Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter 42 Bio-Medical Technologies
![]()
General
- In the modem medical science, many techniques are used for the diagnosis and treatment of several diseases, so that the reason behind the disease and its nature could be identified and proper treatment can be administered.
- The testing procedures used for the disease management are more precise, reliable and are less time consuming than older times. The present chapter deals with some important tests and equipments used in medical sciences.
Haematological Examinations
- The blood is an important constituent of human body which is made up of blood cells and plasma. Blood is the medium which provides all the useful substance to body cells and tissues. Moreover, blood transport many other substances in the body. Any physiological or functional irregularity in the body is reflected in the blood. Therefore, through blood examination, functional and physiological status and irregularity in the body can be judged.
- Some of the haematological examination techniques are as follows :
Estimation of Haemoglobin in blood
- Estimation of haemoglobin in the blood is called Haemogldbinometry. Haemoglobin is a respiratory pigment found in red blood corpuscles. Chemically, it is a chemoprotein which is used for the transport of 02 and co2.
- Working efficiency of a person is affected adversely, if due to some reason his/her haemoglobin content drops below the normal value. Avalue of haemoglobin less than the normal value, is an indicator of Anaemia.
The normal value of Haemoglobin is as follows
![]()
| Age | Haemoglobin g/100 ml blood | |
| 1. | Healthy Adult male | 15.5 ± 2.5 |
| 2. | Healthy Adult female | 14 ± 2.5 |
| 3. | Children (3 months) | 11.5 ± 2.5 |
| 4. | Children (3-6 years) | 12 ± 1 |
| 5. | Children (10-12 years | I 13 ±1.5 |
- Haemoglobin content is measured with Haemoglobinometer. Traditionally Sahli’s Haemoglobinometer is used for this purpose.
- Photohaemoglobinometer and Autoanalyzer are also used.
- Sahli’s Haemoglobinometer:
- This device contains a graduated tube and two standard matching tubes placed in a stand. Between the two standard tubes is placed a measuring graduated tube. In the measuring tube, N/10 HC1 is filled up to zero (2 g%) point. Now using the haemoglobin pipette 20 fxl (0.02 ml) blood is transferred to the measuring tube. Blood is thoroughly mixed with N/10 HCl already present in the tube.
- The N/10 HCl converts haemoglobin into a brown coloured substance called haematin.
- The measuring tube is now kept in between in the two standard tubes. Distilled water is added drop by drop mixing with continuous mixing to the measuring tube till the colour of the haemtin solution matches with the colour of the standard tubes / comparison tubes. When the colour matching between the tube is ensured, haemoglobin content is measured by observing the reading on measuring graduated tube.
Total Leucocyte Counts (TLC)
- The leucocyte are very important for the immunological reactions of the body and works like cops of the body. Their enumeration are very important for the diagonosis of a disease.
- Various types of leucocytes are – Neutrophils, Basophils, Eosinophils, Lymphocytes and Monocytes. Generally their counts are 5000-10000 per mm³.
- Clinical situation in which number of leucocytes increases more than the normal value is called Leucocytosis. While reduction in their number below the normal value is called Leucopenia.
Procedure :
- Neubaur’s Haemocytometer is used to count the leucocytes. Counting chambers located on the four comers of the haemocytometer are used for counting leucocytes. Counting is done with the help of a microscope.
- Using a WT3C pipette, draw blood exactly up to 0.5 mark.
- knmediatly draw WBC diluting fluid up to 11 mark. Mix the blood and the diluting fluid by rotating the pipette.
- Place a coverslip over the Neubaur’s Haemocytometer and allow the diluted fluid to enter in the counting chamber. Allow the cells to settle for 5 minutes.
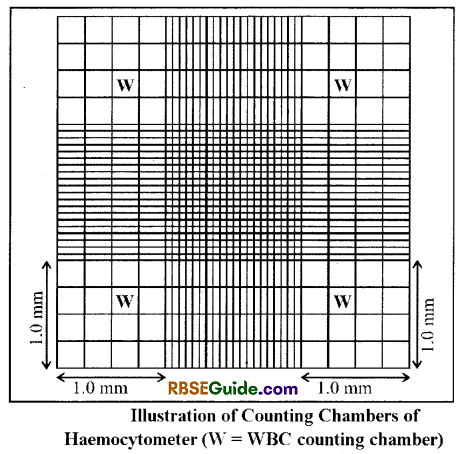
5. As is shown in fig. WBC are counted in 4 larger squares marked by W (total 64 small squares).
![]()
- Following formula is used to count the total WBC.
- Total WBC / mm3 = Average number of Leucocytes in four large chambers Dilution < Volume of the counting chamber Total WBC => Average of WBC > 20 < (1 x 1 x 1/10)
- The diseases are marked by the change in the leucocytes counts. For example in leukemia, the number of WBC increases many folds while in typhoid, tuberculosis, measles, dengue, kala-azar etc, the number of leucocytes decreases.
Differential Leucocyte Count (DLC)
General :
- In this blood test, percentage of various types of leucocytes is counted. This blood test is more useful than the total leucocyte count. It is because number of specific leucocytes get changed in different diseases and hence this test is important for the diagonosis of disease.
- For this test, smear of the patient’s blood is stained with a suitable stain like Leishmann stain or Geimsa stain.
- Then the stained smear is observed using a microscope, different type of leucocytes are identified and counted.
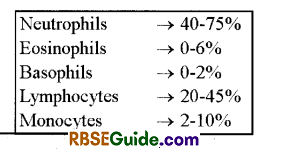
- The blood cell counter machine can be used for counting the cells. Percentage of different types of leucocytes is calculated from the 100 leucocytes counted.
- The number of different leucocytes in a healthy person are as follow :
Medical Uses :
Any irregularity observed in the differential counting of the leucocytes is an indicative of specific disease; further specialized testing can give a proper diagonosis of the disease and thus helps in proper treatment. Some of these conditions are described below.
![]()
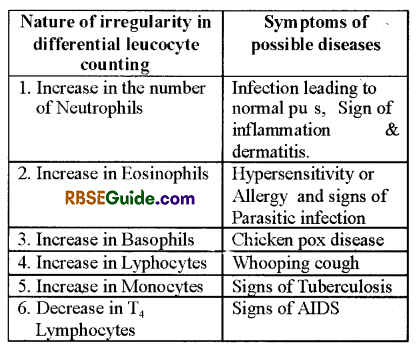
In General differential leucocyte count do not include T4 lymphocytes)
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)
If a blood sample mixed with an anticoagulant like Trisodium citrate and kept undisturbed for sometime in an ESR measuring tube, blood cells being denser than plasma, moves towards the bottom of tubes and settler down. The rate of setting down of the blood cells is called Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate. The ESR measurement can be done by two methods.
- Westergren method
- Wintrobe method
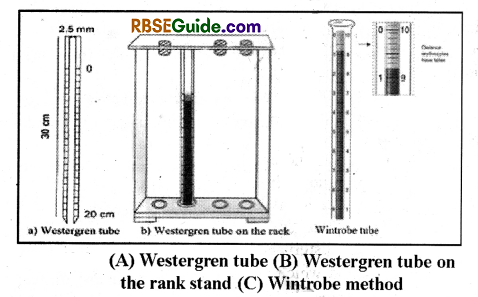
In most of the pathological laboratories only Westergren method is used for ESR testing. Hence, here this method is described.
- Westergreen tube is filled up to zero point with the blood containing anticoagulants. This tube is kept legitimacy in a verticle position in ESR stand.
- After an hour the upper level of erythrocytes is read in the ESR tube. This is the value of Erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
The ESR value of a healthy person is as follows :
- Male = 0-16 mm per hour
- Female = 0-20 mm per hour.
- If the rate of ESR is more than the normal value, it indicates towards irregularities in the body. Value of ESR increases in many chronic diseases like tuberculosis and inflammatory diseases like Rheumatoid arthritis, multiple myeloma or allergy, lymphatic inflammation etc. Moreover, value of ESR increases during pregnancy, Anaemia and with increase in Age.
- These days Automated mini ESR machine is used to enhance the accuracy in the value of ESR. The machine works at a controlled temperature of 18°C. In the traditional methods, temperature regulation is not possible and a chance of 25-30% error exists.
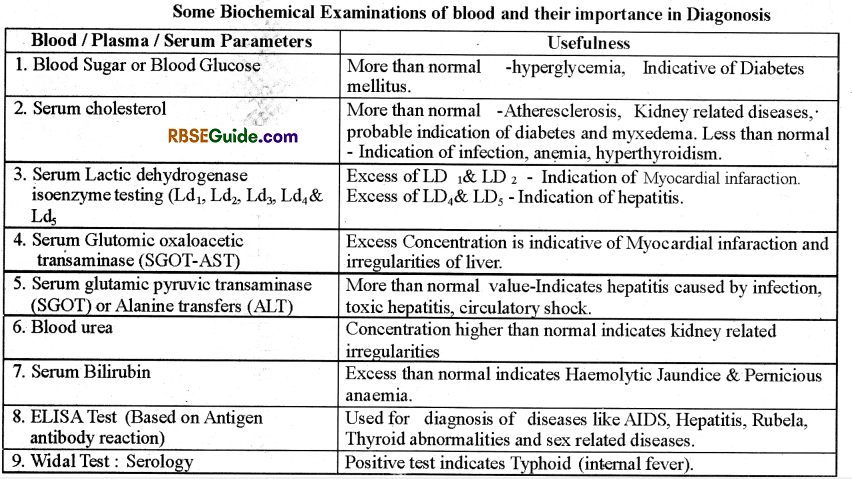
Autoanalyzer
Now a days many biochemical and structural parameters like ESR calculation, leucocyte count, shape of the blood cells, haemoglobin content, concentration of glucose, urea, cholesterol, Enzymes, proteins etc can be estimated with the help of computer controlled instrument called Autoanalyzer. With this machine, many parameters can be assessed at the same time.
![]()
![]()
Major Techniques and Instruments used in Medical Science
Electrocardiography (ECG)
General:
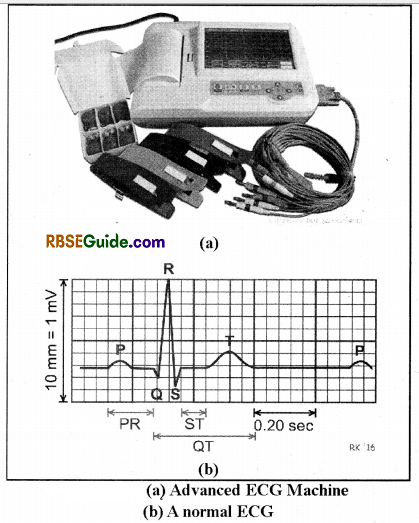
- It is an instrument which is used to record electrical signals produced by nerves & muscles in the beating heat.
- The record of these myoelectrical changes is called Electrocardiogram (ECG).
- The electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphic recording of electric potentials generated in the heart. The signals are detected by means of metal electrodes attached to the extremities & chest wall, and are than applied & recorded by the electrograph. The process of recording ECG is termed as electrography.
Significances:
- It is used to detect cardiac disorders like arrhythmias, conduction disturbances; myocardial ischemia etc.
- It reveals other findings related to life threatening metabolic disturbances like hyperkalemia or increased, susceptibility to sudden cardiac death (e.g.—Q T prolongation syndrome).
- It is used to study the rate of heart beat, and cardiac disorders such as myocardial infarction (MI), coronary’ artery diseases etc.
Salient Features:
- The ECG is recorded on special graph paper which is divided into 1 mm2 gride like boxes.
- The normal ECG includes P wave, QRS complex and ST-T-U complex.
- The P wave is a small upward deflection and it represents atrial depolarisation.
- The QRS Complex represent rapid ventricular depolarisation (systole). It includes a small downward deflection, a rapid upright stroke and a small downward deflection
- The ST—T-U complex includes ST regnrent, T wave & U wave. It represents ventricular repolarisation (diastole)
- The J point is the junction between the end of QRS complex and the begning of ST segment.
Atrial repolarization is too low in amplitude to be detected.
There are four major ECG Intervals
- R-R interval : It is used to compute the heard beats per minute.
- P-R Interval : It is used to measure the time between atrial & ventricular depolarisation.
- QRS interv al : It reflects the duration of ventricular depolarisation & atrial repolarisation.
- Q T interval: It includes both ventricular depolarisation and repolarisation times.
The QRS Complex is subdivided into specific deflections or waves. The initial negative deflection is termed as Q-wave. The first positive deflection is temed as R—wave A negative deflection after the R-wave is termed as S wave. An entirely negative QRS complex is termed as QS wave.
Normal T wave is a dome—shaped upward deflection.
Normal U wave is a small round upward deflection that follows the T-wave.
Major ECG Abnormalities
- An increase in P wave amplitude indicates right atrial overload (enlarged).
- Biphasic or notched P w ave indicates left atria overload.
- Relatively tall R—wave indicates right ventricular hypertrophy.
- An abnormal increase in U wave amplitude is most commonly due to drugs & hypokalemia.
- U wave inversion is a subtle sign of ischemia.
- Prolongation of QRS interval indicates intraventricular condiction disturbances.
- The method which is used to obtain an image of heart structure using ultrasound is called as echocardiography.
Echocardiography
Through this technique, image of the Heart structure can obtained using the ultrasound waves.
Doppler Echocardiography
The technique is indirectly used to measure the velocity of the blood flowing through the heart.
Electroencephalography (EEG)
- In this technique electrical activities of different parts of the brain are measured and recorded-in amplified form.
- Satton in 1875 for the first time exposed the concept of electrical activity in the brain.
- Hans Berger in 1929 for the first time observed and recorded the electrical activity in intact brain.
- Transient waves of microvolt level are obtained for the electrical activity of the brain. Before recording, these waves are amplified to make them more clear and sensitive. The record so obtained is called Electroence phalogram.
- Electroencephalogram is a painless, and free from the unwanted side effects. Sixteen to thirty small electrodes are placed along different parts of the scalp. All these electrodes are joined with a single machine. Electrodes transport the electrical signals from different parts of brain to the main machine where amplified form of these signals is recorded. The whole process takes 45 minutes.
- Now a days using advanced techniques, study of weaker magnetic field of brain is also possible. This technique is called as Super Conducting Quantum Interference Device (SQUID). Along with the brain, irregularities related to spinal cord can also be diagonosed through Magnetoencephalography.
Brain exhibits 4 types of waves in LEG viz.
- α-waves => Frequency-10 to 12 cycles per second
- β-waves => Frequency-15 to 16 cycles per second
- θ-waves=>Frquency-5 to 8 cycles per second
- δ-waves=>Frequency-l to 5 cycles per second
- Alpha waves are produced in awakening stage & are absent during sleep.
- Beta waves are produced during mental work
- Delta waves are produced in awakening child
- Theta waves are found only in children
- Presence of delta waves in EEG of adults indicates mental disorder.
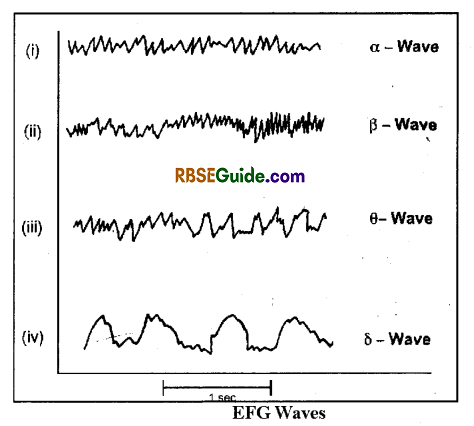
The pattern of EEG reflects the state and conciousness of the patients brain (Fig. 42.4) and is helpful in the diagnosis of many brain related irregularities.
![]()
Applications of EEG
Applications of this technique are as under
- EEG is helpful in the diagnosis of structural abnormalities of the brain like Tumours, Epilepsy, Encephalitis etc.
- It also helps in the diagnosis of infections of brain, effect of metabolities and drugs on brain, sleeping disorders etc.
- It is also helpful is assessment of brain death.
Computed Tomographic Scan or CT Scan
- It is a very important technique of medical science in which X-rays in combination with computer technology are used to generate Two or Three dimensional image of cross section of any body part. This image shows each and every organ separately. This technique was developed by British physicist Godfrey Hounsfield in 1968. For this discovery, he was awarded with Noble prize of 1979.
- The theoritical basis of this technique was illustrated by an Indian scientist name Sh. GN. Ramchandran. In the C.T. Scan (also known as Computed axial tomography scan, CAT scan), a low intensity X-ray beam spinning at 360° passes through patient’s thin cross section like region. At this time, depending upon its density, tissue absorbs some amount of radiation. These radiations beam after coming out of the body are passed through light sensitive detectors which converts them into electronic signals.
- These signals are transmitted to the Computer Scanner. This process is repeated till all the planes of the particular body section are observed from all the possible angles. The obtained datas are then analysed by a computer. In this test, a series of cross sectional images of various planes are obtained. For this reason it is called Scan.
- C T scan can be used to obtained the image of any portion of the body. This technique is helpful in the diagnosis of diseases related to Brain, Spinal Cord, Chest, Abdomen etc. This test provide us information about the examination of tumours and their spread in the nearby tissues.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- MRI was discovered by F. Bloch and E.M. purcell independently and they shared the Nobel prize in 1952.
- In this technique, there dimentional images of body organs is obtained without using X-rays & other radiations.
- MRI detects water because it focuses on the behaviour of hydrogen atoms in water molecules. MRI distinguishes between water-poor & water abundant tissues.
- The tissues with little water such as bones & teeth do not appear in MRI.
This technique is based on the natural behaviour of protons of hydrogen atoms and the most abundant source of protons are the hydrogen atoms in water molecule. - MRI is used mainly to study organs like brain & spinal cord, to examine joint injuries & slip discs and to visualize minute cancerous tumours.
- MRI is based on the phenomenon known as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR).
- During MRI testing, patient is positioned in a two meter wide chamber of a MRI scanner. This chamber is surrounded by large cylinderical electromagnetic field that produces very strong magnetic field and waves.
- Because of the very’ high magnetic field, nuclei of the hydrogen atom get activated and release radio signals.
- These signals are processed by a computer. Through the processing of radio signals, thin high contrast images are obtained.
- The MRI images are much better than the images obtained by CT scan. They provide high contrast, using MRI technique, images from all body axis can be obtained. Although MRI is a costly technique but it is very helpful for the diagnosis and study of the brain and spinal cord.
- This technique can clearly differentiate between the white and grey matter of the brain.
![]()
Ultrasound Scanning
- It is biotechnique which is based on ultrasonicsound, the sound of frequency above 20 KHz.
- In this technique, a ultrasound is beamed into the human body and the returning echoes are recorded. These echoes are processed by a computer into video image.
- The ultrasonography is safer & inexpensive.
- It is used to assess foetal growth & also the abnonnalities in an adult body. It can provide the picture of blood flow through the beating heart.
- The ultrasonic waves are produced by the piezoelectric effect when an electric potential is applied to crystals of lead zirconate.
- When human organs and tissues waves are exposed to Ultrasound waves, they are transmitted back and are absorbed by the transducer. Transducer absorbs these return signals in the form of a series of Echoes.
- Transducer convert the return signals into electric signals, which are then displayed on a monitor screen. They are displayed as two dimensional pictures.
- Using Sonography, reflections displayed on the monitor is can be obtained in the form of pictures.. They are called as Sonogram. Sonogram, can be used to find out the location, position, structure, shape and texture of an organ or tissue.
- Sonography technique, as compared to radiography is cost effective and comfortable. It has vivid uses.
- Sonography can be used to find the growth of the foetus. It is also used to find out the abnonnalities in foetus.
- Sonography can also be used to find out the abnonnalities of kidney, uterus, fallopian tubes, gall stone, intestinal obstructions etc. It is mainly used in child birth and diagnosis of obstetric associated problems.
- Using doppler effect in songoraphy ima ges of blood flow in pulsating heart can also be obtained.

Radio Immuno Assay (RIA)
- Radio immuno assay is an analytic technqiue which is used from last many years. Here, the molecule which is to be analysed, which acts as an antigen is marked with a radiolabelled substance. The labelled and normal antigen molecules are allowed to react with specific antibody. A comparative analysis of reaction is done. In this technique radioisotope is used as a marker molecule.
- This technique was invented by Rosalyn and Yalow.
- Now-a-days it has become an important diagnostic technique. This is especially important for the analysis of those biochemical factors that are present in very minute concentration (microgram, nanogram or picogram) and cannot be analysed by the traditional gravimetric and volumetric processes.
- The radio isotopes used in radio immuno assay are high specificity molecules, which provide very high sensitivity to this technqiue.
- In this technique the standard solution of different concentration of normal molecules of the substance to be analysed are used with the solutions of radio labelled substance of similar concentrations. This mixture is allowed to react with antibodies. At the stage of equilibrium, antigen-antibody complexes are absorbed by suitable reagent. The precipitated and supenatant parts are separated and byT measuring the radioactivity, concentration of the substance is estimated.
- Amajor characteristic of Radio Immuno Analysis is that the patient do not suffer with any side effect. He is never treated with the radio isotopic molecule because the whole process is executed outside the body.
Uses of RIA
- Using this technique, concentration of important biological components like vitamins (B12, Folic acid), hormones (Thyroxine, Triodothyroxine, T3, Cortisol, Testosterone, Estrogen, Tropic hormone etc.) drugs (Digoxin, Digitoxin etc.) and antigenic substances can be determined.
- For the diagnosis of abnormalities of endocrine glands, radio immuno assays are very useful. For example presence of excessive amount of some hormones in blood may be result of hyperactivity of endocrine gland or due to the impact of tropic hormone, such questions can only be answered by this technique.
- This technique is useful for the diagnosis of insulinoma, tumor etc which will help in the proper treatment of these diseases.
![]()
Other Techniques
In addition to the above, bio-medical technqiues, many other medical techniques and procedures are also available. Explanation of each of these is not possible here, as it is out of the periphery of the prescribed syllabi. However for the knowledge of the reader, names of these techniques are given below :
- X-Ray Radiography
- Angiography
- Positron Emission Tomography
- Polygraphy
- Endoscopy
- Laser Microsurgery
- Tissue/Organ Transplantation
- Haemodialysis
- Prosthesis
- Replacement Surgery
- Cryosurgery
- Gene Therapy
