Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 32 Man-Fertilization
General
Fusion of haploid male gamete (spermatozoan) and female gamete (ovum); is called fertilization. As a result of fertilization a diploid zygote is formed.
There is amphimixis in fertilizaton with involves:
- Karyogany – Fusion of pronuclei of both the gametes.
- Plasmagamy – Fusion of cytoplasm of both the gametes.
In the process of fertilization, the sperm activates the ovum to develop.
![]()
Types of Fertilization
The process of fertilization is of two types:
(1) External fertilization : Fertilization which occurs outside the body of parents in the aquatic medium, is called external fertilization. Aquatic medium may be freshwater or seawater. External fertilization found in most of the fishes (Labeo), amphibians (frog), echinoderm (star fish) etc.
(2) Internal Fertilization : In oviparous (egg laying) animals such as reptiles and birds or in animals where eggs are retained within the maternal body (ovoviviparous and viviparous animals), the spermatozoa are delivered internally (in the female’s body) by intromittent organ or copulatory organ. In such forms fertilization occurs in the body of female. In human fertilization occurs in the Fallopian tube.
Artificial Fertilization
Sperm delivery by the male into the body of female is known as Insemination. Sometimes spermatozoa are collected artificially, preserved and stored and as per requirement the semen is deposited in the vagina or the cervical canal or the uterus by artificial means. The reuslting fertilization is called Artificial Insemination”.
This procedure is mostly used in animals to improve their breed. Sometimes also used in human when woman is unable to conceive through sexual intercourse.
The process of fertilization involves following steps:
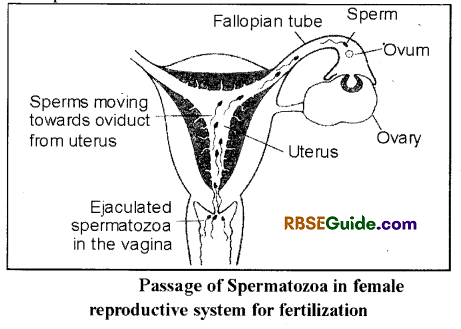
Approach of sperms to ovum
- Male ejaculate semen into the vagina of female close to cervix. It called as Insemination. Ejaculated semen, contains approximately 400 million sperms.
- Out of them about 100 million spermatozoa are capable to reach up Fallopian tube because most of the spermatozoa die due to acidic environment of female reproductive tract and many are eaten by phagocytic cells of vaginal epithelial cells.
- Spermatozoa swims in seminal fluid at the rate of 1-4 mm per minute.
- The uterine contractile activity and peristaltic movement of Fallopian tube maintain sperm motility.
- Sperms become capable for fertilization some time after the entry’ into the uterus.
- The capacity of spermatozoa to fertilize eggs of the same species is called Capacitation. In this process, the spermatozoa became physiologically mature and it requires 5-6 hours to become able to fertilize an ovum.
![]()
Entry of Sperm into ovum
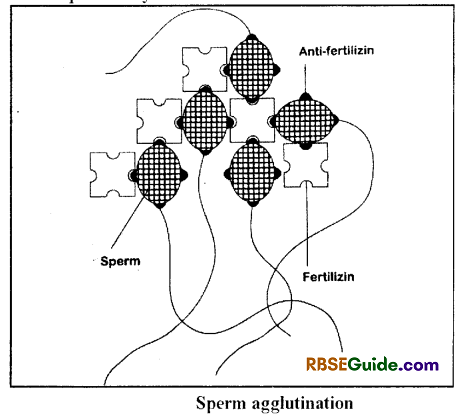
The ovum secretes a chemical called fertilizin on the surface. Similarity, the sperms have antifertilizin on the surface. There is a reaction between fertilizin and antifertilizin of same species. As a result, the sperms get attached to the ovum. It is called as sperm agglutination.
Sperm penetration is a chemical process. In this process anterior end of spermatozoon i.e. acrosome release some sperm lysins, which dissolve the egg coverings and create a path for sperm penetration. Sperm lysins are acidic proteins which contains hyaluronidase enzyme. Hyaluronidase enzyme dissolves hyaluronic acid found between interstitial cells of corona radiata and acrosin enzyme dissolves the zona pellucida and make passage
for sperm entry.
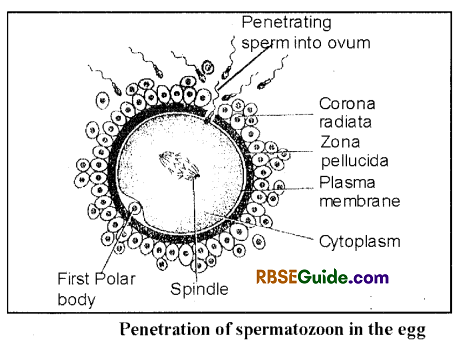
Cortical Reaction (Activation of Ovum)
Immediately after penetration of spermatozoon into the egg, the cortical reaction initiates to prevent further entry of spermatozoa. Chemical substances found in the cortical granules are released in between the plasma membrane and vitelline membrane. These substances fuse with the vitelline membrane to form fertilization membrane. Following metabolic activities are initiated in the ovum after penetration of sperm :
- Fertilization cone is formed on egg surface.
- Fertilization membrane is formed by vitelline membrane and cortical granules.
- Permeability of plasma membrane is increased.
- Rate of protein synthesis is increased.
- Mitotic divisions starts in the fertilized egg.
![]()
Fusion of Pronuclei
Sperm penetration stimulates second maturation division in the secondary oocyte. Spenn rotate by 180° so that the mid piece assumes the leading position. Centriole brought through sperm divides into two parts and developes chromosomal spindle in centre of ovum and now secondary polar body is formed. Expulsion of second polar body from secondary oocyte prepare the ovum for fusion of pronuclei of both gametes.
The movement of male pronutleus towards female pronucleus is called fertilization path. Male pronucleus follows fertilization path and moves straight toward female pronucleus. Very less disturbance in this path occurs in many situation.
