\left( \frac { -2 }{ 7 } ,\frac { -20 }{ 7 } \right)\)
![]()
Question 15.
Find the area of rhombus which has (RBSESolutions.com) vertices (3, 0), (4, 5), (-1, 4) and (-2, -1) respectively. (NCERT)
Solution :
Let co-ordinate of vertices of rhombus ABCD are A(3 , 0) B(4, 5), C(-1, 4) and D(-2, -1) respectively.
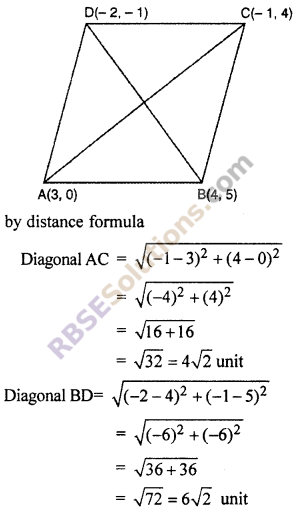
We know that area of rhombus = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × first diagonal × second diagonal
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × 4√2 × 6√2
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × 24 × 2
= 24 square unit
Hence area of rhombus = 24 square unit.
Question 16.
Find the co-ordinate of equidistant (RBSESolutions.com) point from the points A(-2, -3), B(-1, 0) and C(7, -6) respectively.
Solution :
Let P(x, y) is a required point.
i.e., P(x, y) is equidistant from points A B and C
According to question
PA = PB = PC
Now PA = PB
⇒ PA2 = PB2
⇒ (x + 2)2 + (y + 3)2 = (x + 1)2 + (y – 0)2
⇒ x2 + 4x + 4 + y2 + 9 + 6y = x2 + 1 + 2x + y2
⇒ 4x + 6y + 13 = 2x + 1
⇒ 2x + 6y = -12
⇒ x + 3y = -6 …..(i)
and PA = PC
⇒ PA2 = PC2
⇒ (x + 2)2 +(y + 3)2 = (x – 7)2 +(y + 6)2
⇒ x2 + 4x + 4 +y2 + 9 + 6y = x2 + 49 – 14x + y2 + 36 + 12y
⇒ 4x + 6y + 13 = -14x + 12y + 85
⇒ 18x – 6y = 72
⇒ 9x – 3y = 36 …(ii)
Adding (RBSESolutions.com) equation (i) and (ii)
10x = 30
x = \(\frac { 30 }{ 10 }\) = 3
Put x = 3 in equation (i)
3 + 3y = -6
3y = -6 – 3 = -9
y = \(\frac { -9 }{ 3 }\) = -3
Hence, co-ordinate of required point = (3, -3)
![]()
We hope the given RBSE Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 9 Co-ordinate Geometry Additional Questions will help you. If you have any query regarding Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 9 Co-ordinate Geometry Additional Questions, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.