RBSE Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Structure of Earth are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 10 Science. Here we have given Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 10 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Structure of Earth.
| Board | RBSE |
| Textbook | SIERT, Rajasthan |
| Class | Class 10 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 15 |
| Chapter Name | Structure of Earth |
| Number of Questions Solved | 43 |
| Category | RBSE Solutions |
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 10 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Structure of Earth
Textbook Questions Solved
I. Multiple Choice Questions
RBSE Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Question 1:
Which of the following is not a name of earth?
(a) Land
(b) Gaiya
(c) Red planet
(d) Terra
Answer:
(c) Red planet
RBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Question 2:
How much of the earth’s surface is covered with water?
(a) 70%
(b) 30%
(c) 50%
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) 70%
Structure Of Earth Class 10 Question 3:
Which element is in maximum abundance on earth?
(a) Silicon
(b) Gold
(c) Oxygen
(d) Iron
Answer:
(d) Iron
RBSE Solutions For Class 10 Science Question 4:
The largest port of Harappa Civilization was in which city?
(a) Dwarka
(b) Dholavira
(c) Surat
(d) Karnavati
Answer:
(b) Dholavira
Class 10 Science Chapter 15 RBSE Question 5:
What causes tides?
(a) Sun
(b) Moon
(c) Both
(d) Sun and moon aligning along a line
Answer:
(d) Sun and moon aligning along a line
Structure of Earth Very Short Answer Type Questions
RBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Notes Question 6:
What is the reason for solstices on earth?
Answer:
Earth’s tilt on its axis
RBSE Solutions Class 10 Science Question 7:
Earthquake is measured on which scale?
Answer:
Richter scale
RBSE Solution Class 10 Science Question 8:
Where are tectonic plates situated?
Answer:
In the crust of earth
RBSE Solution 10th Class Science Question 9:
What causes tsunami?
Answer:
Earthquake at the bottom of ocean.
RBSE Solutions Science Class 10 Question 10:
Low pressure at centre causes which type of wind?
Answer:
Cyclone
Structure of Earth Short Answer Type Questions
RBSE Solution Class 10th Science Question 11:
What will be the situation after earthquake above the scale 7 Richter at a place?
Answer:
An earthquake of 7 or more on Richter scale can be highly devastating. It usually causes immense damage to houses and buildings. Landslides also happen in case of powerful earthquakes. It can result in loss of life and property.
Science Class 10 RBSE Solutions Question 12:
What are ocean currents?
Answer:
Ocean currents are also referred to as rivers flowing in oceAnswer: The water flows in a certain direction in these rivers. Some ocean currents have warm water, while some others have cold water. Unlike a river, flow of current in ocean does not happen because of slope of land but happen because of difference in temperature and density.
Class 10 RBSE Solutions Science Question 13:
What is the benefit of weathering forces in agriculture?
Answer:
Weathering agents have proved highly beneficial for agriculture. Soil is most important for agriculture and soil is made by agents of weathering. Large plains, which are ideal for farming have been made by agents of weathering. Many minerals could come out of rocks because of weathering.
RBSE Solutions Of Class 10 Science Question 14:
Name four factors which help in weathering.
Answer:
Four factors which help in weathering are as follows:
(a) Temperature
(b) Rain
(c) Snow
(d) Wind
RBSE Solutions For Class 10th Science Question 15:
How did the moon come into existence?
Answer:
About 4.4 billion years ago, a celestial body of the size of the mars hit the earth which resulted in formation of the moon. The moon is the only natural satellite of the earth.
Structure of Earth Long Answer Type Questions
Class 10th RBSE Solution Science Question 16:
With the help of a suitable diagram, explain the internal structure of earth.
Answer:
The earth is composed of three layers, viz. crust, mantle and core. Boundaries of these layers have been determined on the basis of chemical composition and physical properties.
- Crust: The outermost layer of the earth is a solid layer and is called crust. The thickness of the crust is not uniform at every place. Due to this, we get to see mountains and oceans at different places. The crust can be divided into two types, viz. lithosphere and hydrosphere. The atmosphere is usually considered as a part of the lithosphere. Most of the lithosphere is composed of soil. The portion of lithosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere where living beings are found is called biosphere.
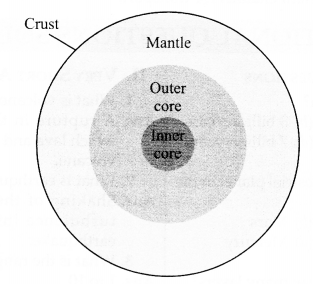
- Mantle: The second layer of earth is called mantle. This is the thickest layer and most of it is composed of hot and molten rocks. These are silicate rocks and have iron and magnesium in greater quantity than in the crust. Bubbles keep on appearing in this layer the way bubbles form in boiling water. Mantle keeps on vibrate in the middle portion of the earth.
- Core: The innermost portion of the earth is called core. This is hottest due to being at the centre. The temperature of the core is about 7000 degree. The heat trapped during formation of earth is the cause of high temperature of core. The core is divided into two parts, viz. outer core and inner core. The outer core is in liquid form and is mainly composed of iron and nickel. The inner core is in solid form is mainly composed of iron.
RBSE Solutions 10 Science Question 17:
What do vou understand bv internal moulding forces of earth? Explain any two of them.
Answer:
These forces continue their work inside the earth and are not apparent from outside. These forces come into origin because of expansion and contraction of rocks due to high temperature inside the earth. These forces also come into origin because of movement of hot molten magma. When the internal moulding forces work perpendicular to the layers of the earth, then some portions of the crust become elevated and some other portions of the crust move deeper. This results in formation of continents, islands, plateau, plain, sea, etc. on the surface. The sedimentary rocks formed inside the oceans, rise and reach the inner portions of the continents. When internal moulding forces work in horizontal direction then waves are formed.
These waves cause heavy shakeup of the rocks on the crust. These results in folds, prolapse, fissures on the surface, formation mountains and valleys.
Class 10 Science RBSE Solutions Question 18:
What is erosion? Explain the significance of any two forces of erosion on human life.
Answer:
External forces which facilitate transport of substances from one place to another on earth are called erosion forces, e.g. moving air (wind), water (rivers) and ice (glaciers).
Significance of wind on human life:
- Wind causes changes in weather and thus affects our life in significant ways.
- Wind helps in navigation of ships.
- Wind energy is being harnessed to produce electricity.
- Wind changes the landform around us.
Significance of river:
- River changes the landform along its course.
- River has always played important role in development of human civilization and many great civilizations have flourished along rivers.
- River brings flood which may cause havoc.
- River serves as important channel for transport.
Structure of Earth Additional Questions Solved
I. Multiple Choice Questions
10th Class RBSE Solution Science Question 1:
What is the age of earth?
(a) 1 billion years
(b) 3 billion years
(c) 4.5 billion years
(d) 7 billion years
Answer:
(d) 4.5 billion years
Class 10 RBSE Solution Science Question 2:
Which is the largest terrestrial planet in the Solar System?
(a) Earth
(b) Mars
(c) Venus
(d) Mercury
Answer:
(a) Earth
Class 10 Science RBSE Solution Question 3:
Earth is composed of how many layers?
(a) One
(b) Two
(c) Three
(d) Four
Answer:
(c) Three
RBSE Solution For Class 10 Science Question 4:
Movement of which of the following causes earthquake?
(a) Wind
(b) Glacier
(c) River
(d) Tectonic plate
Answer:
(d) Tectonic plate
RBSE Solution Science Class 10 Question 5:
The inner core of earth is mainly composed of which element?
(a) Iron
(b) Gold
(c) Nickel
(d) Platinum
Answer:
(a) Iron
Question 6:
Most devastating earthquakes happen along which type of tectonic plate boundary?
(a) Constructive
(b) Convergent
(c) Conservative
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Convergent
Question 7:
Which state of India lies in the low risky zone of earthquake inspite of that suffered from devastating earthquake in 1737?
(a) Jammu & Kashmir
(b) Uttarakhand
(c) Himachal Pradesh
(d) West Bengal
Answer:
(d) West Bengal
Structure of Earth Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1:
What is volcano?
Answer:
A rupture in the earth’s crust through which lava and magma come out is called volcano.
Question 2:
What is earthquake?
Answer:
Shaking of the earth’s surface due to turbulence inside the earth is called earthquake.
Question 3:
What is the range of Richter scale?
Answer:
1 to 10
Question 4:
What is an agent of weathering?
Answer:
Forces which break down rocks are called agents of weathering which are heat from sun, rain, frost and wind.
Question 5:
What is an agent of erosion?
Answer:
Forces which transport substances from one part to another part on earth are called agents of erosion e.g., air, water and ice.
Question 6:
What is a tide?
Answer:
Periodic rise and fall in ocean level is called tide.
Question 7:
What causes tide?
Answer:
When moon and sun align along a line, this alignment causes gravitional pull on ocean water and results in tide.
Structure of Earth Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1:
What is an Astronomical Unit?
Answer:
The earth is at a distance of about 15 crore km from the sun. The distance between sun and earth is called one Astronomical Unit (1 AU).
Question 2:
Write a short note on earth’s crust.
Answer:
The outermost layer of the earth is a solid layer and is called crust. The thickness of the crust is not uniform at every place. Due to this, we get to see mountains and oceans at different places. The crust can be divided into two types, viz. lithosphere and hydrosphere. The atmosphere is usually considered as a part of the lithosphere. Most of the lithosphere is composed of soil. The portion of lithosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere where living beings are found is called biosphere.
Question 3:
Write a short note on mantle of earth.
Answer:
The second layer of earth is called mantle.
This is the thickest layer and most of it is composed of hot and molten rocks. These are silicate rocks and have iron and magnesium in greater quantity than in the crust. Bubbles keep on appearing in this layer the way bubbles form in boiling water. Mantle keeps on vibrating in the middle portion of the earth.
Question 4:
Write a short note on core of earth.
Answer:
The innermost portion of the earth is called core. This is hottest due to being at the centre. The temperature of the core is about 7000 degree. The heat trapped during the formation of earth is the cause of high temperature of core. Proofs have been found which show that the core is cooling down gradually. The core is divided into two parts, viz. outer core and inner core. The outer core is in liquid form and is mainly composed of iron and nickel. The inner core is in solid form is mainly composed of iron. The inner core also contains gold and platinum.
Question 5:
What do you understand by volcano?
Answer:
Volcano is the most unique phenomenon among internal moulding forces. It causes turbulence inside the earth which shakes the earth and smoke, ash, vapour and gases come out by piercing the surface of the earth. Sometimes, very hot rocks melt and come out in the form of lava. This causes large scale destruction all around and does immense damage to life and materials.
Question 6:
What do you understand by Richter scale?
Answer:
Intensity of earthquake is measured on Richter scale. This is done by a device called seismograph. The Richter scale varies from 1 to 10. Earthquakes upto 4 Richter scale are weak and seldom noticed. Earthquakes up to 5.5 Richter are considered as strong and those beyond to Richter are considered as devastating. Earthquakes beyond 7 Richter are highly devastating in nature and cause large scale destruction.
Question 7:
Write a short note on tsunami.
Answer:
Tsunami is a Japanese word which means ocean waves due to earthquake. An earthquake of more than 7 Richter at the bottom of ocean is the prime reason of tsunami. Tsunami travels in two directions from the epicenter, i.e. towards the coast and towards deeper ocean. The tsunami which moves towards the coast causes destruction. The debris which flows along with tsunami can destroy life and material even in the hinterland.
Structure of Earth Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1:
What causes earthquake? Explain tectonic plate theory.
Answer:
The imbalance in internal structure of earth causes earthquake. This imbalance can also be caused by pressure from natural or man-made aquifers and also by explosion. Earthquake is usually explained on the basis of tectonic movement theory.
Earth’s crust is composed of 29 tectonic plates. Six of the tectonic plates are most important. These plates keep on moving at very slow pace. All kinds of moulding activities take place along the edges of these plates. Boundaries of tectonic plates are of three types, viz. transform boundary, divergent boundary and convergent boundary. Transform boundary is conservative in nature, divergent boundary is constructive and convergent boundary is destructive. Highly destructive earthquake happen due to convergent or destructive boundaries. Collision of plates is considered as the prime reason of earthquakes in northern India, Tibet and Nepal. Earthquakes also happen due to other kinds of boundaries of tectonic plates but it is difficult to explain such earthquakes.
Question 2:
How do weathering forces facilitate soil formation?
Answer:
Weathering forces keep on breaking the rocks to convert them into soil. The heat from the sun, rain, frost and wind physically break the rocks. Rocks expand because of heat from the sun and contract when they cool down during night. Continuous contraction and expansion make the rocks weaker and they start to break down. Force of the falling rain increases the rate of breakdown of rocks. The rainwater also weathers down the rocks. Water which gets collected in the fissures in the rock becomes frozen due to frost. We know that volume of water increases on freezing. Increased volume of ice further widens the fissures in rocks. When dust particles hit the rocks because of wind, they work like sandpaper and weather the rock. This is a slow process but its whole effect becomes apparent after thousands of years. Weathering by wind is considered as the reason for lack of mountains in deserts. Mountains which existed in desert changed into sand due to weathering.
Many chemical processes keep on happening in nature, e.g. oxidation, carbonation, coalescing of water molecules, dissolution, etc. These processes also facilitate weathering of rocks by making them weaker. Biological forces like plants, animals, microbes and humans also play important role in weathering of rocks. Roots of plants penetrate the rocks and break the rocks when the roots grow. Many animals break the rocks by making holes. Man has proved to be the biggest enemy of rocks. Weathering potential of man is greatest because of machines and gunpowder. Living beings give off many chemicals in nature and such chemicals help in weathering of rocks.
Question 3:
What is glacier? What is the effect of global warming on glacier?
Answer:
A thick slab of ice in motion is called glacier. Glacier is defined as a persistent body of dense ice which keeps on moving because of its own weight.
Effect of global warming on glaciers: The average temperature of the earth has been increasing in recent years. This is called global warming. Rate of melting of glaciers is more than the rate of their formation due to global warming. Hence, glaciers are shrinking in size. Melting of glaciers has resulted in rise in sea levels. Many cities in coastal areas face the risk of gradually getting submerged in oceAnswer:
Question 4:
What is ocean current? What is the significance of ocean current?
Answer:
Ocean current are also referred to as rivers flowing in oceAnswer: The water flows in a certain direction in these rivers. Some ocean currents have warm water, while some others have cold water. Unlike a river; flow of current in ocean does not happen because of slope of land but happen because of difference in temperature and density.
Significance of Ocean Current: Ocean current has profound effect on human life. Warm currents keep a place warm, while cold currents keep a place cold. Wind flowing through regions of warm current bring plenty of moisture and cause rains at higher altitudes. There are places where a warm current meets with a cold current. There is big temperature differential at such places which causes storms like hurricane or typhoon. Ocean current dlso influences navigation of ships and life of sea creatures.
We hope the given RBSE Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Structure of Earth will help you. If you have any query regarding Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 10 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Structure of Earth, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.