Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 12 Economics Notes Chapter 22 Concept of Excess and Deficient Demand
According to the classical economists, determination of income is affected by the real factors like-capital, stock, supply of labour, etc.
The concept of Keynes’ idea was evolved in 1930 at the time of Great Economic Depression.
According to Keynes, the theory of Income and production Determination assumes that the price level is stable.
Keynes maintained that deficiency of effective demand was the major cause for unemployment and excess production capacity in widespread depression.
Keynesian Model of Aggregate Demand (AD) and Aggregate Supply (AS) gives us an insight in determination of general price level and fluctuations in production.
Aggregate Demand includes the Consumption Expenditure, Private Investment Expenditure, Government Expenses on purchases of goods and services and Net Export.
![]()
The elements of Aggregate Demand can be expressed in an equation form as follows :
Y = C + I + G + Xn
Y = Income
C = Consumption Expenditure
I = Investment Expenditure .
G = Government Expenditure Xn = Net Exports (X – M)
Here, X = Total Exports
M = Total Imports
The curve below shows the relationship between aggregate production demand and general price level.
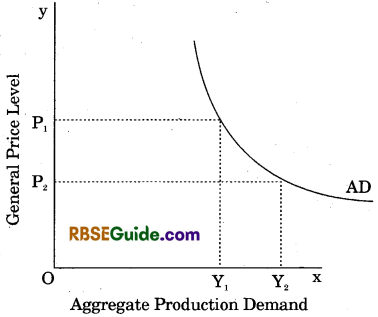
Consumption Expenditure decreases with the increase in prices.
With the increase in prices, people need more money for the purpose of transactions and thus the Rate of Interest rises, resulting in the fall of Investment Demand.
Along with the increase in prices, imports increase and exports decrease.
Aggregate supply, also known as total output, is the total supply of goods and services produced within an economy at a given overall price level.
Principles of classical economists are based on the assumption of Full Employment.
In full employment situation, Aggregate Supply Curve is a vertical straight line parallel to y-axis.
According to Keynes, Aggregate Supply Curve at the time of depression is initially horizontal, and at the point of full employment, it is vertical.
In horizontal Aggregate Supply Curve, along with the increase in the Aggregate Demand the production also increases and the prices remain constant.
![]()
In vertical Aggregate Supply Curve, i.e., at full employment along with the increase in Aggregate Demand, production does not change but price level increases.
At full employment, with the increase in production, per unit cost also increases, which pushes up the prices too.
Vertical range supply curve is a perfectly inelastic, which shows the full employment level of production. It is also called classical range.
Here, price level changes and the production quantity remains unchanged because resources are used at full capacity.
AD-AS model describes how Monetary and Fiscal Policy is effective.
Higher Demand motivates the producer for higher production.
Increase in the demand of resources of production, increases the production cost. Monetary Wage Rate remains stable in the short run.
Equilibrium occurs in long-term when aggregate demand is equal to aggregate supply.
Government adopts suitable fiscal policies when Aggregate Demand is less than the Aggregate Supply.
Government tries to increase the demand by increasing the public expenditure.
Supply of money is increased in monetary policy which results in the fall of interest rates, increase in private investment, etc. This increases Aggregate Demand.
Government adopts Expansionary Monetary and Fiscal Policy during Deficient Demand. At the time of depression, on the comparision of two policies, fiscal policy proves to be more successful.
![]()
With the help of fiscal policy, government tries to bring full employment and price level stability through changes in taxation and government expenditure.
Monetary Policy is adopted by the Central Bank to control the money supply or attain the objectives of economic policy.
At the time, of excess demand (inflationary trend), contractionary fiscal and monetary policy should be adopted.
To check rising prices due to excess demand, the Central Bank may resort to increase in the bank rate, sale of securities in the open market and increase in Reserve Ratio.
Important Terminology
- Aggregate Supply : Aggregate Supply expresses the production of total goods and services at different possible prices by the firm, while other factors remain the same.
- Classical Range : The perpendicular range supply curve is perfectly inelastic, which shows full employment of production. This is called the classical range.
- Depression : When economic activities like – production of goods and services, employment, income, demand and prices decrease significantly, it is called depression.
- Prosperity : When production, employment and income are on a high level, the demand for goods and services is high and prices rise in an inflationary way, it is called prosperity.
- Government Consumption Expenditure : It denotes the expenditure of government for the purchase of various goods and services.
- Fiscal Policy : Fiscal policy is the policy concerning taxation and expenditure of the government to attain special objectives.
- Monetary Policy : It is the central bank’s policy to control money supply and availability of credit in an economy.
- Minimum Demand : When Aggregate Demand is less than the Aggregate Supply.
- Maximum Demand : When Aggregate Demand is greater than the Aggregate Supply. Demonetisation : When government of the country legally bans the old currency.
