Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 6 The Cell
RBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 6 Multiple Choice Objective Questions
Question 1.
Study of cell structure and composition is called as –
(a) Biology
(b) Morphology
(c) Cell Biology
(d ) Genetics
Question 2.
Living cell was first seen by –
(a) Robert Hooke
(b) Robert Brown
(c) VonMohl
(d) Leeuwenhoek
Question 3.
Who stated “Omnis cellulla e cellella” –
(a) Schleiden
(b) R. Virchow
(c) Schwann
(d) Corti
Question 4.
Exception of cell theory is-
(a) Cyanobacteria
(b) Viruses
(c) Bacteria
(d) All
Question 5.
de Duve discovered –
(a) Mitochondria
(b) Ribosomes
(c) Lysosomes
(d) Golgi body
Question 6.
Who discovered electron microscope –
(a) Robert Hooke
(b) Schleiden & Schwann
(c) Watson & Crick
(d) Knol & Ruska
Question 7.
ER was discovered by-
(a) Porter
(b) Brown
(c) Okawa
(d) Duve
Answers:
(1) c, (2) d, (3) c, (4) d , (5) c, (6)d, (7) a
RBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 6 Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define cell.
Answer:
It is a structural & functional unit of life.
Question 2.
Who propounded protoplasmic theory-
Answer:
J.E. Purkinje (1834).
Question 3.
Where the ribosomes are found-
Answer:
Cytoplasm.
Question 4.
Respiration site in prokaryotes is …….
Answer:
Plasma membrane.
Question 5.
Give examples of prokaryotes –
Answer:
Bacteria, Cyanobacteria, Mycoplasma etc.
Question 6.
Give names of orgenelles not bounded by membrane-
Answer:
Ribosome.
Question 7.
Who first seen the living cell-
Answer:
Leeuwenhoek.
Question 8.
What is tissue –
Answer:
It is a group of similar cells which performs a specific function.
RBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 6 Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Showing differences between plant and animals cells
Answer:
| Plant Cell | Animal Cell |
| 1. Presence of dead cell wall made up of cellulose. | 1. Cell wall is absent. |
| 2. Presence of large central vacuole. | 2. Presence of small vacuoles which may be absent. |
| 3. Presence of plastids of many types. Such as chloroplast, chromoplast, leucoplast etc. (They are absent in prokaryotes & fungi). | 3. Plastids are absent. |
| 4. Centrosome is absent except in some algae and fungi. | 4. Presence of centrosome bearing two centrioles. |
Question 2.
Differences between Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Answer:
| SN | Character | Prokaryotic cell | Eukaryotic cell |
| 1 | Example | Bacteria, cyanobacteria, mycoplasma etc | Algae, Fungi, plant & animal cells |
| 2 | Cell size | 0.1 to 5 micron diameter | 5 to 20 micron diameter |
| 3 | Orgenelles | ||
|
|
|
|
Question 3.
Give an account of cell theory.
Answer:
Nigelli (1846) and Virchow (1855) explained cell theory as-
- All organisms are made up of cell or cell products.
- New cells are formed by the division of the preexisting cells.
- Cell is a structural and functional unit of living body.
- Cell bears the hereditary characters of the organism.
- The continuity of life from generation to generation is through the cells.
Question 4.
Differentiate cell wall & plasma membrane
Answer:
The cell wall is non-living and made up of cellulose.
The cell membrane is living and made up of proteins and phospholipids.
Question 5.
Give the names of scientists who discovered ribosomes,mitochondria & Golgi body.
Answer:
Ribosomes – Palade
Mitochondria – Kolliker
Golgi Body – Camilo Golgi
RBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 6 Essay Type Questions
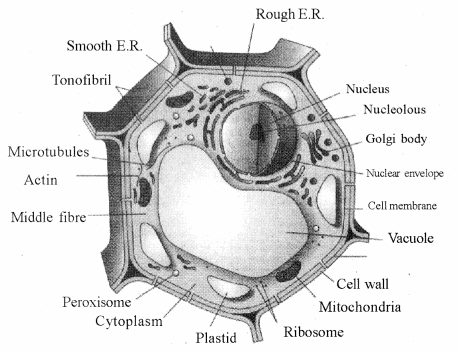
Question 1.
Describe plant cell with suitable diagram
Answer:
Question 2.
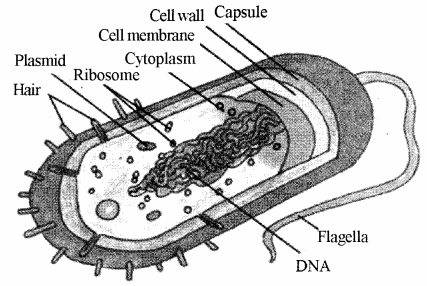
Describe prokaryotic cell with suitable diagram.
Answer:
Prokaryotic cells
[Gr. Pro = Primitive & Karyon = Nucleus]
The prokaryotic cells such as Blue-green algae (cyanobacteria), bacteria, mycoplasma etc. are without organized nucleus and membrane bounded orgenelles. They have nucleic acid in the form of circular bacterial chromosomes called nucleoids. Histone proteins are absent.
They undergo amitosis.
The outer covering of the prokaryotes is three layered viz. –
-
- Outer layer
- Cell wall &
- Plasma membrane.
1 Outer layer : It is made up of glycocalyx (Polysaccharides). It is in the form of hard covering called capsule or soft covery called Slime layers.
2. Cell wall : It forms structural covering and it is strong due to peptidoglycan.
3. Plasma membrane : It is the innermost layer which is semipermeable. It is made up of proteins (lipoprotein), lipids and oligosaccharides. It is the site for respiration, photosynthesis, lipogenesis and metabolic activities.
The prokaryotes have mesosomes which are three-layered and primarily meant for respiration. Some autotroph prokaryotes have pigments in lamellae instead of plastids which perform photosynthesis and nitrogen fixation.
They cytoplasm of prokaryotes consists of cyanophycean granules, glycogen granules, phosphate granules, polyhyderoxybutret granules, sulphur granules, carboxysomes and gas vacuoles. Presence of 70S ribsomes which are made up of two subunits of 50S & 30S and their dimension is 14-15 x 20nM. The genetic material is in the form of nacked DNA and some RNA. Histone proteins are absent.
Examples – Members of Kingdom-Monera such as bacteria, cyanobacteria, Archibacteria, Mycoplasma, Actinomycetes etc.
Question 3.
Draw a labeled diagram of animal cell & differentiate plant & animal cells.
Answer:
| Plant cell | Animal Cell |
| 1. Presence of dead cell wall made up of cellulose | 1. Cell wall is absent. |
| 2. Presence of large central vacuole. | 2. Presence of small vacuoles which may be absent. |
| 3. Presence of plastids of many types. Such as chloroplast. chromoplast, leucoplast etc. (They are absent in prokaryotes & fungi). | 3. Plastids are absent. |
| 4. Centrosome is absent except in some algae and fungi. | 4. Presence of centrosome bearing two centrioles. |
| 5. Spindle fibres are formed by proteins found in the cytoplasm. | 5. Spindle fibres are formed by the centrosome. |
| 6. Presence of plasmadesmata. | 6. Presance of desmosome |
| 7. Presence of spherosome. | 7. Spherosomes are absent. |
| 8. Starch is the stored food. | 8. Food is stored in the form of glycogen & starch. |
| 9. During cell division, the cell plate forms from centre to the periphery (cytokinesis) | 9. The cytokinesis begins from periphery to the centre as groove. |
Question 4.
Differentiate prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Answer:
| SN | Character | Prokaryotic cell | Eukaryotic cell |
| 1 | Example | Bacteria, cyanobacteria, mycoplasma etc | Algae, Fungi, plant & animal cells |
| 2 | Cell size | 0.1 to 5 micron diameter | 5 to 20 micron diameter |
| 3 | Orgenelles | ||
|
|
|
|