Make use of our RBSE Class 12 Accountancy Notes here to secure higher marks in exams.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Accountancy Notes Chapter 2 Admission of a New Partner
Reconstruction of Partnership Firm:
When any change in existing agreement between partner’s, called reconstruction of partnership firm. Reconstruction of partnership firm can be in following situations :
- Admission of a new partner
- Change in sharing profit ratio
- Retirement of a partner,
- Death of any partner
- Merge of any firm. (Amalgamation of another firm).
Admission of a New Partner :
According to Indian Partnership Act, 1932, Section31 “a new partner can be admitted only with the consent of all the existing partner’s.” New Partner is not responsible for the work which was done before his admission. At that time of admission, the new partner brings his share goodwill (Premium) and capital. Old partners sacrifice a share of their profits in his favor and he gets a share in the future profits of a firm.
Adjustment at the Time of a Admission of a Partner :
Following adjustment are needed at the time of the admission of a new partner :
- Calculation of new profit sharing ratio
- Calculation of sacrifice ratio
- Accounting treatment of goodwill (premium)
- Accounting treatment for revaluation of assets and liabilities
- Accounting treatment of reserves and accumulated profits
- Adjustment of capitals on the basis of new profit sharing ratio
Calculation of New Profit Sharing Ratio
New or incoming partner is entitled to share future profit of the firm. In effect there is a change in the old profit sharing ratio. Since new or incoming partner acquires his share from old partners, it is necessary to determine new profit sharing ratio. New profit sharing ratio is the ratio in which all partner’s including new or incoming partner share future profits and losses of the firm. In sundry situation new profit sharing ratio will calculate as follows :
(1) When new partner’s share is given : When in question new partner’s share is given but it is not mentioned that how he will get his share from old partner. In this situation new profit sharing ratio will calculate as follows :
Illustration 1.
A and B are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 2 : 3. They admit C with \(\frac {1}{4} \) share in
profit. Calculate new profits sharing ratio.
Solution:
Let Total Profit be = 1
Share given to C = \(\frac {1}{4} \)
Remaining Share = 1 – \(\frac {1}{4} \) = \(\frac {3}{4} \)
A’s New Ratio = \(\frac {3}{4} \) x \(\frac {2}{5} \) = \(\frac {6}{20} \)
B’s New Ratio = \(\frac {3}{4} \) x \(\frac {3}{5} \) = \(\frac {9}{20} \)
C’s Share = \(\frac {1}{4} \)
New Profit Sharing Ratio = \(\frac {1}{4} \) : \(\frac {1}{4} \) : \(\frac {1}{4} \) = \(\frac{6: 9: 5}{20}\) = 6 : 9 : 5
(2) Sometimes the new partner “Purchase” his share of profit from the old partners equally. In such case, the new profit sharing ratios of the old partners will be ascertained by deducting the sacrifice made by them from their existing share of profit.
![]()
Illustration 2.
‘R’ and ‘S’ are partners sharing profits in the Ratio 7 : 3. They admit ‘P’ with \(\frac {1}{5} \) share in profits which he acquires equally from both, \(\frac {1}{10} \) from ‘R’ and \(\frac {1}{10} \) from ‘S’. Calculate the new profit sharing ratio.
Solution:
R’s Share = \(\frac {7}{10} \) – \(\frac {1}{10} \) = \(\frac {6}{10} \)
S’s Share = \(\frac {3}{10} \) – \(\frac {1}{10} \) = \(\frac {2}{10} \)
P’s Share = \(\frac {1}{10} \) + \(\frac {1}{10} \) = \(\frac {2}{10} \)
New Ratio = 6 : 2 : 2 or 3 : 1 : 1
(3) Sometimes new partner gets his share unequally from old partners, contribution of share made by old partners in favour of new partner will be deducted from old ratio to calculate new profit sharing ratio.
Illustration 3.
‘A’ and ‘B’ are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 7 : 3 ‘C’ joins the firms as a new partner and takes \(\frac {2}{7} \) from A and \(\frac {1}{7} \) from B. Calculate the new profit sharing ratio.
Solution:
A’s New Ratio = \(\frac {7}{2} \) – \(\frac {2}{7} \) = \(\frac {49 – 20}{70} \) = \(\frac {29}{70} \)
B’s New Ratio = \(\frac {3}{10} \) – \(\frac {1}{7} \) = \(\frac {21 – 10}{70} \) = \(\frac {11}{70} \)
C’s New Ratio =\(\frac {2}{7} \) + \(\frac {1}{7} \) = \(\frac {3}{7} \)
New Ratio of A, B and C = \(\frac {29}{70} \) : \(\frac {11}{70} \) : \(\frac {3}{7} \) = \(\frac {29 : 11 : 30}{70} \) or 29 : 11 : 30
![]()
(4) When new or incoming partner acquires his share from old or existing partners in a particular ratio, new or incoming partner may acquire a part of share of profits from one partner and a part of share of profits from another partner. In such a case, existing partners’ profit sharing ratio will change to the extent of share sacrificed on admission of the new or incoming partner. Existing partners’ share of profits in the reconstituted firm is determined by deducting the sacrifice made from the existing share of profits.
Illustration 4.
Ram and Shyam are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 5 : 3, Mohan join the firm as a new partner Ram gives \(\frac {1}{4} \)th of his share and Shyam gives \(\frac {2}{5} \)th of his share to new partner. Find out new profit sharing ratio.
Solution:
Calculation of Surrendered Share
Ram = \(\frac {5}{8} \) x \(\frac {1}{4} \) = \(\frac {5}{32} \)
Shyam = \(\frac {3}{8} \) x \(\frac {2}{5} \) = \(\frac {6}{40} \)
Calculation of New Ratio
Ram = \(\frac {5}{8} \) – \(\frac {5}{32} \) = \(\frac {20 – 5}{32} \) = \(\frac {15}{32} \)
Shyam = \(\frac {3}{8} \) x \(\frac {6}{40} \) = \(\frac {15 – 6}{40} \) = \(\frac {9}{40} \)
Mohan = \(\frac {5}{32} \) + \(\frac {6}{40} \) = \(\frac {25 + 24}{160} \) = \(\frac {49}{160} \)
New Ratio of Ram, Shyam And Mohan = \(\frac {15}{32} \) : \(\frac {9}{40} \) : \(\frac {49}{160} \)
\(\frac {75 : 36 : 49}{160} \) = \(\frac {75}{160} \) : \(\frac {36}{160} \) : \(\frac {49}{160} \) or 75 : 36 : 49
(5) If new partner gets his share from a particular partner or partners, sacrifice made by a particular partner or partners will be deducted from their old share of profits to calculate new profit sharing ratio.
Illustration 5.
A and B are partner in a firm sharing profit in 3 : 1 ratio. C admitted a new partner for – \(\frac {1}{4} \) profit share. He gets his share from A. In this situation calculate new profit sharing ratio.
Solution:
New Profit Share Ratio of A = \(\frac {3}{4} \) – \(\frac {1}{4} \) = \(\frac {2}{4} \)
New profit share ratio of B = \(\frac {1}{4} \)
New profit share ratio of C = \(\frac {1}{4} \)
New profit sharing ratio of A, B and C = \(\frac {1}{4} \) : \(\frac {1}{4} \) : \(\frac {1}{4} \) = 2 : 1 : 1
(6) Sometimes the old partners surrender a particular fraction of their shares in favour of the new partner. In such case, the new partner’s share is calculated by adding the surrendered portion of share by the old partners. Old partner’s shares are calculated by deducting the surrendered share from their old shares.
![]()
Illustration 6.
A and B are partners in a firm, sharing profits in the ratio of 5 : 3. C is admitted as a new partner. A sacrifices 2/5th
of his share in profits in favour of C and B ith of his share in favour of C.
Calculate the new profit sharing ratio between A, B and C.
Solution:
Sacrifice of A = \(\frac {5}{8} \) x \(\frac {2}{5} \) = \(\frac {10}{40} \) or \(\frac {1}{4} \)
Sacrifice of B = \(\frac {3}{8} \) x \(\frac {1}{5} \) = \(\frac {3}{40} \)
New Profit Sharing Ratio A = \(\frac {5}{8} \) – \(\frac {10}{40} \) = \(\frac {25 – 10}{40} \) = \(\frac {15}{40} \)
B = \(\frac {3}{8} \) – \(\frac {3}{40} \) = \(\frac {15 – 3}{40} \) = \(\frac {12}{40} \)
C = \(\frac {10}{40} \) + \(\frac {3}{40} \) = \(\frac {13}{40} \)
So, New profit sharing ratio A, B and C =\(\frac {15}{40} \) : \(\frac {12}{40} \) : \(\frac {13}{40} \) = 15 : 12 : 13
Sacrifice Ratio :
Sacrifice ratio is the ratio in which the old or existing partners forego, sacrifice their share in favour of the new partner. Calculation of sacrifice ratio is necessary because amount of goodwill brought by new partner will distributed in old partners in sacrifice ratio.
![]()
Illustration 7.
(A) A and B are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 3 : 2. C is admitted as a partner. The new profits sharing ratio of A, B and C is 4 : 3 : 2. Find the sacrificing ratio.
(B) A and B are partners sharing profit in the ratio of 4 : 3. C is admitted as a partner. The new profit sharing ratio is 3 : 2 : 1. Find out the sacrificing ratio.
Solution:
sacrifice ratio = Old Ratio – New Ratio
A’s sacrifice ratio = \(\frac {3}{5} \) – \(\frac {4}{9} \) = \(\frac {27 – 20}{45} \) = \(\frac {7}{45} \)
B’s sacrifice ratio = \(\frac {2}{5} \) – \(\frac {3}{9} \) = \(\frac {18 – 15}{45} \) = \(\frac {3}{45} \)
sacrifice ratio of A And B = 7 : 3
(B) Old Ratio = 4 : 3
New Ratio = 3 : 2 : 1
A’s sacrifice ratio = \(\frac {4}{7} \) – \(\frac {3}{6} \) = \(\frac {24 – 21}{42} \) = \(\frac {3}{42} \)
B’s sacrifice ratio = \(\frac {3}{7} \) – \(\frac {2}{6} \) = \(\frac {18 – 15}{42} \) = \(\frac {4}{42} \)
sacrifice ratio of A And B = 3 : 4
Meaning and Definition of Goodwill
Goodwill :
Goodwill is not a tangible asset like other physical assets of the business. It cannot be seen but can be felt only. It has no form. So, it is an “Intangible Asset”. It is very difficult to define it. Every businessman tries to establish his goodwill because it enables him to earn more profits. Goodwill is nothing more than the probability that the old customers will resort to the old place. Goodwill is the present value of a firm’s anticipated excess earnings. It is attributable to the reputation which is acquired by an undertaking operating successfully.
Nature and Characteristics of Goodwill :
The following are the characteristics of goodwill :
- Goodwill is an intangible asset. It is included in the category of intangible assets e.g., patents, trademarks, copyrights etc.
- Depreciation is not charged on goodwill like other fixed assets.
- It has a certain value.
- It helps in the earning more profits over and above normal profits.
- It is an attractive force that draws old customers to the old place.
- Its value keeps on changing though depreciation is not charged but changes occur in its value. Decrease or increase in the profit making capacity affects the value of goodwill.
Factors Affecting the Value of Goodwill :
- Location of business
- Management efficiency
- Long period of business
- Nature of business
- Licence
- Monopoly
- Risk
- Trend of profit
- Condition of market
- Special factor
- Kind of production
- Competition.
Need for Valuation of Goodwill
Need for valuation of goodwill arises when a business is going to be sold but in case of partnership firm the need arises under the following cases :
- On change in profit sharing ratio among the partners
- On admission of a new partner
- On retirement of a partner
- On death of a partner
- On sale of business or conversion of a firm into a company
- On amalgamation of two or more firms.
Types of Goodwill :
Two types of goodwill :
1. Purchased Goodwill :
Purchased goodwill is the goodwill which is acquired by making a payment. For example when a business is purchased the excess of purchase consideration over its net assets (i.e., assets-liabilities) is referred to as Purchased Goodwill.
The following are the important features of purchased goodwill :
- It arises on purchase of business.
- It is recorded in the books of accounts because consideration is paid for it.
- It is shown in the balance sheet as an assets.
- It is amortised (i.e., depreciated) over its useful economic life.
In formula’s Goodwill = Purchase Consideration – Net Assets
![]()
2. Self – Generated Goodwill or Inherent Goodwill :
It is internally generated goodwill which arises form a number of characteristics or attributes which an on going business possesses.
The following are the important features of self-generated goodwill :
- It is internally generated over a long period of time.
- A true case cannot be placed on this type of goodwill. Its valuation depends on the subjective judgement of the values.
- As per Accounting Standard 26 (intangible assets), it is not recorded in the books of accounts because consideration in money or money’s worth has not been paid for it.
Nature of Goodwill :
1. Institutional Goodwill :
This type of goodwill is created due to reputation of business, quality of its goods, particular band etc. Any change in the ownership of business does not affect such goodwill. It attracts highest valuation because it relates to an institution. It is called goodwill of “Cat Nature” because a cat does not change its place in spite of change in ownership of the house.
2. Personal Goodwill :
Contribution of an owner to the reputation of a business is called Personal Goodwill. Customers and/or suppliers associated with the business due to goodwill relations with some owner ability and management prudence of owner influence goodwill of the firm.
Owing to change in the ownership in such a case, the profit making ability of firm will diminish and therefore the value of goodwill. Personal goodwill has lesser value than that of institutional goodwill. It is called Goodwill of a “Dog Nature” because a dog always faithful with his owner, it has no affinity with a particular house.
3. Goodwill Related to Casual Event :
Some enterprises has no unvarying goodwill. Goodwill may increase or decrease due to any unintentional event. In such a case, the customers are not associated with the firm permanently. It is called Goodwill of “Rat Nature.” This kind of goodwill has least value.
Basis of Valuation of Goodwill :
It is very difficult process to assess the value of goodwill as it is an intangible asset. Its value depends on the mutual agreement between the seller and the purchaser of the business. The type of method to be used to assess the goodwill depends on the natw of goodwill and prevailing circumstances.
Sundry methods of valuation of goodwill are :
(i) Average Profit Base
(A) Simple Average Method : Actual average profits of past few years earned by the firm called Future Maintainable Profit or Expected Profits.
Points to be Noted :
(a) If net profits show an increasing or decreasing trend, calculate weighted, average inplace of simple average.
(b) Income from non-trading investments should be deducted from net profits.
(c) Abnormal profit of any year, say profit on sale of land or speculation profit should be deducted from the profit of that year.
(d) Abnormal loss or abnormal expenses should be added in net profit. : ;
(e) Fair remuneration of the proprietor is also to be deducted from average profits.
After making above adjustments such adjusted profits should be considered for valuation of goodwill. These are called Average Maintainable Profits.
![]()
Actual average profit = Average profit – Remuneration of partners
Goodwill = Actual average profit x No. of years purchases
Illustration 8.
Calculate the amount of goodwill at four year’s purchase of the last five year’s average profit. The profits of the last five year were ₹ 40,000, ₹ 50,000, ₹ 60,000, ₹ 50,000 and ₹ 60,000.
Solution:
Total profits for five years = 40,000 + 50,000 + 60,000 + 50,000 + 60,000
= ₹ 2,60,000
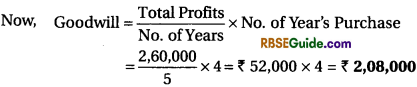
Illustration 9.
Mona purchased Babita’s business from 1st April, 2016. The Profits disclosed by
Babita’s business for the last three years were as follows:
2015-16 ₹ 50,000 (Including Profit on Sale of Fixed Assets ₹ 10,000)
2016 – 17 ₹ 45,000 (Including Loss by Fire ₹ 5,000)
2017 – 18 ₹ 50,000 (Excluding ₹ 5,000 Depreciation)
Calculate the value of firm’s goodwill on the basis of 2 years purchase of the average profit for the last 3 years.
Solution:
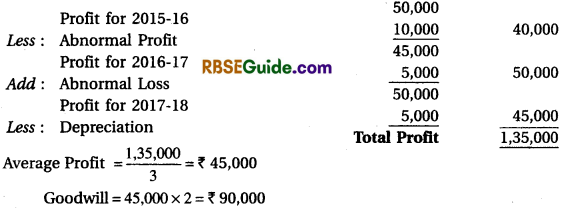
(B) Weighted Average Profit : Under the weighted average profit method, each year’s profit is multiplied by the number of assigned weights, i.e., 1, 2, 3, 4 etc. and the value is ascertained. The products are added and divided by the total of weights to arrive at the average profit. The weighted average profit so arrived at multiplied by the agreed “Number of years’ purchase to arrive at the value of goodwill.”
![]()
Goodwill = Weighted Average Profit x Agreed Number of Years’ Purchase It may be noted that more weightage is assigned to the recent profits because it represents profits for the latest year and it is likely that in the following years same trend will continue. This method is considered better than the simple average profit method because it gives more weightage to the profits of recent years. This method is particularly effective when the profits show a rising or falling trend.
Illustration 10.
The profits of a firm for last 5 years were as follows :
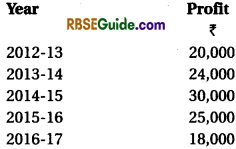
Calculate the Value of goodwill on the basis of ‘Three years’. Purchase of Weighted Average Profit based on weights 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 respectively to the profits for 2012-13, 2013-14, 2014-15, 2015-16 and 2016-17.
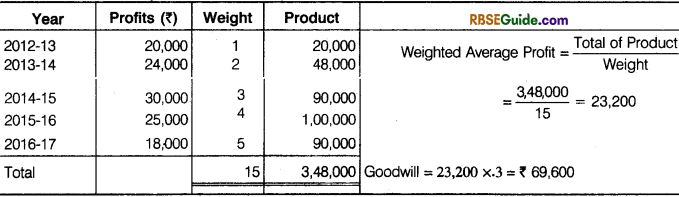
Illustration 11.
Calculate goodwill of a firm on the basis of three year’s purchase of the weighted average profits of the last four years. The profits of the last four years were : 2013 : ₹ 20,200 ; 2014 : ₹ 24,800 ; 2015 : ₹ 20,000 and 2016 : ₹ 30,000. The weights assigned to each year are : 2013 : 1 ; 2014 : 2 ; 2015 : 3 and 2016 : 4.
You are supplied the following information :
1. On September 1, 2015 a major plant repair was undertaken for ? 6,000, which was charged to revenue. The said sum is to be capitalised for goodwill calculation subject to adjustment of depreciation of 10% p.a. on reducing balance method.
2. The Closing Stock for the year 2014 was overvalued by ₹ 2,400.
3. To cover management cost an annual charge of ₹ 4,800 should be made for purpose of goodwill valuation.
Solution:
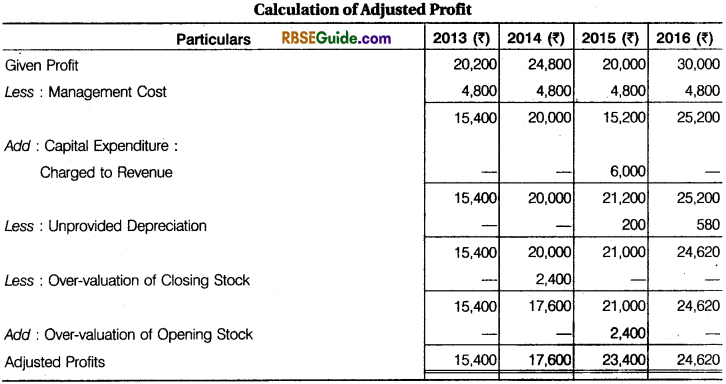
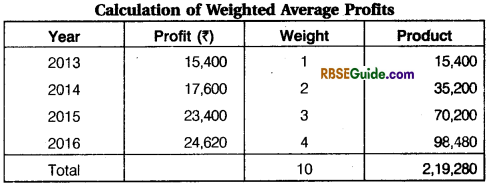
Waightage Average Profit = \(\frac{2,19,280}{10}\) =₹ 21,928
Goodwill = 21,928 x 3 = ₹ 65,784
Working Notes:
(i) Depreciation of 2015 = 10% of ₹ 6,000 for 4 months
= ₹ 6,000 x \(\frac {10}{100} \) x \(\frac {4}{12} \) = ₹ 200
(ii) Depreciation of 2016 = 10% of (₹ 6,000 – ₹ 200 for one year)
= ₹ 5,800 x \(\frac {10}{100} \) = ₹ 580
(iii) Closing Stock of 2014 will become opening stock for the year 2015.
![]()
(ii) Super Profit Base :
Excess of annual profit or future maintainable profit over normal profit of a business is called Super Profit.
Super Profit = Average Profit – Normal Profit
Method of calculating average profit has already been described. In order to find out normal profit of a business, following two important points are necessary to be known :
(i) Capital inverted in the business during the year.
(ii) Normal rate of return keeping in view the profit and rate of interest available in the similar type of business.
Normal profits are calculated by implementing this rate of return on capital invested.
Hence, the following step by step procedure is adopted to compute the super profit of the firm.
(a) First of all calculate annual average profit (future maintainable profit).
![]()
(c) Super Profit = Average Profit – Normal Profit
Capital employed = Assets employed – Outside Liabilities
Normal rate of return = Rate of Interest + Risk Factor
Goodwill = Super profit x No. of year purchase
Illustration 12.
A partnership firm earned net profits during the last five years as follows:

The capital investment of the firm is ₹ 5,00,000. A fair return on the capital having regard to the risk involved is 8%. Calculate the value of goodwill on the basis of 3 years purchase of average super profits earned during the above mentioned period.
Solution:
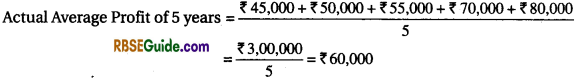
Normal Profit = ₹ 5,00,000 x \(\frac {8}{100} \) = ₹ 40,000
Super Profit = ₹ 60,000 – ₹ 40,000 = ₹ 20,000
Goodwill = Super Profit x no. of years purchase = ₹ 20,000 x 3 = ₹ 60,000
2. Capitalisation Method :
Under this method, goodwill can be calculated in two ways :
(i) By capitalising the average profit
(ii) By capitalising the super profit.
(i) Capitalising the Average Profit Method : Under this method, first of all we calculate the average profit and then we assess the capital needed for earning such average profit on the basis of normal rate of return. Such capital is also called Capitalised Value of Average Profit. It is calculated as under.
![]()
Goodwill = Capitalised Value of Profit – Capital Employed
Illustration 13.
Average profit of a firm is ₹ 25,000 and capital is ₹ 2,00,000. Normal rate of return is 10% calculate the value of goodwill by capitalisation of average profit method.
Solution:
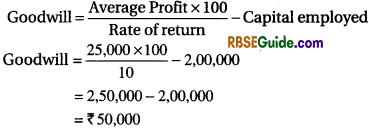
(ii) Capitalisation of Super Profit Method : Under this method, first of all we calculate the super profit and then we assess the capital needed for earning such super profit on the basis of normal rate of return. Such capital is actually the amount of goodwill. Following formula is used to calculate goodwill:
![]()
Super profits are calculated in the same manner as calculated in super profit method.
Illustration 14.
Rama Brothers earn an Average Profit of ₹ 30,000 with a capital of ₹ 2,00,000. The normal rate of return in the business is 10%. Using capitalisation of Super Profits Method work out the value of goodwill of the firm.
Solution:

3. Hidden Goodwill Method
Sometimes, the value of goodwill is hidden in the question. In such cases, the amount of goodwill is calculated on the basis of total capital of the firm and the profit sharing ratio of the partners.
Illustration 15.
A and B are partner in a firm. Their capital account balance is ₹ 15,000 and 25,000. Undistributed reserve is ₹ 10,000 in Balance Sheet. C admitted as a new partner he brings ₹ 25,000 as a capital. Calculate the goodwill amount from the above information.
Solution:
Total capital on the Basis of C’s capital
= 25,000 x \(\frac {4}{1} \) = ₹ 1,00,000
Adjusted capital of A and B =(15,000 + 5,000) +(25,000 + 5,000) = ₹ 50,000
C’s Capital = 25,000
Goodwill of firm = 1,00,000 – (50,000 + 25,000) = ₹ 25,000
Goodwill = ₹ 25,000
4. Purchase Consideration Method :
In this method, purchasing of the business purchase consideration is surplus from Net Assets (Assets – Liabilities) value thats called goodwill:
Goodwill = Purchase consideration – Net Assets
Net Assets = Assets – Liabilities
![]()
Illustration 16.
In a business their are ₹ 3,00,000 of assets and ₹ 75,000 of liabilities. Purchase consideration was fixed on ₹ 2,60,000. What will be value of goodwill.
Solution:
Net Assets = Assets – Liabilities
= 3,00,000 – 75,000 = ₹ 2,25,000
Goodwill = Purchase consideration – Net Assets
= 2,60,000 -2,25,000 = ₹ 35,000
Goodwill = ₹ 35,000
5. Annuity Method :
Under this method present value of an annuity is calculate for a fixed period and on fixed rate of interest. Present value may be calculated with the help of annuity tables. Following formula may also be used :
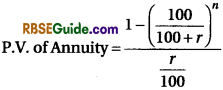
r stands for annual rate of interest,
n stands for number of years.
Illustration 17.
Average profit = ₹ 40,000, Capital employed = ₹ 2,00,000, Normal rate of return = 10%, Present value = ₹ 2.487. Calculate value of goodwill by Annuity Method.
Solution:
Normal Profit=Capital Employed x N.R.R.
= 2,00,000 x \(\frac {10}{100} \) = ₹ 20.000
Super profit = Average Profit – Normal Profit
= 40,000 – 20,000
= ₹ 20,000
. Goodwill = 20,000 x 2.487 = ₹ 49,740
Accounting Treatment of Goodwill :
1. When the Amount of Goodwill is Paid Privately to the Old Partners : When the new partners pays the amount of goodwill in cash to the old partners privately outside the business, no entries are required to be passed. Its not an appropriate method, in which goodwill is paid privately and no entry is passed in the books of the firm because in case of any dispute arises in future, there is no any evidence that a partners had paid goodwill to the old partners.
2. When the New Partner Bring Goodwill (Premium) in Cash

3. When the New Partner Does Not Bring His Share of Goodwill in Cash

4. When New Partner Brings His Share of Goodwill in Part

5. When New Partner Brings His Share of Goodwill in the Form of Assets

6. Accounting Treatment of Hidden Goodwill
![]()
(Being amount of goodwill adjusted through sacrificing partners capital account)
7. Adjusted Goodwill Due to Change in Profit Sharing Ratio
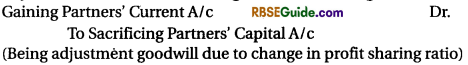
Note : Above in all condition if goodwill account is already opened in the book, it should be closed. Entry will made :
 (Bein existing Goodwill A/c is written off in old profit sharing ratio)
(Bein existing Goodwill A/c is written off in old profit sharing ratio)
Illustration 18.
M and J are partners in a firm sharing profits in the ratio of 3 : 2. They admitted R as a new partner. The new profit sharing ratio between M, J and R will be 5 : 3 : 2. R bring ₹ 75,000 as capital and ₹ 25,000 for his share of goodwill/premium. Pass necessary Journal entries.
Solution:
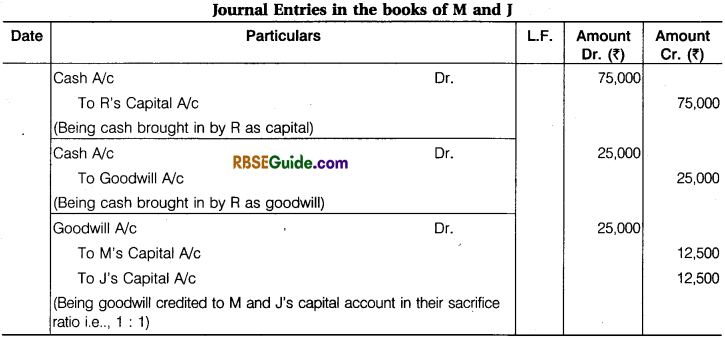
Working Notes:
(1) Sacrifice Ratio = Old Profit Sharing Ratio – New Profit Sharing Ratio
Sacrifice Ratio of M = \(\frac {3}{5} \) – \(\frac {5}{10} \) = \(\frac {6 – 5}{10} \) = \(\frac {1}{10} \)
Sacrifice Ratio of J = \(\frac {2}{5} \) – \(\frac {3}{10} \) = \(\frac {4 – 3}{10} \) = \(\frac {1}{10} \)
Sacrifice Ratio of M and J = \(\frac {1}{10} \) : \(\frac {1}{10} \) or 1 : 1
(2) Distribution of Goodwill between M and J in sacrifice ratio :
Share of M in Goodwill = 25,000 x \(\frac {1}{2} \) = ₹ 12,500
Share of J in Goodwill = 25,000 x \(\frac {1}{2} \) = ₹ 12,500
Illustration 19.
A and B sharing profits in ratio 5 : 4, admits C for 2/9th share. C pays ₹ 30,000 for capital and ₹ 9,000 for goodwill which he acquires as share of profits equally from A and B. Give necessary Journal entries.
Solution:
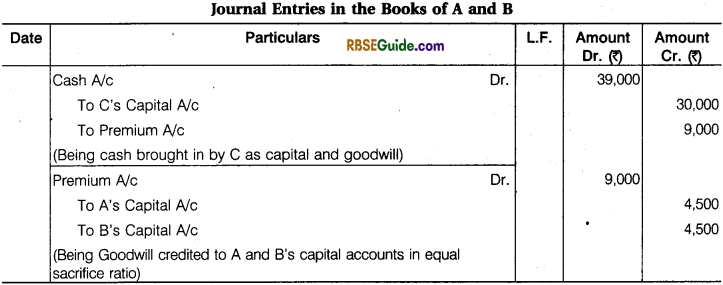
Working Notes:
C’s Share of Profit = \(\frac {2}{9} \)
Calcution of New Profit Sharing Ratio :
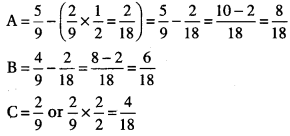
New Ratio = 8 : 6 : 4 or 4 : 3 : 2.
Sacrifice Ratio = \(\frac {1}{2} \) : \(\frac {1}{2} \)
Illustration 20.
X and Y are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 5 : 4. They admit Z in the firm for l/3rd profit which he takes 2/9th from X and l/9th from Y and brings ₹ 1,500 as premium. Pass necessary Journal entries on Z’s admission.
Solution:
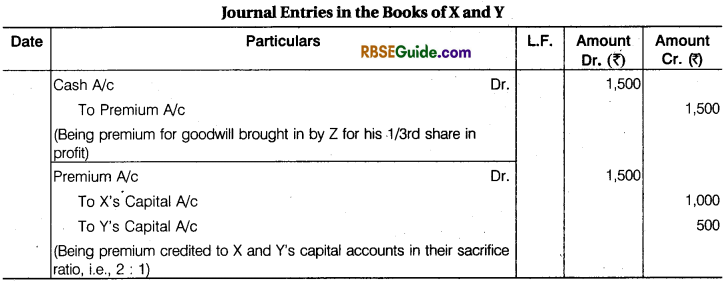
Working Notes:
(1) Calculation of new profit sharing ratio :
Profit sharing ratio of X = \(\frac {5}{9} \) – \(\frac {2}{9} \) = \(\frac {5 – 2}{9} \) = \(\frac {3}{9} \)
Profit sharing ratio of Y = \(\frac {4}{9} \) – \(\frac {1}{9} \) = \(\frac {4 – 1}{9} \) = \(\frac {3}{9} \)
Profit sharing ratio of Z = \(\frac {1}{3} \)
New Profit sharing ratio ofX, Y and Z = \(\frac {3}{9} \) =\(\frac {3}{9} \) =\(\frac {1}{3} \) = \(\frac {3 : 3 : 3}{9} \) = 3 : 3 : 3 or 1 : 1 : 1
(2) Sacrifice ratio of X and Y :
Sacrifice ratio of X = \(\frac {5}{9} \) – \(\frac {1}{3} \) = \(\frac {5 – 3}{9} \) = \(\frac {2}{9} \)
Sacrifice ratio of Y = \(\frac {4}{9} \) – \(\frac {1}{3} \) = \(\frac {4 – 3}{9} \) = \(\frac {1}{9} \)
Sacrifice ratio of X and Y = \(\frac {2}{9} \) : \(\frac {1}{9} \) or 2 : 1
(3) Distribution of Goodwill between X and Y in sacrifice ratio :
Share of X in Goodwill = 1,500 x \(\frac {2}{3} \) = ₹ 1,000
Share of Y in Goodwill =1,500 x \(\frac {1}{3} \) = ₹ 500
![]()
Illustration 21.
X and Y are partners in a firm sharing profits in the ratio of 5 : 3. They admitted Z as a new partner. The new profit sharing ratio will be 4 : 3 : 2. Z brings in ₹ 1,00,000 in cash as his share of capital but could not bring any amount of goodwill in cash. The firm’s goodwill on Z’s admission is valued at ₹ 1,80,000. At the time of Z’s admission, goodwill is existed in the books of firm at ₹ 2,40,000.
Pass necessary Journal entries in the books of the firm on Z’s admission. Show your working note clearly.
Solution:
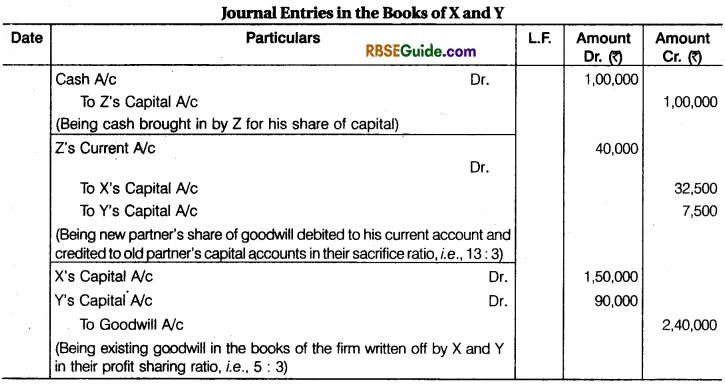
Working Notes :
(1) Calculation of Sacrifice ratio of X and Y :
Sacrifice ratio of X = \(\frac {5}{8} \) – \(\frac {4}{9} \) = \(\frac {45 – 32}{72} \)= \(\frac {13}{72} \)
Sacrifice ratio of Y = \(\frac {3}{8} \) – \(\frac {3}{9} \)= \(\frac {27 – 24}{72} \) = \(\frac {3}{72} \)
Sacrifice ratio of X and Y = \(\frac {13}{72} \) : \(\frac {3}{72} \) = 13 : 3
(2) Calculation of Z’s share in present goodwill:
Firm’s Goodwill on Z’s admission = ₹ 1,80,000
Z’s share in Goodwill =1,80,000 x \(\frac {2}{9} \) = ₹ 40,000
(3) X’s Share in present Goodwill = 40,000 x \(\frac {13}{16} \) = ₹ 32,500
Y’s share in present Goodwill = 40,000 x \(\frac {3}{16} \) = ₹ 7,500
illustration 22.
A and B are partners sharing profits equally. They admit C for l/4th share. C pays only ₹ 1,000 for premium out of his premium of ₹ 1,800. Goodwill already appears in the Balance Sheet at ₹ 6,000. Give Journal entries.
Solution:
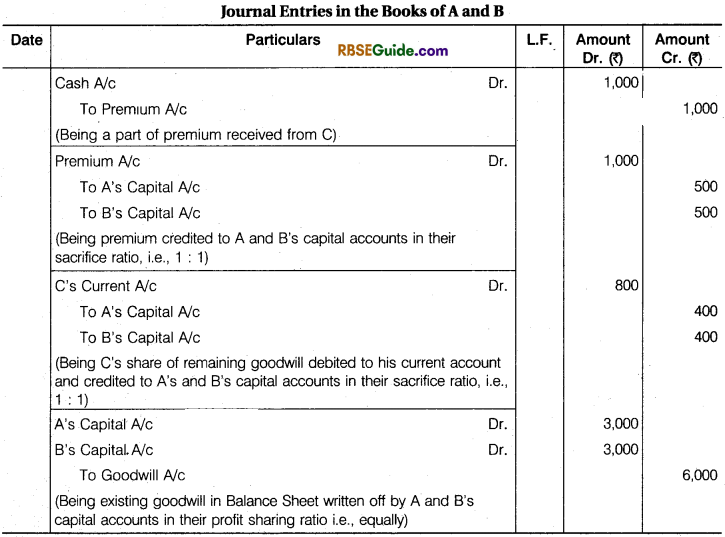
Working Notes :
(1) Calculation of new profit sharing ratio :
Suppose Profit = 1; After C’s share of profit remaining profit =1 – \(\frac {1}{4} \) = \(\frac {3}{4} \)
Profit sharing ratio of A = \(\frac {1}{2} \) x \(\frac {3}{4} \) = \(\frac {3}{8} \)
Profit sharing ratio of B = \(\frac {1}{2} \) x \(\frac {3}{4} \) = \(\frac {3}{8} \)
Profit sharing ratio of C = \(\frac {1}{4} \)
New profit sharing ratio of A, B and C = \(\frac {3}{8} \) : \(\frac {3}{8} \) : \(\frac {1}{4} \) = 3 : 3 : 2
(2) Calculation of sacrifice ratio of A and B :
Sacrifice ratio of A = \(\frac {1}{2} \) – \(\frac {3}{8} \) = \(\frac {4 – 3}{8} \) = \(\frac {1}{8} \)
Sacrifice ratio of B =\(\frac {1}{2} \) – \(\frac {3}{8} \) = \(\frac {4 – 3}{8} \) = \(\frac {1}{8} \)
Sacrifice ratio of A andB = \(\frac {1}{8} \) : \(\frac {1}{8} \) = 1 : 1, i.e., equal sacrifice by A and B.
(3) Remaining goodwill ₹ 1,800 – ₹ 1,000 = ₹ 800 will be debited to C’s current A/c and credited to A’s Capital A/c and B’s Capital A/c in their sacrificing ratio, i.e., equally.
(4) Premium brought in cash by C will be credited to A and B’s Capital A/cs in their sacrificing ratio, i.e., equally.
(5) Existing goodwill ₹ 6,000 written off by A andB equally (Old Profit Sharing Ratio).
Illustration 23.
A and B are partners in a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3 : 2. They admit C into partnership for l/3rd share in profits. C brings capital of ₹ 20,000. Goodwill is valued at ₹ 15,000. Show what entries shall be made in the following cases:
1. Goodwill does not appear in the books.
2. Goodwill appears in the books at ₹ 9,000.
Solution:
1. When goodwill does not appear in the books :

2. When goodwill appears in the books at ₹ 9,000
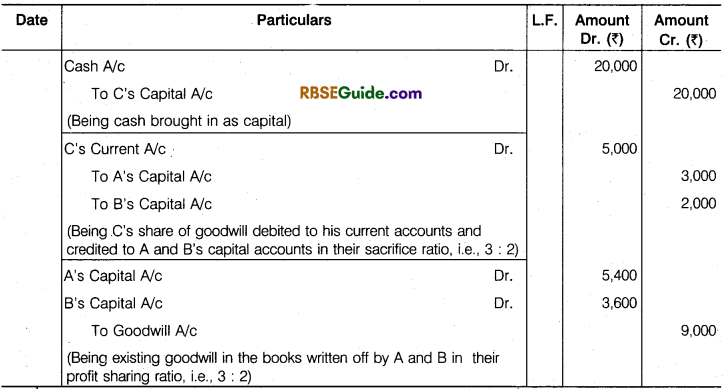
Working Notes :
(1) Calculation of New Profit Sharing Ratio :
Suppose Profit = 1
After C’s l/3rd share in profit remaining profit = 1 – \(\frac {1}{3} \) = \(\frac {2}{3} \)
Profit sharing ratio of A = \(\frac {3}{5} \) x \(\frac {2}{3} \) = \(\frac {6}{15} \)
Profit sharing ratio of B = \(\frac {2}{5} \) x \(\frac {2}{3} \) = \(\frac {4}{15} \) ‘
Profit sharing ratio of C = \(\frac {1}{3} \)
Profit sharing ratio of A, B and C = \(\frac {6}{15} \) : \(\frac {4}{15} \) : \(\frac {1}{3} \) = \(\frac {6 : 4 : 5 }{15} \) = 6 : 4 : 5
(2) Ca1cuIation of Sacrifice Ratio :
Sacrifice ratio of A = \(\frac {3}{5} \) – \(\frac {6}{15} \) = \(\frac {9 – 6}{15} \) = \(\frac {3}{15} \)
Sacrifice ratio of B = \(\frac {2}{5} \) – \(\frac {4}{15} \) = \(\frac {6 – 4}{15} \) = \(\frac {2}{15} \)
Sacrifice ratio of A and B = \(\frac {3}{15} \) : \(\frac {2}{15} \) = 3 : 2
(3) C’s share in C’s Part of goodwill = 15,000 x \(\frac {1}{3} \) = ₹ 5,000
(4) A’s share in Cs Part of goodwill = 5.000 x \(\frac {3}{5} \) = ₹ 3,000
(5) B’s Share in C’s Part of goodwill =5,000 x \(\frac {2}{5} \) = ₹ 2,000
Illustration 24.
A and B are partners with capital of ₹ 26,000 and ₹ 22,000 respectively. They admit C as partner with l/4th share in the profits of file firm. C brings ₹ 26,000 as his share of capital. Give journal entries to record goodwill on C’s admission.
Solution:

Working Notes :
(1) Calculation of Hidden Goodwill :

Total capital of all partners = ₹ 26,000 + ₹ 22.000 + ₹ 26,000 = ₹ 74,000
Hence, Hidden Goodwill = ₹ 1,04.000 – ₹ 74,000 = ₹ 30.000
II nd Method :

Capital of A and B = ₹ 26,000 + ₹ 22.000 = ₹ 48,000
Hence, Hidden Goodwill = ₹ 78,000 – ₹ 48,000 = ₹ 30,000
(2) CsShareinGoodwill=30,000 x \(\frac {1}{4} \) = ₹ 7,500
(3) Calculation of new profit sharing ratio :
Suppose Profit = 1
After C’s 1/4 share in profit remaining profit = 1 – \(\frac {1}{4} \) = \(\frac {3}{4} \)
Profit shanng ratio of A = \(\frac {1}{2} \) x \(\frac {3}{4} \) = \(\frac {3}{8} \)
Profit sharing ratio of B = \(\frac {1}{2} \) x \(\frac {3}{4} \) = \(\frac {3}{8} \)
Profit sharing ratio of C = \(\frac {1}{4} \)
New profit sharing ratio ofA, B and C = \(\frac {3}{8} \) : \(\frac {3}{8} \) : \(\frac {1}{4} \) = 3 : 3 : 2
![]()
(4) Calculation of Sacrifice Ratio:
Sacrifice ratio of A = \(\frac {1}{2} \) – \(\frac {3}{8} \) = \(\frac {4 – 3}{8} \) = \(\frac {1}{8} \)
Sacrifice ratio of B = \(\frac {1}{2} \) – \(\frac {3}{8} \) = \(\frac {4 – 3}{8} \) = \(\frac {1}{8} \)
Sacrifice rano ofAand B = \(\frac {1}{8} \) : \(\frac {1}{8} \) = 1 : 1
Hence, A and B sacrifice their ratio equally.
Determination of Capital of a New Partner :
When a new partner cpmes in firm he brings his share of capital in two ways, first he brings his share of capital In cash, secondly he brings the capital as fixed assets, or he admitted with his business. in both condition transaction will be :

(2) When he brings his business, his assets and liabilities will be taken by business. Assets should be debited and liabilities should be credited. Difference amount is capital. Entry made as follows :

Illustration 25.
A and B are partper in a firm. They admitted C as a new partner for ₹ 1 ,00,000 capital. C brings his business assets and liabilities. Building ₹ 60000, Machine ₹ 20,000, Furniture ₹ 5,000, Debtors ₹ 20,000 (Provision is made for Bad Debts for 10%). CredItors ₹ 10,000, Bills payable ₹ 5,000. Give journal entry for admission of C.
Solution:

RevaLuation of Assets and Reassessment of LiabiLities :
Whenever a new partner is admitted, It becomes necessary to revalue the assets and liabilities of the firm to their true and fair values. This is done because with the passage of time, the value of certain assets might have increased, while the value of certain other assets might have decreased. Thus, the actual value of various assets and liabilities may be different from the values stated in the balance sheet.
New partner should not suffer because of reduction in the value of assets nor should he be benefited by increase in the value of assets. Thus, the entire profit or loss arising from revaluation is divided between the old partners In their old profit sharing ratio. Revaluation of assets and liabilities is done with the help of a new account called “Revaluation Account” Sometimes, this account is called as “Profit and Loss Adjustment Account’ This account is a nominal account in nature. Therefore, if there is a Loss due to revaluation, revaluation account is debited and if the revaluation results in a profit, the revaluation account is credited.
Following entries are passed for the purpose of revaluation :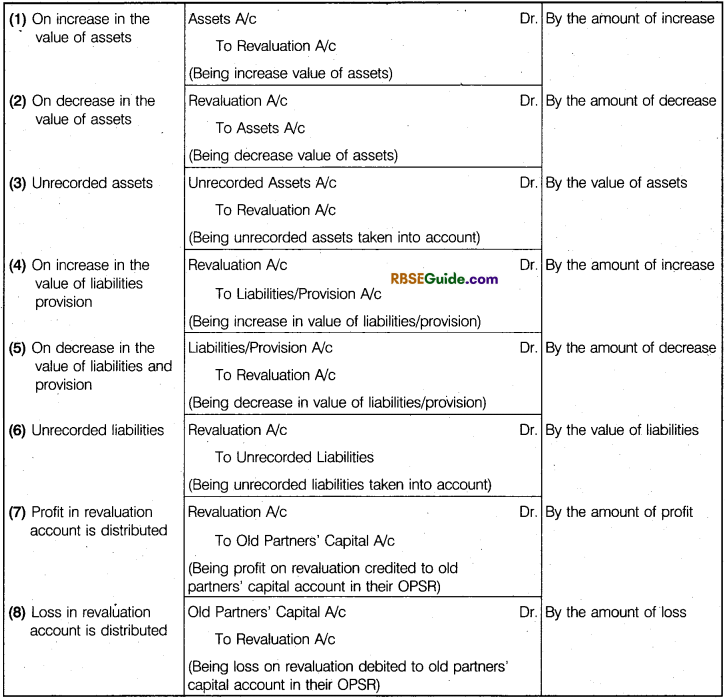
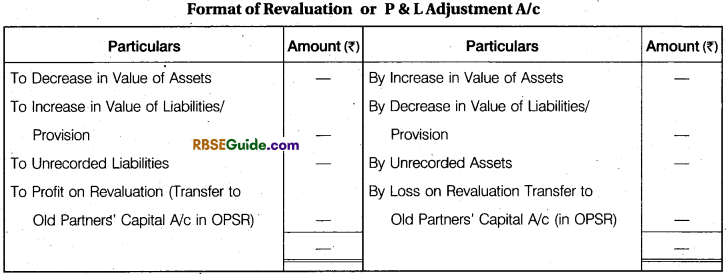
Note : There are some important statement which can be given in question paper. Mind it when we are solving the question.
(1) In question, it is given that assets are reduced by ………… percent. For its calculation formula will apply.
![]()
(2) In question, it is given that assets are increased by ………… percent. For its calculation formula will apply.
![]()
Illustration 26.
X and Y are in partnership sharing profits and losses equally and their position is shown in the following Balance Sheet:
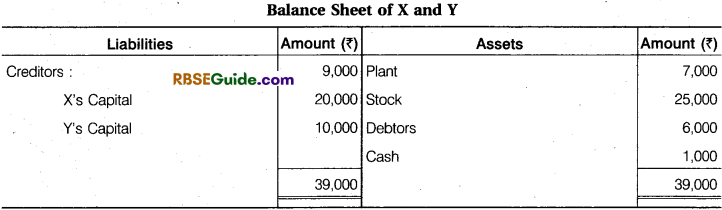
It was decided to admit Z into partnership on the following terms :
(a) The firm’s goodwill is valued at ₹ 6,000.
(b) Stock is to be written down by 10% and Plant 12.5%.
(C) Reserve of 5% is to be made on Sundry Debtors.
(d) Z is to bring ₹ 10,000 as his capital for one-fourth share in the future profits and his proportionate share of goodwill in cash.
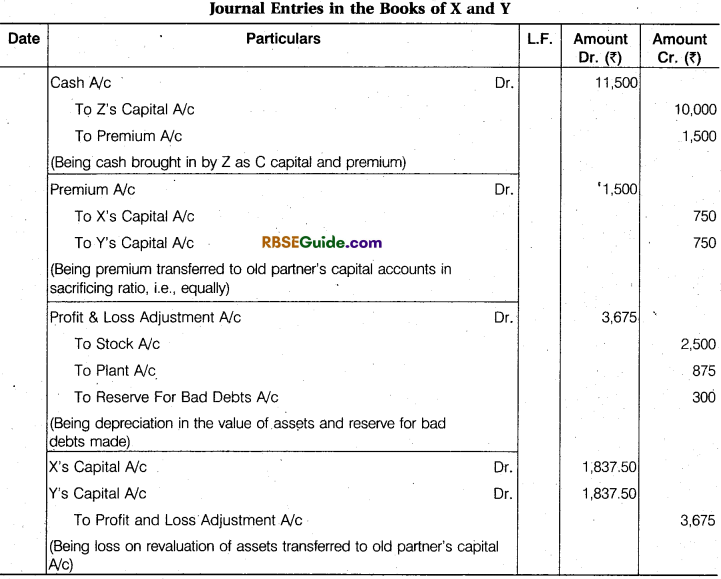
Pass Journal entries to give effect to the above arrangement and show the Profit and Loss Adjustment Account and the Balance Sheet of the New Firm.
Solution:
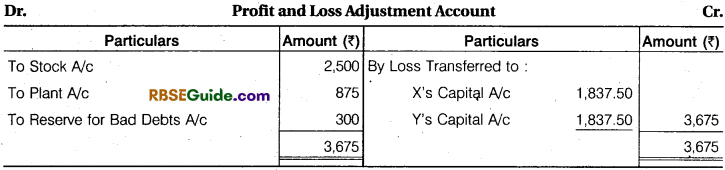
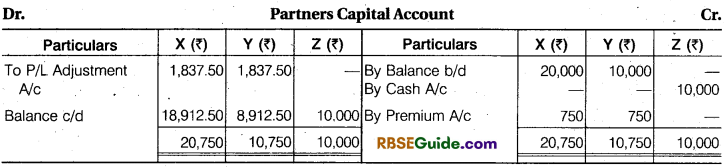
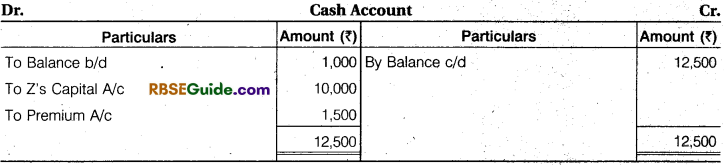
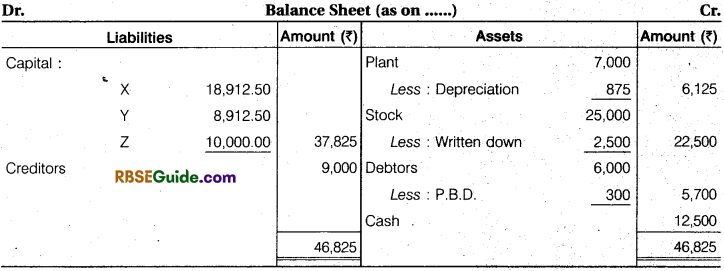
Note : Profit and Loss Adjustments second name is Revaluation Account.
Illustration 27.
Ajay and Ashok are in partners, sharing profit in the ratIo of 3 :2 respectively. Their balance sheet is as follows:
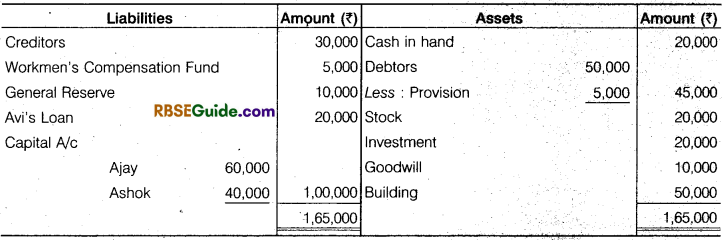
Avi is Admitted in to Partnership on the following terms:
- The new profit sharing ratio will be 5 : 3 : 2 between Ajay Ashok and Avi.
- Avi’s loan should be treated as his capital.
- Goodwill of the firm is valued at ₹ 40,000.
- ₹ 10,000 of investment were to be taken over by Ajay and Ashok in his profit sharing ratio.
- Stock to be reduced by 20%.
- Provision for doubtful debts should be @ 12% on debtors and a provision for discount on debtors @ 2% too should be made.
- Ajay is to withdrew ₹ 10,000 in cash.
Prepare Revaluation Account, Partners Capital Account, Cash Account, and Balance Sheet.
Solution:
Sacrifice or Gain :
Ajay \(\frac {3}{5} \) – \(\frac {5}{10} \) = \(\frac {6 – 5}{10} \)= \(\frac {1}{10} \) (Sacrifice)
Ashok \(\frac {2}{5} \) – \(\frac {3}{10} \) = \(\frac {4 – 3}{10} \) = \(\frac {1}{10} \) (Sacrifice)
Avi’s Share of Goodwill = 40,000 x \(\frac {2}{10} \)= ₹ 8,000
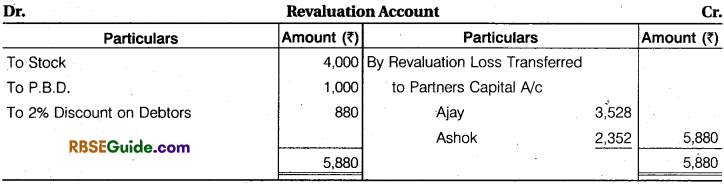
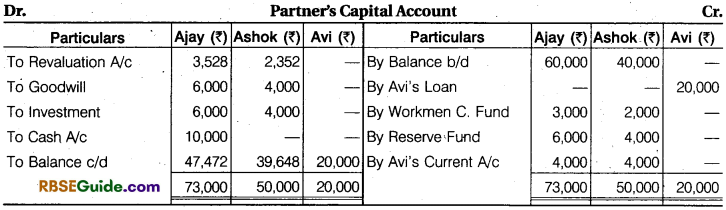
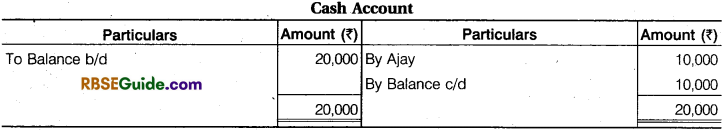
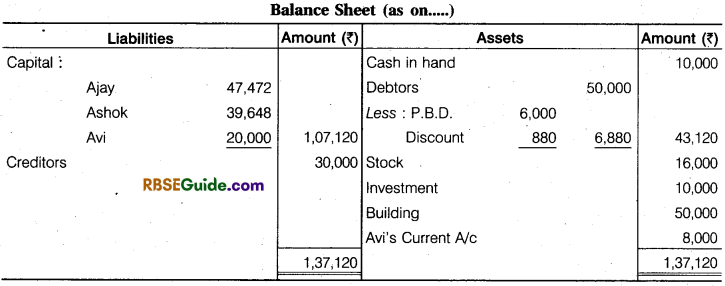
Illustration 28.
A and Bare partners with profit sharing ratio 2 : 1. Their Balance Sheet on 31.3.2018 was as follows: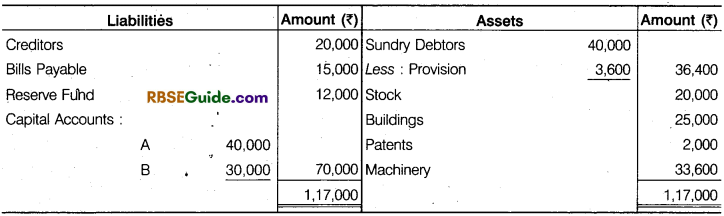
They admitted C into partnership on this date. New profit sharing ratio is agreed as 3 : 2 : 1 C brought in proportionate capital after the following adjustments :
(a) C brought ₹ 10,000 in cash as his share of goodwill.
(b) Provision for doubtful ebtsto be reduced by ₹ 2,400.
(C) There is an old typewriter valued at ₹ 2,600. It does not appear in the books of the firm. ¡Lis now to be recorded.
(d) Patents are valueless.
Prepare Revaluation A/c, Captial A/c and the Opening Balance Sheet of A, B and C.
Solution:
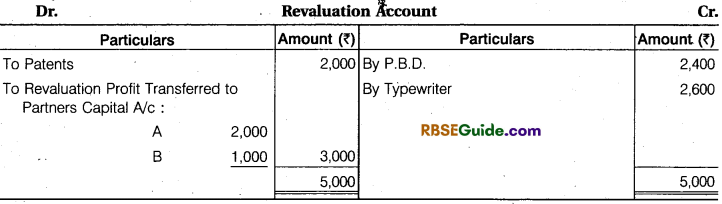
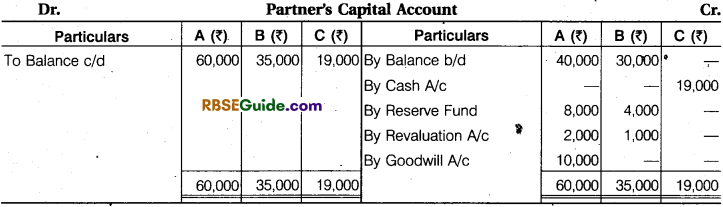
Working Note :
Total share of A and B = 1 – \(\frac {1}{6} \) = \(\frac {5}{6} \)
Total Capital of ‘R and ‘B’ = ₹ 95,000
Total capital of the firm = 95,000 x \(\frac {6}{5} \) = ₹ 1,14,000
C’s Capital = 1,14,000 x \(\frac {1}{6} \) = ₹ 19,000
Note : Whole amount of goodwill will received/credited to A. Because sacrifice made by only A.
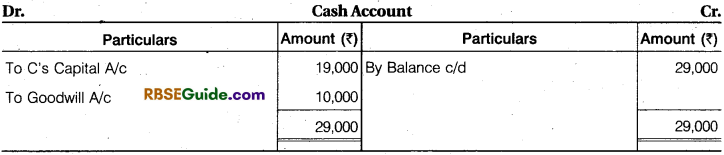
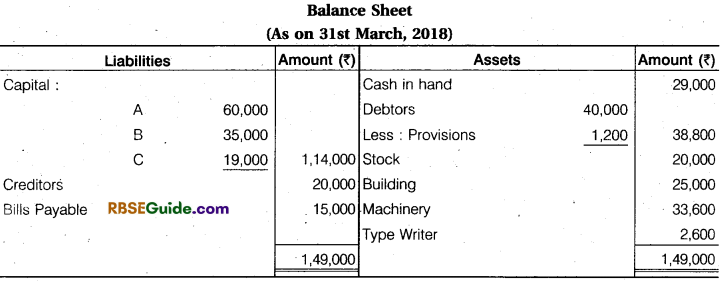
Illustration 29.
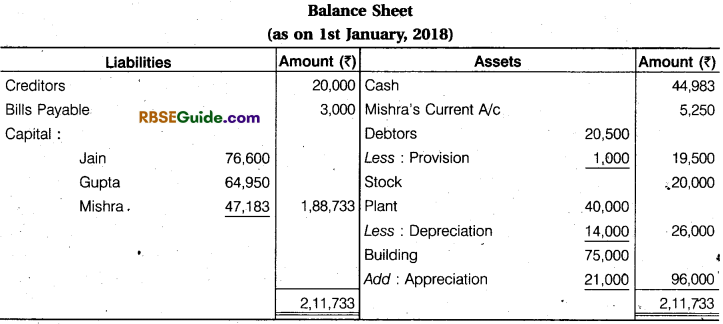
Jain and Gupta were partner in a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 4 : 3. The following were the Balance Sheet of the firm as on 31st December, 2017 :
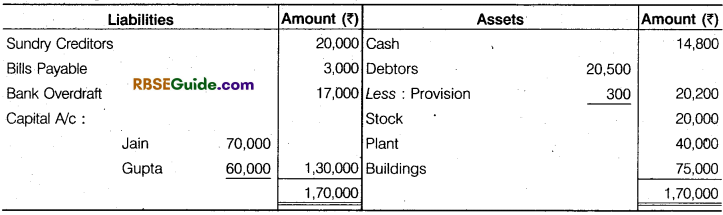
They agreed to admit Mishra as partner with effect from 1st January, 2,018 with 1/4 share in profits on the following terms:
(a) Mishra will bring in capital to the extent of 1/4th of the total capital of the new firm after
all adjustments have been made,
(b) Buildings are to be appreciated by ₹ 21,000 and Plant to be depreciated by ₹ 14,000.
(c) The provision on debtors is to be raised to ₹ 1,000.
(d) The goodwill of the firm has been valued at ₹ 21.000.
Prepare the Revaluation Account, Partner’s Capital Accounts and Balance Sheet of the new firm immediately after Mishra’s admission.
Solution:
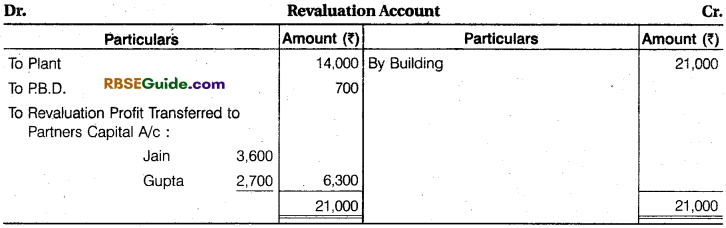
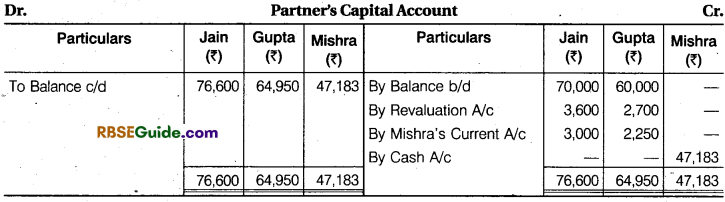
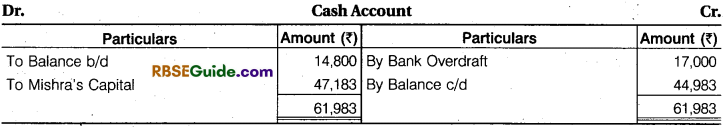
Note : In question, goodwill is ₹ 21,000 of the firm. Mr. Mishra does not bring goodwill in cash.
Working Note :
(1) Total Goodwill of the Firm = ₹ 21,000
Mishra’s Share of Goodwill =21.000 x \(\frac {1}{4} \) = ₹ 5,250
Total Capital of Jam and Gupta = 76,600 + 64,950 = ₹ 1,41,550
Mishra’s Share of Profit = \(\frac {1}{4} \)
Share of Profit of Jam and Gupta =1 – \(\frac {1}{4} \)= \(\frac {3}{4} \)
(2) Total Capital of the Firm = 1 ,41,550 x \(\frac {1}{4} \) = ₹ 1,88,733
Mishra’s Share of Capital =1,88,733 x \(\frac {1}{4} \) = ₹ 47,183
Accounting Treatment of Reserves and Accumulated Profits or Losses :
At the time of admission, if there is any general reserve, reserve fund or the balance of profit and loss account appearing in the balance sheet, it must be transferred to old partners’ capital account in their old profit sharing ratio. The new partner is not entitled to any share of such reserves or profits as these are undistributed profits earned by the old partners. For this purpose, the following journal entries are recorded.
(i) For Distributing Reserves and Accumulated Profits

(ii) For Distributing Accumulated Losses Among Old Partners in Old Ratio : If there is any balance of P&L account appearing on the assets side of the balance sheet, the capital account of old partners are debited from the amount of this loss. The entry will be :
![]()
(iii) For Distributing Surplus of Specific Reserves : The firm may have created some specific reserves like “Workmen’s Compensation Reserve” or investment Fluctuation Reserve” to meet certain future obligations. At the time of admission of a new partner, such reserves may be in excess of actual obligations.
Such excess reserves will be transferred to capital account of old partners in oLd ratio. The entry wili be

Entries for transfernng the reserves and accumulated profits or tosses must be passed even if the question is silent on this pornt
Employee’s provident fund or employee’s saving account appearing on the liabilities side of the balance sheet are not distributed among òld partners as they are not reserves but are the outside liabilities payable by the firm.
Adjustment of Capital :
1. Adjustment of capital of old partners on this basis of new partners’ capital.
2. Adjustment of new partners’ capital on the basis of old partners’ adjusted capital.
1. Adjustment of Old Partners’ Capital on the Basis of Capital of New Partner :
- Calculate new profit sharing ratio of all partners.
- Find out total capital of the firm on the basis of new partners’ capital and his share of profit.
- Total capital be divided in new profit sharing ratio.
- Excess capital of old partner, if any be withdrawn in cash deficiency be brought in cash or record the same as provided in the question.
![]()
2. DetermInation of Share of Capital of New Partner on the Basis of Capitals of Old Partners
- Find out old partners’ capital balance after making all adjustments regarding revaluation of assets and liabilities, share of goodwill brought ¡n by new partner distributing undistributed profit and losses etc.
- Thereafter, find out residual share of profit after new partners share. For example, 1 – \(\frac {1}{4} \) = \(\frac {3}{4} \) share of old partners as per above example.
- Then, find out total capital of the ftrm on the basis of combined adjusted capital of the old partners and their share of profit.
- New partners’ capital = Total capital of the firm x His share in profit
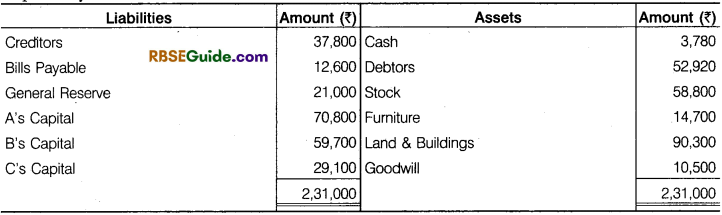
Illustration 30.
The following is the Balance Sheet of A, B and C, they sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 6/14, 5/14 and 3/14 respectively :
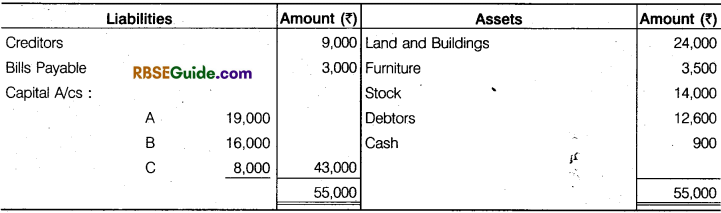
They agreed to take D into partnership and give him a share of 1/8th in the rupee on the following terms :
(a) That D should bring in 4,200 as goodwill and 7,000 as his capital.
(b) That Furniture be depreciated by 12%.
(c) That Stock be depreciated by 10%.
(d) That a provision of 5% be created for Doubtful Debts.
(e) That the value of Land and Building having appreciated be brought up to 31,000.
(f) After making the above adjustments the capital accounts of the old partners (who continue to share in the same proportion as before) be adjusted on the basis of proportion of D’s Capital to his share in the business, i.e., actual cash to be paid off to, or brought in by the old partners as the case may be.
Prepare necessary accounts and the Balance Sheet of the new firm.
Solution:
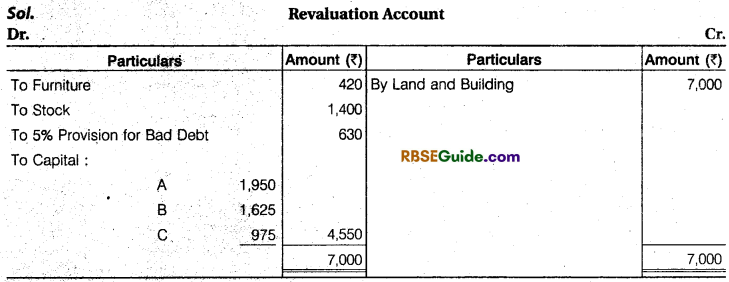
New Ratio
Working Note :
1. 1 – \(\frac {1}{8} \) = \(\frac {7}{8} \)
A = \(\frac {7}{8} \) x \(\frac {6}{14} \) = \(\frac {42}{112} \)
B = \(\frac {7}{8} \) x \(\frac {5}{14} \) = \(\frac {35}{112} \)
C = \(\frac {7}{8} \) x \(\frac {3}{14} \) = \(\frac {21}{112} \)
D = \(\frac {1}{8} \) x \(\frac {14}{14} \) = \(\frac {14}{112} \)
New Ratio = 42 : 35 : 21 : 14 or 6 : 5 : 3 : 2
2. Total Capital of the Firm = 7,000 x \(\frac {8}{1} \) = ₹ 56,000
Capital of:
A 56.000 x \(\frac {8}{1} \) = ₹ 21 .000
B 56.000 x \(\frac {5}{16} \) = ₹ 17,500
C 56,000 x \(\frac {3}{16} \) = ₹ 10,500
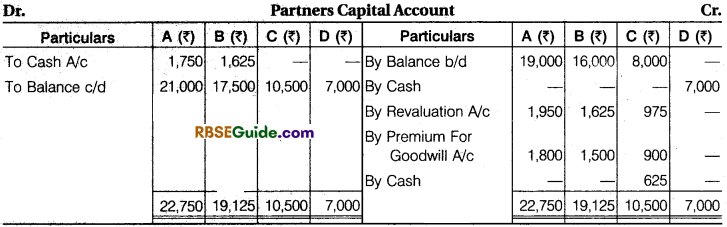
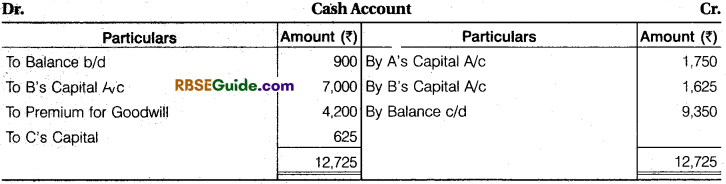
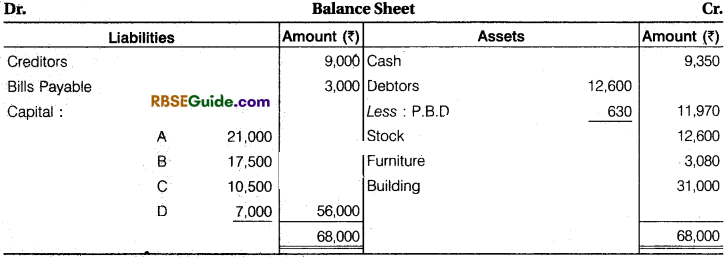
Illustration 31.
Following is the Balance Sheet of A, B & C sharing profit in the ratio of 6 : 5 : 3 respectively :
They agreed to take D into partnership giving 1/8 share in profits on the following terms :
(a) Furniture to be depreciated by ₹ 1,840 and Stock by 10%.
(b) A provision of ₹ 2,640 to be made for an outstanding bill for repairs.
(c) Land and building be brought upto ₹ 1,19,700.
(d) D should bring in ₹ 28,140 as goodwill.
(e) D should bring in ₹ 35,400 as his capital.
(f) After making the above adjustments, the capitals of old partners be adjusted in proportion to D’s capital by bringing in cash or excess to be paid off.
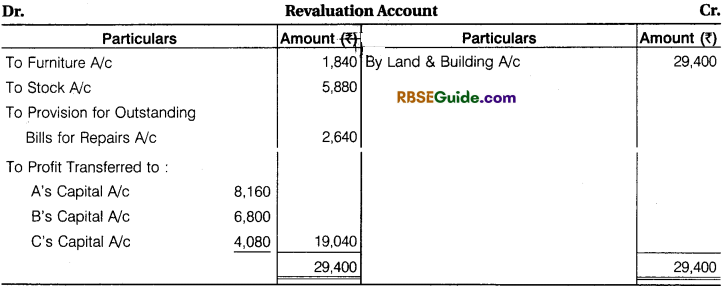
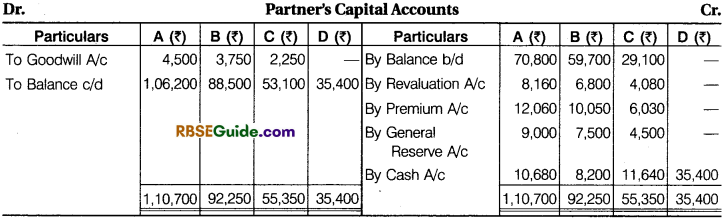
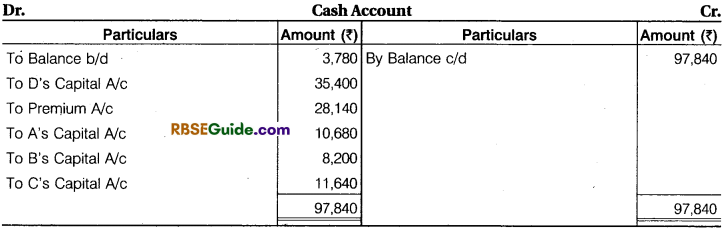
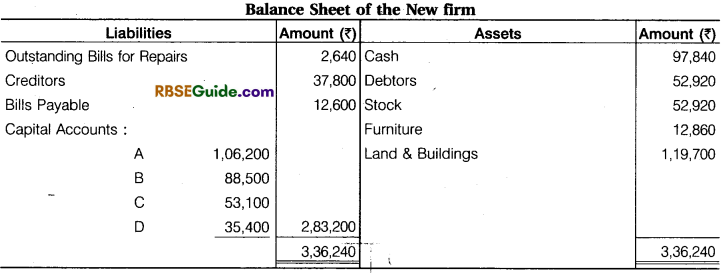
Prepare Revaluation Account, Capital Accounts of Partners and Balance Sheet of new firm.
Solution:
Working Note :
1. Calculation of New Ratio : 1 – \(\frac {1}{8} \) = \(\frac {7}{8} \) New Ratio of A, B, C and D
A’s New Ratio = \(\frac {1}{8} \) x \(\frac {6}{14} \) = \(\frac {42}{112} \) 42 : 35 : 21 : 14 or 6 : 5 : 3 : 2
B = \(\frac {7}{8} \) x \(\frac {5}{14} \) = \(\frac {35}{112} \)
C = \(\frac {7}{8} \) x \(\frac {3}{14} \) = \(\frac {21}{112} \)
D = \(\frac {1}{8} \) x \(\frac {14}{14} \) = \(\frac {14}{112} \)4
Working Note :
2. Total Capital of the Firm Base of D’s Capital :
35,400 x \(\frac {8}{1} \) = ₹ 2,83,200
A’s Capital =2,83,200 x \(\frac {8}{1} \) =₹ 1,06,200
B’s Capital = 2,83,200 x \(\frac {8}{1} \) = ₹ 88,500
C’s Capital =2,83,200 x \(\frac {8}{1} \) = ₹ 53,100
D’s Capital = 2,83,200 x \(\frac {8}{1} \) =₹ 35,400
Illustration 32.
J and K are partners in a firm sharing profits in the ratio of 3 : 2, They decided to admit L as a new partner w.e.f. April 1, 2018. The Balance Sheet of J and K and terms of admission as at April 1, 2018 as follows.
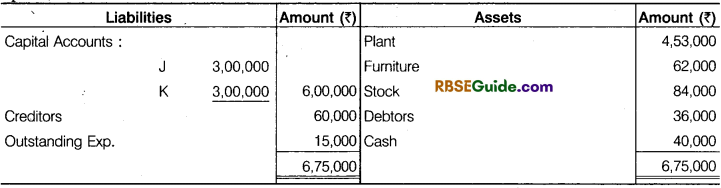
The terms of admission are given below:
(a) In future, profits will be shared equally.
(b) Capital of the firm was fixed at 6,00,000 to be contributed by all partners in the profit
sharing ratio.
(C) L to bring his share of capital and goodwill in cash.
(d) Goodwill of the firm is to be valued on the basis of two year’s purchase of Super Profit.
The average net profit expected in future by the firm is 90,000 per year. The normal rate of
return on capital in similar business is 10%.
Calculate goodwill and prepare all partners Capital Accounts, Cash Account and Balance Sheet
of the new firm.
Solution:
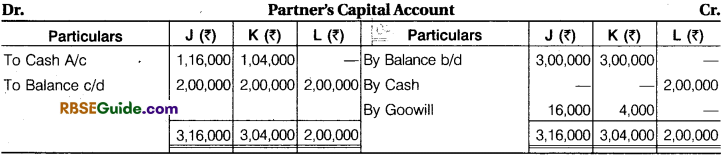
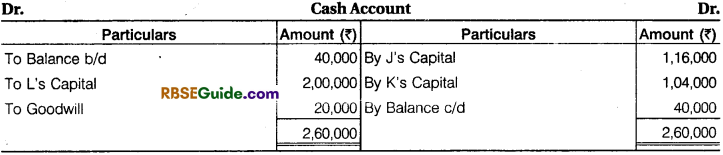
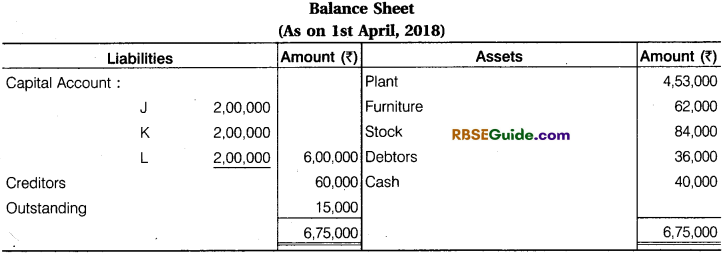
Working Note :
1. Sacrifice Ratio = Old Ratio – New Ratio
Old Ratio = 3 : 2
New Ratio = 1 : 1 : 1
J = \(\frac {3}{5} \) – \(\frac {1}{3} \) = \(\frac {9 – 5 }{15} \) = \(\frac {4}{15} \) (Sacrifice)
K = \(\frac {2}{5} \) – \(\frac {1}{5} \) = \(\frac {6 – 5}{15} \)=\(\frac {1}{15} \) (Sacrifice)
Sacrifice Ratio of J and K = \(\frac {4}{15} \) : \(\frac {1}{15} \) or 4 : 1
2. Goodwill : Average Profit = ₹ 90.000
![]()
Super Profit = Average Profit – Nonnal Profit
= 90,000 – 60,000 = ₹ 30,000
Goodwifi =30,000 x 2 = 60,000
L’s Share of Goodwill = 60,000 x \(\frac {1}{3} \)= ₹ 20,000
3. Capital of J, K and L
J = 6,00,000 x \(\frac {1}{3} \) = ₹ 2,00,000
K = 6.00,000 x \(\frac {1}{3} \) = ₹ 2,00,000
L = 6,00,000 x \(\frac {1}{3} \) = ₹ 2,00,000
When Assets and UabiLities of Old Firm are to be Shown at Old Values Not at Revalued Figures (Menmorandum Revaluation A/c):
Under this case, memorandum revaluation account is prepared. It is a kind of statement which is prepared in two parts. In the first part, the entires regarding increase or decrease in the value of assets and liabilities are recorded. The resultant profit or loss is transferred to old partners’ capital account ¡n old profit sharing ratio. Thereafter, the entries passed are reversed in the second part of this statement. The resultant profit or loss in second part is transferred to capital account of all partners including the new partner in new profit sharing ratio.
If the Profit on Revaluation :
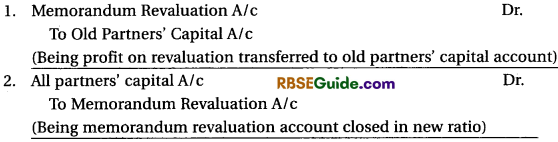
In case of loss on the Revaluation :
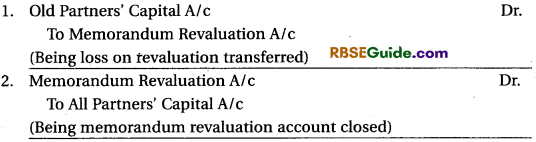
Points to be Noted :
Under this case in Balance Sheet
- BalanceofcashorbankWcandthecapitalaœountofthepartnersarechged.
- Reserves and surpluses (undistributed profits) or tosses are transferred to capital account of old partners.
- Remaining assets and liabiithes will be shown at book values (old values).
Illustration 33.
A and B are partners in a firm sharing profits in their capital ratio. Their Balance Sheet is as on 31st March, 2018 is as under :
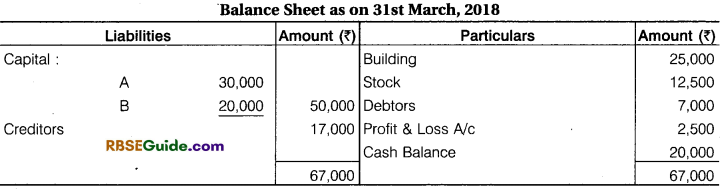
On 1st April, 2018 they decide to admit C for 1/5th share on the following terms:
- C will get his share equally from A and B. He brings cash 20,000 for capital.
- Firm’s goodwill is valued at 15,000 and C brings his share in cash.
- Make a provision for Bad debts @ 10% on Debtors
- Stock is to be Valued 120O0 and the value of building is to be increased by 3,200
- Book values of Assets and Liabilities are not to be changed. Prepare Memorandum
Revaluation Account, Partner’s Capital Account & Balance Sheet.
Solution:
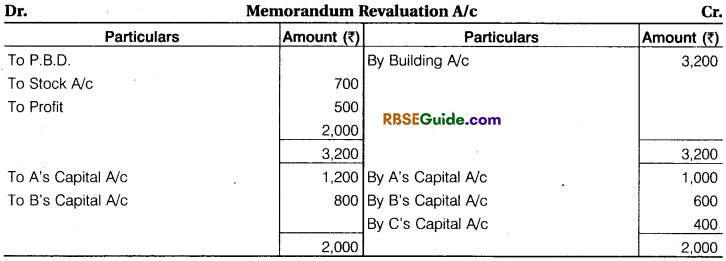
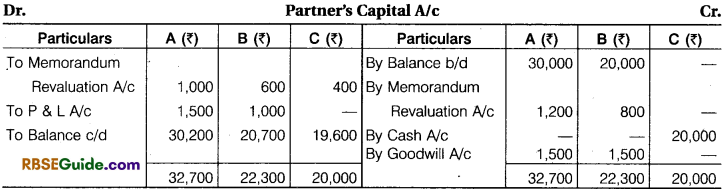
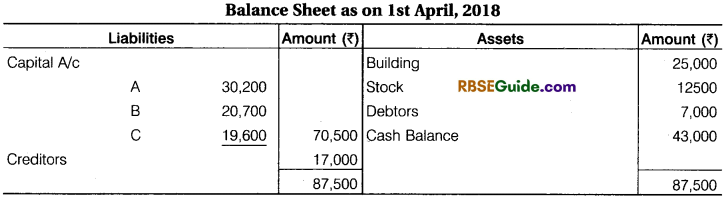
Working Notes :
(1) Cash Balance 20,000 + 20,000 + 3,000 = ₹ 43,000
(2) C will get his share equal to A and B.
A’s sacrifice = \(\frac {1}{5} \) x \(\frac {1}{2} \) = \(\frac {1}{10} \)
B’s sacrifice \(\frac {1}{5} \) x \(\frac {1}{2} \) = \(\frac {1}{10} \)
New Profit sharing Ratio = Old profit sharing ratio – Sacrifice ratio
A = \(\frac {3}{5} \) – \(\frac {1}{10} \) = \(\frac {5}{10} \)
B = \(\frac {2}{5} \) – \(\frac {1}{10} \)= \(\frac {3}{10} \)
New profit sharing ratio is \(\frac {5}{10} \) : \(\frac {3}{10} \) : \(\frac {1}{5} \) = 5 : 3 : 2
Workmen Compensatton Reserve :
This is prepared for the possible compensation of workmen such as : accident claim etc. from
the firm’s profit. Its accounting in various different situation can be understood with the following
example :
Illustration :
A and B are partners in a firm sharing proit in ratio of 5:4. They admit C on 1-4-18 at the profit of 1/5 share.
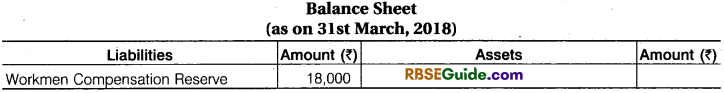
From five following situations workmen Compensation Reserve can be done at admission :
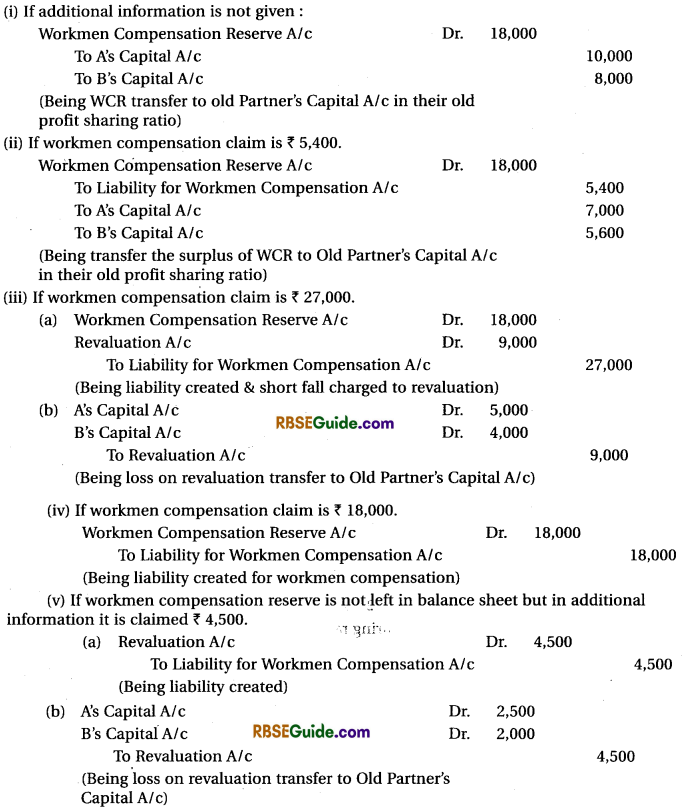
Investment FluctuatLon Reserve :
It is prepared to adjust the deficiency in market value of investment. Here are various situations of accounting concerning it as follows :
Illustration :
A and B are partners for profit sharing ratio 3:2. They admitted to ‘C’ on 1-04-2018 fork share of profit.
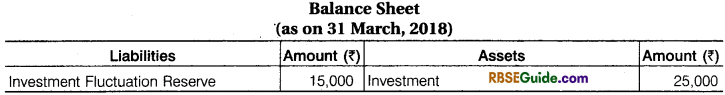

Illustration 34.
A and B are partners. On 1st Jan, 2018 they decide to admit C into partnership on the basis of the following Balance Sheet :
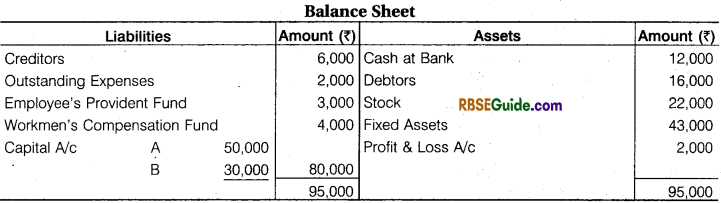
The following terms were agreed upon:
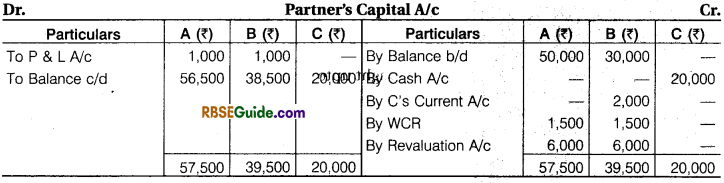
- New profit sharing ratio should be 2: 1: 1 respectively and C brought in 20,000 as capital.
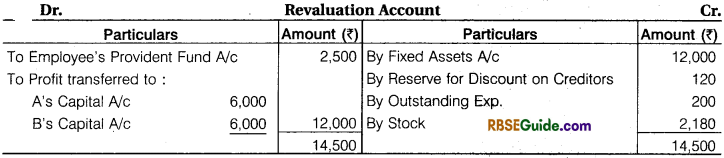
- Fixed Assets is to be appreciated by ₹ 12,000.
- A Provision of 2% was tobe made for discount on creditors.
- Outstanding expenses be brought down to ₹ 1,800.
- The liability on Workmen’s compensation fund is determined at ₹ 1,000.
- Employee’s provident fund be raised by ₹ 2,500.
- C is unable to bring goodwill in cash. Goodwill valued at ₹ 8,000.
- Stock is valued at ₹ 24,180.
Prepare Partner’s Capital Accounts and Balance Sheet of the new firm.
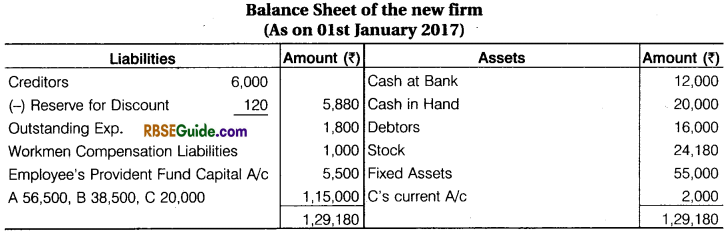
Working Note :
(1) Sacrifice Ratio = Old Profit Sharing Ratio – New Profit Sharing Ratio
(2) Workmen compensation fund deducted by relating liabilities and Balance Amount of Fund Distributed among Old Partners their Old Profit Sharing Ratio.
Change in the Profit Sharing Ratio among the Existing Partners :
Sometimes the existing partners’ decide to change their current profit sharing ratio. As a result of change in profit sharing ratio, one or more partners may acquire extra share of profit at the cost of one or more other partners. As such the following adjustments are made :
- Profit or loss on revaluation of assets and liabilities are divided in old profit sharing ratio.
- Undistributed profits and losses are distributed in old profit sharing ratio.
- On account of change in profit sharing ratio losing partners should be credited with the value of sacrifice and the gaining partners should be debited.
- Other adjustments are made in the same way as are made at the time of admission of a new partner.
At that time some following entries made :
(1) CalculatIon of Sacrifice and Gain Ratio:
(A) Sacrifice Ratio = Old Profit Sharing Ratio – New Profit Sharing Ratio
(B) Gaining Ratio = New Profit Sharing Ratio – Old Profit Sharing Ratio
(2) AccountIng Treatment of Goodwill

(3) AccountIng Treatment of Reserves and Undistribuied Profit or Loss
(a) Distribution of Reserve and Undistributed Profit :

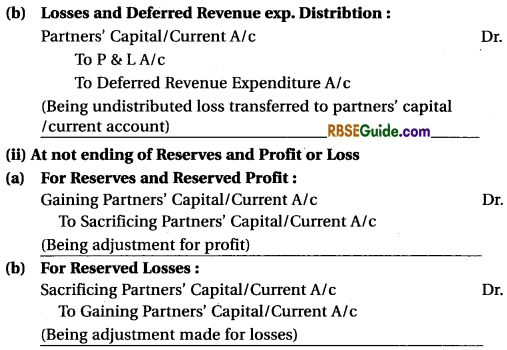
(4) AccountIng Treatment of Assets and Liabilities Revaluation :
(a) If on re-establishment of firm partners wants to show assets and liabilities at revaluate value them :
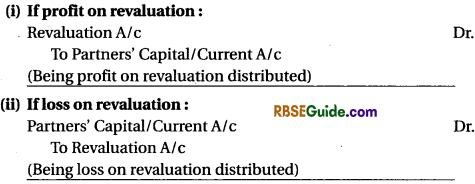
(b) When correction value of assets and liabilities is not shown in books means adjusted by the capital account of partners.
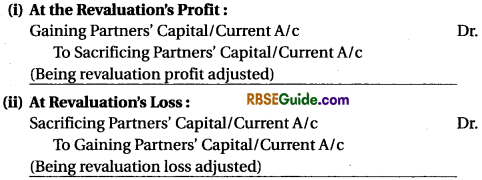
(5) Adjustment of Capital : The partner who has more capital at the adjustment of capital, takes away it from business and which partner’s capital is not enough, he brings the needed capital.
Admission of a New Partner Notes Important Terms
→ Admission of a Partner : Admission of a partner means new partner being admitted in the firm.
→ New Profit Sharing Ratio : New profit sharing is the ratio in which all the partners including the new or incoming partner, share future profits and losses of the firm.
→ Sacrificing Ratio : Sacrificing ratio is the ratio in which the old or existing partners forego, i.e., sacrifice their share in favour of the new partner.
→ Goodwill: Goodwill is an intangible assets resulting from the efforts made by the existing partners of the firm which results in continuous profits.
→ Revaluation of Assets : Revaluation of assets means change in the value of assets, i.e., present value being different from the book value of the assets.
→ Reassessment of Liabilities : Reassessment of liabilities means reassessing the liabilities and determining the change, i.e., whether the liability is more or less than that shown in the books of accounts. ‘
→ Revaluation Account or Profit and Loss Adjustment Account : It is an account to which increase in the value of assets and decrease in the value of liabilities is credited. Decrease in the value of assets and increase in the value of liabilities is debited. It is closed by transferring the profit or loss to the capital accounts of the old or existing partners in their old profit sharing ratio.
→ Reserve : Reserve means accumulated or undistributed profit. It is created out of profit.
Workmen Compensation Reserve : It is a reserve created out of profit for payment of compensation to workers.
Investment Fluctuation Reserve : It is a reserve created to meet the fall in the value of investment.
