Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 33 Embryonic Development in Man
General
The process of formation of multicellular embryo from single cell zygote is called as embryogenesis.
It involves cleavage, morulation, Blastulation, Gastrulation, differentiation etc.
Cleavage and Morulation
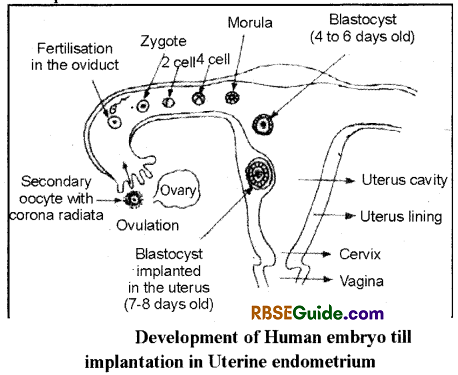
Fertilization occurs in Fallopian tube, where sperm and ovum fuse to form zygote. The division of zygote by a series of mitotic cell division into a multicellular embryo is called Cleavage.
Human zygote divides by mitotic cell division into two cells and forms two celled stage. Second division takes place in cells and four celled stage is formed. Cell divisions continue and number of daughter cells increase but the size of zygote remains same, (means progeny cells reduce in their size after each division). It reaches upto 16 cell stage. It looks like a solid ball fike structure which is known as Morula.
The process of divisions till morula formation is called Morulation. This process takes about 3 days. Outer membrane (Zona pellucida) of morula prevents its implantation at site other than uterus.
![]()
Blastulation:
Formation of blastula / blastocyst from morula is known as blastulation.
In human morula the outer cuboidal cells become flattened when it reaches into uterus. These flattened cells are called as Trophoblast, by which it adhere with uterine epithelium.
Cleavage continued and a cluster of cells differentiates into two distinct groups, the epithelial like trophoblast or nutiritive cells surrounding the expanding cavity and inner cell mass of formative cells of the embryo.
The cavity is called blastocoel and embryo is known as blastocyst (a kind of blastula) in human.
![]()
Implantation
The attachment of blastocyst from uterine wall is known as Implantation. Slowly, endometrium of Uterus surrounds the embryo from all sides, hence it is interstitial type of implantation. Implantation becomes necessary to get nourishment and support for further development.
Gastrulation
During implantation zona pellucida disappears and the trophoblast cells become giant sized and aggressively invode the uterine tissue and make contact to forming placenta. Inner cell mass at this time undergoes differentiation and a layer of very flat cells appear on the interior surface of the inner cell mass that forms future endoderm. The remaining dorsal inner cell mass is called epiblast, which is presumptive material for ectoderm and mesoderm.
Formation of three germinal layers from a single layered blastocyst. The bastocoel get obliterated & a new cavity called gastrocoel or archenterone is formed. It is called gastrula. The method by which blastula becomes or converted into gastrula is called Gastrulation.
The mesodermal cells soon involute through the primitive streak and diverge anteriorly and laterally, occupying position between ectoderm and endoderm. Epiblast also contribute some cells fo endoderm. The cells migrating to their future places by amoeboid movements.
Fate of Germinal layers
Every germinal layer out of three germ layers form definite tissues, organs and organ system of human body.
The fate of these germinal layers in the developing embryo and in adult is mentioned in table
![]()
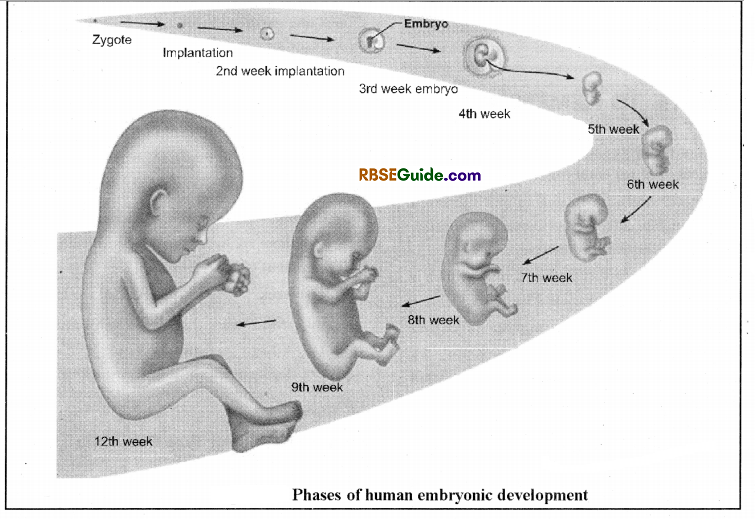
Summary of Embryonic Stages in Man
First Week
Fertilization of ovum within 24 – 30 hours, two celled stage within 48 hours from fertilization. Formation of morula by third day and entry of blastocyst into the uterus on 4th day. Implantation of blastocyst by 7 – 8 days.
Second Week
Blastocyst completely invade in Uterin endometrium and formation of extraembryonic membranes from trophoblast completes. Primitive streak is formed till 14th day
Third to Sixth Week
Formation of mesoderm and endoderm germ layers.
Neurulation begins on 20th day.
On 28th day heart beats (113 beat/minute) begins and quantity of amniotic fluid is increased. Lungs and kidney rudiments are formed. Development of brain begins repidly.
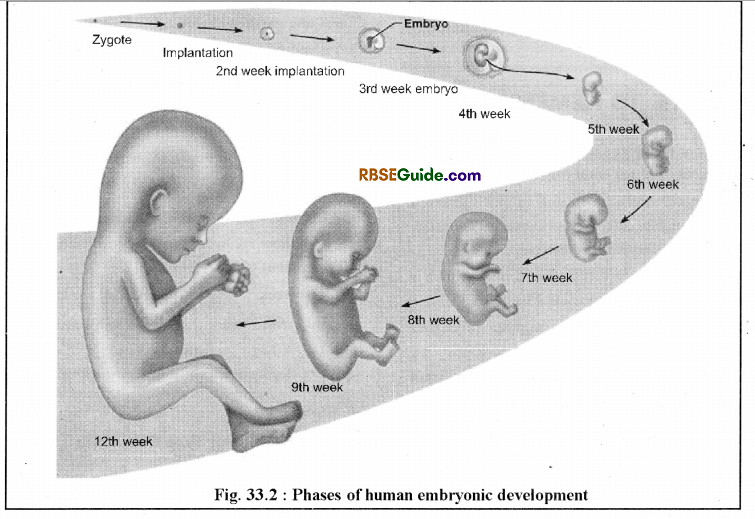
6th t0 8th Week
- External ear buds appears.
- Formation of RBC;’s in liver, nipples and diaphragm
- development in Sixth week of development takes place.
- In 7th week bone formation starts. At the end of VIIIth week a small human like structure appears, now it is called Foetus in which heart is fully developed and heart beat at the rate of 167 times per minute.
- In 80% embryos the right hand or in remaining left hand becomes active in 8th week of development.
- It acts as first proof about the upcoming child be right handed or left handed. 8th week embryo changes its position & becomes active.
- Development of eye lids also begin and embryo starts to move on left or right side up to 90% of structures developed upto the end of 8th weak.
9th to 12th Week
- Movement in hands and feet is possible, sucking of thumb, development of vocal cords initiates.
- Development external sex organs hence
 can be identified in 9th week.
can be identified in 9th week. - The weight of embryo increases 75% in 9th and 10th week of development.
- In eleventh week, they started yawning and suck their right thumb.
- In 10th and 11th week fingers are mashed & nail develope fully.
- Lips & Nose develop by end of 12th week.
- Development of taste buds in mouth, digestion of glucose in intestine and extruded fecal of developing child is called miconium.
- Movement of child in the womb is called as clinking.
- Movement of girl child is more as compared to male child during pregnancy.
- Formation of Teeth
![]()
5th to 6th Month
Complete development of respirator 7 tubes, developing child is covered with a whitish fluid, called Vernix.
Internal ear develops completely. Development or growth of hairs on the head begins and skin glands development begins.
7th Month till birth
Child start moving eye-lids Extensively brain development in size and its capacity.
Development of lacrymal glands, capacity of smell. The brown fat below the skin develops for temperature control after birth.
Before parturition secretion of oxytocin from corpus luteum of ovary causes labour pains which are followed by birth of young one.
