Make use of our RBSE Class 12 Accountancy Notes here to secure higher marks in exams.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Accountancy Notes Chapter 7 Joint Venture Accounts
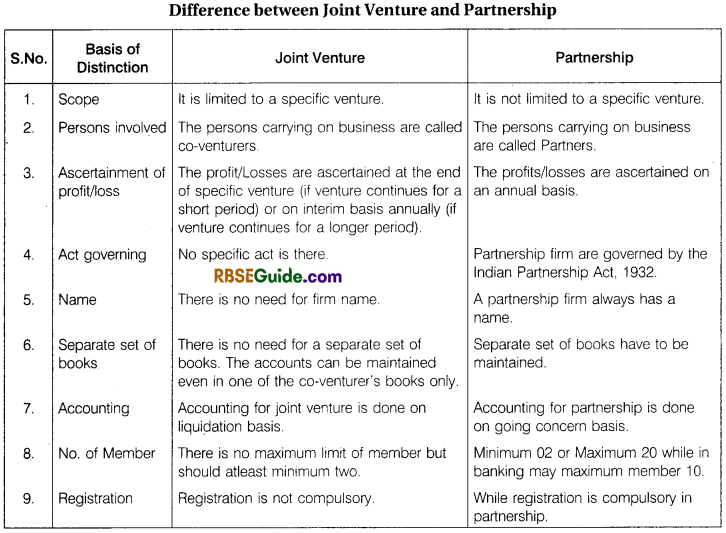
Meaning of Joint Venture:
A joint venture is a business agreement in which two or more parties agree to pool their resources for the purpose of accomplishing a specific work/task. This task can be a new project or any other business activity.
A joint ventre is a very short duration “business” (generally confined to a single transaction, like buying some surplus stores and selling them) entered into by two or more persons jointly. Joint venture may be described as a temporary partnership between two or more persons without the use of the firm name, for a limited purpose.
In other words, under joint venture two or more persons agree to undertake a particular venture (e.g., joint consignment of goods, joint construction of a building, joint underwriting of a particular issue of shares or debentures) and to share the profits and losses thereof in an agreed ratio (if agreement is silent on this point then in equal ratio).
Venture may be for the construction of a building or a bridge for the supply of certain quantity of materials or labour and even for the supply of technical services. The persons who have so agreed to undertake a joint venture are known as “Joint Ventures” or “Co-venturers”. If the co-venturers are in business, then they often supply goods from their regular business for the venture. This limited partnership automatically expires on the completion of the venture for which it was formed.
![]()
Characteristics of Joint Venture
Some important features of joint venture business are as follows :
- It is short duration special purpose partnership, parties in venture are called Co-venturers.
- Co-venturers may contribute funds for running the venture of supply Inventories from their ’ regular business.
- Co-venturers share profit/loss of the venture at an agreed ratio likewise partnership.
- Generally profit/loss of the venture is computed on completion of the venture.
Going concern assumption of accounting is not appropriate for joint venture accounting. There does not arise problem of distinction between capital and revenue expenditure.
Plant, machinery and other fixed assets when used in venture are first charged to venture account at cost. On completion of venture such assets are revalued and shown as revenue of the venture. Thus, accounting approach for measurement of venture profit is totally different.
![]()
Accounting Method of Joint Ventures
There are two methods of joint ventures accounting like as follows:
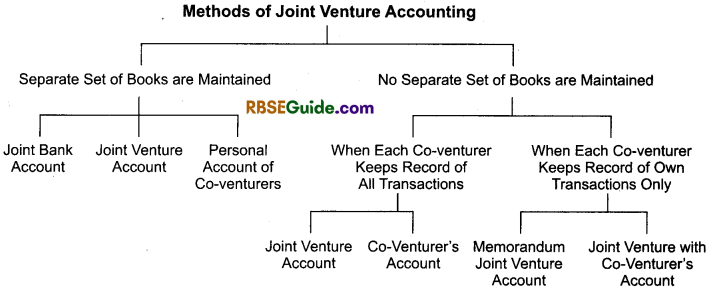
When Separate Set of Books are Maintained
When size of the venture is fairly big the co-venturers keep separate set of books of account for the joint venture. Joint venture transactions are separate from their regular business activities. In the books of joint venture the following accounts are opened.
- Joint bank account
- Joint venture account
- Personal accounts of the co-venturers or co-venturer’s accounts
Joint Bank Account : The co-ventures open a separate bank account for the venture transactions by making initial contributions. The bank account is generally operated jointly. Expenses are met from this joint bank account. Also sales or collections from transactions are deposited to this account. However sometimes the co-venturers may make direct payments and direct collections. On completion of the venture the joint bank account is closed by paying the balance to co-venturers.
Joint Venture Account: This account is prepared for measurement of venture profit. This account is debited for all venture expenses and is credited for all sales or collections. Venture profit/loss is transferred to co-venturer’s accounts.
Co-venturer’s Accounts: Personal accounts of the venturers are maintained to keep record of their contributions of cash, goods or meeting venture expenditure directly and direct payment received by them on venture transactions. This account is also closed simultaneously with the closure of joint bank account.
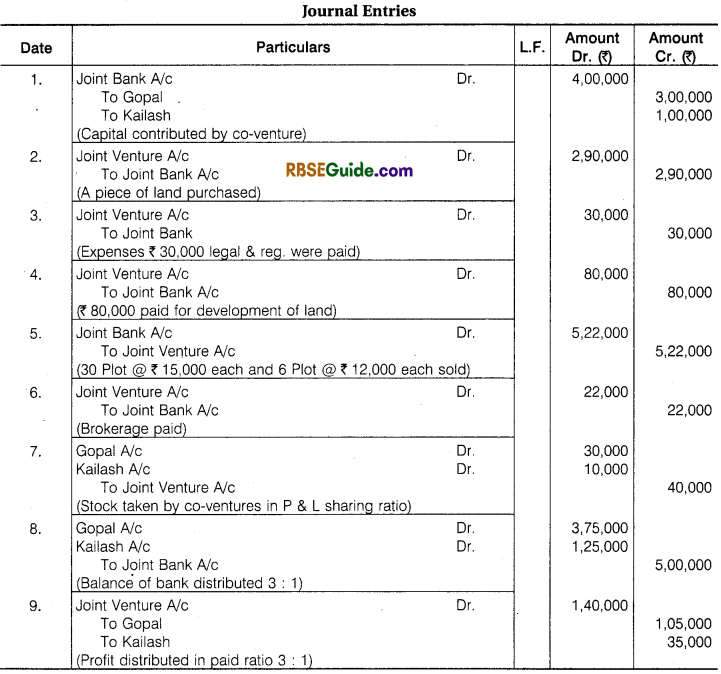
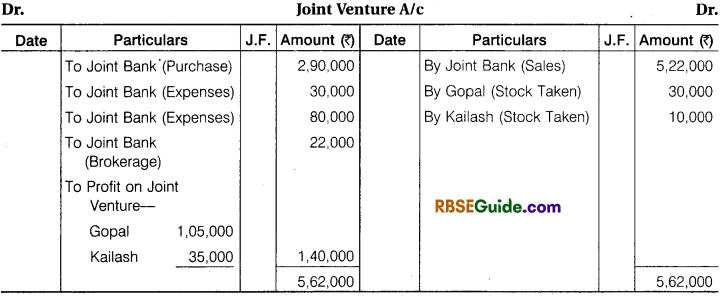
The following journal entries are necessary in the books of joint venture :

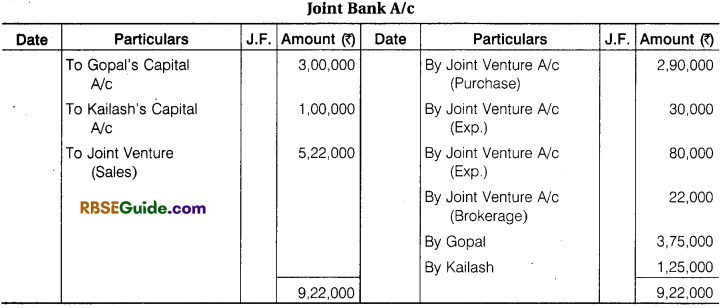
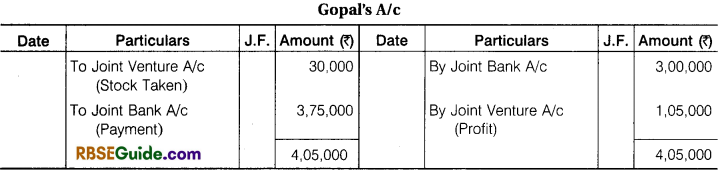
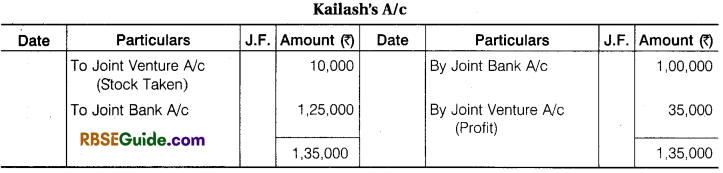
Illustration 1.
Contractor Gopal and Engineer Kailash enter into a Joint Venture for the sale of Plots. A Joint Bank Account was opened in which Gopal deposited ₹ 3,00,000 and Kailash ₹ 1,00,000. They Share Profit and Loss in the Ratio of their Capital.
A Piece of Land was purchased for ₹ 2,90,000, ₹ 30,000 were paid for Legal and registration charges. ₹ 80,000 were Incurred on Development of Land. The piece of Land was divided into 40 plots. 30 plots @ ₹ 15,000 per plot and 6 plot @ ₹ 12,000 per plot were sold. They paid ₹ 22,000 for Brokerage on Sale of Plots. The Remaining Plots were Taken at Cost price by both Gopal and Kailash in their profit sharing Ratio.
Make Journal Entries from above transactions & prepare Joint Venture A/c, Bank A/c and Co-venture Accounts.
Working Notes:
(1) Calculation of Sale Amount as follows :
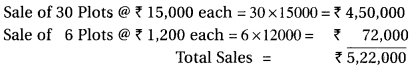
(2) Total Cost of Plots :
Purchase 2,90,000 + Expenses 30,000 + Develop Exp. 80,000 = 4,00,000 Cost of per plots = ₹ 4,00,000 40 = ₹ 10,000 each.
![]()
Illustration 2.
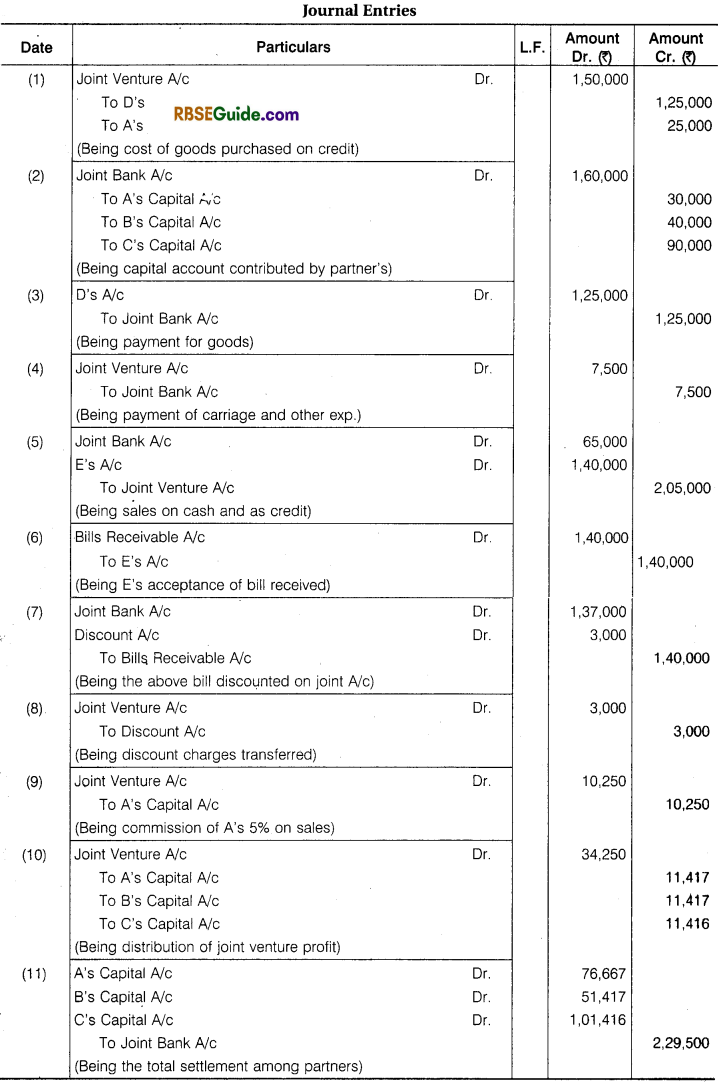
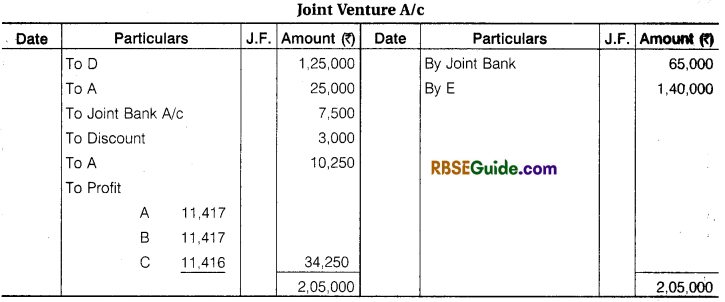
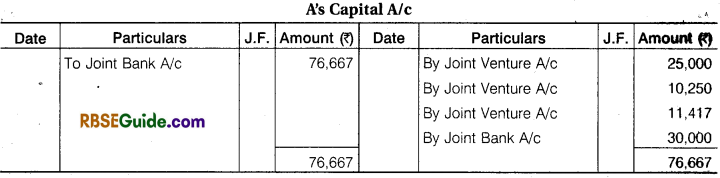
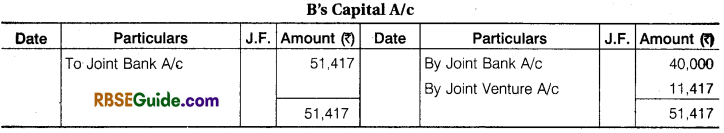
‘A’, ‘B’, ‘C’ enter into a Joint Venture to divide profit equally. They bought Goods from D ₹ 1,25,000 and from ‘A’ ₹ 25,000. A contributed, ₹ 30,000, B ₹ 40,000 and C ₹ 90,000 which amount were Banked in a Joint Account. They settled their Account with D by Cheque and paid for Carriage and other Expenses for ₹ 7,500.
They sold goods for Cash ₹ 65,000 and to E on Credit ₹ 1,40,000 who accepted a Bill for the amount. The acceptance was cashed from Bank ₹ 1,37,000. A was allowed 5% Commission on Sales for effecting the transaction. Pass the necessary Journal Entries and open Accounts. Assuming that the Final settlement between parties was made by cheques.
Solution:
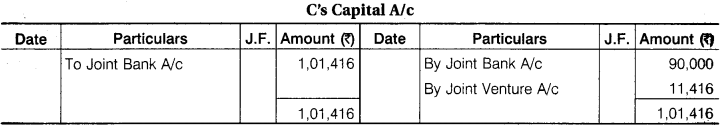
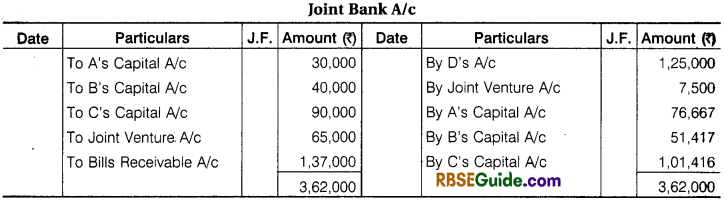
![]()
Illustration 3.
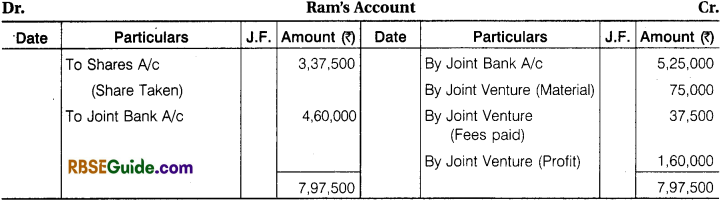
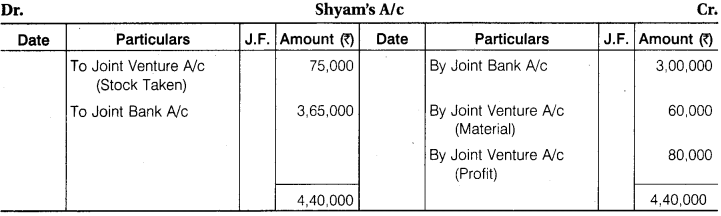
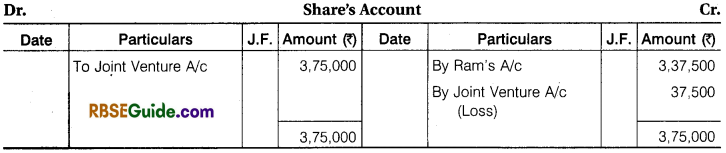
Ram and Shyam entered into a Joint Venture to Contract a Building for a Newly started, Jai Industries Limited. The Contract Price was fixed at ₹ 18,75,000 to be settled as follows ₹ 15,00,000 in Cash and ₹ 3,75,000 in fully paid up shares. A Joint Bank Account was opened in which Ram and Shyam deposited ₹ 5,25,000 and ₹ 3,00,000 respectively. The Profit or Loss is to be shared in the ratio of 2 : 1.
The detail of their Transactions are:
Wages ₹ 3,75,000, Material Purchased ₹ 11,25,000, Material Supplied by Ram from his own stock ₹ 75,000, Material Supplied for by Shyam from his own stock ₹ 60,000, Architect’s Fee paid by Ram ₹ 37,500.
Contract was completed and payment was received as per agreement. Joint Venture was closed by Ram taking up all shares at an agreed valuation of ₹ 3,37,500 and Shyam taking up the stock of material at an agreed valuation of ₹ 75,000.
You are required to prepare Ledger Account of Joint Venture assuming that the separate books are maintain for this purpose.
Solution:
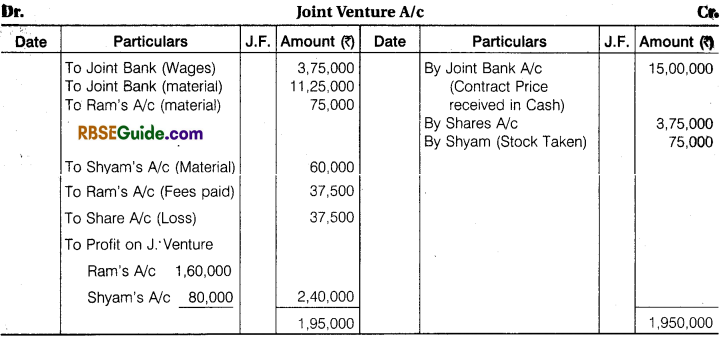
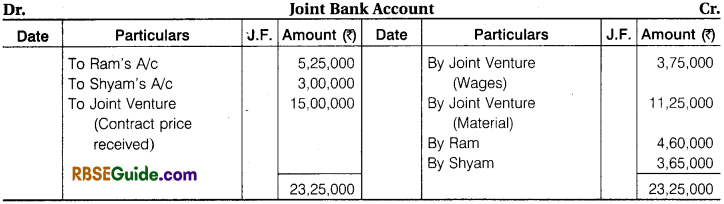
When Separate Books are Not maintained for Joint Venture:
When all co-venturers are not living at the same place and venture business is not so big enough than separate books of accounts for joint venture may not be kept. In such a situation co-venturers can record the transactions of joint venture in their own books also for this purpose one of the methods described hereafter may be adopted
Each co-venturer records in his books only those transactions concluded by himself (Memorandum joint venture method).
Each co-venturer records all the transactions of joint venture including transactions concluded by other co-venturer.
1. Each Venturer Records only those Transactions Concluded by Himself Only
Under this method of accounting, each co-venturer open joint venture with … account in his books of accounts. This account is individual account in nature. At the end of the venture business, balance of this account shows the amount due to or due from such co-venturer.
For every payment made for joint venture purchase of goods and any other expenses joint venture with … account is debited. Similarly, for sale proceeds and other income of joint venture this account is credited.
For any cash remittance to other co-venturer above account is debited and on cash receipts this account is credited.
On termination of joint venture each co-venturer sends the copy of joint venture with …. account to other co-venturer. Then a memorandum joint venture account is opened. This account is nominal in nature.
Amounts paid for purchase of goods for joint venture and all expenses made for joint venture are debited to memorandum joint venture account. Similarly, all sales proceeds and other incomes are credited to this account. Debit balance of this account shows the loss and credit balance shows the profit of the joint venture.
For the distribution of profit shown by joint venture account, joint venture with… account will be debited and profit and loss account will be credited. In case of loss, reverse entry will be made.
Special Note : There will be no entry for transfer of goods for venture business by any co-venturer.

![]()
Illustration 4.
‘ D’ of Delhi and ‘B’ of Bhilwara entered into a Joint Venture to purchase and sell of old machine. ‘D’ to make the Purchase and ‘B’ to make the Sales. It is also decided to Share profit or Loss in Proportion of 2 : 3 respectively. ‘B’ Remitted ₹ 40,000’to ‘D’ towards the joint venture.
‘D’ Purchased old Machines worth ₹ 45,000 and Paid 2% Purchase Commission. ₹ 12,000 for its Repairs and ₹ 600 for Other Sundry Expenses. He dispatched the machine to Bhilwara.
‘B’ took Delivery of the Machinery Paying ₹ 2400 for Freight and ₹ 600 for Octroi. He sold same Machine for ₹ 85,000 and kept the remaining Machine for himself at an agreed value of ₹ 7,200.
His other expenses were Godown Rent ₹ 500 and Advertisement for Selling Expenses ₹ 1700. Final Settlement was made on Joint Venture. Pass the Journal Entries and Open necessary accounts in the Books of Each Co-ventures to record the transaction. The Joint Venture under Memorandum Joint Venture Method.
Solution:
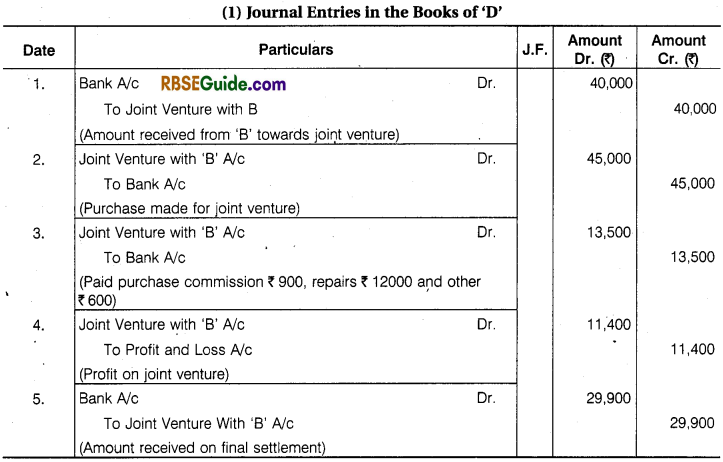
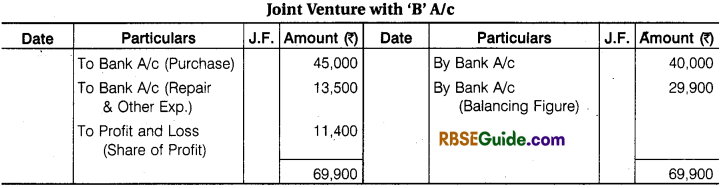
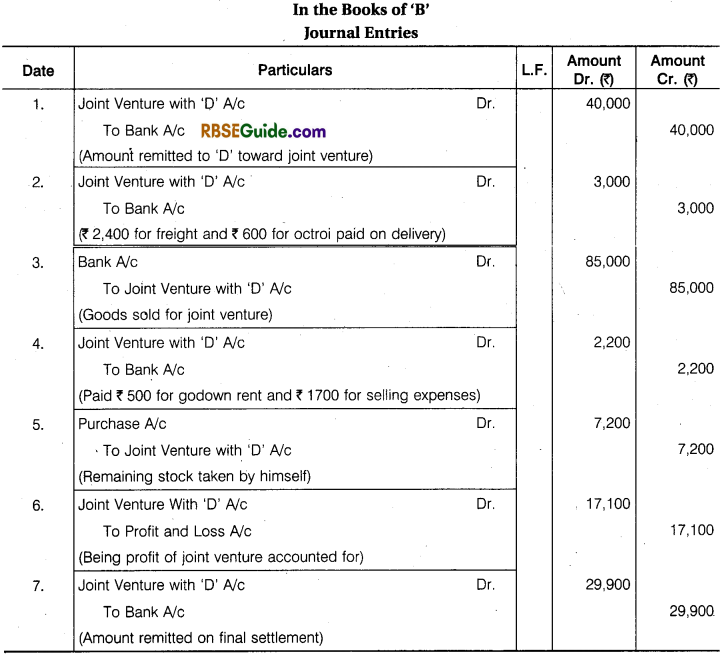
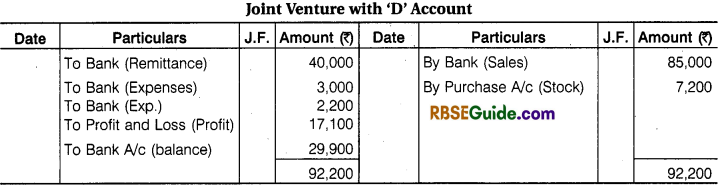
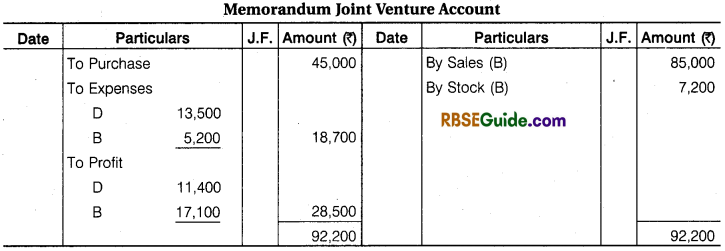
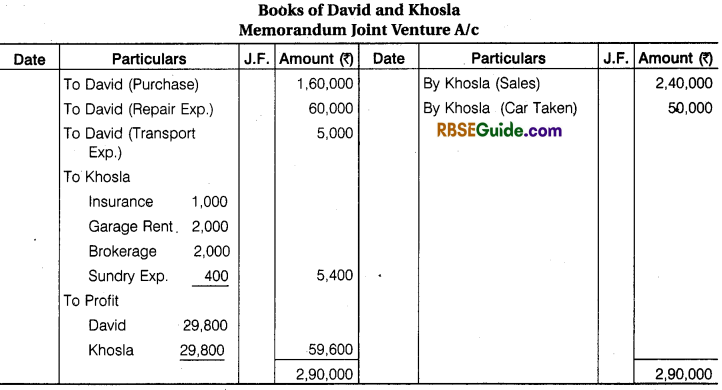
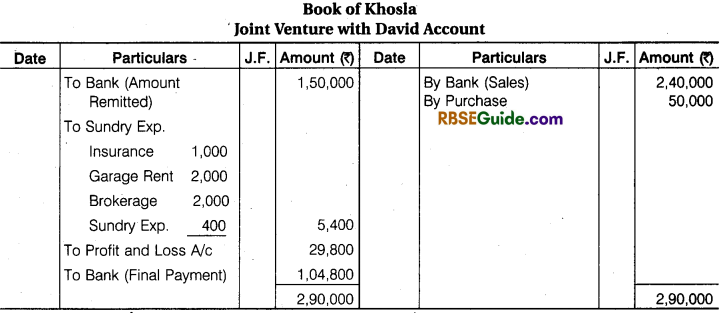
Illustration 5.
David of Mumbai and Khosla of Delhi entered into a Joint Venture for the purpose of buying and selling second hand Motor Cars. David to make purchase and Khosla to effect sales. The Profit and Loss to be shared equally. Khosla remitted a sum of ₹ 1,50,000 to David toward the joint venture.
David purchased 5 Cars for ₹ 1,60,000 and paid of ₹ 5,000 in transporting the Cars to Delhi. Khosla sold 4 Cars for ₹ 2,40,000 and retained the fifth Car for himself at an agreed value of ₹ 50,000. His expenses were Insurance ₹ 1,000, Carriage Rent ₹ 2,000, Brokerage ₹ 2000 and Sundry Expenses ₹ 400.
Each Party’s Ledger contains a record of his own transactions on Joint Venture. Prepare a statement showing the result of the joint venture and the joint venture account with ‘David’ in the Books of Khosla as it will finally appear. Assuming that the matter was finally settled between the parties.
Solution:
![]()
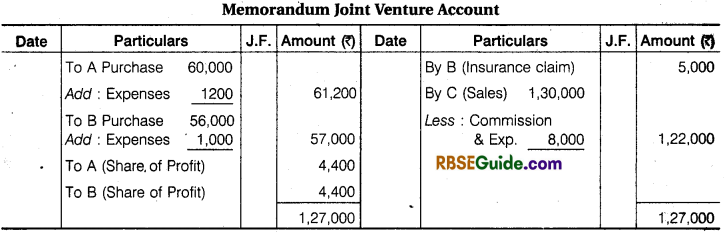
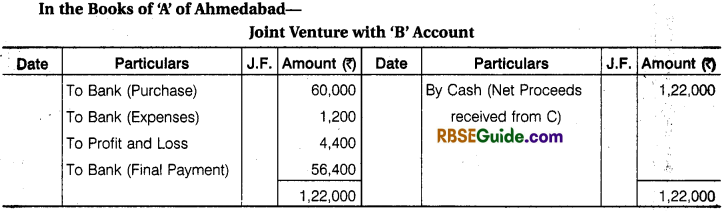
Illustration 6.
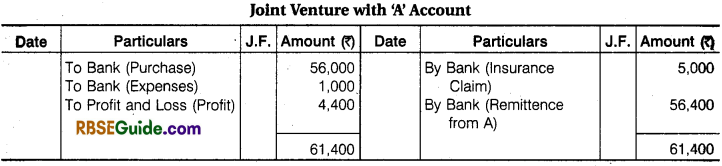
‘A’ of Ahmedabad and ‘B’ of Mumbai entered into a Joint venture to consign 100 bales to C of Kolkata to be sold of their joint risk. They agreed to share Profit or Losses equally.
‘A’ sent 50 bales valued at ₹ 60,000 and paid ₹ 1200 for freight and expenses. ‘B’ sent 50 Bales valued at ₹ 56,000 paid ₹ 1000 for sundry expenses. All the bales reached Kolkata in time – 5 Bales were found damaged and ‘B’ could recover ₹ 5000 from Insurance Company for its claim. C sold the remaining bales for ₹ 1,30,000.
He remitted the Balance of Amount to A’ after deducting 5% Commission on Sales and ₹ 1500 for Other Expenses. Prepare Memorandum Joint Venture Account and also A’s Account in the Books of ‘B’ and B’s Account in the Books of ‘A’.
Solution:
2. Each Co-venturer records all the Transactions of Joint Venture including Transactions concluded by the Other Co-venturers
Under this method of accounting for joint venture, each co-venturer records all the transactions of joint venture in his own books of accounts. For this purpose they open two accounts in their books which are joint venture account and other co-venturer’s personal account. In such a Situation, joint venture account is nominal account in nature and it shows the profit or loss on joint venture. Each co-venturer sends his transactions details to others on time to time, so that others can record the transactions of senders, in their respective books of accounts. At the end, the Co-venturer’s account are settled.
![]()
Illustration 7.
On 1st July, 2016 Amar and Bihari entered into a Joint Venture. Profit will be shared in the Ratio of 2 : 1 after following interest @ 5% per annum and money invested by Amar and 2% commission on sales to Bihari. Amar purchased Furniture for ₹ 28,000 and sent it to Bihari.
Bihari paid for Railway Freight ₹ 1000, Rent ₹ 500. Insurance ₹ 300 and other Exp. ₹ 200. Some part of Furniture was sold by Bihari for ₹ 40,000 and Remaining furniture of ₹ 6,000 was returned to Amar. Who remitted it at ₹ 5,000 for his own business. Joint venture was dissolved on 31st Dec. 2017. Prepare Joint Venture A/ c and Bihari’s Account regarding all the transactions in the Books of Amar.
Solution:
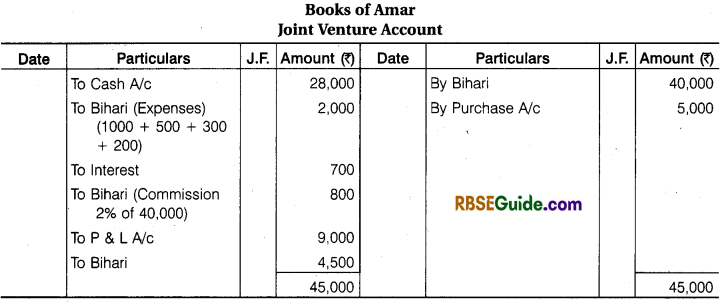
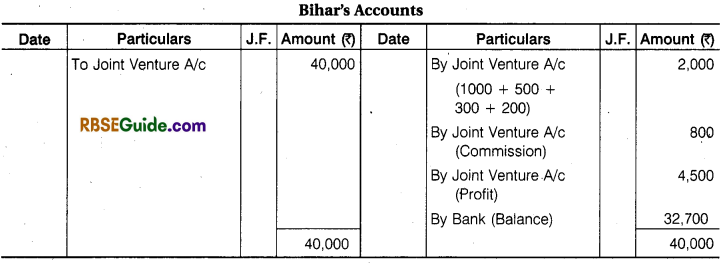
Calculation of Interest for 6 month – = 28,000 x \(\frac { 6 }{ 12 } \) x \(\frac { 5 }{ 100 } \) = ₹ 700
![]()
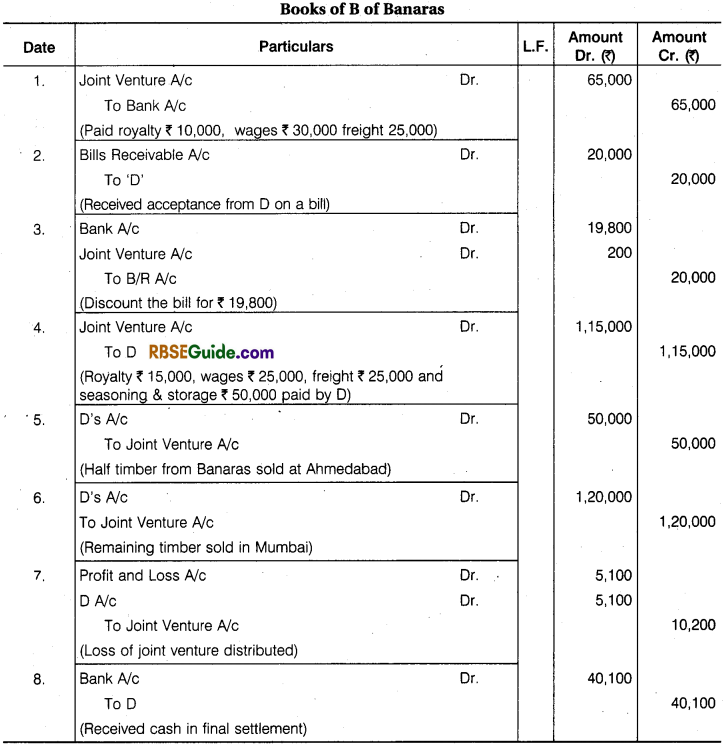
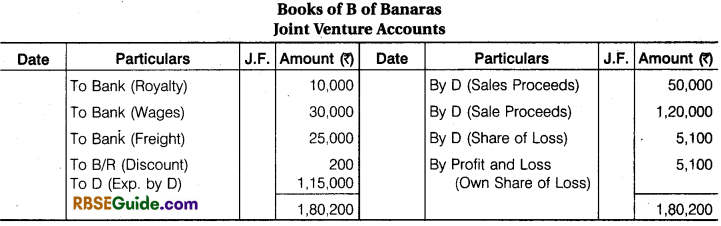
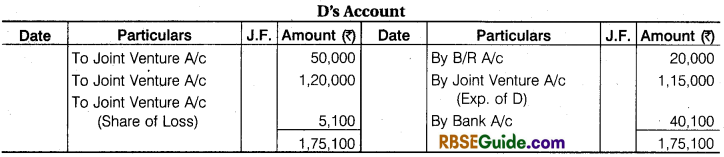
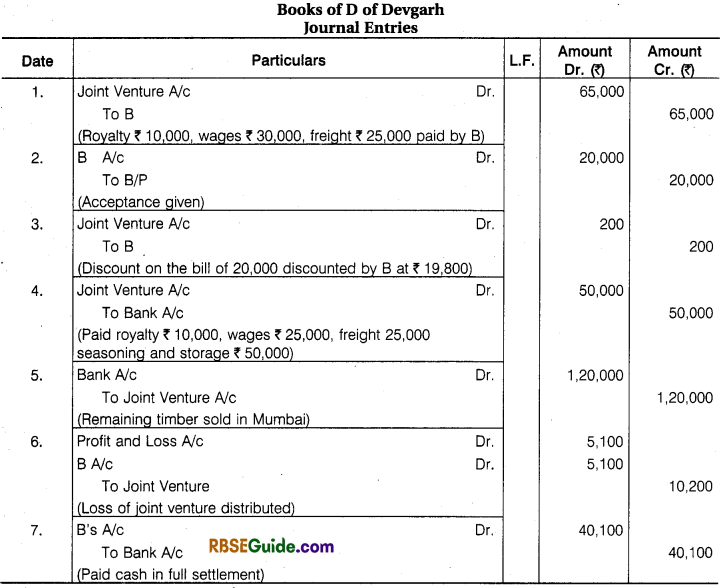
Illustration 8.
B of Banaras and D of Devgarh entered into a Joint Venture for cutting and selling timber. They took Forest on lease at Banaras and Devgarh, B Paid ₹ 10,000 as royalty, ₹ 30,000 as wages to workers and ₹ 25000 Freight and Cartage. B Drew upon D a Bill for ₹ 20,000 at 3 months after date and got it discounted for ₹ 19,800 after acceptance.
D Paid Royalty ₹ 15,000, wages to workers ₹ 25,000, Freight and Cartage ₹ 25,000 and for Seasoning and Storage space ₹ 50,000. Half of the Timber from Banaras was sold at Ahmadabad for ₹ 50,000 and the remaining lot from Banaras and Devgarh at Mumbai for ₹ 1,20,000. Payment was received by D in both the cases. Draft Journal Entries and prepare accounts in the books of both the parties assuming that Final Settlement has been done.
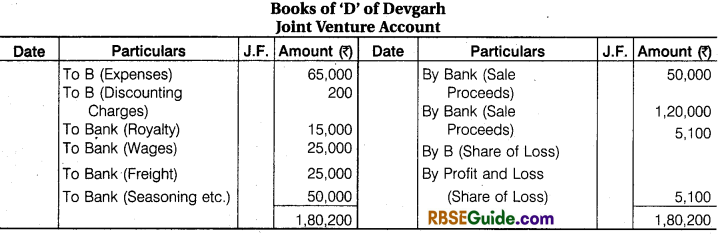
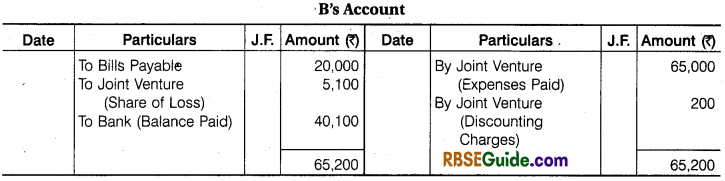
![]()
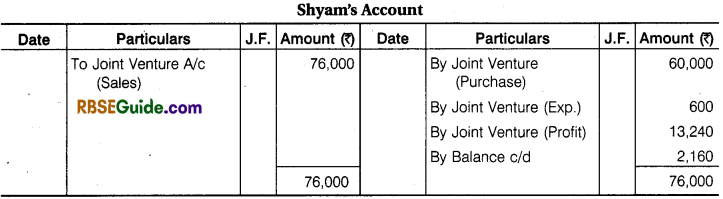
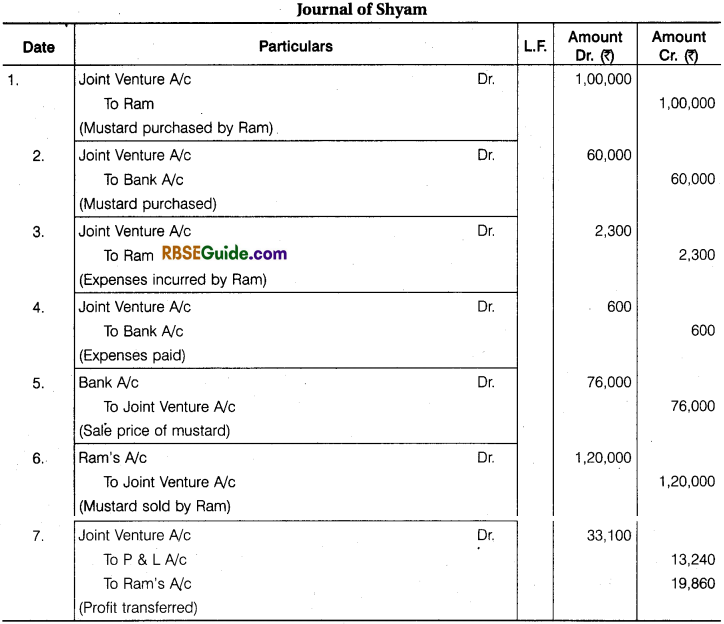
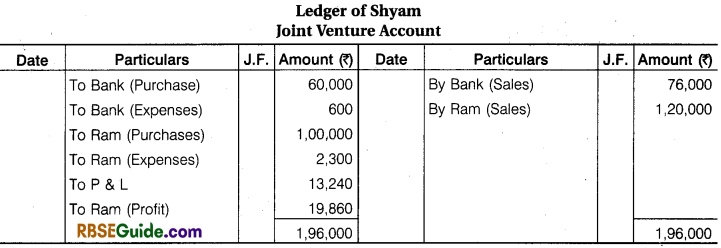
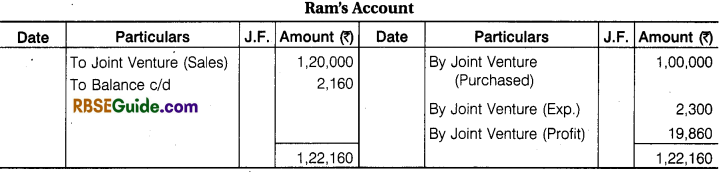
Illustration 9.
Ram and Shyam entered into a Joint venture for the Purchase and Sale of mustard and agree to divide Profit and Losses in the Ratio of 3 :2, Ram purchased mustard for ₹ 1,00,000 and paid ₹ 1000 godown rent, ₹ 200 for Insurance, ₹ 800 for Carriage and ₹ 300 for Sundry Exp.
Shyam purchased , mustard for ₹ 60,000 and paid ₹ 400 Godown Rent and 100 ₹ for Insurance and ₹ 100 for Carriage. Ram sold the mustard for ₹ 1,20,000 and Shyam for ₹ 76,000. Prepare the above transactions in the Journal and Ledger of both the partners.
Solution:
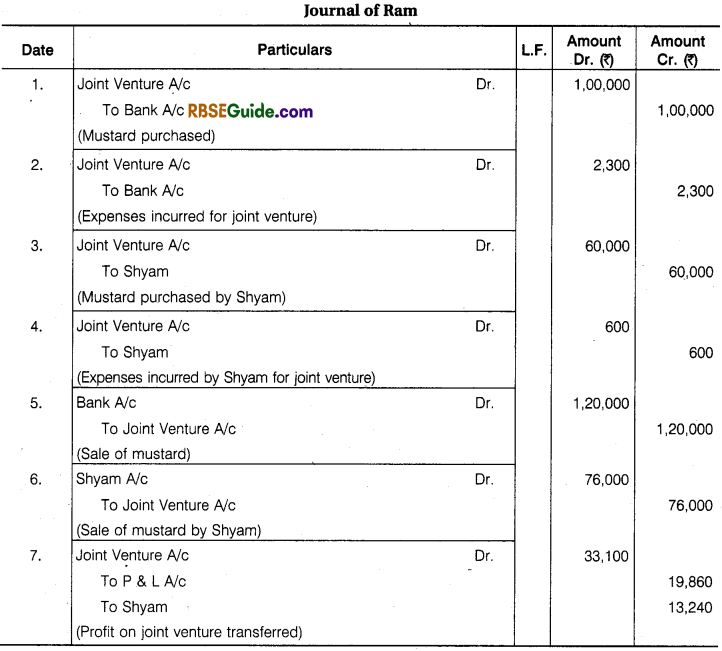
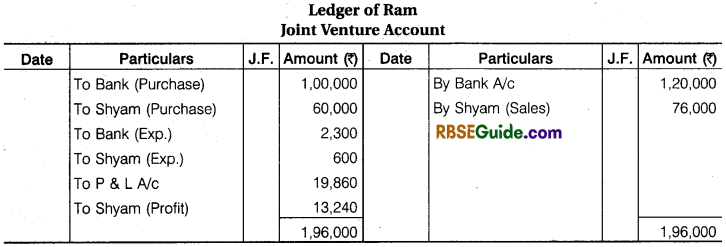
Joint Venture Accounts Notes Important Terms
→ Joint Venture : Joint venture is a very short duration special type business, entered into by two or more persons jointly.
→ Jint Ventures : The persons who have so agreed to undertake a joint venture are known as “Joint Ventures” or “Co-ventures”.
→ Joint Bank Account : The co-ventures open a separate bank account for the venture transaction by making initial contribution, called joint bank account.
→ Discounted Bill : Received payment of Bills Receivables from bank before maturity date Called discounted bill.
→ Memorandum Joint Venture Account : On termination of joint venture each co-venture sends the copy of joint venture with account to other co-venture, then a memorandum joint venture account is opened.
→ Special Work : Special work means a certain work begin when certain work complete joint venture terminated.