Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 19 Sustainable Agriculture
Introduction
The term “sustainable” means helping hand or worthy or able to contine over a period of time or causing little or no damage to environment. Similarily, the meaning of term “agriculture” is cultivation of crop and live stock. Hence, this chapter concerns with the study of agriculture and agricultural practices which are in use since long time without any adverse effects.
Definition
Sustainable agriculture is an integrated system of practice of cultivation of agricultural plants and live stock (animals) in which cultivation sites can be maintained for a long period of time without any harm, so that human requirement can be fulfilled for long time.
In ancient time, the three basic needs of human being namely food, cloth and shelter were fulfilled using the plants. However, as the time passed away the human requirements increased manyfolds. The population explosion, industrial revolution and development of transport facilities created tremendous pressure on the natural resources and some of them are depleting at an alarming rate.
![]()
If this situation continues, the future generation will have to suffer for lack of resources. There may be lack of fresh air for breathing, pure and potable water for drinking and lack of nutritive food. Now, we have started thinking globally that how the present human needs are fulfilled without creating imbalance in nature and without compromising the needs of further generation. Looking into this context, the concept of sustainable agriculture has developed.
Since last few decades, many techniques have been applied in the agriculture such as use of chemical fertilizers, use of insecticides and other pesticides, excess use of underground water for irrigation, dense farming, use of petroleum products etc. This has resulted in to sharp depletion of natural resources and caused environmental pollution. Such problems can be solved by using sustainable agriculture in which new sources can be used with conservation of non-renewable resources.
Methods of Sustainable Agriculture
It can be achieved by using following methods :
- Organic agriculture
- Mixed farming
- Mixed cropping
- Crop rotation
- Use of biopesticides
Organic Agriculture
1. Today, food and shelter are the major problem for human beings. Although, there is increase in food production but it is unable to combat with increasing human population. To increase agricultural (food) production we started using chemical fertilizers and pesticides enormously which resulted in loss of soil fertility. Further, manufacturing chemical fertilizers is costly and requires our natural resources such as coal, petroleum etc. As a result, level of pollution is increasing day by day.
![]()
2. Organic agriculture is helpful in making the nature pollution free, in increasing soil fertility by providing micronutrients to the plants and in the conservation of biodiveristy. Soil is a living system which inhabits useful microorganisms. These microorganisms are an important link among plants, animals and human beings. They assist plants to obtain nourishment from the soil. The concept of organic agriculture aims to make microbial cycle more strong.
3. Organic farming is a natural technique of agriculture in which no artificial techniques/devices are used.
Aims of Organic Agriculture.
- To increase the soil fertility and to ensure its continuity for long.
- It results in to increased metabolic activities of microbes, soil organisms, plants and organisms related with agricultural process.
- Eco friendly use of natural ecosystem.
- Promotes use of local agricultural practices and alternative sources of energy in agriculture.
- Increase in production of food with high nutritious values.
- Prevents pollution by use of new technology related to agriculture. –
Biofertilizers
These days, scientists are cultivating the microbes which can fix atmospheric nitrogen at commercial scale. The microbes which enrich the soil in nutrients by their biological activities are called as
The biofertilizers also accelerates the process of mineralization in addition to increase in soil fertility. Some of the examples of biofertilizers are-Bacteria; Cyanobacteria, Fungi etc. These biofertilizers are mainly of six types :
(i) Symbiotic bacterium : Rhizobium
These bacteria are found in the root nodules of leguminous plants and obtain nutrition from the plant. They fix (trap) atmospheric nitrogen and convert it into ammonia and liberate it outside, which intum is consumed by the plant.
Rhizobium can fix atmosphric nitrogen at a rate of 50 to 150 kg per hectare per year. The use of these bacteria as biofertilizer can increase production up to 15-20%. Even the next crop grown after its application will yield more because of increased soil fertility .
![]()
(ii) Non-symbiotic Bacteria
Non-symbiotic bacteria such as Azotobactor, Azospirillum, Clostridium can also fix the nitrogen present in the soil and make it available to the plant. These bacteria absorb the free nitrogen of soil and convert it into organic nitrogenous compounds. After death of these bacteria, the nitrogenous compounds contained in these are decomposed by decomposing bacteria and the ammonia is released. The released ammonia is converted into nitrite and finally into nitrate which is finally usd by the plants.
Azotobactor is used as biofertilizer during rice, maize, cotton cultivation. The production is increased upto 20%.
(iii) Blue Green Algae or Cyanobacteria :
Cyanobacteria such as Anabaena, Nostoc, Plectonema and other non-symbiotic prokaryotes perform nitrogen fixation. Cyanobacteria have special cells called The Nif gene present in these cells does nitrogen fixation. Rice fields are ideal for growth of blue green algae, hence use of blue green algae in paddy fields increases production of rice.
Now a days, one aquatic pteridophyte called Azolla is also used along with blue green algae as algal biofertizer in Southern and South-East Asia. The Azolla is a floating aquatic fern. Leaves of Azolla contain blue green algae Anaebaen azollae which fixes atmospheric nitrogen.
Anaebaena pinnata is also a good biofertilizer. When it is used in combination with Azolla, it can increase the rice production by 50%.
Anaebaena azollae is commercially produced at Central Rice Research Institute, Cuttack.
(iv) Mycorrhiza
Symbiotic association of fungi with roots of higher plants is called Fungus absorbs nutrients from soil and provide to host plant and in turn host plant provides nutrition to the fungus.
(v) Phosphate dissolving Bacteria :
Some bacteria such as Pseudomonas, Microbacterium, Bacillus Convert non-available inorganic phasphate into available organic phosphate which is easily absorbed by plants.
![]()
(vi) Organic manure
In India organic waste products are available in large amount in the form of domestic wastes, urban waste, sewage, remains of crops, animal excreta, bone powder etc. These wastes can be converted into organic manure by microbial degradation and can be used by plants.
Economic & Ecological Importance of Organic Agriculture.
- It is a very simple and cheap technique, hence can be adopted by even small farmer.
- Use ofbiofertilizers increases water holding capacity and aeration of soil.
- Temperature and pH of soil is maintained by use of biofertilizers as a result bacteria in soil remain functional.
- By organic farming, toxicity of soil is reduced and ecological balance is maintained.
- By use ofbiofertilizers we can convert barren land into fertile land. Degradation of the biofertilizers produces organic acids which reduces soil alkalanity.
- It is pollution free and maintain soil fertility.
- Soil erosion can be prevented by organic agriculture.
- The biofertilizers release balanced amount of nutrients and thus leads to increased ferility of soil.
- Soil fertility is maintained for years by organic farming and leads to increase in yield for long duration.
- Cost of crop production is reduced by use ofbiofertilizers and ultimately leads to economical profit.
Mixed Farming
Introduction
Term “Farming” means agriculture. It includes many acts such as dairy fanning, fish farming, poultry, piggery etc. Although the above farming also involves various animals which yield milk, ghee, meat, eggs and fishes. All the animals eat plants or plant products as food. Mixed farming is a system in which different types of agricultural works are carried out simultaneously at one farm (place) such as poultry, dairy production, crop production etc. Mixed farming depends on many factors such as quality of soil, nature of livestock, availability of water, technical help, economic resources etc.
Systems of Mixed Farming
Following system can be established under mixed farming:
- Food-fodder farming system : In this system food crops such as rice, wheat, maize and fodder crops such as barseem, jowar etc. are cultivated.
- Agro-forestry System : Under this systems along with seasonal crops, trees can also be grown.
- Horti-pastrol system : Fruit bearing trees, shrubs and grasses are grown together. In this way mixed farming is a composite effort through which agricultural products are produced for long time without causing any harm to environment.
Mixed Croping
Cultivation of more than one crops in same field is called mixed crop production or mixed cropping. This process is practiced since ancient time. This method is mostly adopted in areas dependent on rains. Main objective of this farming is to reduce the harmful effect on the crops in absence of rain. When one crop in field gets destroyed or production is less, even then the other crop will give some revenue.
While doing mixed farming, nature of both crops, soil and water availability should be kept in mind. Mixed farming has many advantages like if one crop is lost still there will be some profit, more than one agricultural products are produced, increase in fertility of soil and less loss by pests infection and many more benefits.
Under mixed cropping, the crops which are produced jointly are cultivated Some of the examples are :
- Soyabean + Arhar
- Maize + Urd
- Arhar + Moong
- Groundnut + Sunflower
- Maize + Gram
- Maize + Mustard.
Crop Rotation
Growing same crop in the same field constantly for many years create many problems. Some of the major problems are—deficiency of some specific hutrients in the soil and increase in soil bom plant diseases. The simple solution of these problems is “crop rotation”.
Cultivation of new crop/crops every year in one field is called as crop rotation. Since the nutrient requirement of different crops is different, hence the soil will not be deficient in particular nutrient. Moreover, pathogens present in soil will also be destroyed in absence of specifc host. Hence crop rotation is most effective method for management of soil borne pathogen.
The crop rotation may be of one yearly or two yearly or three yearly basis. For example
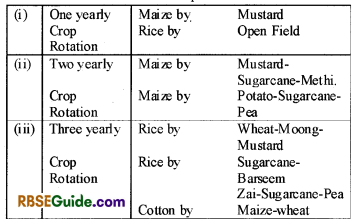
Biopesticides
1. The animals or plants which cause harm to crops or their products are called as pests. Fungi, insects and large sized animals can also be pest.
2. The biological-factors which are used to destroy insects, weeds and pathogens are called as bio pesticides. Certain viruses, bacteria, fungi and protozoa can be used as biopesticide.
3. Some microorganisms such as viruses, bacteria, fungi etc. attack insects and kill them. Such organisms are now used at commercial level. One of the good example is Bascillus thuringiensis at commercial level. One of the good example is Bascillus thuringiensis bacterium.
4. Spores of Bascillus thuringiensis produce a crystal protein which acts as a pesticide. These spores are used to kill the eggs of certain insects. The biopesticide obtrained from this bacterium was first used at commercial level.
5. Some other bacteria and fungi are used to control weeds and pathogens of other crops.
6. Destruction of pests and pathogens using bacteria, fungi and other organisms is called as biocontrol.
7. Problem of pests can also be controlled by producing pest resistant plants by hybridization.
8. The crop rotation also helps to control some pests.
9. Pests can be controlled by using pest eater / predators. They cause diseases in the pests.
![]()
Some other methods of biological control of pests are as follows :
- By adopting planned crop rotation.
- Sterilization of males of pest organisms by raidation or by chemicals so that their population growth can be controlled.
- By disturbing life cycle of pathogens by using hormones.
- Infection of pests by pathogen living on them.
Use of chemical pesticides is delitereous to human beings and other animals because these chemicals are toxic and poisonous. Presence of these chemicals and their by products in the agricultural products are dangerous for human health. Use of biopesticides will reduce the use of chemical pesticides. This is the reason that biological control of pest is beneficial.
