Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 15 Genetic Engineering
Introduction
In last century the knowledge regarding cell and its function has increased considerably^ In this, Genetics has provided basic and important information about structure of DNA, it’s replication construction and gene expression. Specially in last three decades lot of development has taken place in the field of Science, which has led to DNA sequencing, cloning a gene, developing a technique for transferring gene.
This is possible only because of similar “Genetic Code” in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. In 1970, Dr. Hargobind Khurana provided a solid base in the field of knowledge of recombinant DNA technology by synthesizing gene (artificial gene synthesis) in test tube.
Biotechnology is considered as the most important of all the recent’branches of biology. Biotechnology aims to incorporate improvement in the hereditary features of different animals and plants. In order to achive this objective several techniques have been employed which are collectively known by different names such as DNA cloning or genetic engineering etc.
Recombinant DNA
- Incorporation of foreign DNA segment into the basic DNA of any organism leads to the modification of the DNA. The modified DNA so formed is called recombinant DNA. Various effective measures required to incorporate changes in the DNA makeup of any organism is called recombinant DNA technology (RDT). Genetic engineering means, incorporating useful alterations in the genome of any organism by changes in the gene make up of the organism.
- Recombinant DNAtechnique was discovered by Stanley Cohen, Herbert Boyer, al (1973). These scientist succesfully incorporated recombination in DNA of Salmonella and E.coli bacteria.
- In this chapter we will study basic principles of recombinant DNA technology under the topic Genetic Engineering.
Genetic Engineering
- The main technique of genetic engineering is recombinant DNA technology. Basic steps involved in recombinant DNA technology are as follows :
- Identification of desired gene and its isolation.
- Selection of a suitable cloning vector.
- Incorporation of desired gene in the cloning vector.
- Multiplication of the recombinant DNA in the host cell.
- Identification of the cloned gene and its transfer in other animals.
- Expression of desired gene.
![]()
Following components/tools are required for getting recombinant DNA by genetic engineering.
- Restriction Endonuclease enzyme.
- Vector
- Host or receptor cell
- Gene Bank.
Identification and isolation of Desired Gene
The desired gene or DNA segment is identified and for its isolation restriction endonuclease enzyme is used. Restriction endonuclease enzyme was discovered by Werner Arber and Hamilton O. Smith (1970)
Restriction Endonuclease :
- These enzymes are just like molecular scissors, which cut DNA at specific sites.
(2) These enzymes are found naturally in bacteria such as E.coli, Bacillus, Streptococcus and Thermus aquaticus.
(3) Restriction endonuclease enzymes are of three types:
Type I Endonuclease (RI)
Type II Endonuclease (R-H)
Type III Endonuclease (RHI). Type II.
Note : Restriction endo nucelase (RII) is most commonly used in gene cloning and restriction mapping. Example E’.co.RI, Hind II etc.
Nomenclature of Restriction Endonuclease :
1. The first alphabet of the name of enzyme represents the genus from which it has been isolated. This is always written in capital letter.
2. The two alphabets after this represent the species of that genus. These are written in small letters.
Note- All the three letters are written in italics
Example- Eco from Eshcherichia coli.
Hin- From Haemophilus influenzae.
![]()
3. The fourth word represents the strain of the genus from which the enzyme has been isolated.
Example- Eco R – From R strain of E.coli.
4. In case more than one restriction enzymes are obtained from one organism, their number is indicated by Roman numbers. Example- Eco RI, (First from R strain of E.coli) Eco RH etc. (Second from R. strain of E.coli) Endonuclease enzyme Eco RI recognizes specific base sequence in DNA molecule and cuts between the base G and A.
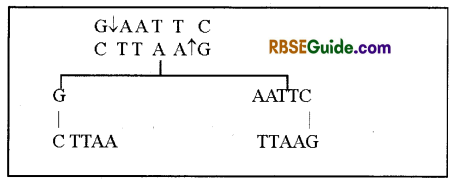
Note : When, DNA segments obtained from two different sources are mixed together in the presence of DNA ligase enzyme, then both DNA segements are joind together by phospho-di-ester bonds and form a double stranded structure.
Other Enzymes used in Genetic Engineering.
1. RNA dependent DNA Polymerase- This enzyme brings about polymerisation of nucleotides of DNA strand on RNA template.
2. DNA dependent DNA Polymerase – This enzyme brings about polymerisation of nueleotides of complementary DNA strand on DNA template.
![]()
3. Ligase – This enzyme joins the ends of DNAsegments on the template.
4. Lysozymes – These enzymes dissolve the cellwall of bacteria so that the bacterial DNA can be easily isolated.
5. Alkaline Phosphatases – This enzyme cuts the phosphate at the 5′ end of circular DNA and helps to keep it in linear form, so that the foreign DNA segment can be inserted in it. This enzyme prevents the circular nature of DNA.
Selection of Cloning Vectors
The desired gene is isolated with the restriction endonuclease. This desired gene containing segment of DNA is then incorporated in a suitable vector. This vector should be able to enter in to the target host or receptor cell and should replicate it’s DNA in the host cell.
Essential features of Vector:
- It can be inserted easily into host cell and can be isolated easily.
- It should freely replicate in host cell.
- The vector must posses specific Restriction sites so that restriction enzyme can cut the DNA at those sites and the desired DNA fragment can be incorporated easily.
- It should have one marker gene or marker site which can helps in selection of recombinants cells.
- Transformation by it should be easy and perfect.
- For expression of desised foreign DNA, the vector should essentially posses components such as promoter, operator regulating sites.
Note : In E.coli both natural as well as man-made vectors can be used. Some important vectors used in E. coli are :
- Plasmid
- Bacteriophage
- Cosmid
(i) Plasmid: Lederber, (1952) first observed the piasmids as extra chromosomal material in Bacterial cell. It has following important features.
- These are extra chromosomal (Other than chromosomal DNA) components.
- These are -circular, double stranded DNA molecules .
- They contain an origin of replication (ori). Hence are able to replicate independently within the cell.
- These are not necessary for growth and survival of Bacteria.
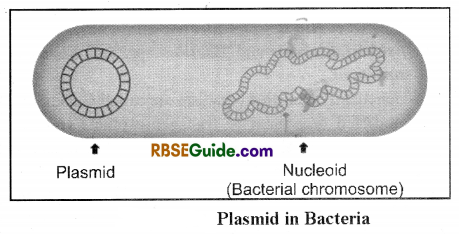
- These contain specific restriction sites where desired gene can be inserted.
- Marker genes or marker sites are also found.
- Plasmid may contain three to one thousand genes.
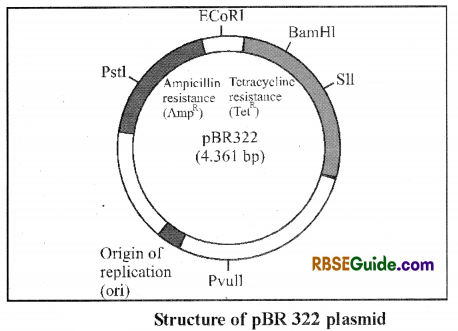
Note : The Most commonly used plasmid vector is pBR322.
In this plasmid, two marker sites TetR (Tetracycline resistant) and AmpR (Ampicillin resistant) are found. It contains recognition sites for 12 different restriction enzymes. Desired DNA (foreign DNA) is inserted in between TetR and AmpR gene with the help of restriction enzyme.
![]()
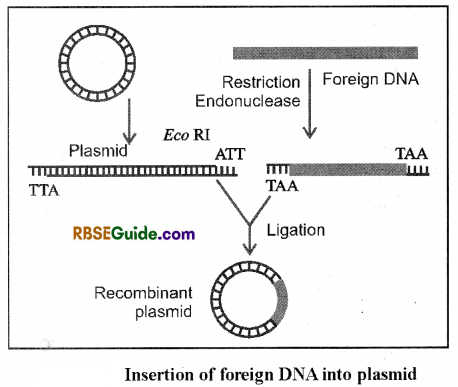
To insert the foreign DNA in the plasmid it’s DNA is made linear by use of restriction enzyme and after that in between the two ends of the DNA of plasmid, foreign DNA of 5-10 Kb is inserted or incorporated.
.
Note—Depending upon the condition of replication the extra chromosomal material found in the bacterial cell is called plasmid or episome. The extra chromsomal structure capable of replicating independenly is called plasmid but if it replicates only when joined with the bacterial chrmosome along with it. then is called as episome.
(ii) Bacteriophage : The Viruses which infect Bacteria are called Bacteriophages.
Example-7, (Lambda) and M13 etc.
Bacteriophages are better vector than plasmids due to the following reasons:
- DNAfragment of large size (24Kb) can be cloned in these.
- Every bacteriophage produces one plague area through which testing is comparatively easy.
λ phage is more widely used as a vector than M13 because of the following:
- They are bacteriophage of coli.
- DNA is linear and double stranded.
- Non essential part of 7, phage DNA can be removed. As a result the size of vector molecule is reduced hence large sized foreign DNA can be easily inserted in it.
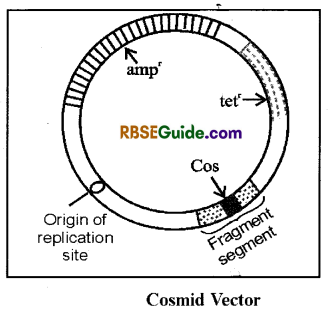
(iii) Cosmid : It is a hybrid of plasmid and lambda (λ) phage
- It was first of all constructed by Barbara Horn and John Collins (1978).
- Such plasmids, in which DNA sequences of ‘Cos’ site of lambda phage DNA are inserted, are known as cosmids. Hence the cosmid posseses the features of both plasmid as well as the lambda bacteriophage.
- Cosmids replicate in the bacterial cell just like the plasmid and on account of presnce of’Cos’ site these are packed like lambda phage particles.
- Cosmids can be used to clone DNA segments of up to 45 Kbp in size.
- There are present two Cos sites, 6 restriction endonuclease sites, origin of replication site and tetracycline antibiotic resistance genes, in this cosmid.
Example : Cosmid PLFR‘5
Note – Besides plasmid, bacteriophages and cosmid, there are certain other vectors also being used in genetic engineering
- Phagemids
- Shuttle vectors
- Transposons
Transposons are also known as Jumping genes.
![]()
Insertion of desired gene in cloning vector
For insertion of desired gene into cloning vector, first similar restriction sties are made in both the genes. After this both are joined together (as both have same restriction sites). This process is called Ligation. In this process following enzymes are required.
- Restriction endonucleases.
- Methylases
- DNAligases
- Alkaline phosphatases
- Reverse transcriptase
- Terminal transferases.
Multiplication of recombinant DNA in host cell
Recombinant DNA may be inserted into host cell by following two methods :
- Transformation
- Transduction
- In this process, coli bacterial cell is mainly used as host. These processes (Transformation and Transduction) have been studied earlier. The Recombinant DNA multiplies in the E.coli cells
Identification of cloned gene and its transfer in other organism
1. We are using certain genes such as antibiotic resistant gene or LacZ gene (which produces p galactosidase) as marker genes so that if cloning sites are present in these genes and DNA is inserted in between them the genes become non functional and called as insertions! On the basis of expression or non expression of a particular gene as marker gene, we can select recombinants from non-recombinants.
2. Besides marker genes there are certain other genes which produce specific features. These are called reporter genes which look entirely different from other cells due to special features. Example-LUC (Leuciferase) gene which is found in firefly and produces Bioluminescence.
Expression of Desired Gene
- The cloned gene derived from coli is inserted into any other microbe, plant or animal cell so as to get desired product. Example-Insulin production by E.coli.
- Those plants and animals which contain foreign DNA are called Transgenic plants and Transgenic animals
c-DNA (Complementary DNA) and ft Genomic Library
- c-DNA (Complementalry DNA)-The copy of DNA formed on the RNA strand by reverse transcriptase enzyme is called c-DNA or complmentary DNA.
- c-DNA Library-Maintaining all or several c-DNA of any organism by inserting in the host cell through gene cloning is called c-DNA library.
Construction of c-DNA Library-
- First of all m-RNA is derived from the cells of tissue synthesizing functional proteins. Example- Cells of root or leaf of plant or ovary of the mammals.
- Now c-DNA is formed from each m-RNA molecule with the help of reverse transcriptase enzyme.
- This c-DNA. is cloned in the vector and introduced in the bacterial cell.
- After this, c-DNA is hybridized by probe & its identification and specification is done.
Note-c-DNA is used for identification of eucaryotic gene in the procaryotes because in procaryotes introne of eucaryotic gene is lacking.
![]()
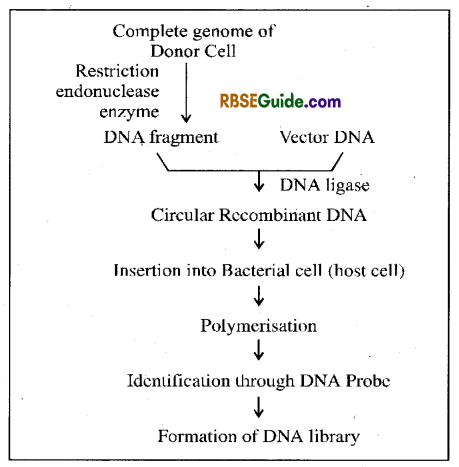
Genomic Library
Collection of the cloned segments of the entire genome of any organism is called it’s genomic library. The complete DNA content of haploid set of chromosomes of an organism is called it’s genome. Genomic library is formed by isolating entire DNA from a cell. It is fomed by the following method.
Molecular Probes
Segments of DNA or RNA with the help of which c- DNA or RNA segments of any organism present in it can be identified, are colled molecular probes. The molecular probes are of two types.
- DNA probes
- RNA probes
Importance of Probes-
- These are used to identify specific DNA segments used in the research of genetic engineering.
- Pollutants in food can be detected with the help of probes.
- These are used in the field of forensic science, in resolving disputed paternity issues and establishing family relationship.
- These can be used to identify improved variety of crops and hybridized seeds of crops.
Techniques of Analysis of Cloned Genes
Several techniques have been developed for analysis of cloned genes in fast decade. In this chapter some important techniques are being described.Techniques of Analysis of Cloned Genes
Gel Electrophoresis
Electrophoresis is an analytical device which is generally used to purify and then isolate the DNA segments.
In this process by the effect of electric field negatively charged DNAsegments are separated on the basis of their size. Two types of gels are used in this apparatus
- Agarose gel
- Polyacrylamide gel.
There are found pores in between the atoms of gel. Due to this, these function like molecular sieves. The DNA segments are stained and when these are subjected to the electric field and passed through gel some of the DNA segments move faster and some others move slower and form bands of similar length at different locations. After this the gel is stained and when observed under UV light, these DNA segments appear fluorescently orange coloured.
![]()
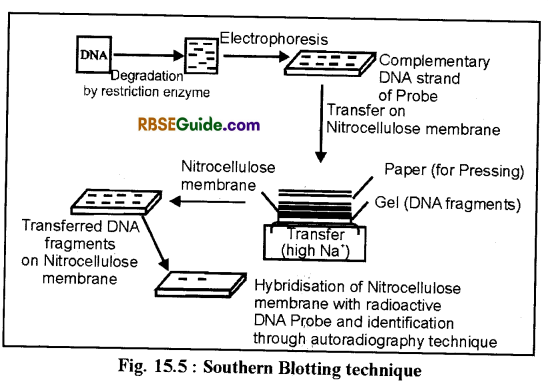
Blotting Technique
In this technique, DNA segments are derived on agarose gel by electrophoresis and are then transferred and stabilised on nitrocellulose filter. These are then identified by hybridization with DNA probes. This process is called blotting technique.
(a) Southern Blotting Techniq ue-E. M. Southern (1975) first used this method and transferred DNA segments on nitrocellulose filter. This technique was named as Souther blotting technique. By this technique analysis of DNA segments is done. (Fig. 15.5)
(b) Northern Blotting Technique-Alwin et al (1979) transferred RNA segments after electrophoresis on amino benzyl oxymethy (OBM) membrane in place of nitro cellulose filter. This technique was named as Northern blotting technique. This technique is used for the analysis of RNA segments.
(c) Western Blotting Technique-Tobin etal. (1979) first break down proteins in to polypeptides with the help of sodium-do-decyl sulphate (SDS). After separating them with the help of electrophoresis, transferred these on nitrocellulose filter or nylon membrane. These were then decoded on X-ray plate and identified the protein. By this technique analysis of proteins is done. This is called western blotting technique.
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
- Up to 1985 vectors were considered as necessary tool for replication of genes in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. But in 1989 Mullis discovered a powerful technique by which millions of copies of one DNA molecule can be obtained in a very short time. This is known as polymerase chain reaction.
This technique involves three steps which are cycled repeatedly and by repeating 20-30 times lacs of copies of DNAare formed. This process is performed in DNA thermal cycler. Each cycle is completed in 225 seconds
i.e………….less than 4 (four) minutes.
Uses of PCR-
- For molecular mapping and research objectives.
- In genetic engineering and gene therapy experiments.
- In study of polymorphism of DNA.
- Used in forensic science for detecting criminals.
- Used in detection of hereditary diseases such as haemophilia, sickel cell anaemia etc.
DNA Fingerprinting.
- This method was discovered by Alec Jeffreys and co workers (1985). The identity of a specific person can be established by the specific base sequence found in the DNA of that person. The DNA print of a specific person is the same whether the DNA has been taken from the cell from any part of the body.
- In this method, DNA is cut in to small segments by restriction endonuclease and is separated in the form of bands by gel electrophoresis. After this by using Southern blotting technique, these bands are decoded on X-ray plate or by the help of UV light. This is called DNA finger printing.
Uses of DNA finger Printing-
- Used in resolving disputed parentage of any child.
- To detect genetic diseases such as haemophilia etc. prior to birth of infant.
- To identify murderers and rapists.
Mapping Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP)
When some restriction endonuclease cuts the segments of genomic DNA of different races or related species
then it is called restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP).
- In this method the DNA of related species is isolated separately and it is digested by restriction endonuclease. After this it is separated by gel electrophoresis. These DNA bands are transferred on nitrocellulose filter and are kept with radio active probe and finally detected by autoradiography.
Note-The DNA isolated from an individual organism has a unique sequence and even the members within a species differ in some parts of their base sequences. On account of this the restriction sites would vary and hence the DNA of a given individual subjected to digestion with a restriction endonuclease produces segments, which will show difference from the segments of another individual. These variations in size of segments produced by restriction endonuclease among individuals within a given species is termed RFLP.
![]()
Uses of RFLP-
- To establish relationship in different species or races.
- To determine the structure and function of genes producing quantitative symptoms.
- This method is also ued in DNA fingerprinting.
- RFLP map of Maize, Rice, Wheat, etc have been prepared with the help of this method.
Achievements of Recombinant DNA Technoiogy (RDT)
Human has already achieved a lot of advantages in the field of Medical sciences, Agricultural sciences and industrial areas by the help of biotechnology. By using the techniques of biotechnology human can improve the varieties of domestic animals and agricultural crops. Achievements of Recombinant DNA Technoiogy (RDT)
Some of the important achievements in field of recombinant DNA technology are:
- Cloning of Nitrogen fixation (Nif) gene.
- Cloning of Haemophilic gene.
- Gene cloning of Hepatitis B virus.
- Cloning of Human growth hormone gene and insulin gene.
- Cloning of Penicillin G acylase gene for production of Penicillin.
