Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 40 Important and Common Human Diseases
General
- Disease is a stage of body in which vital activity becomes abnormal/irregular.
- The abnormalities in the body activities are caused by pathogens like bacteria viruses, protozoans etc or excess/ deficiency of hormones or deficiency/lack of vitamins or pollutants or deficiency of other nutrients.
- Disease can effect a part/organ of body or the whole body. According to W.H.O., when all the organs of living body interacts in correct manner with each other while maintaining the proper and desirable balance with the
- external environment, then in such a situation body is called healthy or disease free.
- On the other hand, the abnormality in normal functioning of body or its parts, due to one or more reasons, is called diseased condition.
- Disease is the incomprehensible action or deformity of the body that results from the infections, contaminated diet, heredity, atmospheric or mental imbalance.
![]()
Types of Diseases
Human diseases are of following types :
1. Infections : This is caused by biological agents which are called as pathogens. For example viruses, mycoplasma, chlamydia, bacteria, fungi, protozoa, helminths etc.
2. Nutritional Disorders : Caused due to excess or deficiency of vitamins, minerals, salts, energy rich food etc.
3. Biochemical Disorders : Results due to the excess or deficiency of biochemicals like hormones, enzymes, Urea, Uric acid, Creatinine.
4. Exogenous Chemical disorders : Pollutants and allergens produce these diseases.
5. Life Style Disorders : These are caused due to the choice of food, lack of exercise, sitting habits, bad habits etc.
6. Mechanical Disorders : These are caused by organ amputation, sprains, Joint disruptions and injuries.
7. Degenerative Disorders : These are old age related problems. For example Atherosclerosis, over stress, heart disease and arthritis.
8. Genetic Disorders : These are caused by defects in genetic makeup. For example colour blindness, hemophilia, Down’s syndrome etc.
Categories of Diseases
The disease have two broad categories :
Congenital Diseases
The diseases which exist since birth are called as congenital diseases. They are of three types :
- Hereditory disease : Example – Side Cell Anaemia.
- Functional/Developmental defects : Example- Hare lip.
- Transmitted through Placenta : Example – Syphillis Germal Measel.
Acquired Diseases
- These diseases are caused after the birth. They may result
- from infections, disruptions, diet, addictions or bad habits, stress, mutations etc. .
- The acquired diseases are further divided into two categories :
Infectious Diseases
The diseases which are caused by the pathogens and parasites. They can be transfered from one infected person to a healthy person. Therefore infectious diseases are also called as Communicable or Transmissible or Circulating diseases.
They can be transmitted directly or through some factors like blood and serum, Hence are of two types :
- Contagious diseases : These diseases in a healthy person are caused through direct contact with a infected person, e.g. Ringworm, Conjunctivitis.
- Non-Contagious diseases : Such infections are spread through vectors (e.g. dengue, malaria), blood, serum (like AIDS, typhus fever).
Non-Infectious diseases
These diseases are caused by other factors rather than the pathogens. They are not transmitted through direct contact of one person with another. Because of this reason non-infectious diseases are also called as non- communicable or non-transmissible diseases.
They are of many types :
(i) Deficiency Diseases : Caused due to deficiency of some nutrient in the diet. Example- Kwashiorkar, anemia, blood deficiency disorder, Beri-Beri etc.
(ii) Degenerative Disease : These diseases are caused by weakness or old age eg. Atherosclerosis.
(iii) Allergy : Entry of foregin material the body results in excess stress to some people eg. Rhinitis (nasal related)
(iv) Addiction : These diseases are caused when person becomes addict to medicines, alcohol and tobacco.
(v) Mental disorders : These diseases are related to stress, anxiety, mental inability, madness, schizophrenia and phychosis.
(vi) Cancer : This is one of the main reasons of death in which cells divide continuously, the normal cells pulverizes and die due to hunger and the vital body organs start degenerating.
![]()
Air Born Diseases
- Pneumonia
- Meningitis
- TB
- Influenza
- Measels
- Whooping
- Cough
- Diptheria
- Mumps
- Common cold
- Polio
Food/Water born Diseases
- Cholera
- Jaundice
- Dysentry
- Polio
- Polio
- Typhoid
Body / Blood Contact
- Syphilis
- Gonorrhoea
- AIDS
- Chicken pox
- Measels
- Small pox
- Leprosy
- Tetanus
- Eczema
- Scabies
- Pyorrhoea
diseases Caused by Other Animals
- Yellow fever
- Aedes mosquito
- Malaria
- Female anopheles
- Typhus
- Lice
- Rabies
- Sleeping sickness
- Chagas disease
- Plauge
- Trench
- Elephantiasis
- Dracunculus
- Kala azar
- Rabid dog
- Tsetse fly
- Bed bug
- Rat fleas (Xenopsylla)
- Lice
- Culex mosquito
- Cyclops
![]()
Infectious Diseases
The diseases which are caused by some pathogens (Bacteria / viruses/Other animals).
They are capable of being transmitted from person to person.
Their infection is through air or food or water or blood contact or body contact or other vectors.
Diseases caused by Bacteria
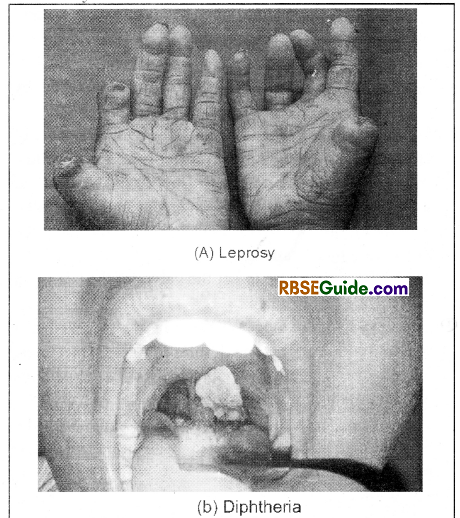
Leprosy or Hansen’s Diseases
- It is caused by the infection of Mycobacterium leprae bacteria.
- In this disease the nervous system, muscle, skin etc. gets badly affected. The symptoms of the disease starts to appear from 1 to 7 years.
- The disease spreads through the discharge released from wounds. Staying with patient for long time may also spread the disease. Leprosy is found only in humans.
Symptom : Deformatiy in finger & toes.
Type : Leprosy is mainy of three lypes :
(i) Tuberculoid :
Patient suffering from tuberculoid leprosy has high immune power. In this disease scales and wounds appear on the skin. The hands-legs and fingers twists (bends).
(ii) Lepromatous
Patients suffering from Lepromatous leprosy disease have compromised immune power.
In this disease bacterial cells aggregates and appear in the form of Globi. Lumps emerges on the surface. Very high numbers of wounds are also seen in such patients.
(iii) Border line
- Patients suffering from Border line Leprosy exhibits symptoms of both tuberculoid and lepromatous leprosy.
- Skin becomes scaly, lumps emerges and wounds also appears.
Prevention - Patients suffering from leprosy should be kept in isolation from the healthy normal people.
- Clothes & other belongings used by them should not be used by others.
Tuberculosis (TB)
- It is an infectious disease which caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria
- These bacteria can infect any body part bill commonly infect lungs.
- The infection occurs mainly by droplets. Also spreads through water.
- These bacteria release a toxin called tuberculin which degenerates body tissues.
- Test : Mantoux test
Symptoms :
- This disease results in cough and fever. Body weight decreases and man feel tiredness. The eyes get stuck inside. Appetite decreases as a result the person becomes weak.
- Germs of the pulmonary TB enters in the atmosphere through spitting, mucus, sneezing and sputum of the diseased person and through respiration these germs enters in the body of any healthy person. When there is less immunity in the body then the pathogens multiply very rapidly and comes out with sputum. Some times blood also appears in the sputum.
![]()
Prevention :
The person should take special precautions to protect himself from the disease. The diseased person should be kept in isolation. His cloths, utensils etc. should be cleaned by boiling using water. The sputum, stool etc. of the diseased person should be put down in the soil. One should not use hookah, beedi, cigarette etc. used bv others.
Vaccination :
Complete prevention is possible by BCG (Bacille Calmette Guerin) Vaccine.
Diphtheria
- It occurs in children up to 5 years.
- It is an example of droplet infection.
- It is caused by Corynebacterium diphteriue
- Symptoms – Obstruction of trachea due to swelling in the throat.
- Test – Schik test.
- Caccine : DPT Vaccine
- Prevention : As a preventive measure, patients of diphtheria should be kept in isolation. Children should be vaccinated with the appropriate vaccine designed against this disease i.e. DPT vaccine Children should be given pasteurized milk only.
Tetanus
- It is also called as lock jaw disease.
- It is caused by Clostridium tetani bacteria.
- It’s infection occurs by blood contact.
- This bacteria is found in rust, dust & dung.
- There is sustained permanant contraction of the skeletal muscles.
- Complete prevention is possible by ATS (Anti—tetanus serum) vaccine.
- Injection of tetanus toxoid is also useful.
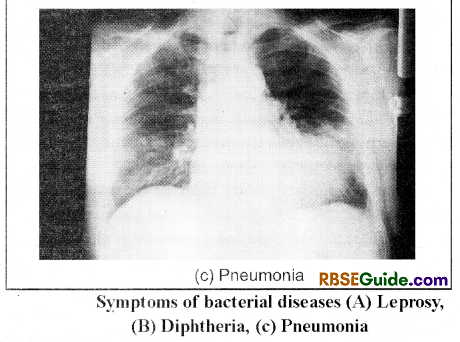
Pneumonia
It is a bacterial disease which is caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Symptoms – Fever, Inflammation irilungs, Short breaths, yellow-green cough etc.
Septicemia and burning sensation occurs in the liver and gall bladder. Patient feels pain in his chest Immunity of the patient decrease due to reduction in the number of white blood corpuscles in the blood. The Breathing becomes difficult. The symptoms of the disease appears in 1-3 days after infection.
Prevention :
For prevention of the disease special attention should be given on individual health. One should remain away from the crowded places, so that he can avoid the infection from the pathogens.
In addition, by keeping the patient in isolation, avoiding the use of personal belongings of the patients and dumping the sputum etc. in the ground, spreading of this disease can be prevented.
Diarrhoea
- It is caused by the infection of bacteria of shigella group.
- Symptoms : In this disease intestine expel excessive amounts of water and electrolytes out of the body. This cause dehydration in the body.
- In this disease patients starts to vomit. Another symptom is the appearance of blood and mucus in the faeces. Patient develops fever and feels weakness.
- Prevention : For prevention of the disease, boiled and filtered water should be used. The faeces and vomit expelled out by the patient should be burned in the soil. Food kept in open and rotten fruits should not be consumed.
Meningitis
Prevention : For prevention of this disease, cloths and other belongings of the patient should be washed in boiling water. The sputum, vomit and faeces of the patient should be dumped in the ground.
It is caused by the infection of Neisseria meningitis bacteria.
This bacteria infects the brain, spinal cord and spinal fluid.
Gonorrhoea
- It is disease of genital organs, which is caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacteria.
- Symptoms : These bacteria attack the epithelial layer of the genitalia. About 3 to 9 days after infection, a yellow coloured discharges begins to flow from the Urethra. Irritability or buminng sensation begins in the genitalia.
- Within few days, urithritis develops in females and the menstrual cycle is affected badly.
- The pathogen can also infect the valves of the heart and cause Endocarditis disease.
- Infection : The pathogenic bacteria are spreaded and transmited through sexual intercourse. Sometimes, touching or contacting the objects used by the patients can also result in disease transmission.
- Prevention : To prevent the disease, pateint should be kept in isolation. Sexual intercouse with the patient should be avoided.
Cholera
- It is an epidemic which is caused by Vibrio cholerae bacteria.
- This bacteria was discovered by Robert Koch.
- It’s infection is by contaminated food & water.
- Symptoms: Diarrhoea and vomitting begins on the onset
of this disease. This results in dehydration. Patient feels weakness and his body temperature drops down. - Urination stops. Cramps starts in hands and feets.
- Prevention: For prevention, cholerae vaccination should be administered. Rotten eatables must not be consumed. Always keep own house and surroundings clean.
- Treatment : Solution of salt and sugar (ORS) is very effective for the treatment of this disease. Patient should be given rice starch, (water obtained after boiling rice).
Typhoid
It is caused by Salmonella typhi bacteria.
It’s infection is caused by contaminated food and water.
Symptoms
- The patient feels headache and becomes dull. He feels stomachache
- Fever (103°-105°F).
- Pimples all over the body.
- Loose motion and reduced urine Volume.
- The fever of the patient lower down after 15 days.
Test – Widal Test
- Prevention : For the prevention of this disease excretory material of the patient should be hurried in the soil.
- Patient should take controlled diet. He should take fruit juices, eggs, milk, rice starch etc. He should be kept in isolation. T’A.B. Vaccines should be administered.
- Vaccine : TAB Vaccine
![]()
Whooping cough or Pertusis
- This disease in humans is caused by the bacteria Bordetetlapertussis. This disease persists for six weeks.
Symptoms: The effected person suffers from intense cold and dry cough, i.e. cough is not associated with mucus. Patient suffers from mild fever. Intensity of cough is so high that it is hard to breathe and produces a hup-hup voice. As a preventive measure, child should be administrated with D.P.T. Vaccine.
Infection : Droplet technique
Vaccine : DPT Vaccine
Diseases Caused by Viruses
Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS)
(A) General
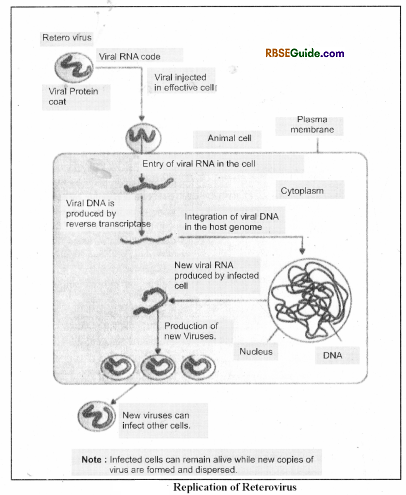
- It is a viral infectious disease which is caused by HIV (Human immuno deficiency virus) or HTLV-3 (Human T- Lymphocyte virus – 3) or LAV (Lymphodenopathy associated virus). This virus belongs to retrovirus family.
- This virus was discovered by Montagnier (1982).
- This virus infects helper T – lymphocytes.
- This virus does not survive in the air.
- It destroys the infected CD4 or T4 – cells, which are formed in the thymus during childhood.
- A healthy man contains about 300-400 million T4 cells.
(B) Structure of HIV
- AIDS virus is a RNAretro virus. It’s RNAforms DNAin host cell.
- Structurally, AIDSA virus is bounded by bilayer of phospholipids in which GP-120 & GP-41 glycorproeins remain embedded. It has 2 single stranded RNAmolecules & each RNA is attached with a reverse transcriptase enzyme. There are two protein layers around the RNA molecules viz.-P – 24 proteins (Inner) & P-17 proteins (outer).
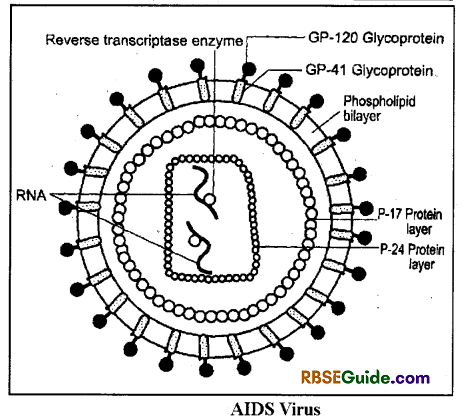
- With the help of reverse transcriptase enzyme, HIV can synthesis DNAfrom RNA. Two subtypes of HTV has been found-HIV 1 and HIV 2. HTV 1 is responsible for AIDS.
(C) Modes of Infection of HIV
- Infection takes place by blood contact.
- Infection is possible by sexual contact.
- The virus infects embryo in the uterus, as infilters through the endomatrium of the uterus.
- This virus is also found in the colostrum.
- Maximum 80% transmission occurs homobisexuality.
(D) Symptoms
- Contant loss of body weight.
- Prolonged diarrhoea
- Prolonged fever
- Swelling of lymph nodes
- Prolonged coughing
- AIDS infected person normally develops Pneumocystic carinie pneumonia and Kasposi sarcoma
- Profuse sweating.
(E) Preventions : The only way of prevention from this disease is to avoid the reasons which spread this disease:
- Always use disposable or sterilized needles for injection.
- Alway use safe blood free from HTV, obtained from authorized blood banks.
- Sexual relationship should be restricted to one reliable partner only. Use nirodh (condoms) for safe sexual relations.
- By using condoms, sufficient level of safety against AIDS can be achieved.
- Never use needles used by other humans to administer narcotic drugs.
- AIDS infected women should never conceive.
(F) Diagnosis : 6-8 Weeks after the HIV infection, distinct immunological reactions starts to appear in the body. These tests are used for identify ing such reactions :
- Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA Test) : In this test AIDS KIT containing HTV antigens are used.
- Western Blot Test : This is more reliable and exact testing process. It involves low cost and less time.
- Ora Quick Test : It can be performed at home. It takes about 20 miute. Blood is not required. Gum swipe is used to test the HTV presence.
(G) Treatment
Till now, no treatment of AIDS is available. Hence this formulated but none has proved effective. These disease is very deadly medicines include. Azidothymidine (AZT), Foscamet,
Few medicines for the treatment of AIDS have been Dideoxycytidine (DDC). Stavudine (D4T) etc. are nucleotide analogues which stops the synthesis of DNA form RNA. Some other drugs are protease suppresses like saqvinavir or invirase, Indinavir.
(I) Vaccine
No vaccine for AIDS is available till todate. Although scientist throughout the world are working hard to formulate an effective vaccine for the prevention of AIDS. Some vaccines like HTV-HIG (Hyper-immunoglobulin), Biocin etc. have been developed but practically none of the vaccine can provide complete protection against this disease.
As per a report published in Journal of Virology’ (2008), a group of researches working in Albert Einstein College have successfully developed, genetically transformed Cytotoxic-T-Lyniphocytes (CTLS). Strong futuristic possibility is being expressed by the scientists t.o effectively destroy the IIIV infected cells with the help of the genetically modified lymphocytes.
(J) Miscellany
There are many delusion about the spread of AIDS. It does not spread through general social affiliations like hand shaking, living together in the same house, playing together, reading and writing, eating together, using same lavotary, coughing, sneezing, hugging etc. This disease even does not spread through mosquitos bite, bedbugs bite, biting to other insects and moth. Hence it is very’ important that we should never neglect an .AIDS patient rather he should be treated sympathetically. We should help him to get complete medical facilities, which is a holy duty.
First HTV infected patient in our country’ was found in Chennai in 1986. This disease is also known as Death Warrent. For making the people around the globe aware of this disease from 1988, 1st December every year is observed as World’s AIDS Day.
Looking to the possibility of spread of this disease in the form of an’epidemic. National AIDS Control Organization (NACO) was set up in India in 1992. This organization along with state level. AIDS control committees works works for the control and prevention of AIDS.
![]()
Polio
- It is caused by the infection of Polio virus
- It is the smallest virus (size-10 nM) and it belongs to the group Picorna virus and consists of SSRNA.
- Its infection is by air/water/food.
- Complete prevention is possible by vaccination.
- For the prevention of this disease, Jonas Salk in America discovered a Yaccine in 1952. Albert in 1955 designed a drug that could be administered through oral route. This drugs is given thrice to the children of one year age.
WHO declared polio free on March 27, 2014.
Rabies
- It is also called as hydrophobia which means Fear of Water.
- It is caused by the infection of Rhabdo virus which is a RNA virus.
- This virus is found in the saliva of many animals like mad dogs, cats, wolf, fox and monkey etc.
- Symptoms : The symptoms of this disease appears 4-5 days after the dog or animal bite. There is inflammation and pain at the site of bite and liquid discharge at the site of bite. Patient does not allow any one to come near him. Mouth fills with scum. The patient becomes scare of water. (Hydrophobes)
- For the treatment of this disease, primary dressings at the site of dog bite, is essential.
- Louis Pasteur in 1885 discovered a vaccine. Such 14 vaccines are administered in the abdomen for 14 days.
- These are very painful and are meant for abdominal muscles.
- Rabies vaccine is next generation vaccine. It’s five doses are to be given on 0 3 7 -14-2Sth day.
- Now a days, a new vaccine is injected thrice on hand. This vaccine is called as Merieux human diploid vaccine.
- These vaccines were firstly used in America in 1980 and now-a-days they are also used in India.
Mumps
- This viral disease is also called as Epidemic Parotitis. Pathogen affects the salivary glands. Specially parotid gland swells as a result of which patient feels difficulty in swallowing.
- Symptoms : Diseased Person feels cold and suffers from fever. Patient feels pain in the back portion of head and ear. Testicles of a adult patient swells and appears larger than the normal. This results in decrease of sperms in the semen.
- To avoid the disease, one should not come in direct contact with the patient. The materials used by them should not be used.
- For treatment of the disease, cold and hot bandage strips should be used to compress the swollen parts of the throat. Pain killer tablets such as aspirin can be used.
Influenza
- It is a viral disease which caused by Influenza virus. As a result of this disease mucus secretion in trachea and nostrils increases.
- Symptoms : Patient feels pain in legs, head and back and shivering. High grade fever (104°F) within a twenty four hours, chest congestion and pain are also associated with the disease.
- The disease spreads through saliva, coughing, sneezing, loud speaking. Salivary droplets spreads to distant places and pathogens transmits along with these droplets.
Jaundice
- This disease is also caused by viruse. Its this transmition is through unhvgenic food and water.
- Symptoms : After infection, patient develops fever and lose of apetite is another symptom. Patient becomes unconscious, and the patient feels headache and vomits. Person becomes weak and his liver get inflammed.
- Few days after the infection, patient’s eyes, nails etc. becomes yellow.
- For the treatment of the disease, patient should be given proper rest. He should take fat free diet. He should follow the advice of the doctor.
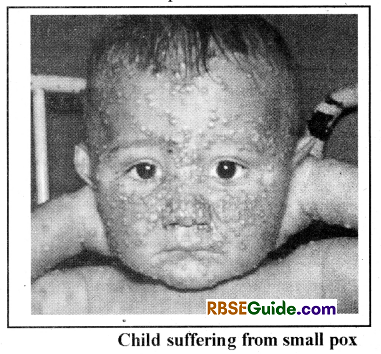
Small Pox
This is a highly contagious and epidemic disease. This disease has been eradicated from our country. WHO has announced that this disease has been completely eradicated from the earth.
It is a viral disease. It virus inhabits the blood, throat and nasal mucosa. This disease spreads through coughing, sneezing and by contact with the patient.
Symptoms :
- Patient develops high fever, eyes becomes red, weakness and dullness. After three days of infection red pimple line appears as rashes on the skin. These rashes are initially present on legs, hands and face but slowly they spreads on other body parts. These rashes gets filled with fluids.
- These rashes dries after one day. At this time, patient develops high fever which subsidies in a day or two and rashes falls down as scales.
- The wounds should be washed with the red solution of iodine (la) dawa). Use of penicillin and sulfa drugs is helpful in curing this disease. Children should be vaccinated with small pox vaccine.
- Hepatitis is infectious disease caused by virus. This disease affects both the children and adults.
- Although hepatitis is caused by six different type of viruses but the disease caused by two of them are main and important.
![]()
(A) Hepatitis – A
- It is normally called as Jaundice in which liver gets damaged. The causative agent of this disease is Hepatitis- Avirus (HAV).
- Its infection is caused by contaminated food and water.
- The pathogenic virus also exist in the body even after recovery and comes out with excretory substances.
- Therefore, this disease can spread like a endemic disease.
(B) Hepatitis – B
- It is also called as Serum hepatitis and is caused by the infection of Hepatitis B virus. It is a DNA virus and is more dangerous than HTV.
- Hepatitis B Virus was discovered in the blood of an Australian tribal by Dr. Blumbarg in 1965. Therefore this is also called as Australian antigen. For this discovery Dr. Blumbarg was awarded nobel prize in 1977.
- This disease is transmitted by the blood of the infected person. This is normally caused in adults only and spreads through
(i) Transfusion of infected blood.
(ii) Use of infected tools and needles.
(iii) Infected pregnant women to new bom child.
(iv) Infected partner through sexual contact.
(v) Shaving the beard of many persons with a single blade or use of single needle for piercing nose and ears.
Symptoms of Hepatitis-B :
The person suffering from this disease shows the following symptoms : fever, vomiting, jaundice, yellow urine (dark yellow), loss of appetite etc. If the disease remain untreated for long duration, it can lead to liver cancer or swelling in liver.
Diagnosis :
Hepatitis elicit the production of specific antibodies in the body. These are IgM type of antibodies. Therefore identification of viruses can be done by observing the presence of specific antibodies against the hepatitis vims in body fluids (like serum)
Preventive measures and Cure
- Use fresh and clean water
- Use suitable lavotories for urination and defaecation
- Always use disposable syringe and needles
- All the tools used for surgery should be sterilized
- Avoid transfusion of infected blood
- Should have safe sex
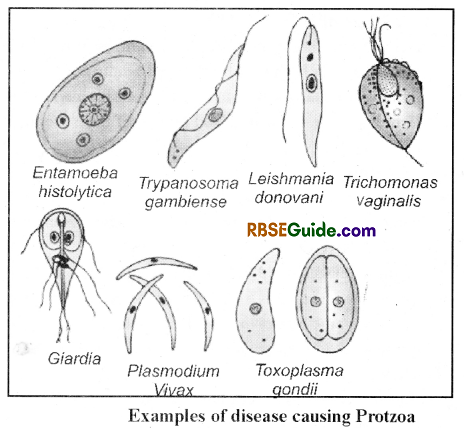
Diseases caused by Protozoans
Amoebiasis
- Amoebiasis disease is also called as Amoebic dysentry.
- This is caused by a protozoa called Entamoeba histolytica.
- Symptoms :
- In this disease, the pathogen in its trophozoite stage enters in the intestinal wall and secretes tissue decomposing enzymes which cause disintegr ation of cells. This results in small mucus filled ulcers in the affected area. The ulcers brusts in the lumen of intestine and release mucus which comes out along with the faeces.
- The patient do not suffer with fever, however he develops diarrhoea with abdominal cramps tluoughout the day. Some times blood also comes out along with stool. Patients becomes very weak.
Mode of Infection :
- It spreads thorugh food, water and flies.
- Prevention :
- For prevention from this disease we, boiled water, we must not consume uncovered food.
- Treatment
- For the treatment of this disease Amitine, Fusegilin, matrinidazole medicine are available.
Diarrhoea / Giardiases
It is a protozoan disease which is caused by a flagellated protozoan named Giardia. This enters in to the body along with water, food etc. and reaches up the intestine.
Symptoms :
- This leads to functional irregularities in the intestine.
- Patients suffers from loose motion
- Stomachache & reduced appetite
- Headache and restlessness
- Treatment :
- For the treatment of this disease, drugs such as chloroquinone. camocoine. Atrobin etc. are administered.
Trypanosomiasis
- It is also called as Sleeping sickness. This disease is caused by Trypanosoma gambiense. It is transmitted through a Tsetse fly (Glossina palpalis).
- This protozoa enters in the lymphatic system of our body and secretes poisonous substances. W hich results in swelling of the lymphatic system
- Trypanosoma enters in the cerebrospinal fluid and cause malfunctioning of the brain.
- Symptoms : Patient remain in sleepy state.
- Treatment: For the treatment ofthis disease Primaquine and Puromycin drugs are used.
Malaria Fever
This disease is caused by various species of Plasmodium which are as follows :
- Plasmodium vivax : Most common
- Plasmodium falciparum : Most dangerous
- Plasmodium malariae
- Plasmodium ovale
The transmission of disease is through biting of female Anopheles mosquito.
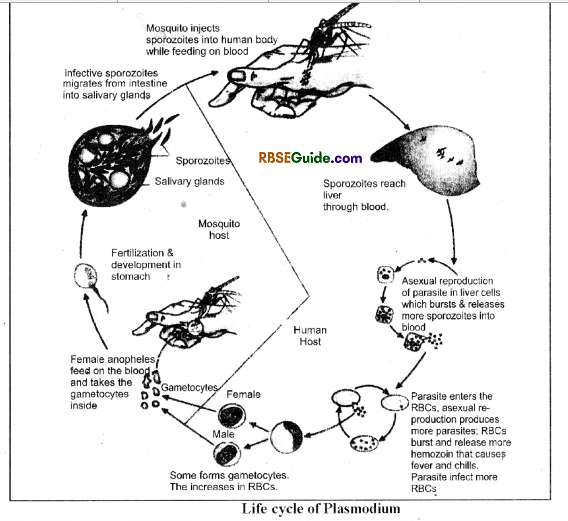
Life Cycle of Plasmodium
The life cycle of Malaria parasite is digenetic. It is divided into three phases :
- Schizogony => Asexula; Human liver cells & RBC.
- Gamogony => Sexual; Begins in Man and completes in female Anopheles.
- Sporogony => Asexual; Stomach of female Anopheles.
The Schizozogony is further divided into four phases :
- Preerythrocytic phase : Human Liver Cells.
- Exoerythrocvtic phase : Human Liver Cells
- Erythrocytic phase : Human RBC
- Postertythrocytic phase : Human liver cells.
![]()
Infective Stage: The infective stage in Man is sporozoite.
Through biting of fema le .Anopheles mosquito, sporozoite of Plasmodium enters in the blood and multiplies in the liver cells and red blood corpuscles. Haemozine is produced which results in Shivering, Chills and Fever. The parasite in its gametocyte phase enters in the mosquito when a mosquito bites an infected person. Further maturation of the parasite occurs in female Anopheles.
Male & Female gametoevte through the process of gametogenesis produces male and female gametes. The gametes fuse and to form zygote. The zygote divides and forms new sprozoites that migrates to the salivary gland of the mosquito. When the mosquito bites a person, the sporozoites enters in his body. For the treatment of this disease medicines containing antimony compounds are used.
Symptoms :
Release of haemozoin along with merozoites causes malaria symptoms or paraxysm viz.
- Rigor stage : Patient experience chill and shivering.
- Fibril stage : Body temperature rises to 104-106°F.
- Defervescent stage : Profuse sweating. It occurs 6 hrs. after rigor stage.
Medicines :
(i) Quinine is the oldest known medicine for the treatment of malaria fever. It is obtained from the bark of Cinchona tree. This tree is found in Peru, Shri Lanka,Java, India etc.
(ii) Other useful medicines are Nivaquin, Resochin, Camaquin, Chloroquin, Paludrin, Plasmaquin, Daraprim, Mapacrine etc. Sulfadoxin & Pyrimethanine are the new & most effective medicines. Now a days a single dose of sulfadoxin- 750 mg. & Pyrimethamine 37.5 mg. is given.
Prevention :
- According to National malaria eradication programme (NMEP), malaria control involves three methods viz. destruction of mosquitoes, prevention from infection & treatment of patients.
- Destruction of mosquito larvae using fishes is called as biological control of malaria.
- Stickle back, Gambusia, Minnows, Trout, Channa etc. are some Larvicidal fishes.
- Allethrin is the most recent mosquitocidal chemical. 3.6% of allethrin is used in various trade marks like All out, Good night, Jet etc.
- Other common insecticides are Pyrethrum, BHC, 1)1 I ,Nephella etc.
Leishmaniasis (Kala – Azar)
- This disease is caused by different various of Leishmania. It is a flageller parasite which is found in the blood of vertebrates. Kala-Azar is caused by Leishmania donovani.
- The vector host is sand fly (Phelobotomus)
- Symptoms:
- The pathogens of this disease blocks the Reticulo-endothelial system, as a result the spleen enlarges in size. It forms boil like bulges all over the body especially in the nasal, oral and pharyngeal regions.
Trichomoniasis
- This disease is caused by various species of Trichomonas.
- It is a flagellar protozoan. The most common species of Toxoplasma is Trichomonas vaginalis. This pathogen resides in the vagina of women and cause vaginitis disease in them.
- Symptoms : This disease cause secretion of a foamy substance from the vagina. This also cause itching and inflammation in the vagina.
![]()
Toxoplasmosis
This disease is caused by Toxoplasma gondii which is a sporozoa protozoan. This pathogen is pandemic.
Symptoms : This pathogen is found in the cells of reticulo-endothelial system and central nervous system of humans. Hydrocephalus and chlorioretinitis are major symptoms of this disease.
Diseases caused by Helminths
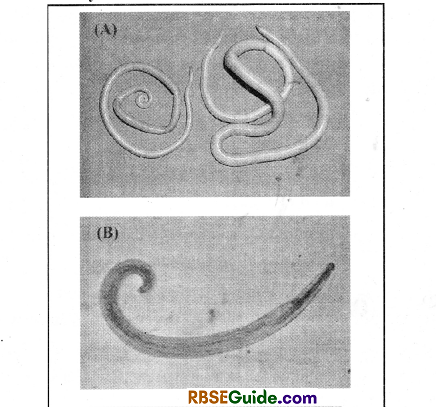
Acariasis
This disease is caused by Round worm Ascaris lumbricoides. As compared to adults, its frequency is higher in children. The fertilized eggs of this worm comes out along with the faecal material of the infected person and contaminate the soil, water and plants. Consumption of contaminated food and water can infect a healthy person.
Sometimes this worm make holes in the epithelial layer of the intestine and reaches to the blood stream. Through blood, this worm reaches to vital organs like kidney, spinal cord, brain and muscles and cause their damage.
Acute infection may lead to severe pneumonia. Sometimes immediately after the infection, fever, bloodlessness, muscular spams, intestinal blockage and eosinophila occur in the infected person.
The adult worms cause Gastroenteritis. They may cause swelling in the appendix, gall bladder and bile duct.
The adult worm obtains their food from the digested food present in the intestine. They can suck blood from the intestinal walls.
These worms releases poisons which can result in the symptoms like cramps, fits, unconsciousness, deep sleep and nervousness.
Enterobiasis
- This disease is caused by Enterobius vermicularis. The worms are also called as Pinworm or Seat worm.
- In the human body they are found near edges of anal part of the rectum. This disease is more prevalent in children as compared to adult.
- Symptoms:
- This disease cause itching all around the Anus. Loss of appetite & sleeplesness. Child gnashs teeth while sleeping and urinates in the bed. In girls, this worm enters in the vagina and cause vaginitis disease.
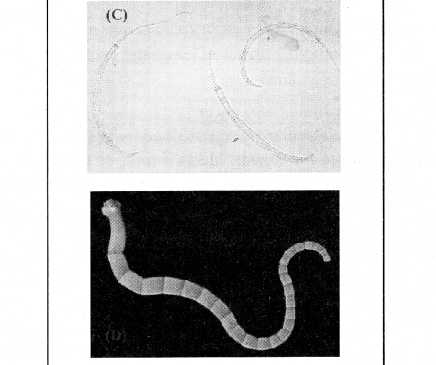
Dracunculiasis
- This disease is caused by worm called Dracunculus. This pathogen is also called as Guinea Worm or Naru worm. In humans, this worm resides beneath the layer of subcutaneous tissues of arms, legs and shoulder skin.
- Symptoms:
- In the effort to release the embryo, the bearing female tries to move out of the skin. The area of skin from where it attempts to move out suffers from itching and inflammation.
- The poisonous substances released by the female worm forms small ulcer or blister through which the posterior portion of the female worm comes out to release young ones.
- Local inflammation, swelling and pain are associated with this process. Blisters gets cured in few days.
- Treatment:
For the treatment, worm is removed through surgery. In villages, the worm is removed with the help of wooden stick. Villages do it very carefully by wrapping and pulling the worms which are peeping out of the skin on the wooden stick. In this process there are many chances of breaking of the worm inside the body.
Taeniasis
- This is caused by various species of Tapeworm (Taenia) Symptoms.
- The patient suffers from stomachache and vomitting. A condition of anaemia may also arise. Patient feels excess hunger. Excess eating results in indigestion or dyspepsia.
- The poisonous substances released by the worm cause increase in the number of eosinophils and disorders in nervous system.
- Such diseases are not caused by infection, therefore they are called as non-infectious diseases. Some of them are as follows :
![]()
Canror
General
- It is a complex disease which may occur in any body part.
- Cell division in human body is a nonnal feature but as and when the regulatory process of division gets disturbs, the cells starts to divide in an uncontrolled manner, i.e.
- cancer is a stage when “cell gets mad”. This results in the formation of a cellular lump. Which is called as Tumour.
- Lung cancer is the most common in human beings.
- In women, mammary cancer is most common.
Types of Tumour
It is of two types :
(1) Benign Tumour
They are generally confined to the point of origination and do not have ability to spread to other parts of the body. They are not deterimental.
(2) Malignant Tumour
Malignant tumours are called as cancerous. They can spread from one part to another part of the body. New tumour starts to appear at different places. Which is called as Metastasis.
Diagnosis
(A) Precancer stage & tumour stage of cancer can be investigated on the basis of following symptoms-
- Any swelling or blister or boil which do not cure or reoccures after getting cured.
- Fluidy discharge from some body orifice in a continuous or periodic manner.
- Presence of some lump of tissue in an organ or lump like structure. It occurs with breast cancer.
- Indigestion or Irregularity in stomach which occurs repeatedly.
- Severe constipation and diarrhoea which may get cured but appears repeatedly.
- Sudden loss of body weight.
- Regular coughing or sore throat for long time.
(B) (i) The diagnosis of cancer is based upon biopsy and by counting increase in number of cell of blood or bone marrow examinate is done. (In case of Leukemia or blood cancer). Biopsy of a doubtfull tissue is carried out for microscopic examination of the stained thin sections & pathology is observed.
(ii) Radiography (using X-ray), comptued tomography and magnetic tomography etc. are some techniques which are used for the detection of cancer in internal organs. For detection of certain type of cancers, specific antibodies are used against cancer specific antigens. MRI requires the use of strong magnetic field while X-rays (ionizing radiations) are used for radiography.
Types of Cancer
On the basis of affected tissue cancers are of different types, such as
(i) Carcinoma : Cancer originating from epithelial cells are called Carcinoma. They normally originates on skin and internal organs surface.
(ii) Sarcoma : Such cancers originates from connective tissues. They are normally associated with the mesodermic structures.
(iii) Osteoma : Cancers associated with bones are called Osteoma.
(iv) Fibroma : Cancers associated with filamentous tissues are called fibroma.
(v) Glioma : Such cancers are associated with the connective tissues of nervous system and brain.
(vi) Melanom : They are the fast growing pigmented tumour on the skin. It is caused by excess growth of melanocytes.
(vii) Lymphoma : Cancers which arises in lymph nodes and other tissues of lymphatic system are called lymphoma.
Treatment of Cancer
Tools of molecular biology are used to find out the genes responsible for cancer. Identification of such genes is essential which predipose the person for cancer Treatment.
The following are some treatment procedures.
(1) Radiotherapy : In this treatment cancer cells are destroyed by using radiation.
(2) Chemotherapy (Chemical treatment) : In this therapy, cancer cells are treated with anticancer medicines. Alopecia and anaemia are major side effects of this treatment.
Now a days most of the cancer treatments are based upon a combination of surgery, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy. Interferons are also used to destroy the cancer cells. Interferons activates the immune system which in turn destroy the cancer cells.
Causes of Cancer
The factors which cause conversion of normal cells into cancer cells are called Carcinogens. Some of them are as follows :
- Ionizing and Noti-ionizing Radiations:
Examples: X rays, Gama Rays, UV rays etc. - Physical Stimuli: Such as Kangri used in Kashmir.
- Chemical Factors: Testosterone, Caffein, Estrogen, Cigar, Tobacco prdoucts, heavy metals mustard gas etc.
- Biological factors : .
- Oncoviruses: Ejstine Barr virus, Herpes simplex virus, SV-40 virus etc.
- Oncogenes.
Allergy or Hypersensitivity
Body respond characteristically to,some substances i.e. the body is hypersenstive to some substances which is called as allergy.
The substances which cause allergy are called as allergens. For examples carbon particles, pollan granules, dust particles, some proteins etc.
Term”allergy” was coined by Perquet.
The allergy is of 4 types
- Anaphylactic reactions
- Cytotoxic reactions
- Toxic-complex syndrome reactions
- Delayed-hypersensitivity cell mediated reactions
In allergy, the mast cells secrete histamine. In mast cells, the histamin is found in the form of inactive histidine
The mast cells also secrete seratonin which is secreted in the allergy caused by food. It causes muscles contraction & increases cellular permeability.
Antihistamines & steroids give fast relief in allergy.
IgE type of antigen are generally produced against allergens. Running nose, sneezing and coughing, difficulty in respiration are some of the symptoms of allergy.
![]()
Asthma
Asthma is an example of disease caused by interruption of lungs. It involves constriction of the bronchioles and as a result patient suffers from respiratory disorders (laboured breathing). This leads to coughing, difficulty in breathing, wheezing etc.
Hypersensitivty is the maj or cause of respiratory allergies in persons of less than 30 years of age. This is generally caused by pollen grains. In aged persons, this disease can be caused by the nonallergic stimulants, dust, smoke etc. present in inhaled air.
Symptoms of disease :
- Red spots on the skin of the patient
- Difficulty in Breathing.
- Itching on skin
- Common cold and frequent sneezing
- To prevent himself from this disease, one must avoid all those factors which may cause allergy.
- Before starting the treatment of the allergy, it is important to find out the factors responsible for this disease.
- Antihistamine, Adrenaline, Steroids etc. are used to control the symptoms of allergy.
Hyportontiinn
Blood in human arteries flow at a specific pressure but because of certain reasons pressure in arteries may increase. The standard systolic and diastolic blood pressure is 120 mm Hg and 80 mm Hg respectively. The cardiac output increases in this disease.
If high blood pressure persists for long, following fatal consequences may appear in the patients
- Heart failure
- Brain Stroke
- Kideny damage
Cardio – Vascular Diseases
The diseases associated with the blood and heart are called as Cardio – Vascular diseases.
They are as follows:
(a) Rheumatic heart disease – It is an autoimmune disease. It occurs in children after a severe throat infection by Streptococcus bacteria.
(b) Hyper/hypotensive heart disease
(c) Angina pectoris – It is a chest pain which is caused by myocardial ischemia.
(d) Myocardial infarction – It is commonly called as heart attack. It is normally due to blockade in the coronary artery.
Sudden reduction in the supply of blood to the coronary artery is the major cause of this disease. As a result, the blood supply and hence oxygen supply in certain parts of heart muscles gets obstructed. This impairs the function of heart muscles. In one way they can be considered dead. The myocardieal infarction can also be considered as synonym of heart attack.
The major reasons for obstruction of coronary artery is the formation of thrombus or clot, hyperactivity or aggregation of platelets, or atherosclerosis of blood vessels.
Symptom : Severe pain in chest that may generally persists for 30 minutes or more. Along with pain, patient suffers from nausea, vomiting and laboured breathing. The severe pain spreads in other parts of the body. Intense infarction may cause death of patient.
(e) Cyanosis – It is caused due to too much deoxygenated haemoglobin (excess of C02) in the blood. There is blue colouration of skin, nails, lips etc.
(f) Arteriosclerosis – It is caused due to hardning of arteries wall by the deposition of cholesterol inside the arteries & thickning of arterial cells.
Emphysema
This is one of the common pulmonary disease. It is caused as a side effect of smoking and air pollutants.
Emphysema word means presence of excess amount of air in the lungs. As a result lungs become inelastic. A large number of alveoli and alveolar wall get destroyed.
This results in the formation of large sized emphysema lumen in place of small sized alveoli. The larged sized lumen so formed, have low elasticity. Degradation of alveolar wall reduces the net surface area of the alveoli. As a result gaseous exchange between the alveoli and blood is hampered.
Cataract
- This is most common disease of eyes found in our country.
- Cataract is more common in old age. With the increasing age, lens of the eye becomes flat, dense appears brown and ultimately becomes opaque. As a result vision of the patient is lost.
- Now-a-days, this disease is treated by surgically replacing the old lens with new resilens (artificial lens).
Giannnma
Glaucoma is an eye disease is mainly caused by increased intraoccular fluid pressure (vitrous humor and aqueous humor). Normally, this fluid exerts a pressure on eye and maintain it shape. In certain conditions, the volume of this liquid increases and exerts an extra pressure. When this pressure increases beyond a certain level, eyeball expands and if not controlled, it may damage the nerve fibres and other other paits of eye. This disease can impair the vision and leads to blindness.
![]()
Strabismus
- This type of eye defect is found in many persons.
- There are, six eye muscles which help to rotate the eye in the eye orbit.
In some cases, due to one or more reasons one or more muscles undergoes change is size (i.e. becomes smaller or larger). As a result eye ball in the orbit becomes inclined and person looks squint. - This disease damages the retina & may leads to blindness.
- It can be corrected by microsurgery.
