Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 Economics Notes Chapter 8 Arithmetic Mean
→ To understand the group of data easily by classification and tabulation methods, these are expressed in a concise form as a frequency distribution.
→ There is a central point in each data category around which other data has a tendency of being centered around. It is located in the center of the value series. This value is the measure of central tendency.
→ According to Simpson and Kafka- “ The measure of central tendency is such a modular reflective value towards which other values are centralized.”
![]()
→ The measures of central tendency are also known by the names of statistical mean, place-related measure, reflective value.
→ Arithmetic mean is. the most popular and important means among mathematical means, which is generally used by the common man in routine life.
→ The arithmetic mean of a series is the value which is obtained by dividing the sum of all the value of the series by the number of items present in it.
→ The mean should by defined very clearly so that it has only one implication.
→ The mean should be such that it is simple to understand and simple to compute.
→ An ideal mean should be based on all the values of the series. Without this, this mean will not represent the data-item series correctly.
![]()
Types of Averages
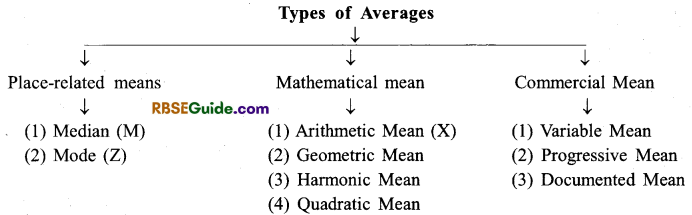
→ Arithmetic mean is of two types
- Simple (unweighted) arithmetic mean
- Weighted arithmetic mean
Calculation of Arithmetic Mean in Individual Series-
(i) Direct Method
\(\overline{\mathrm{X}}=\frac{\mathrm{X}_{1}+\mathrm{X}_{2}+\mathrm{X}_{3}+\ldots \ldots \ldots \mathrm{X}_{\mathrm{N}}}{\mathrm{N}}\)
\(\overline{\mathrm{X}}=\frac{\Sigma \mathrm{X}}{\mathrm{N}}\)
N = No. of Terms, ∑ X = sum of all values
(ii) Indirect Method or Short-Cut Method-
\(\bar{X}=A+\frac{\Sigma d}{N}\)
Where A = Assumed mean
d = (X – A)
N = No. of term values
Note: In both of the above methods, the same value of arithmetic mean is obtained.
![]()
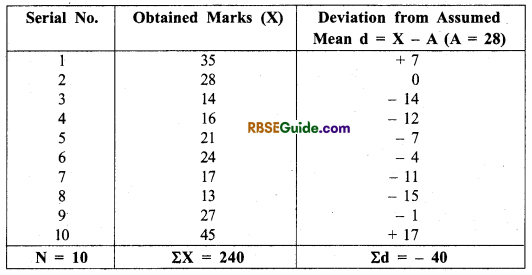
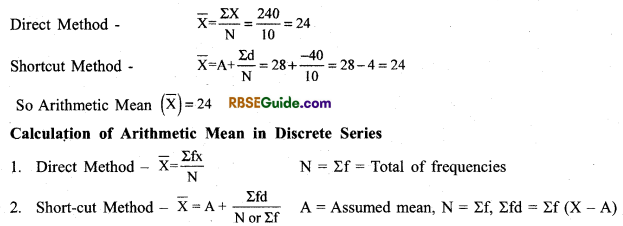
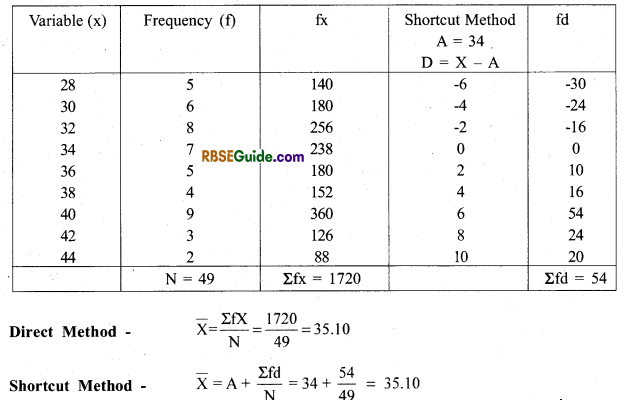
Example 1. Calculate the arithmetic mean \((\overline{\mathbf{X}})\) with the following data by direct and shortcut method.

Answer:
Example 2. Calculate the arithmetic mean from the following data series-
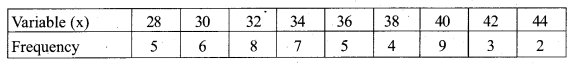
Answer:
![]()
Calculation of Arithmetic Mean in Continuous Series
The class-intervals in continuous series can be exclusive (0-10, 10-20, etc) or inclusive
(0-9, 10-19, etc) or of unequal magnitude (0-20, 20-50, etc.). However the arithmetic mean is calculated in all these situations by the same method.
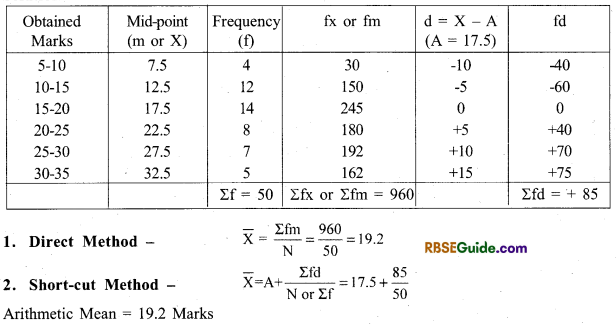
3. Direct Method- \(\bar{X}=\frac{\Sigma f m}{N}\) where m = mid point
4. Short-cut Method \(\overline{\mathrm{X}}=\mathrm{A}+\frac{\Sigma \mathrm{fd}}{\mathrm{N} \text { or } \Sigma \mathrm{f}}\) A – Assumed Mean, m – midpoint, N -∑f, d = m – A
Example. 3 Find out the arithmetic mean by direct and shortcut method in the following disribution.

Answer:
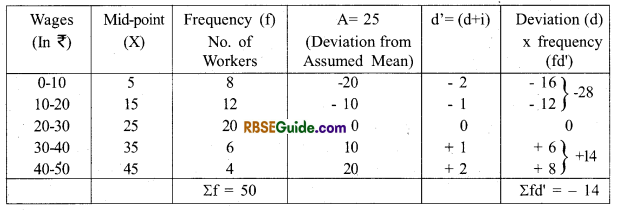
(iii) Step-Deviation Method – When the class-magnitude is equal in continuous series and the number of class-intervals is also relatively large, then to make short-cut method more simple, the step-deviation method is used.
\(\begin{aligned}
\bar{X} &=A+\frac{\Sigma f d^{\prime}}{N} x i \\
\text { Where, } d^{\prime} &=\frac{(X-A)}{i}
\end{aligned}\)
i = Class magnitude,
A = Assumed mean
![]()
Example 4. Calculate arithmetic mean from the following series through step-deviation method.

Answer:
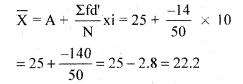
Weighted Arithmetic Mean – The arithmetic mean calculated on basis of weight, is called weighted arithmetic mean.
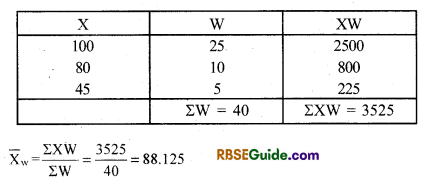
Example 5. Calculate the following arithmetic mean through the weighted average mean-

Answer: