Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Economics Notes Chapter 15 National Income and its Related Aggregates
In economics, the study of a country’s income level is considered very important.
National income was first used by Professor Simon Kuznets in 1934 to calculate economic growth.
After achieving independence, a National Income Committee was constituted to estimate
national income.
The National Income Committee was formed under the chairmanship of Prof. Prafulla Chandra Mahalanobis (1949).
Simon Kuznets was the member and adviser of National Income Committee.
Estimation of National Income in India is published by the Central Statistical Organization every year from 1956.
The sum of the monetary value of the final goods and services produced in a country in 1 year is called national income.
National income is calculated on two bases
- Geographical basis
- Political basis.
![]()
The sum total of the values of final goods and services produced by residents of a country and foreign resident companies within the country’s geographical boundaries, and the increase in the unfinished goods and services, is called Gross Domestic Product (GDPMP).
GDPMP = C + I + G + (X – M)
The Net Domestic Product (NDPMP) at market price is calculated by subtracting price depreciation from gross domestic product.
NDPMP = GDPMP – D [where D – depreciation]
While calculating Net Domestic Product on factor cost (NDPFC), indirect taxes are deducted from Net Domestic Product at market price, and subsidies are added.
NDPFC = NDPMP – IT + S [IT = indirect taxes, S = subsidies]
The following elements are included in Gross National Product –
GNPMP = GDPMP+ NFIA[where : NFIA = Net Factor income received from abroad; X – M = Net Export]
Or
GNPMP = C + I + G + NFIA + (X – M)
Net National Product is determined at market price as follows –
NNPMP = GNPMP – D [where D = depreciation]
The expenditure done on the factors needed for production of goods/services in a country, is the Net National Production on factor cost.
NNPFC = NNPMC – IT + S [IT = indirect tax; S = subsidy]
NNPFC = R + I + W + P
[R = Revenue; I Interest, W = wages; P = Profit]
The most suitable measure of a country’s national income is the Net National Product at factor cost (NNPFC)
![]()
Public Income = NNPFC + TP + IPD – CSS – PPU
TP = Transferred payments from government and abroad
IPD = Interest on public loans
CSS = Social security grant
PPU = Surplus demand of Public Sector units
Public Income (PI) – National Income – undistributed profit – net interest payment by families – Corporation tax + income given by government and firms to families.
Public Disposable Income (PDI) = Public Income (PI) – (income tax of people) – (fee of people, penalties)
Per Capital Income (PCI) = 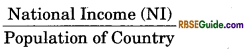
National Disposable Income (NDI) is an indicator of the level of goods and services of a country and thus the standard of living in an economy.
NDI = NI + NIT + NETW
NIT = Net Direct Tax
NI = National income
NTEW = Net transfer Earning from Rest of the world
Important Glossary
- National Income – National income is the total value of a country’s net production of all new goods and services produced in one year.
- Gross Domestic Product – Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is one of the primary indicators of the country’s economy. It represents the total value of all goods and services produced in a period of one year, which is often referred to as the size of the economy.
- Net Domestic Product- The net domestic product (NDP) is the value of goods and services produced in a country in one year within the country’s economy. It does not include value depreciation in capital stock.
- Gross National Product- Gross national product is the value of all goods and services created by the residents and businesses of the country, regardless of the production location.
- Net National Product at Factor Price- It is obtained by deducting indirect tax and subsidy depreciation from gross domestic product.
- Rent- It is the payment for receiving the service of land.
- Non-Tax Payment- The non-tax payment made by families to firms or government is called non-tax payment.
- Private Income – It is the total income from all factors (factor income as well as current transfers) that accrues to the private sector during the period of one year.
- Personal Income – It is the sum total of factor income and transfer income obtained from all sources by individuals. National income is not the sum of personal income.
- Factor Income – The income received in return for the services rendered by the factors of production, is called factor income.
- Transfer Income – Income received without giving any service is called transfer income, i.e. old-age pension, scholarship, unemployment allowance, etc.
