Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 21 Human Integumentary System
Genaral
- The body is covered by skin. The skin and its derivatives together form integumentary system.’
- The derivatives are the structures which orginate from the skin such as nails, hair, skin glands etc.
- The skin is ecto-mesodermal in origin.
- The skin remains attached to the rest body with the help of special areolar tissues.
Histology of skin
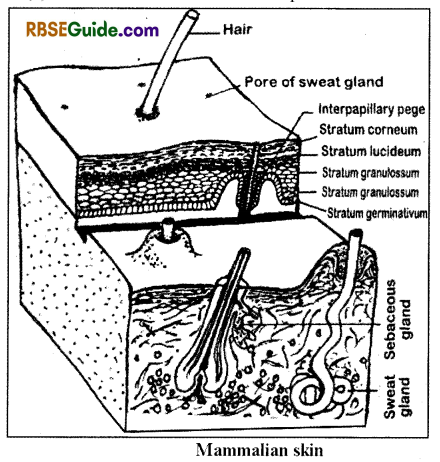
The skin consists of two layers-
- Epidermis and
- Dermis.
![]()
Epidermis
- It originates from the embryonic ectoderm.
- It is thickest in the body regions subjected to wear and tear such as soles and plam. It is very thin in eye lids and cornea.
- The epidermis is without nerves and blood vessels.
- It is a stratified epithelium and consists of five types of They are as follows from inside to outside :
Stratum malpighii or stratum germinativum
- It is the innermost layer of the epidermis which is living.
- It is made up of one layer of columnar cells. These cells divide constantly to form upper layers of the epidermis.
- This layer inpushes into the dermis. These inpushings are called as rete pegs.
- This layer also contains some melanocytes. These cells contain melanin pigments which impart colour to the skin.
Stratum spinosuml
- This layer is situated outside the stratum malpighii.
- It consists of many layers of branched polyhedral cells.
- These cells bear hook-like structure.
- This layer provides strength to the skin.
Stratum granulossum
- It is situated outside the stratum spinosum. It includes 5
6 layers of cells having granules of keratohyalin protein.
Stratum corneum
It is the outermost layer which is made up of flat squanous cells. These cells are dead because of presence of dead Keratin
- It is the thickest layer of the epidermis and consists of 8-10 layers of cells.
- It’s outermost layers sloughed off constantly.
- Keratinization : The process of formation of Keratin protein in the epidermis is called as This process leads in the formation of hair, nails etc.
![]()
Dermis
1. It originates from the embryonic parietal mesoderm. It is situated below the epidermis and it is 2-3 times thicker than the epidermis. It is elastic and made up of fibrous connective tissues.
2. It consists of collagen fibres, yellow elastin fibres, blood vessels, Nerves, smooth muscle fibres, cutaneous receptors, hair follicles etc.
It is divisible into two parts :
Papillary layer
- It is the outer layer of the dermis which forms rete pegs with the epidermis.
- It contains blood vessels and the sense organs.
- The collagen fibres are less in this layer.
Reticular layer
- It is situated below the papillary layer.
- It has more collagen fibres.
- It keeps the skin stretched.
Sub-dermis
- It is an extra layer which is situated below the dermis.
- It is divisible into two layers
(i) Stratum adeposum
It is also called as penniculus adeposum.
- It consists of adepose tissues which store extra food & it functions as heat resistant layer.
- Stratum Carnosus
- It is also called as penniculus carnosus
- It consists of areolar connective tissue which connects the skin with the rest body.
Derivatives of the skin
- The structures of the skin which originate from the skin itself are called as derivatives. Such as hair, cutaneous glands, cutaneous receptors etc.
Hair
- The hair are found only in the skin of mammals which are ectodermal in origin.
- The hair is situated in a hair follicle which is formed as in invagination of the stratum germinativum.
- The base of the hair follicle is everted cup-like which encloses a hair papilla or dermal papilla. The hair papilla is made up of blood vessels & the nerves.
- The hair consists of two parts viz. hair shaft & hair root.
- The cells of the hair root divide constantly causing growth of the hair follicle.
- The part of the hair shaft inside the hair follicle is covered by two sheaths viz.
![]()
(a) Huxley’s sheath-Outer
(b) Henle’s sheath—Inner & made up of cuboidal cells
The exposed part of the hail’ shaft is dead due to deposition of the keratin protein.
- Structurally, the hair shaft consists of three parts viz.
- Cuticle-Outermost & made up of squamous cells.
- Cortex—It is the outer part which contains melanin pigments. The melanin pigments are absent in the hair of rabbit.
- Medulla-It is the central part of the hair follicle. The lanugo is without medulla.
- There is an erector pilli muscle which is attahced be tween the epidennis & the hair follicle. The contraction of this muscle results in raising of hair which is a reflex action and called as goose flesh or cutis ansernia. This process is stimulated by the adrenalin hormone.
- The grey hair is without melanin pigments and its medulla develops air cavities which provide shine to the hair:
Cutaneous glands
- The skin has many types of glands.
- These glands orginate from the stratum germinativum of the epidermis but they are situated in the dermis.
- All the skin glands are exocrine and they secrete various secretions.
- The mammalian skin has following glands
Sweat or Sudorphic glands
- They arc coiled tubular Iands which open outside directly.
- They secrete sweat which contains 95% water ánd % other substances (e.g. lysozyme, salt, ammonia, urca etc.).
- The sweat lowers tue body temperature & exerete excess of salts. The lvsozyme fuund in it acts as hacteriacidal.
- The sweat glands in rabbit are apocriiw.
- In human beings. most of the sweat glands are cecrinc or merocrine. But the sweat glands found in ann pits. teats, eve lids are apocrine in function.
- Seat can be called as diluted urine.
- In rabbit, the sweat glands are found only at the manins oithc lips.
- There are myoepithelial cells around the coiled part of the gland. The sweat is released due to contraction of these cells.
![]()
Sebaceous glands
- They are compound alveolar glands which are formed as an outgrowth of the hair follicle.
- They are holocrine in function & open outside through the hair follicle.
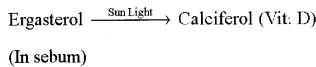
- They secrete an oily substance called sebum. The sebum’makes the skin & hair waterproof.
- The sebum has ergasterol which forms vitamin-D in presence of U-V rays of sun-light.
Ceruminous glands
- They are modified sweat glands.
- They are found in external auditory metaus and they secrete ear wax which is also called as cerumin. The cerumin is a type of carbohydrate.
- The cerumin makes the tympanun water proof.
Mammary glands
- In prototheria, human beings and other primates, the mammary glands are modifed apocrine sweat glands. In remaining mammals, they are modified compound alveolar sebaceous glands.
- Each mammary gland has a teat through whcih the mammary gland opens out. The area around the teat is darkly pigmented which is called as areola mammarae.
- The mammary glands secrete the milk.
- The milk contains mainly caesinogen, lactoglobulin, lactoalbumin, lactose and fats.
In huamn biengs, there is a pair of mammary glands on the thorax.
Perineal glands
- It is formed by the modification of the sebaceous glands.
- They are also called as scent glands or inguinal glands.
- They are situated near the rectum in the perineum region.
- They secrete a pheromone which acts as sex attractant.
Meibomian glands
- They are modified sebaceous glands and are also called as tarsal glands.
- They are found on the inner side of the eye-lids.
- They secrete an oily substance which keeps the eyes moist.
Glands of Zies
- They are modified sebaceous glands.
- They are associated with the hair follicles of the eyelashes.
- Their oily secretion lubricates the eye-lashes.
![]()
Cutaneous Receptors
- The skin receptors originate from the embryonic ectoderm but they are found in the dermis.
- They are lacking in the epidemisto avoid unnescessary stiumulation.
The various skin receptors are as follows :
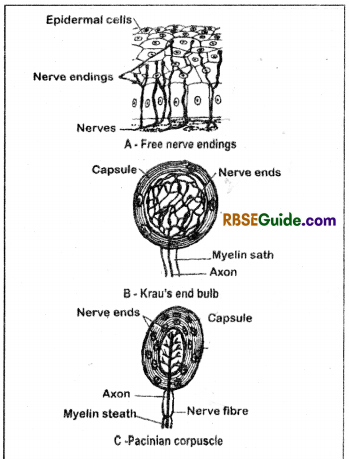
(i) Free Nerve endings
- They are naked or non-capsulated ends of the nerves which form a network.
- They are algesireceptors i.e. sensory to the pain.
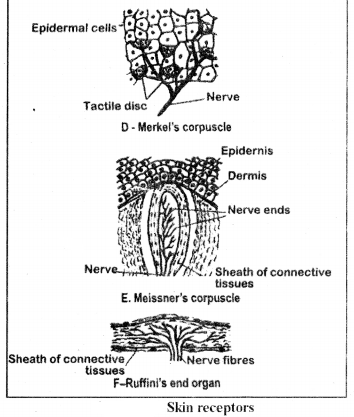
(ii) Meissner’s Corpuscles
- They are capsulated corpuscles which are found in the dermal papilla. They are some what cylendrical.
- They are tangoreceptor and particularly sensory to the surface texture.
- They are more in the skin of teats, external genetelia & tips of the fingers.
(iii) Merkel’s discs
- They are non-capsulated & cup-like.
- They are found in the reticular layer of the dermis.
- They are tangorecptors & particularly sensory to continuous touch. •
(iv) Pacinian corpuscles
- They are bulb-like corpuscles which are encapsulated. Their capsule is comparatively thick.
- They are found deep in the dermis.
- They are pressuroceptors & also known to receive vibations.
(v) Krau’s end bulbs
- They are encapsulated & found deeply in the dermis.
- They are frigido-receptors i.e. sensory’ to cold.
(vi) Ruffini’s end organs
- They are non-capsulated & found deeply in the dermis.
- They are thermoreceptors or caloreceptors i.e. sensory to heat.
![]()
Functions of Skin
1. Skin is the largest functional organ which performs vivid functions. Hence,- it is called as “Jack of all trades”.
2. It performs following main functions
- It protects the soft body organ from the germs, radiations & injuries.
- It protects the body from dehydration by preventing water loss.
- It controls body temperature. There is vasodilation in the skin when body temperature is high & vasoconstriction when body temperature is less. The vasodilation & vasoconstriction are under the control of hypothalamus.
- Being elastic, the skin helps in locomotion.
- The skin acts as respiratory organ, sensor} organ, absorptive organ, secretory organ, nutritive organ,
