RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 8 Micro-Organisms are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Science. Here we have given Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 8 Micro-Organisms.
| Board | RBSE |
| Textbook | SIERT, Rajasthan |
| Class | Class 6 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 8 |
| Chapter Name | Micro-Organisms |
| Number of Questions Solved | 67 |
| Category | RBSE Solutions |
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 8 Micro-Organisms
Intext Questions
Question 1.
How to preserve the left food at home? (Page 67)
Answer:
We keep it in refrigerator.
Question 2.
What changes occur in bread kept in open and moist place? (Page 67)
Answer:
Green and black patches are seen on bread.
Question 3.
What happens when food is contaminated by micro-organisms? (Page 67)
Answer:
Then the food is not edible and we can become sick if we eated.
Question 4.
Is the contamination of food a chemical reaction? (Page 67)
Answer:
Yes, it is a chemical reaction.
Question 5.
Before one decade, glass syringe and needle were kept in boiling water before using them. Why were they heated? (Page 67)
Answer:
They were heated to make them bacteria free.
Question 6.
Which type of syringes are used in hospitals now a days?
Answer:
Now a days, sterilized needles and syringes are used and they can be used only once.
Activities
Activity – 1 (Page-62)
Question 1.
In how many days its surface got covered with white filament – like structures and black spots?
Answer:
In two or three days.
Observe these spots with the help of a magnifying glass.
Question 2.
Which type of structures do you see?
Answer:
Thin, white and black coloured patches are seen.
Question 3.
Can you see these structures without a magnifying glass?
Answer:
No, these structures are not seen without the magnifying glass.
Question 4.
What are these structures?
Answer:
These structures are the filaments and spores of fungi.
Question 5.
Where did these structures come from?
Answer:
Spores of many micro-organisms remain suspended in air. In presence of favorable environment and nutrient, they grow and form filament – like structures.
Activity – 2 (Page 62)
Question 1.
Which type of structures do you see?
Answer:
Round, cylindrical, etc. shaped structures are seen.
Question 2.
What are these structures?
Answer:
These structures are micro-organisms.
Activity – 4 (Page 65)
Question 1.
What do you see in roots?
Answer:
We see node – like structures.
Question 2.
What are these node – like structures called and how are they formed?
Answer:
These node – like structures are called root nodes or nodules. Root nodules are formed on the roots of plants that associate with rhizobium bacteria.
Question 3.
What is their function?
Answer:
They help in converting atmospheric nitrogen into nitrates.
Question 4.
Are they found in the roots of all types of plants?
Answer:
No, they are found in the roots of leguminous plants.
Activity – 5 (Page 67)
Question 1.
Observe them after 6 – 7 days and see what has happened?
Answer:
They are rotten.
Question 2.
Have you ever imagined that the mangoes were rotten but the mango pickle made by your grand mother or mother does not spoil for a long time. Why this happens?
Answer:
This is possible due to the preservation of food stuff.
Exercises
Choose the correct option
Question 1.
Which of the following is a micro-organism?
(a) Virus
(b) Fungi
(c) Bacteria
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 2.
Which micro-organism possess characters of both – living and non – living?
(a) Bacteria
(b) Fungi
(c) Virus
(d) Protozoa
Answer:
(c) Virus
Question 3.
Which of these is an antibiotic?
(a) Penicillin
(b) Insulin
(c) Aldrin
(d) Auxin
Answer:
(a) Penicillin
Question 4.
Which of these is an unicellular organism?
(a) Amoeba
(b) Cow
(c) Star fish
(d) Humans
Answer:
(a) Amoeba
Fill in the blanks
1. ………………. can be seen with the help of a microscope.
2. Food ingredients are prepared by unicellular organism named …………. .
3. …………… bacteria convert the atmospheric nitrogen into nitrates.
4. The process of removal of water from food items is called …………… .
Answer:
1. Micro-organisms
2. Yeast
3. Rhizobium
4. dehydration
Match the following correctly
1. Virus (a) Nitrogen fixation
2. Rhizobium (b) AIDS
3. Yeast (c) Curd
4. Lactobacillus (d) Fermentation
Answer:
1. (b), 2. (a), 3. (d), 4. (c).
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write names of the different types of micro-organisms?
Answer:
The different types of micro-organisms are :
Virus, bacteria, fungi, protozoa, algae and mycoplasma.
Question 2.
Explain about micro-organisms which are useful in our life?
Answer:
Useful micro – organisms in our life are :
- Lactobacillus bacteria – Useful is making curd from milk.
- Rhizobium bacteria – It helps in fixation of nitrogen.
- Xenthomonas compestris – It is used to make tooth paste.
- Pencillium – Pencillin is used as a vaccine and antibiotic.
Question 3.
What is pasteurization?
Answer:
It is a technique of killing genus. Before packaging milk or other food items in cans or bottles, milk or the food items are heated at 60°C for 30 minutes and then cooled down. This process is repeated 2 – 3 times and it kills the harmful micro organisms present in them.
Question 4.
What is food poisoning? Why does it happen?
Ans.
Food poisoning is the process that makes food toxic. A bacteria called Clostridium botulinum, causes food poisoning and the person who eats this food suffers from vomiting and diarrhoea and in some cases, it may lead to death.
Question 5.
Write the harms caused by micro – organisms? .
Answer:
Some micro – organisms are harmful in the following ways :
- Some micro – organisms cause disease like T.B., whooping cough, diptheria, tetanus, cholera, malaria, skin diseases etc.
- Some micro – organisms spoil food stuff.
- Some micro – organisms causes food poisoning.
- Some micro – organisms damage valuable items.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are micro-organisms? Explain different types of micro-organisms with example.
Answer:
Micro-organisms Organisms that can be seen only with the help of a microscope are called micro-organisms. Micro – organisms are of 6 types.
- Virus : They are the minutest structures. They are also called the connecting link between living and non-living because they possess both living as well as non – living characteristics.
- Micro plasma : It is the smallest cell which can be sieved even through a virus filter. It causes diseases in plants.
- Bacteria : They are unicellular prokaryotes. Bacteria are found in all places around us.
- Fungi : They are micro-organisms with simple structure and can be unicellular or multi cellular. Science They lack chlorophyll in their cells. So, they can not prepare their own food.
- Protozoa : They are unicellular organisms.
Example : amoeba, paramecium etc. - Algae : They are micro – organisms having simple structure and may be unicellular or multi – cellular. Water in ponds, puddles and drains appear green due to the presence of algae.
Question 2.
What is food preservation? Write the remedies for preventing contamination of food items.
Answer:
The process of maintaining the nutrient richness and quality of food and other edible substances is called food preservation. Remedies for preventing contamination of food items :
- Through refrigeration
- Through sterilization
- With the help of pasteurization
- With the help of dehydration
- Using boiling method
- By using chemicals
- By using salt, sugar, oil and vinegar
- By using disinfectants
- By making water bacteria free.
Question 3.
Draw diagrams of the following:
1. Amoeba
2. Paramaecium
3. Algae
4. Fungi
5. Virus
6. Root nodules of plants belonging to leguminous family
Answer:
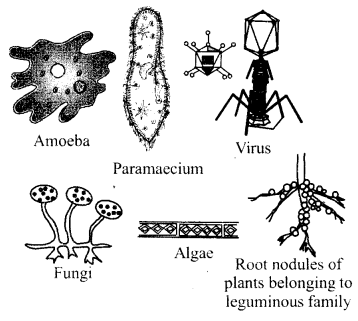
Practical Work
Question 1.
Examine the benefits and harms caused by micro-organisms in our daily life and make a list.
Answer:
Beneficial micro – organisms:
- Yeast – used in bakery
- Chlorella – Source of protein
- Clostridium botulinum, Anthracoid bacilli – for making immun logical substances.
- Penicillium – Used as a vaccine and antibiotic
- Rhizobium bacteria – used for biological nitro-gen fixation.
- Xenthomonas compestris – Used to make tooth-paste.
Harmful micro – organisms :
- Virus – Causes AIDS, mumps, rabies, etc.
- Bacteria – Causes T.B., whooping cough, tetanus, cholera, etc.
- Protozoa – Causes malaria
- Clostridium botulinum – This bacteria causes food poisoning.
Question 2.
Collect information from a nearby hospital or medical store about antibiotics and make a list of them.
Answer:
List of Antibiotics :
- Neomycin
- Amikacin
- Gentamicin
- Kanamycin
- Netilmicin
- Tobramycin
- Paromomycin
- Streptomycin
- Rifaximin
- Clindamycin
Question 3.
Make a model of any one micro-organism.
Answer:
Students should do it on their own.
Other Important Questions
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
The connecting link between living and non – living is
(a) Virus
(b) Bacteria
(c) Fungi
(d) Protozoa
Answer:
(a) Virus
Question 2.
HIV is a
(a) Virus
(b) Bacteria
(c) Fungi
(d) Mycoplasma
Answer:
(a) Virus
Question 3.
Milk is converted into curd by
(a) Rhizobium
(b) Clostridium
(c) Lactobacillus
(d) Spirogyra
Answer:
(c) Lactobacillus
Question 4.
Rust of wheat is done by
(a) Fungi
(b) Bacteria
(c) Protozoa
(d) None
Answer:
(a) Fungi
Question 5.
To make water germ – free, we use
(a) Bleaching powder
(b) Chlorine
(c) Potassium permanganate
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Fill in the blanks
1. …………. of many micro-organisms remain suspended in air.
2. Some fungi live as …………… on plants and animals.
3. ……………………… a life saving drag is prepared from a fungi named penicillium.
4. The process of keeping food items at low temperature is called …………… .
Answer:
1. Spores
2. parasites
3. Penicillium
4. Refrigeration
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write the full from of TMV.
Answer:
Tobacco Mosaic Virus.
Question 2.
Write the full form of HIV.
Answer:
Human Immuno Deficiency Virus
Question 3.
Write the names of two diseases caused by mycoplasma in plants.
Answer:
- Little leaf of brinjal
- Sesame phyllody
Question 4.
Write the names of any two protozoans.
Answer:
Amoeba, paramaecium.
Question 5.
Write the names of a prokaryotic algae.
Answer:
Blue green algae.
Question 6.
Write the name of the vector of black rust disease in wheat.
Answer:
Puccinia graminis tritici
Question 7.
Write the name of two unicellular, eukaryotic algae.
Answer:
- Chlamydomonas
- Chlorella
Question 8.
Which fungi is used in making bread and jalebi?
Answer:
Yeast
Question 9.
Which, micro-organism is used in making toothpaste?
Answer:
Xenthomonas compestris.
Question 10.
Which instrument is used to make the equipment’s and objects used in an operation germ – free?
Answer:
Autoclave.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is an algae? Give few examples.
Answer:
They are micro-organisms having simple structure and may be unicellular or multi cellular. Water in ponds, puddles and drains appear green due to the presence of algae.
Example : Chlamydomonas, Chlorella, spirogyra, ulothrix and blue – green algae.
Question 2.
What is a nitrogen cycle? Explain.
Answer:
When decomposition of dead animals and plants occur, then nitrogen present in them is released into the atmosphere. This nitrogen is again obtained by plants. In this way, this cycle continues in nature. As a result, the amount of nitrogen in the soil remains constant. The process of conversion of free atmospheric nitrogen into usable compounds and reaching in living beings and then again release of nitrogen in the atmosphere is called Nitrogen cycle.
Question 3.
Explain the disease causing microorganisms.
Answer:
Disease causing micro-organisms are called pathogens. T.B., whooping cough, diptheria, tetanus, cholera, malaria, skin diseases etc. in humans are caused by these micro-organisms. Anthrax is a disease caused by micro-organisms in humans and animals. Foot and mouth disease in cows is caused by a virus. Citrus canker (bacterial), rust of wheat (fungal), yellow mosaic in lady finger (viral) are caused by micro – organisms.
Question 4.
How do micro-organisms spoil food stuff and valuable items?
Answer:
Cereals, pulses, ripe fruits, pickels, etc. get spoiled due to micro-organisms. So, they must be protected from being infected by micro-organisms. Micro – organisms damage valuable items made of clothes, paper, wood, leather, etc. which lowers their quality.
Question 5.
Write the ways to protect items from harmful micro – organisms.
Answer:
- Cereals, pulses, clothes, etc. must be kept in sunlight from time to time.
- Cooked dal, milk, etc. must be kept in cool place.
- Oils in pickles and sugar in jams can be used.
- Food stuffs can be prevented by using vinegar.
- Neem leaves and balls of mercury must be used in grains of paddy and pulses.
Question 6.
What is refrigeration? How are food items preserved in a refrigerator?
Answer:
The process of keeping food items at low temperature is called refrigeration. In process of refrigeration, the temperature is low. Biological activities of micro-organisms become slow at low temperature. So, food stuff does not get spoiled easily when kept in refrigerator.
Question 7.
What is a sterilization? Explain.
Answer:
The process of keeping syringes and needle of an injection in boiling water to make them germ free is called sterilization. To make the equipment’s and objects used in an operation germ free, an instrument named auto – clave is used. It works like a pressure cooker. UV rays can also be used to make objects germ – free.
Question 8.
Write about two common methods of food preservation.
Answer:
- Dehydration : In this process, water is removed from food items, e.g. keeping wheat and pulses in sunlight to remove moisture.
- Using salt, sugar, oil and vinegar : Salt, sugar, oil and vinegar are used in the preservation of meat, pickles, jam, jelly and vegetables.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Give two examples of each
1. Virus
2. Bacteria
3. Fungi
4. Protozoa
5. Algae
Answer:
- Virus – TMV (Tobacco Mosaic Virus), HIV Human Immune deficiency Virus.
- Bacteria – Lactobacillus, E. Coli.
- Fungi – Yeast, Pencillium.
- Protozoa – Amoeba, paramaecium.
- Algae – Spirogyra, chlamydomonas.
Question 2.
What is a fungi? Explain.
Answer:
Fungi is also called fungus or moulds. They are micro-organisms with simple structure and can be unicellular or multicellular. They lack chlorophyll in their cells. So, they cannot prepare their own food. Some fungi obtain food as saprophytes by absorbing nutrients from decaying organic substances. e.g. mushroom. Some fungi live as parasite on plants and animals, e.g. Puccinia graminis tritici (black rust disease) in wheat and Sclerospora graminicola (downy mildew disease) in millet. Some fimgi live in symboitic relation with algae.
Question 3.
Explain the role of microorganisms in production of food and medicines.
Answer:
Production of food – Micro-organisms are used for the production of curd, cheese, vinegar, etc. Yeast is used for making bread and in fer menting the solution used in the preparation of jalebi. Chlorella is used to make soup and other food ingredients. Food ingredients produced by chlorella are used for making ice – creams. Preparation of medicines – Vitamin B12 is prepared from a bacteria named Clostridium botulinum and another bacteria named Anthracoid bacilli is used for preparing immunological substances. Penicillin, a life saving drug which is used as a vaccine and antibiotic, is prepared from a fungi named penicillium. Penicillin was discovered by Alexander Fleming.
Question 4.
Explain biological nitrogen fixation.
Answer:
Certain species of bacteria and some other micro-organisms convert the atmospheric nitrogen into such compounds that can be absorbed by plants. This process is called nitrogen fixation, e.g. Rhizobium bacteria is present in the root nodules of leguminous plants such as kidney bean, gram, pea, etc. These root nodules are present only in leguminous plants. Rhizobium bacteria are present in it. They are helpful in converting atmospheric nitrogen into nitrates. Nitrates make soil more fertile. Nitrates are the main source of nitrogen for plants. Nitrogen is an integral constituent of protein. Due to this reason, farmers grow leguminous crops like kidney bean, moth, cluster bean (guar) etc. in one year and cereal crops like millet, sorghum etc. in the next year.
Question 5.
Explain the process of pasteurization.
Answer:
Now a days, the use of canned food items is increasing. Before packaging milk or other food items in cans or bottles, milk or the food items are heated at 60°C for 30 minutes and then cooled down. This process is repeated 2 – 3 times and it kills the harmful micro-organisms present in them. This technique of killing germs is called pasteurization. Air is removed from the cans after pasteurized food items are packaged in cans because the micro-organisms cannot grow in the absence of air. The date mentioned on the cans before which the food item must be consumed is known as expiry date. We must always see the expiry date of canned food items before buying them. Such food items must be consumed before their expiry date.
We hope the RBSE Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 8 Micro-Organisms will help you. If you have any query regarding Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 8 Micro-Organisms, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.