Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 20 Bioenergy
RBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 20 Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Example of fossil fuel is?
(a) Alcohol
(b) Gobar Gas
(c) Petrol
(d) Hydrogen
Answer:
(c) Petrol
Question 2.
Major component gas in Gobar gas is?
(a) CO3 and H2
(b) CH2 and H2
(c) CH4 and CO2
(d) CO2 and SO2
Answer:
(c) CH4 and CO2
![]()
Question 3.
Energy obtained from living organisms/biological factors is?
(a) Bioenergy
(b) Biofuel
(c) Mechanical Energy
(d) Biomass
Answer:
(a) Bioenergy
Question 4.
Presence of which gas makes biogas less effective in terms of natural gas?
(a) H2
(b) CH2
(c) CO2
(d) SO2
Answer:
(c) CO2
![]()
Question 5.
Which chemical component is added with petrol in automobiles/automotive?
(a) Ethanol
(b) Methanol
(c) Propanol
(d) Butanol
Answer:
(a) Ethanol
RBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 20 Very Short Answer Questions
Fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
- ……………. source is available in limited quantity in nature?
- Energy obtained from biological factors is called ……….?
- All those products obtained by the process of photosynthesis are collectively called …….?
- The ………………. gas is obtained by fermentation of organic compounds by Bacteria.
- Gobar gas contains ……….. % of carbon dioxide.
Answer:
- Nonrenewable source of energy.
- Bio-Energy
- Bio-mass
- Bio-gas or Gobar gas
- 31
![]()
Question 2.
Write the names of two petrol plants.
Answer:
- Euphorbia Lathyrus.
- Hevea brasiliensis.
Question 3.
What is Petro farming?
Answer:
Some plants are used to obtain biodiesel to be used in place of diesel/petrol. These are called as petrol plants. Their cultivation is called a Petro crop.
Question 4.
What is meant by energy crop?
Answer:
Some plants are used as raw material for the production of ethanol.
Example: sugarcane, sugarbeet, potato, maize, turnip etc. These plants are called as energy plants and their cultivation is called an energy crop.
RBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 20 Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is Biodiesel?
Answer:
Seeds of many plants such as of Soyabean, Mustard, Castor, Flaxseed, Sunflower, Groundnut, Jatropha, Pongamia (Karen) have an adequate amount of lipids and fatty acids. These lipids contain a tremendous amount of energy. When esterification of fatty acids present in lipids is done a liquid is formed which is known as biodiesel.
Question 2.
Write the importance of Biodiesel.
Answer:
- Biodiesel acts as a lubricant as a result efficiency of the engine is increased and the cost of maintenance is reduced.
- By using this biodiesel, carbon monoxide and suspended particles in the exhaust are comparatively less.
- This is an important source of alternative sources of energy and can lead to employment, increasing income etc.
- Biodiesel may prove effective in economic stability and development in our country as these plants can be grown on barren land, near the roadside and non irrigated lands.
Question 3.
What are the salient features of fuelwood?
Answer:
The fuelwood should have –
- High combustion efficiency.
- High-calorie value.
- It should not break and degrade into small pieces on burning.
- Less water and resin content so that can be easily dried.
- On burning, produces less smoke and no odour.
![]()
Question 4.
Why the efficacy of Biogas is less than Natural gas.
Answer:
The capacity of Biogas is a little less than natural gas because of 31% of carbon dioxide gas present in Biogas. If the percentage of CO2 is reduced then the calorific value of this gas can be increased.
Question 5.
Write the benefits of alcohol as fuel.
Answer:
Ethanol can be used in auto vehicles. It can be used in pure form or mixed with petrol at 5% or 10% or 25% or 50%. Use of ethanol increases engine energy value and minimises pollution.
Question 6.
Give examples of Petro-plants.
Answer:
There are some plants whose products can be used in place of fossil fuel (petrol and diesel). These plants belong to plant families such as Apocynaceae, Asclepiadaceae, Euphorbiaceae, Sapotaceae, Urticaceae, Compositae etc.
Some plants are as follows:
- Euphorbia Lathyrus.
- Calotropis prose.
- Plumeria sp.
- Ficus sp.
- Acharyas Zapata.
Question 7.
What is Biomass?
Answer:
The chief source of bioenergy is sunlight. Out of total solar energy reaching earth, only 0.2% is stored in plants in the form of biomass. All the materials formed by photosynthesis form the bio-mass. As all living organism depend for their needs one plant and derive energy directly or indirectly from plants, hence all living organisms and their by-products can be included as biomass.
RBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 20 Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain in brief the examples of energy resources which are used against fossil fuel.
Answer:
The main sources of alternative energy are:
1. Biomass:
The basic source of bioenergy is sunlight. Out of total solar energy reaching earth, 0.2% of light is stored in plants in the form of biomass. All those materials formed from photosynthesis is called bio-mass. We can include all living organisms and their by-products in the category of biomass, which may be a source of energy.
Example:
- Plants containing lignocellulose: Eucalyptus, Leucaena, Maize, Sugarcane, Sugarbeet, Pine tree.
- Aquatic plants: Water hyacinth (Jal Kumbha).
- Waste products: Manure, refuse, wood, remains of crops-straw, lemon rinds, remains of sugarcane, jaggery, fibres of coconut, flower-leaf, cow-dung etc.
2. firewood:
Wood is the most commonly used fuel and is being used by a human for a long time back. About 50% of the Indian population use wood fuel for domestic and cottage industries because it is easily available and its use does not require specific knowledge.
It is used in a maximum amount in developing and undeveloped countries of Asia and Africa. Use of wood as fuel in our country is a major cause of deforestation and destruction of wildlife and also a major source of environmental pollution in our country.
Salient features of good wood fuel:
- It must have high combustion potential.
- It must have high-calorie value so as to generate more heat on combustion.
- It should not split and break into pieces on combustion.
- The amount of moisture and resin content should be low.
- It should not produce stinking odour on combustion and should produce minimum smoke.
Some plants which provide good quality fuelwood are as follows:
| Hindi Name | Botanical Name |
| Desi babool | Acacia Nilotic |
| Kumba | Acacia Senegal |
| Angrezi babool | Prosopis juliflora |
| Khair (Kattha) | Acacia catechu |
| Siris | Albizzia lebbeck |
| Jamun | Syzygium cumin |
| Khejri | Prosopis cineraria |
| Ardu or Mahaneem | Aclenthes axels |
| Aam (Mango) | Mangifera indica |
| Sali, Lobban | Boswellia cirrela |
| Dhokla | Anogeisus pendula |
| Houzz (Safed Kikar) | Acacia leucoFlorida |
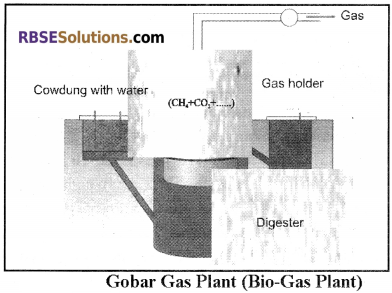
3. Gobar gas or Biogas:
More than 70% population of our country resides in villages where animal livestock is plentiful and easily available. Generally, the dung obtained from cattle is used for burning by making cow-dung cakes. Instead of burning, the dung should be utilized for making biofertilizer. For this, the dung should be filled into big pits regularly. Pits should be made on a higher level and its depth should not exceed one metre.
Fermentation of organic compounds is done by bacteria and the gas so formed is known as biogas. In India, cow dung is used for biogas production. In many villages “Gobar” gas plant (bio-gas plant) is being operated for energy production. This is not only a cheap source of energy instead it plays its important role in controlling environmental pollution.
In “Gobar” gas plant anaerobic fermentation is completed in three steps:
- In the first phase, anaerobic bacteria convert complex organic compounds such as cellulose, hemicellulose, into simple compounds.
- In the second phase, both partially aerobic and anaerobic bacteria convert simple components first into carbonic acid and finally into acetic acid.
- In the third phase, Methanobacteria converts acetic acid into methane gas. The residue in biogas plants is called slurry. It is dried and further utilized as manure.
The capacity of Biogas is a little less than natural gas because of 31% carbon dioxide gas present in Biogas. If the percentage of CO2 can be reduced then the calorie value of this gas can be increased. Presently extensive research is going on so that the calorie value of gases produced by fermentation of biowaste materials can be increased. In 1961, Gobár Gas Research Station was established at Aieetmal in Ottawa district of Uttar Pradesh.
4. Biodiesel:
- Liquid substances derived from biological products resembling diesel are called biodiesel.
- Biodiesel is environment-friendly renewable fuel composed of vegetable oils, fats and latex.
- Chemically it is named as fatty acid methyl ester, FAME.
- Solar energy is used by the plants and it is stored in the form of fats, sugar or starch.
- Plants also store hydrocarbon in a special form of storage oil in their seeds which is used as a source of energy at the time of germination of seeds.
- It is this hydrocarbon which has said the foundation of the biodiesel hypothesis. Rudolf Diesel (1895) made an engine by using these oils only.
5. Algal hydrogen factory:
- Algae are photosynthetic aquatic plants and under normal conditions produce carbohydrates and oxygen by photosynthesis as of higher plants.
- In the year 2000, Anastasios Melis proved in his experiments that if during day time supply of Oxygen and Sulphur is stopped to algae then metabolic reactions in algae change and these start producing H2 in place of O2 in photosynthesis.
- We know that H2 is highly inflammable so can be an important source of energy. If these experiments will be successful, this would become a great source of energy in future.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the process of formation of gobar gas.
Answer:
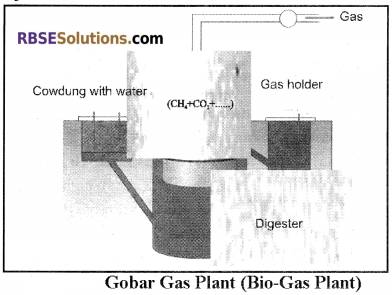
More than 70% population of our country resides in villages where animal livestock is plentiful and easily available. Generally, the dung obtained from cattle is used for burning by making cow-dung cakes. Instead of burning, the dung should be utilized for making biofertilizer. For this, the dung should be filled into big pits regularly. Pits should be made on a higher level and its depth should not exceed one metre.
Fermentation of organic compounds is done by bacteria and the gas so formed is known as biogas. In India, cow dung is used for biogas production. In many villages “Gobar” gas plant (bio-gas plant) is being operated for energy production. This is not only a cheap source of energy instead it plays its important role in controlling environmental pollution.
In “Gobar” gas plant anaerobic fermentation is completed in three steps:
- In the first phase, anaerobic bacteria convert complex organic compounds such as cellulose,
hemicellulose, into simple compounds. - In the second phase, both partially aerobic and anaerobic bacteria convert simple components first into carbonic acid and finally into acetic acid.
- In the third phase, Methanobacteria converts acetic acid into methane gas. The residue in biogas plants is called slurry. It is dried and further utilized as manure.
The capacity of Biogas is a little less than natural gas because of 31% carbon dioxide gas present in Biogas. If the percentage of CO2 can be reduced then the calorie value of this gas can be increased. Presently extensive research is going on so that the calorie value of gases produced by fermentation of biowaste materials can be increased. In 1961, Gobár Gas Research Station was established at Aieetmal in Ottawa district of Uttar Pradesh.
Question 3.
Explain how alcohol can be obtained from starch and cellulose.
Answer:
- Starch crops (Rice, Millets) and Sugar plants (Sugarcane and Beetroot) are important crops for biofuel production. By using these important sources of energy, we can produce many products.
- Starch and Sugars obtained from these plants can be converted into ethanol. Cellulose is an important product of plants and with the help of cellulase enzyme, it can be broken down into glucose and finally into ethanol.
- In woody plants lignin is also found along with cellulose as lignocellulose. With the help of enzymes, lignocellulose can be converted into sugar and afterwards with the help of yeast this sugar is converted into ethanol by the fermentation process.
- Some plants such as sugarcane, potato, beetroot are used as raw materials for ethanol production. These plants through which ethanol is produced are called energy plants. New techniques are being developed to use this ethanol in automotive.
- Brazil is the leading country to use this technique. In Brazil, the Brazilian National alcohol program was started in 1975.
- Now in Brazil, all cars are running on alcohol or 20% mixture of ethanol mixed with petrol.
- Sugarcane is one of the main cash crop grown in many states in India. Molasses (Black treacle is a viscous product resulting from refining sugarcane or sugarbeets into sugars) are a by-product of the sugar industry.
- 65.5% pure ethanol is produced from molasses but for mixing with petrol, 66.8% ethanol purity is required. By using a distillation plant, 66.8% ethanol can be derived from molasses by modification.
- Government of India has established three plants for mixing 5% ethanol with petrol for experimentation. These are established in Bareilly (UP) and Manmard and Meeraj (Maharashtra).
![]()
Question 4.
Write an essay on “How biodiesel can be an alternate source of energy as liquid fuel”.
Answer:
Production of Biodiesel in Rajasthan and India:
- At present India is able to produce only 30% of petroleum products of its requirements, and rest 70% of petroleum products have to be imported.
- At present even if 5% biodiesel is mixed with diesel, then we will be able to save a lot of foreign currency.
- According to research, the oil obtained from Jatropha cùrcas can be used as biodiesel. Planning Commission (now Niti Aayog) has planned to grow the trees of Jatropha and Pongamia pinnata as a source of biodiesel.
- These can be grown even in a barren land. The planning commission has identified 200 districts in 18 states for growing Jatropha, which includes Rajasthan also. Rajasthan State Government under the leadership of Chief Minister has constituted a “Biofuel mission”.
- Transesterification plant (device), as well as oil-producing units from seeds, will be established. This will be a part of the Biofuel mission.
- Cultivation of Jatropha is not only important from the viewpoint of biodiesel production but through this, the uncultivated land can also be brought under cultivation.
- This will be important for the ecology and conservation of biodiversity. This will become a source of employment and will generate income for financially backward people and farmers.
Importance of Biodiesel:
- Biodiesel also acts as a lubricant. It increases the efficiency of the engine and the cost of maintenance is reduced.
- By using this biodiesel, carbon monoxide and suspended particle emission is comparatively less.
- This is alternative sources of energy and can lead to generating employment and increasing income etc.
- The Petro plants can be grown in less productive, barren, non irrigated and roadside land.
- The biodiesel thus can play an important role in the proper use of wasteland, economic stability and development of the nation.
- Biodiesel is one of the best alternative fuel. This can be obtained by growing Petro plants in less productive and barren lands.
- By growing Petro crops high-quality fuel can be obtained along with environmental protection and conservation, improvements in the efficiency of automobiles, rural employment, and increased independence as well as savings in expenditure incurred on petrol products.